Enhancing Soundscape Characterization and Pattern Analysis Using Low-Dimensional Deep Embeddings on a Large-Scale Dataset
Abstract
1. Introduction
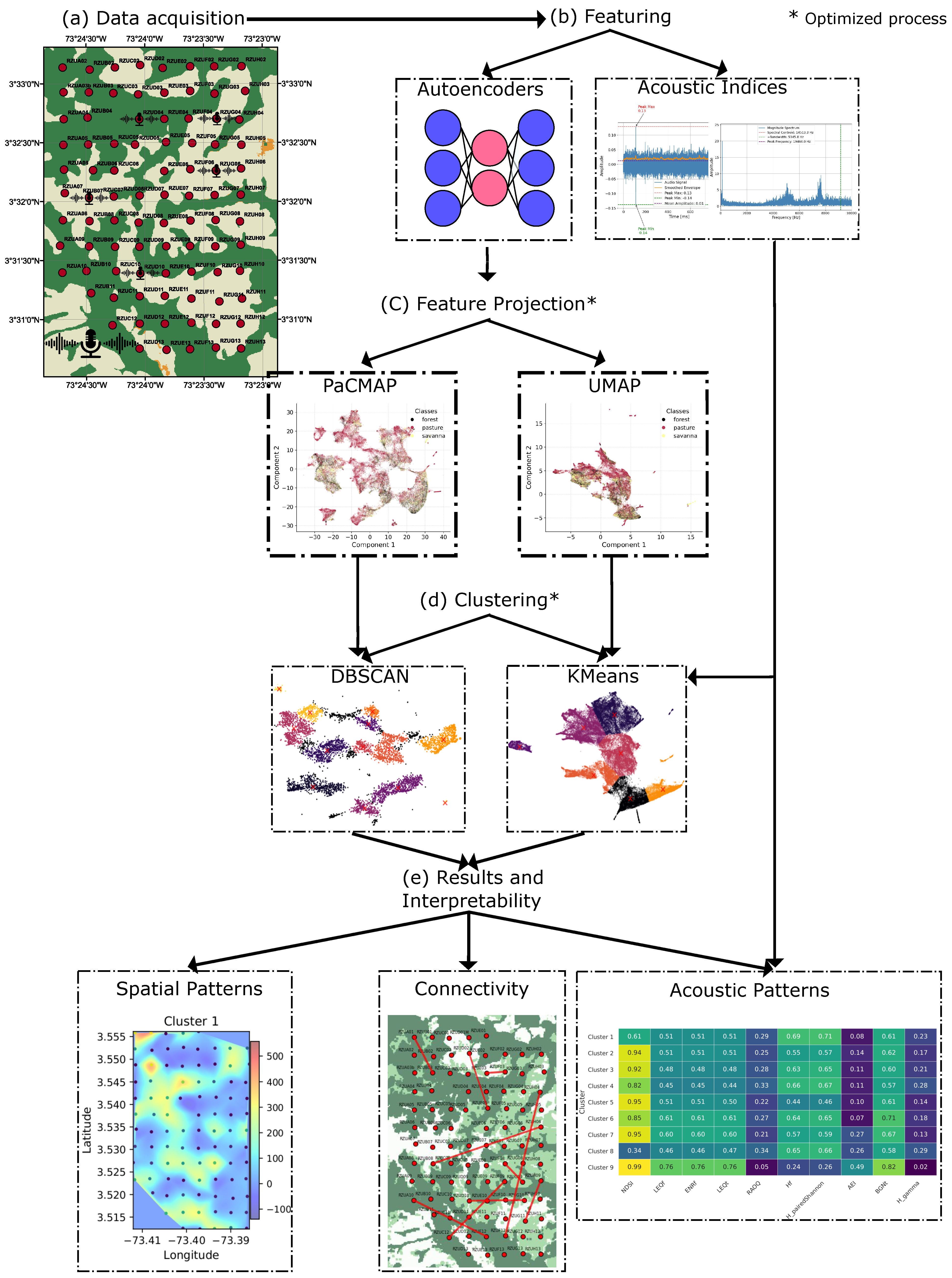
2. Materials and Methods
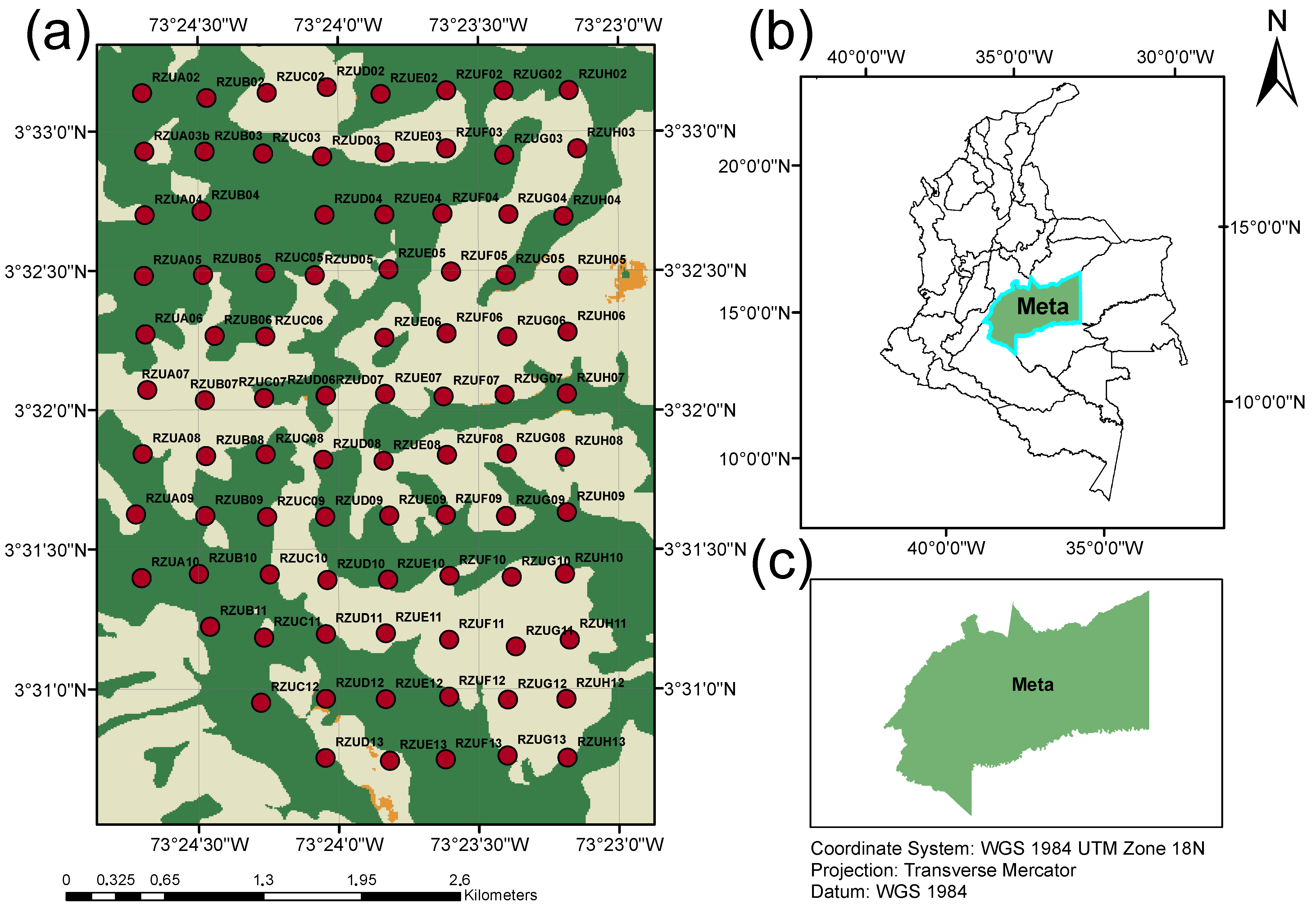
2.1. Dataset Description
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Acoustic Indices
2.2.2. VGGish Embeddings
2.2.3. Autoencoder Feature Extraction
2.2.4. Feature Projection and Dimensionality Reduction
2.3. Evaluation of Embedding Projections
- is the set of points that are among the k nearest neighbors of in the embedding but not among the k nearest neighbors of in the original space.
- is the rank of point in the ordered list of distances from in the original space.
