Multi-Target Inhibition of Cancer Cell Growth by SiRNA Cocktails and 5-Fluorouracil Using Effective Piperidine-Terminated Phosphorus Dendrimers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Cationic Phosphorus Dendrimers AE2G3, AE2G4
2.2. SiRNAs
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Complex Formation Studies
2.5. Cellular Uptake
2.6. Assessment of Cancer Cell Growth Inhibition
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of Cationic Phosphorus Dendrimers AE2G3, AE2G4
3.2. Complex Formation Studies
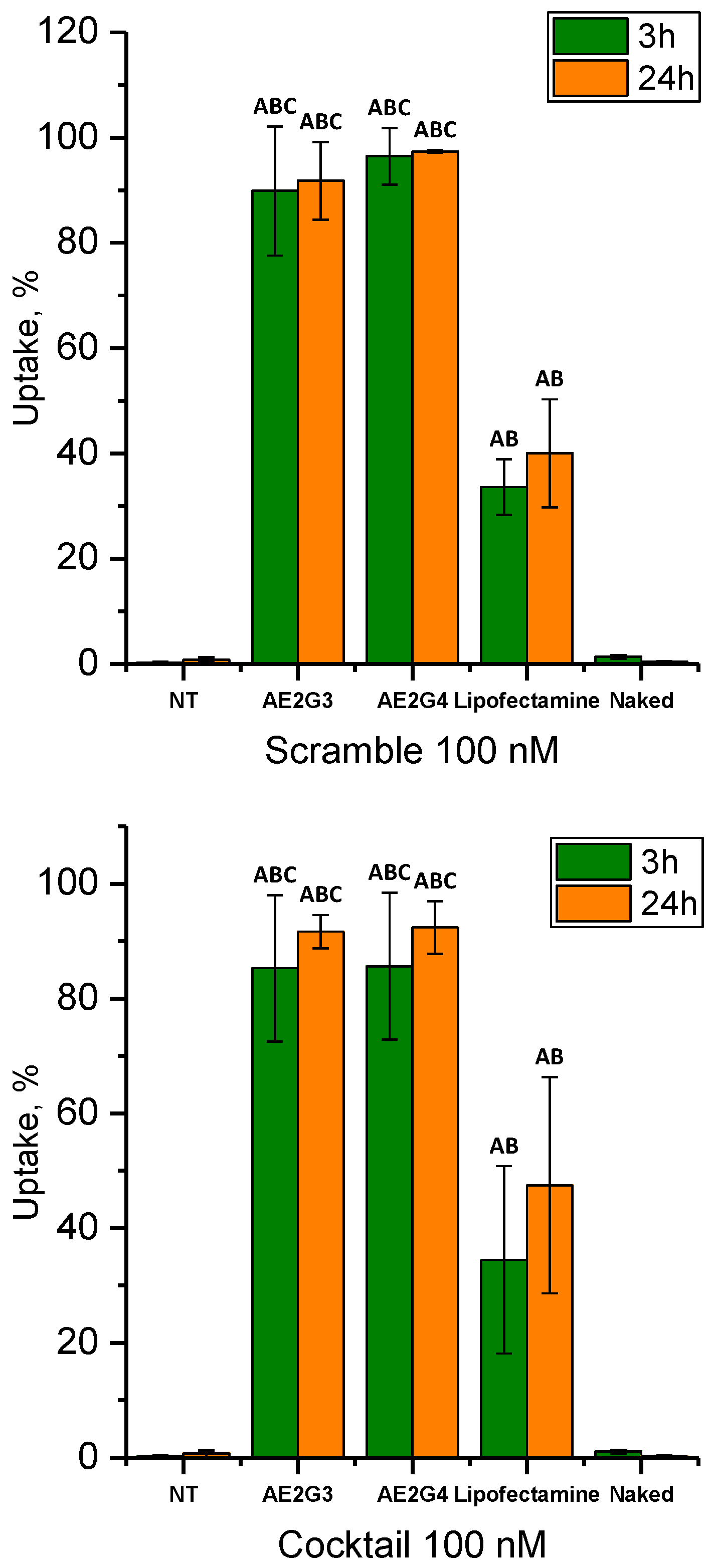
3.3. Cellular Uptake
3.4. Assessment of Cancer Cell Growth Inhibition
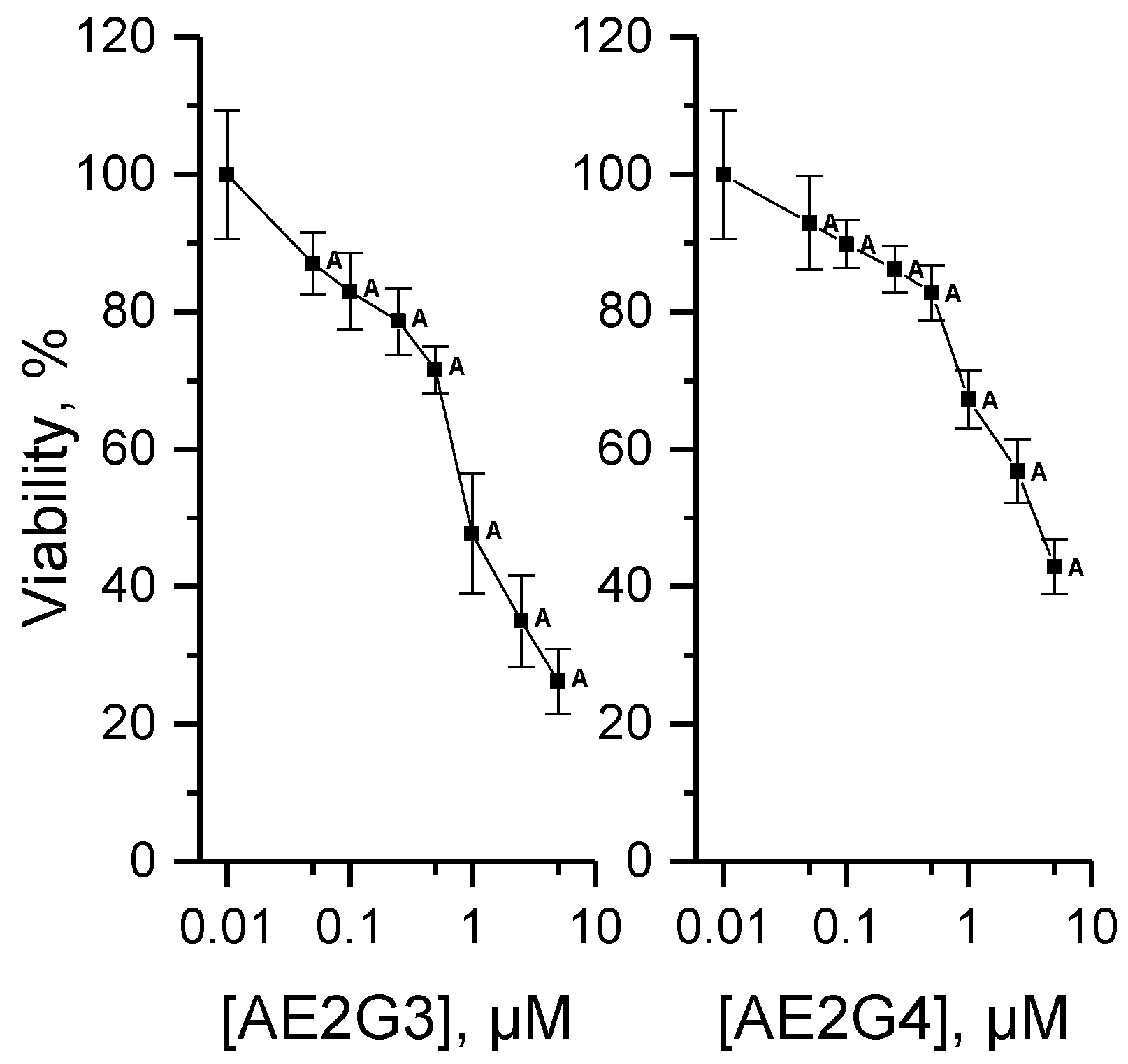
3.4.1. Cytotoxicity of Dendrimers
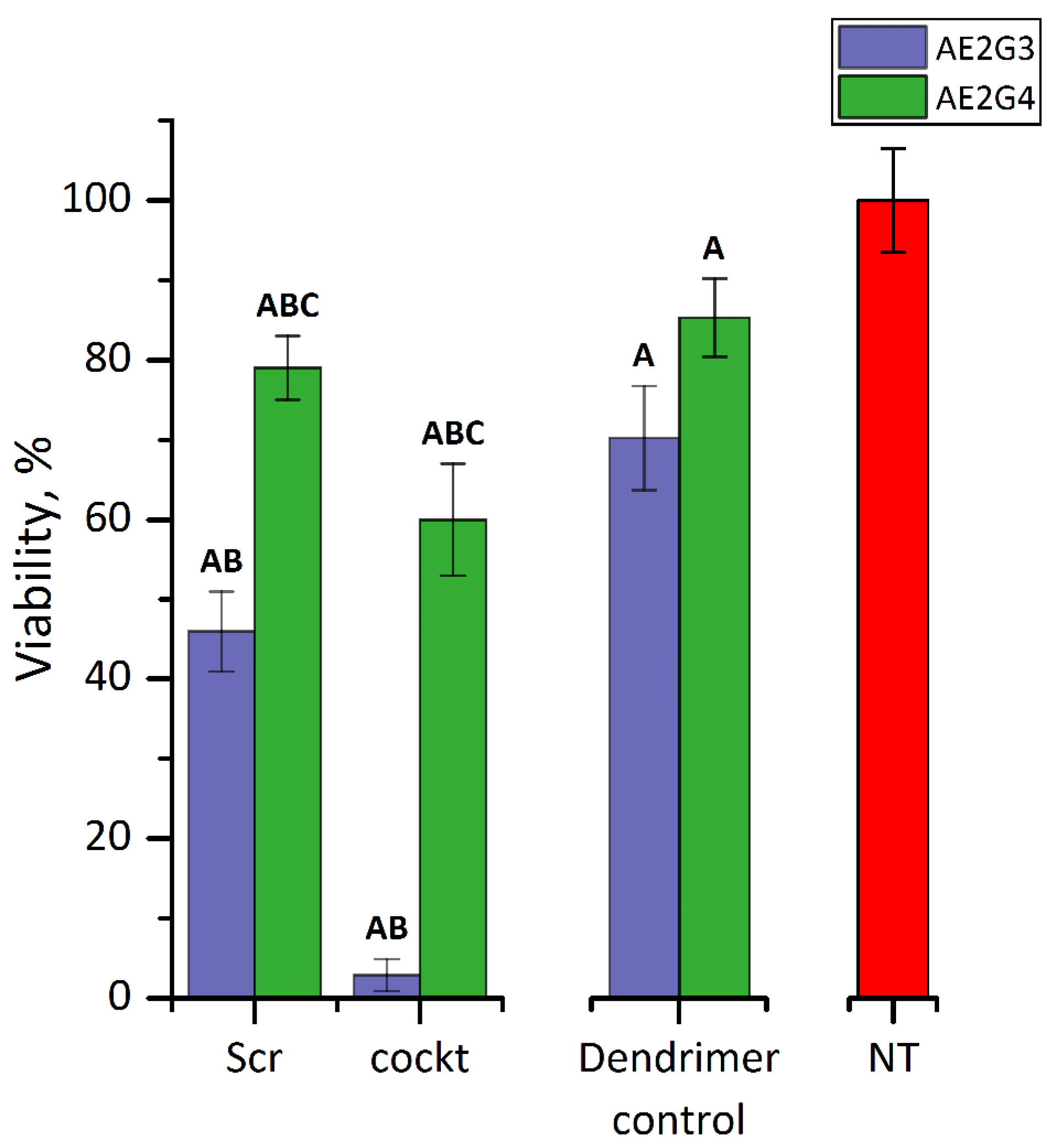
3.4.2. Cytotoxicity of Dendriplexes
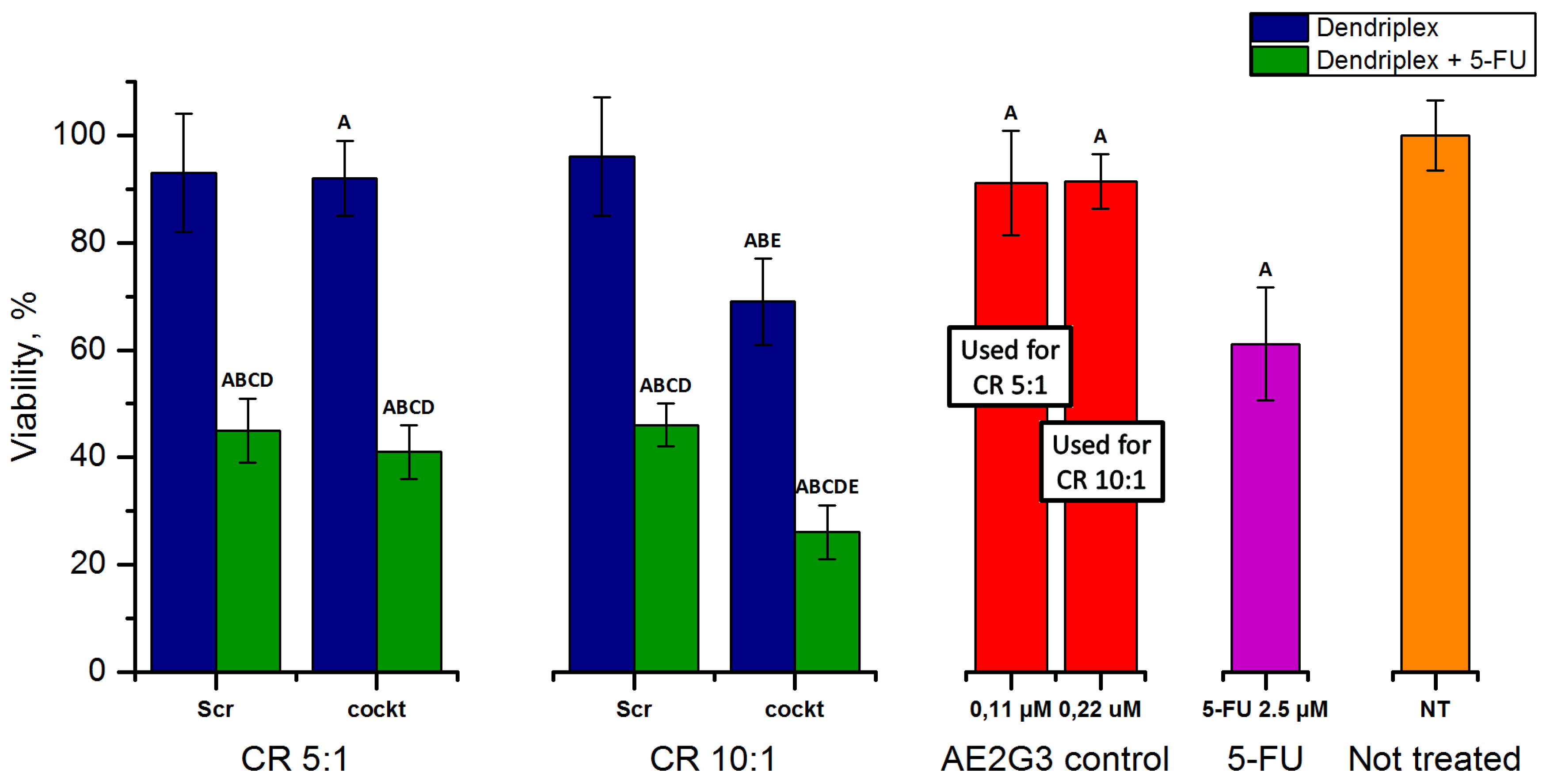
3.4.3. Cytotoxicity of Dendriplexes in Combination with 5-FU
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agrawal, N.; Dasaradhi, P.V.N.; Mohmmed, A.; Malhotra, P.; Bhatnagar, R.K.; Mukherjee, S.K. RNA interference: Biology, mechanism, and applications. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 657–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnier, P.; Montier, T.; Mathieu, V.; Benoit, J.P.; Passirani, C. A review of the current status of siRNA nanomedicines in the treatment of cancer. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6429–6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Wientjes, M.G.; Au, J.L.S. Delivery of siRNA Therapeutics: Barriers and Carriers. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menjoge, A.R.; Kannan, R.M.; Tomalia, D.A. Dendrimer-based drug and imaging conjugates: Design considerations for nanomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Torchilin, V.P. Dendrimers for siRNA delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Huang, W.; He, Z. Dendrimers as carriers for siRNA delivery and gene silencing: A review. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, R.M.; Nance, E.; Kannan, S.; Tomalia, D.A. Emerging concepts in dendrimer-based nanomedicine: From design principles to clinical applications. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 579–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminade, A.M.; Majoral, J.P. Biological Properties of Phosphorus Dendrimers. In Dendrimer-Based Drug Delivery Systems: From Theory to Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 139–155. ISBN 9780470460054. [Google Scholar]