2.3.1. Clustering Methods
2.3.2. Density Peak-Based Validation of Clusters (DPVC)
2.3.3. Connectivity and Graph Construction
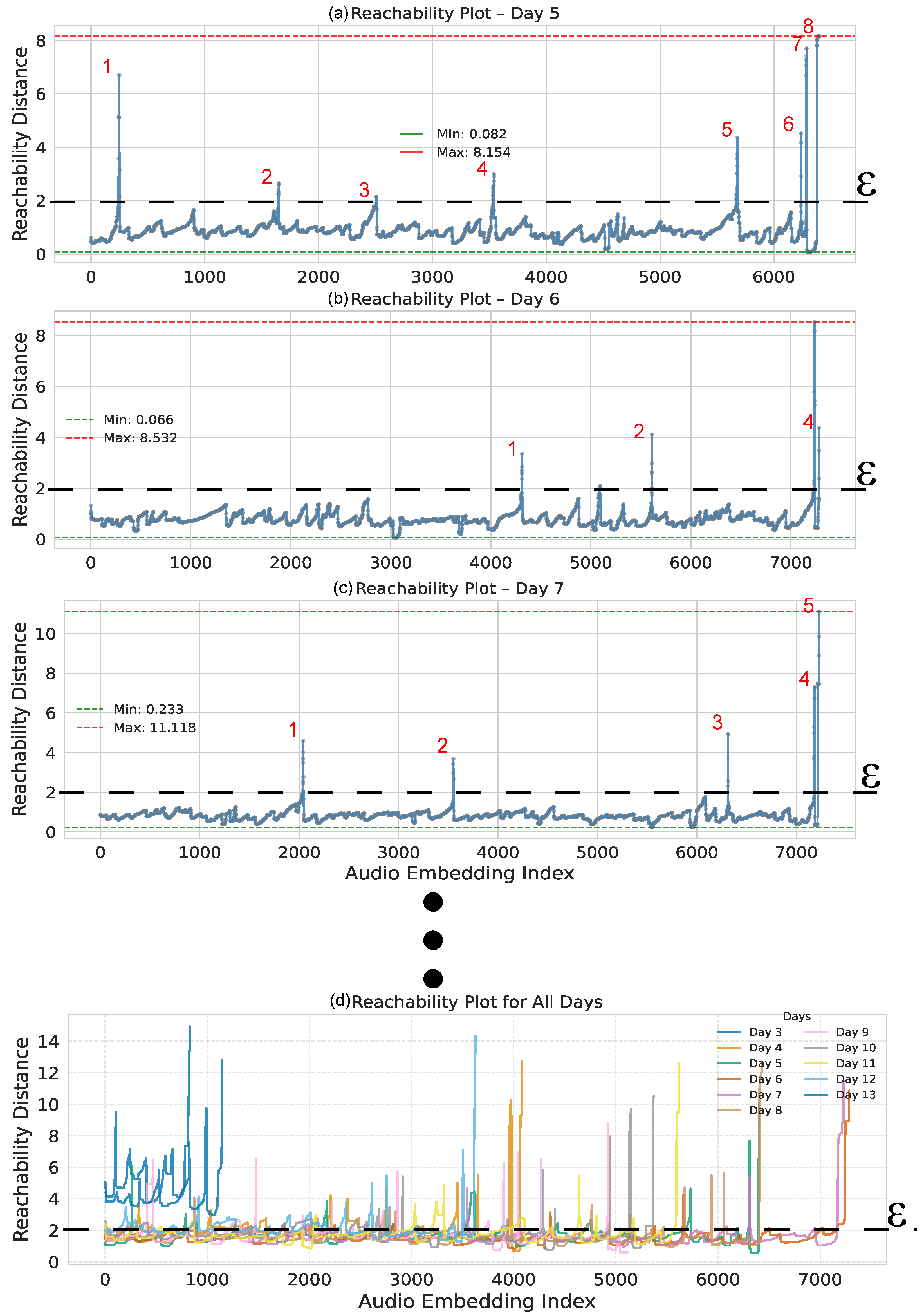
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Multiclass Classification Using Cover Type and Time Metadata as Labels
3.2. Low-Dimensional Feature Embedding and Clustering
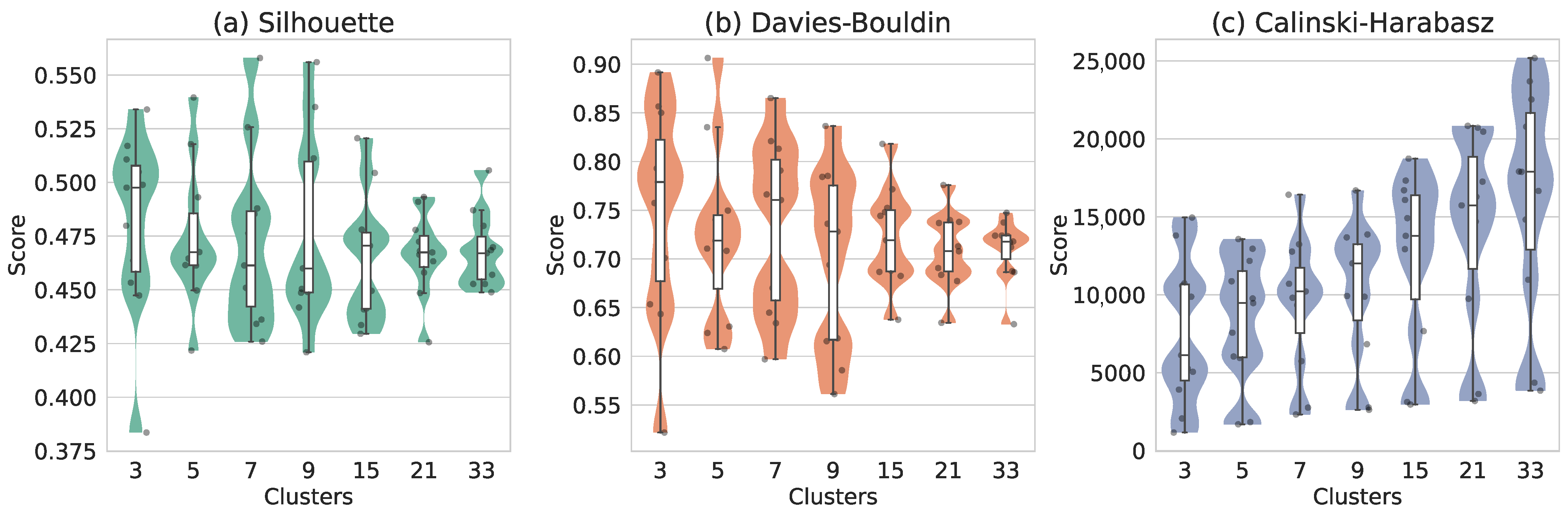
3.2.1. Feature Projections and Method Optimization
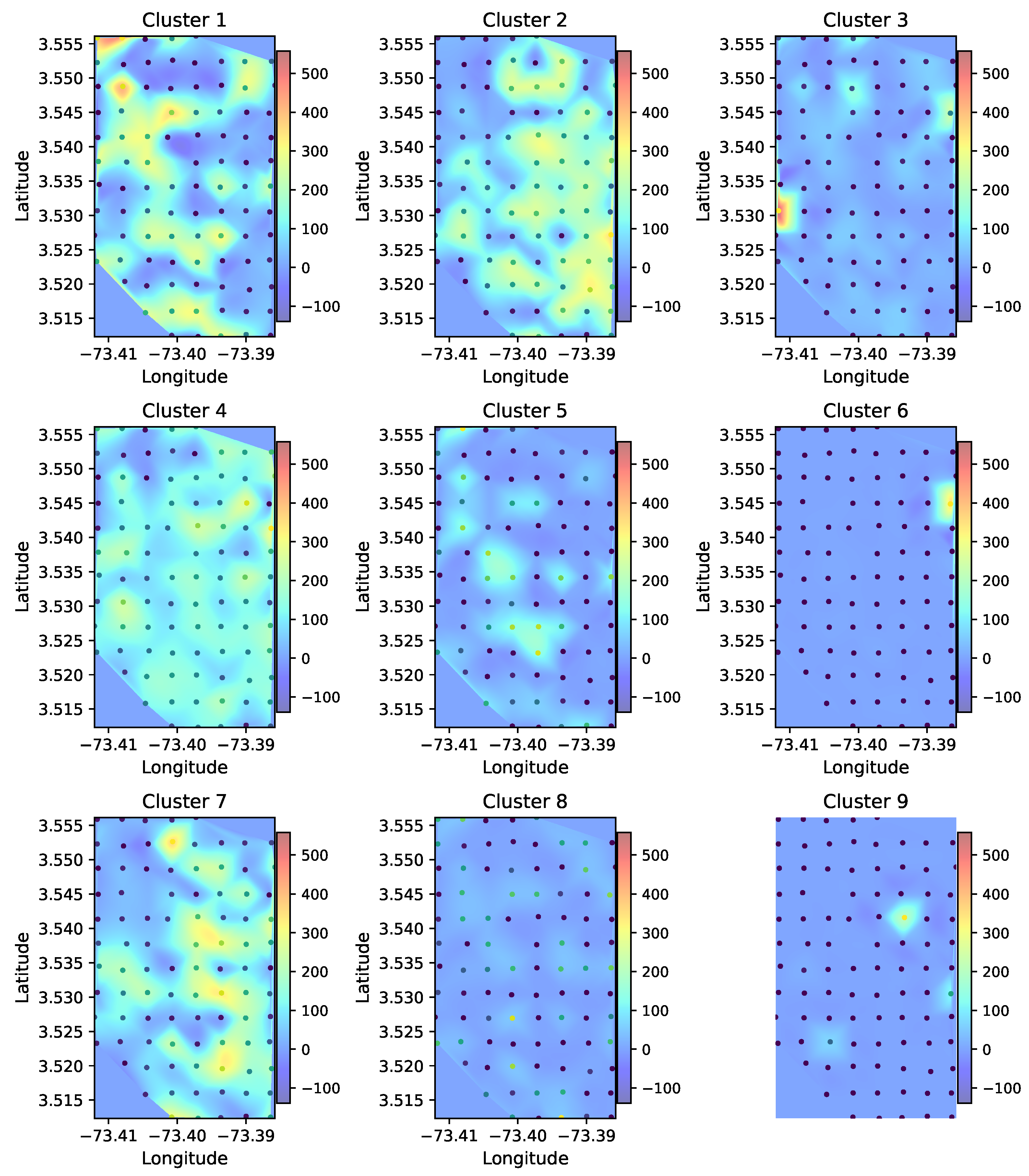