- Caminade, A.-M.; Majoral, J.-P. Positively charged phosphorus dendrimers. An overview of their properties. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 3358–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignani, S.; Majoral, J.-P. Dendrimers as macromolecular tools to tackle from colon to brain tumor types: A concise overview. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 3337–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasiak, T.; Marcinkowska, M.; Pieszynski, I.; Zablocka, M.; Caminade, A.-M.; Majoral, J.-P.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. Cationic phosphorus dendrimers and therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 4852–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignani, S.; Bryszewska, M.; Zablocka, M.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B.; Cladera, J.; Shcharbin, D.; Majoral, J.P. Can dendrimer based nanoparticles fight neurodegenerative diseases? Current situation versus other established approaches. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 64, 23–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loup, C.; Zanta, M.; Caminade, A. Preparation of Water-Soluble Cationic Phosphorus-Containing Dendrimers. Chem. Eur. J. 1999, 5, 3644–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maszewska, M.; Leclaire, J.; Cieslak, M.; Nawrot, B.; Okruszek, A.; Caminade, A.-M.; Majoral, J.-P. Water-soluble polycationic dendrimers with a phosphoramidothioate backbone: Preliminary studies of cytotoxicity and oligonucleotide/plasmid delivery in human cell culture. Oligonucleotides 2003, 13, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shcharbin, D.; Dzmitruk, V.; Shakhbazau, A.; Goncharova, N.; Seviaryn, I.; Kosmacheva, S.; Potapnev, M.; Pedziwiatr-Werbicka, E.; Bryszewska, M.; Talabaev, M.; et al. Fourth generation phosphorus-containing dendrimers: Prospective drug and gene delivery carrier. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briz, V.; Serramía, M.J.; Madrid, R.; Hameau, A.; Caminade, A.-M.; Majoral, J.P.; Muñoz-Fernández, M. A Validation of a generation 4 phosphorus-containing polycationic dendrimer for gene delivery against HIV-1. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 5044–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzmitruk, V.; Szulc, A.; Shcharbin, D.; Janaszewska, A.; Shcharbina, N.; Lazniewska, J.; Novopashina, D.; Buyanova, M.; Ionov, M.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. Anticancer siRNA cocktails as a novel tool to treat cancer cells. Part (B). Efficiency of pharmacological action. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 485, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padié, C.; Maszewska, M.; Majchrzak, K.; Nawrot, B.; Caminade, A.M.; Majoral, J.P. Polycationic phosphorus dendrimers: Synthesis, characterization, study of cytotoxicity, complexation of DNA, and transfection experiments. New J. Chem. 2009, 33, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenc, M.; Pedziwiatr-Werbicka, E.; Nowak, K.E.; Klajnert, B.; Majoral, J.P.; Bryszewska, M. Phosphorus dendrimers as carriers of siRNA-characterisation of dendriplexes. Molecules 2013, 18, 4451–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionov, M.; Lazniewska, J.; Dzmitruk, V.; Halets, I.; Loznikova, S.; Novopashina, D.; Apartsin, E.; Krasheninina, O.; Venyaminova, A.; Milowska, K.; et al. Anticancer siRNA cocktails as a novel tool to treat cancer cells. Part (A). Mechanisms of interaction. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 485, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazniewska, J.; Milowska, K.; Zablocka, M.; Mignani, S.; Caminade, A.M.; Majoral, J.P.; Bryszewska, M.; Gabryelak, T. Mechanism of cationic phosphorus dendrimer toxicity against murine neural cell lines. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 3484–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, M. Short interfering RNAs as a tool for cancer gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessene, G.; Czabotar, P.E.; Colman, P.M. BCL-2 family antagonists for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotin, E.; Meryet-Figuière, M.; Simonin, K.; Duval, R.E.; Villedieu, M.; Leroy-Dudal, J.; Saison-Behmoaras, E.; Gauduchon, P.; Denoyelle, C.; Poulain, L. Bcl-XL and MCL-1 constitute pertinent targets in ovarian carcinoma and their concomitant inhibition is sufficient to induce apoptosis. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 885–895. [Google Scholar]