3.2.2. Clustering Analysis
3.2.3. Evaluation of Optimal DBSCAN Parameter Settings
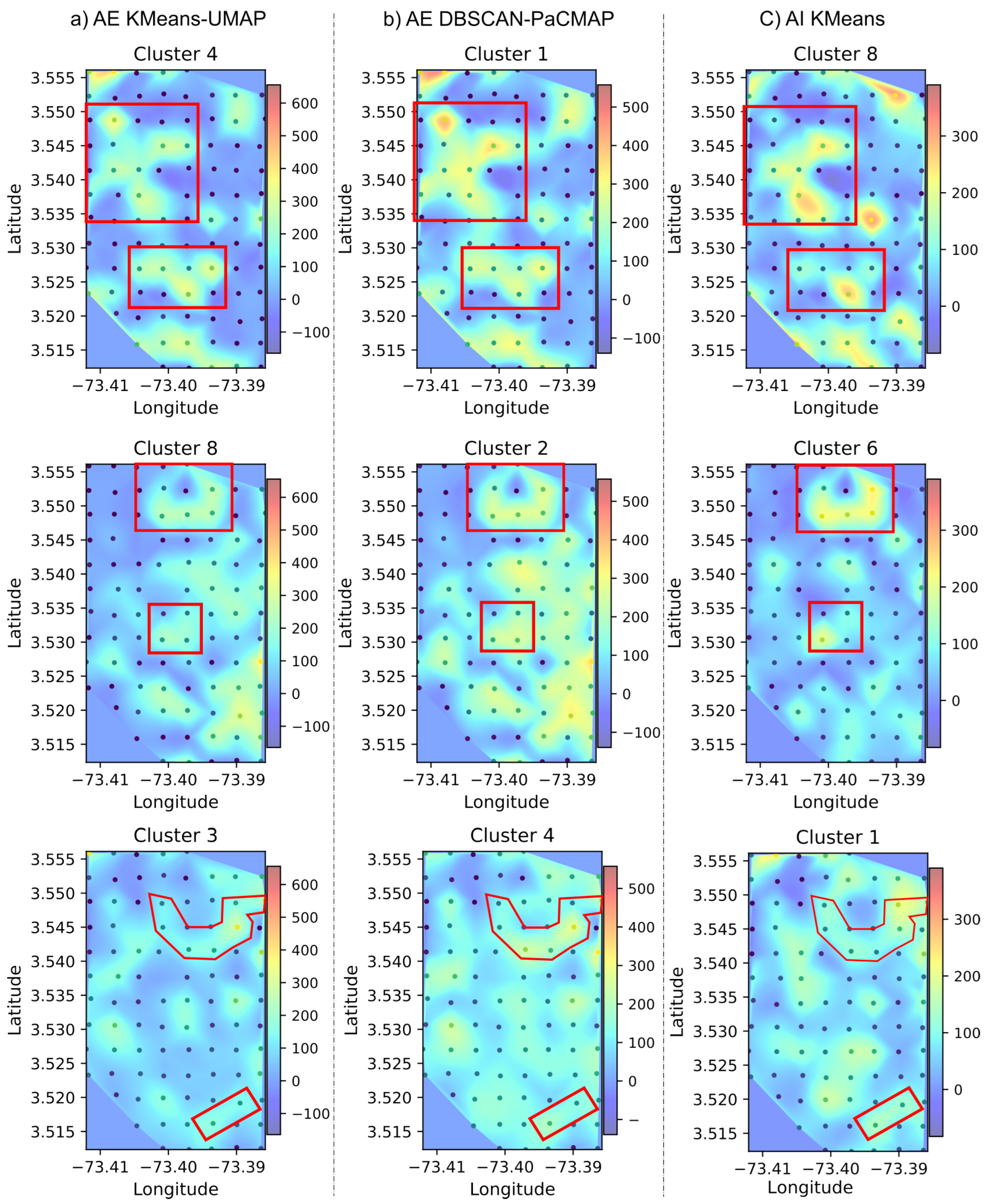
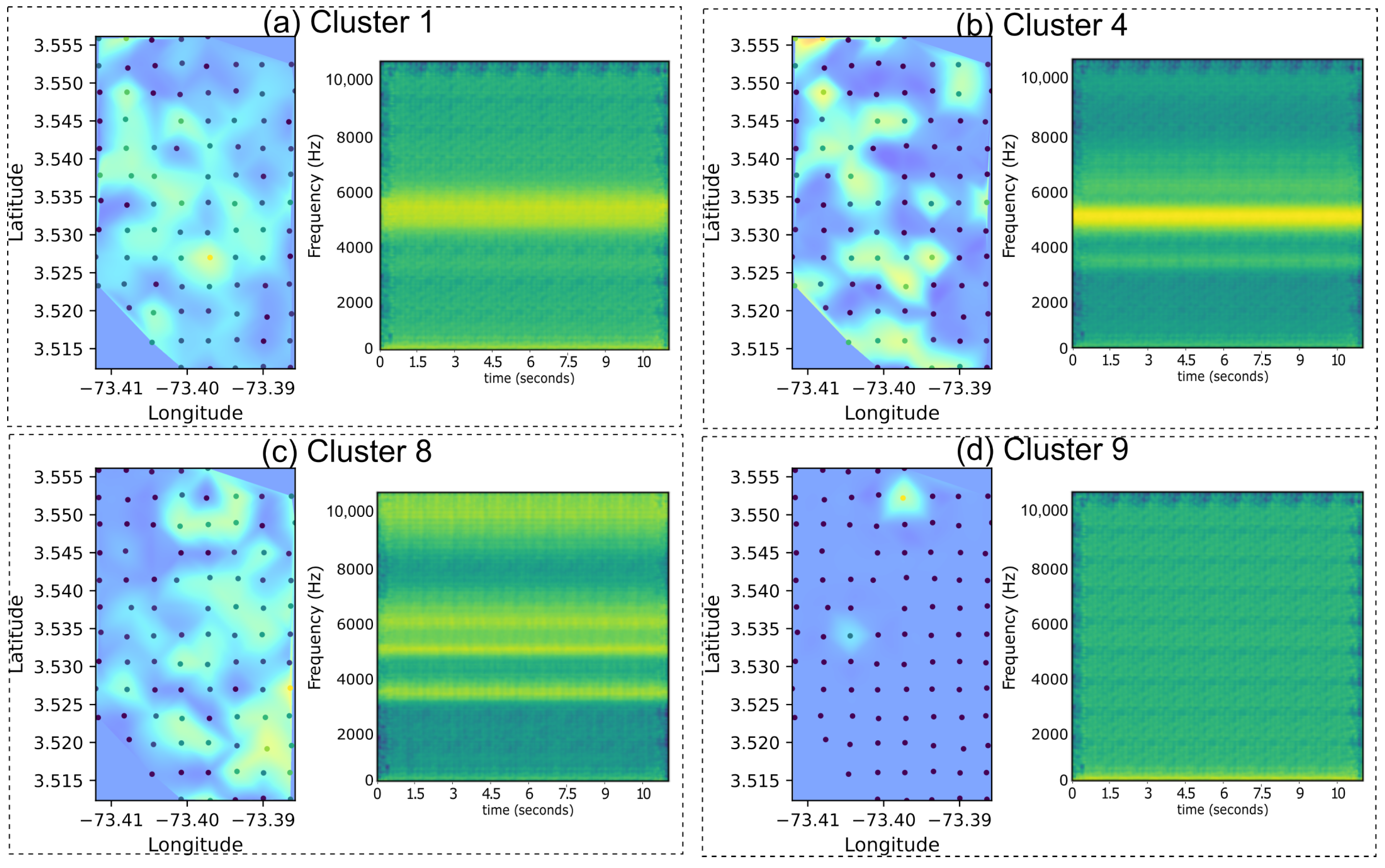
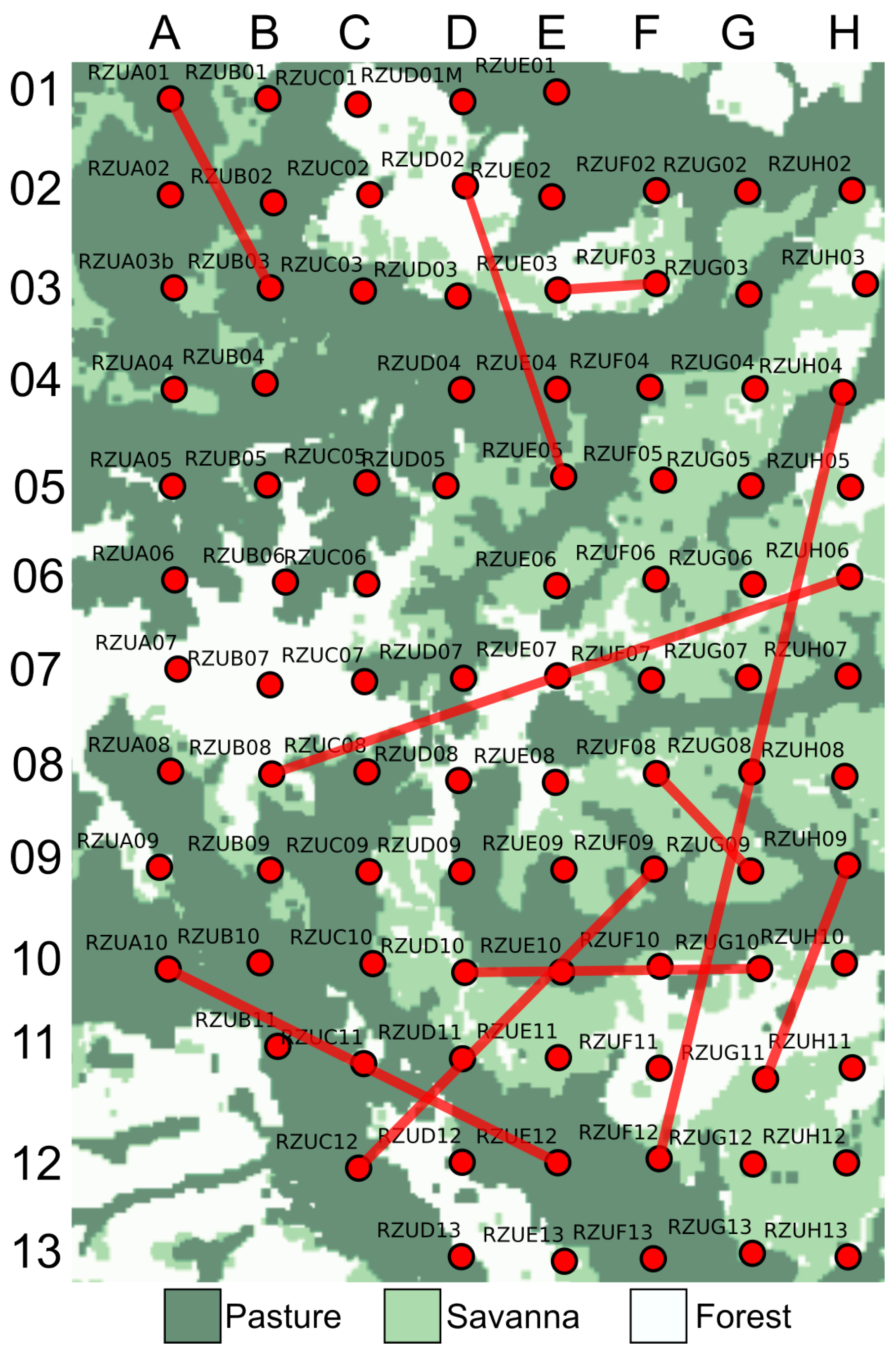
3.3. Soundscape Spatial Pattern Analysis
3.3.1. Methodological Description of the Spatial Pattern Analysis