- Vestin, A.; Khazanov, E.; Avni, D.; Sergeyev, V.; Barenholz, Y.; Sidi, Y.; Yakobson, E. siRNA-lipoplex-mediated Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL gene silencing induces apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells. Open Chem. Biomed. Methods J. 2008, 1, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, H.M.; Mahdipoor, P.; Uludağ, H. Polymeric delivery of siRNA for dual silencing of Mcl-1 and P-glycoprotein and apoptosis induction in drug-resistant breast cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Chen, M.C.; Pham, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Ishiguro, H.; Reber, H.A.; Takeyama, H.; Hines, O.J.; Eibl, G. Simultaneous knock-down of Bcl-xL and Mcl-1 induces apoptosis through Bax activation in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 2980–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, H.; Baradaran, B.; Esfehani, A.; Sakhinia, M.; Sakhinia, E. Down-regulation of Mcl-1 by small interference RNA induces apoptosis and sensitizes HL-60 leukemia cells to etoposide. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetoui, N.; Sylla, K.; Gagnon-Houde, J.-V.; Alcaide-Loridan, C.; Charron, D.; Al-Daccak, R.; Aoudjit, F. Down-regulation of mcl-1 by small interfering RNA sensitizes resistant melanoma cells to fas-mediated apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Lila, A.A.S.; Matsunaga, M.; Doi, Y.; Ishida, T.; Kiwada, H. A Double-modulation Strategy in Cancer Treatment With a Chemotherapeutic Agent and siRNA. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launay, N.; Caminade, A.-M.; Majoral, J.P. Synthesis of bowl-shaped dendrimers from generation 1 to generation 8. J. Organomet. Chem. 1997, 529, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kazzouli, S.; Mignani, S.; Bousmina, M.; Majoral, J.-P. Dendrimer therapeutics: Covalent and ionic attachments. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignani, S.; El Kazzouli, S.; Bousmina, M.; Majoral, J.P. Dendrimer space concept for innovative nanomedicine: A futuristic vision for medicinal chemistry. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomalia, D.A. In quest of a systematic framework for unifying and defining nanoscience. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 1251–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomalia, D.A. Dendritic effects: Dependency of dendritic nano-periodic property patterns on critical nanoscale design parameters (CNDPs). New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomalia, D.A.; Khanna, S.N. A systematic framework and nanoperiodic concept for unifying nanoscience: Hard/soft nanoelements, superatoms, meta-Atoms, new emerging properties, periodic property patterns, and predictive mendeleev-like nanoperiodic tables. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2705–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, P.; Renfrew, A.K.; Clavel, C.M.; Dyson, P.J.; Therrien, B.; Smith, G.S. Antiproliferative activity of chelating N,O- and N,N-ruthenium(II) arene functionalised poly(propyleneimine) dendrimer scaffolds. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michlewska, S.; Ionov, M.; Shcharbin, D.; Maroto-Díaz, M.; Ramirez, R.G.; de la Mata, F.J.; Bryszewska, M. Ruthenium metallodendrimers with anticancer potential in an acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL60). Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 87, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-S.; Garg, H.; Joshi, A.; Manjunath, N. Strategies for targeted nonviral delivery of siRNAs in vivo. Trends Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, P.; Iyer, A.K. Recent advances in dendrimer-based nanovectors for tumor-targeted drug and gene delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannus, M.; Beitzinger, M.; Engelmann, J.C.; Weickert, M.T.; Spang, R.; Hannus, S.; Meister, G. SiPools: Highly complex but accurately defined siRNA pools eliminate off-target effects. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8049–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longley, D.B.; Harkin, D.P.; Johnston, P.G. 5-Fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucquier, J.; Guedj, M. Analysis of drug combinations: Current methodological landscape. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruponen, M.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Urtti, A. Interactions of polymeric and liposomal gene delivery systems with extracellular glycosaminoglycans: Physicochemical and transfection studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 1999, 1415, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, G.; de ILarduya, C.T. Activated and non-activated PAMAM dendrimers for gene delivery in vitro and in vivo. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2009, 5, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennig, J. Gene transfer in eukaryotic cells using activated dendrimers. In Dendrimers V; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Klajnert, B.; Stanislawska, L.; Bryszewska, M.; Bartlomiej, P. Interactions between PAMAM dendrimers and bovine serum albumin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1648, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, E.; Mandeville, J.S.; Jennings, C.J.; Sedaghat-Herati, R.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A. Dendrimers bind human serum albumin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6986–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandeville, J.S.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A. Complexes of dendrimers with bovine serum albumin. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwed, A.; Milowska, K.; Ionov, M.; Shcharbin, D.; Moreno, S.; Gomez-Ramirez, R.; de la Mata, F.J.; Majoral, J.P.; Bryszewska, M.; Gabryelak, T. Interaction between dendrimers and regulatory proteins. Comparison of effects of carbosilane and carbosilane–viologen–phosphorus dendrimers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97546–97554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionov, M.; Ihnatsyeu-Kachan, A.; Michlewska, S.; Shcharbina, N.; Shcharbin, D.; Majoral, J.-P.; Bryszewska, M. Effect of dendrimers on selected enzymes—Evaluation of nano carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 499, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aied, A.; Greiser, U.; Pandit, A.; Wang, W. Polymer gene delivery: Overcoming the obstacles. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Concentration of siRNA | Charge Ratio | Dendrimer | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AE2G3 | AE2G4 | ||
| 100 nM | 10:1 | 0.88 µM | 0.44 µM |
| 50 nM | 10:1 | 0.44 µM | - |
| 25 nM | 10:1 | 0.22 µM | - |
| 5:1 | 0.11 µM | - | |
| AE2G3 H+ | MW 16 862 |
|---|---|
 | |
| AE2G4 H+ | MW 34 856 |
 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ihnatsyeu-Kachan, A.; Dzmitruk, V.; Apartsin, E.; Krasheninina, O.; Ionov, M.; Loznikova, S.; Venyaminova, A.; Miłowska, K.; Shcharbin, D.; Mignani, S.; et al. Multi-Target Inhibition of Cancer Cell Growth by SiRNA Cocktails and 5-Fluorouracil Using Effective Piperidine-Terminated Phosphorus Dendrimers. Colloids Interfaces 2017, 1, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids1010006
Ihnatsyeu-Kachan A, Dzmitruk V, Apartsin E, Krasheninina O, Ionov M, Loznikova S, Venyaminova A, Miłowska K, Shcharbin D, Mignani S, et al. Multi-Target Inhibition of Cancer Cell Growth by SiRNA Cocktails and 5-Fluorouracil Using Effective Piperidine-Terminated Phosphorus Dendrimers. Colloids and Interfaces. 2017; 1(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids1010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleIhnatsyeu-Kachan, Aliaksei, Volha Dzmitruk, Evgeny Apartsin, Olga Krasheninina, Maksim Ionov, Svetlana Loznikova, Alya Venyaminova, Katarzyna Miłowska, Dzmitry Shcharbin, Serge Mignani, and et al. 2017. "Multi-Target Inhibition of Cancer Cell Growth by SiRNA Cocktails and 5-Fluorouracil Using Effective Piperidine-Terminated Phosphorus Dendrimers" Colloids and Interfaces 1, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids1010006
APA StyleIhnatsyeu-Kachan, A., Dzmitruk, V., Apartsin, E., Krasheninina, O., Ionov, M., Loznikova, S., Venyaminova, A., Miłowska, K., Shcharbin, D., Mignani, S., Muñoz-Fernández, M. A., Majoral, J.-P., & Bryszewska, M. (2017). Multi-Target Inhibition of Cancer Cell Growth by SiRNA Cocktails and 5-Fluorouracil Using Effective Piperidine-Terminated Phosphorus Dendrimers. Colloids and Interfaces, 1(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids1010006