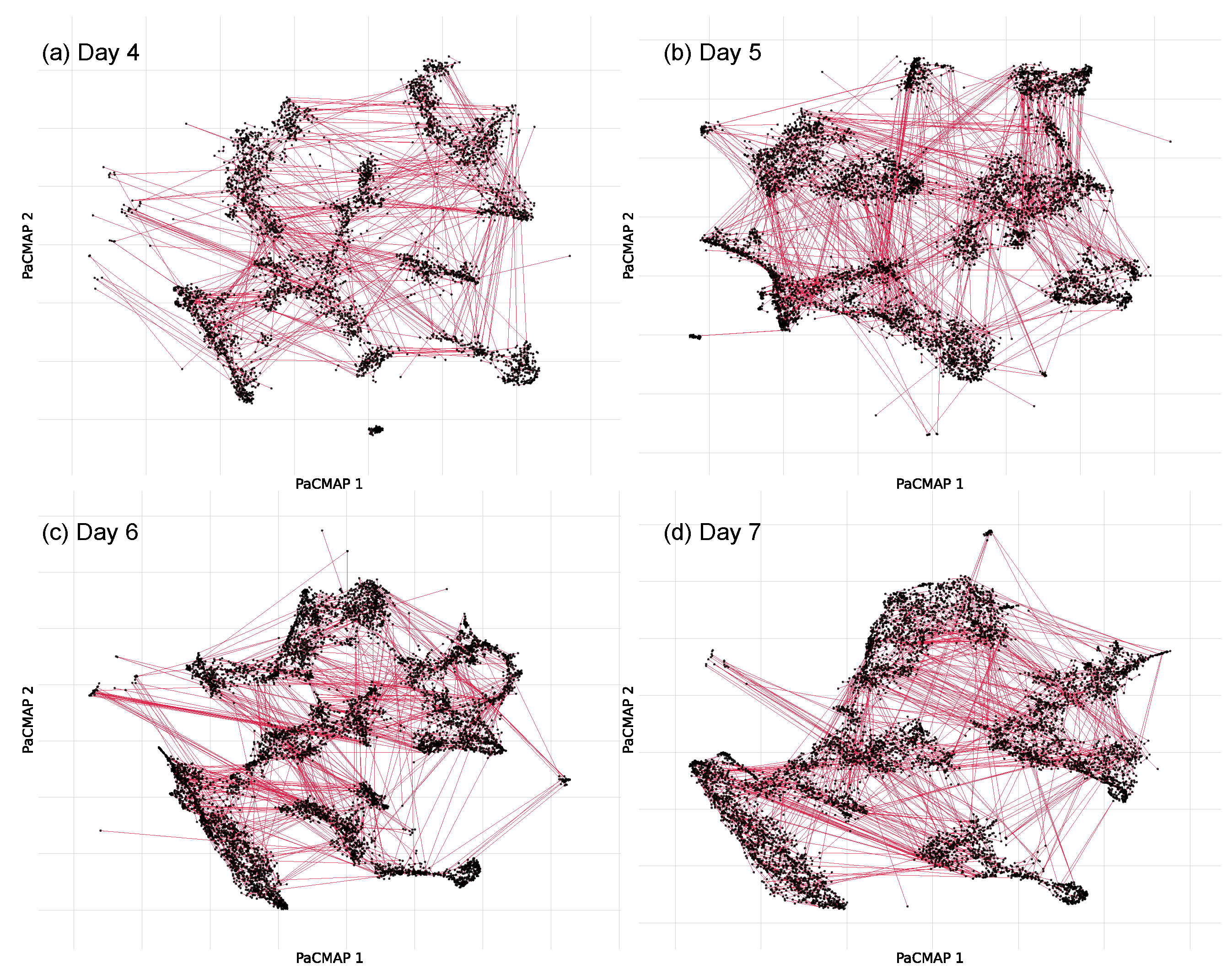
3.3.2. Spatial Pattern Results of the PaCMAP and DBSCAN Approach
3.3.3. Spatial Pattern Results of the UMAP and K-Means Approach
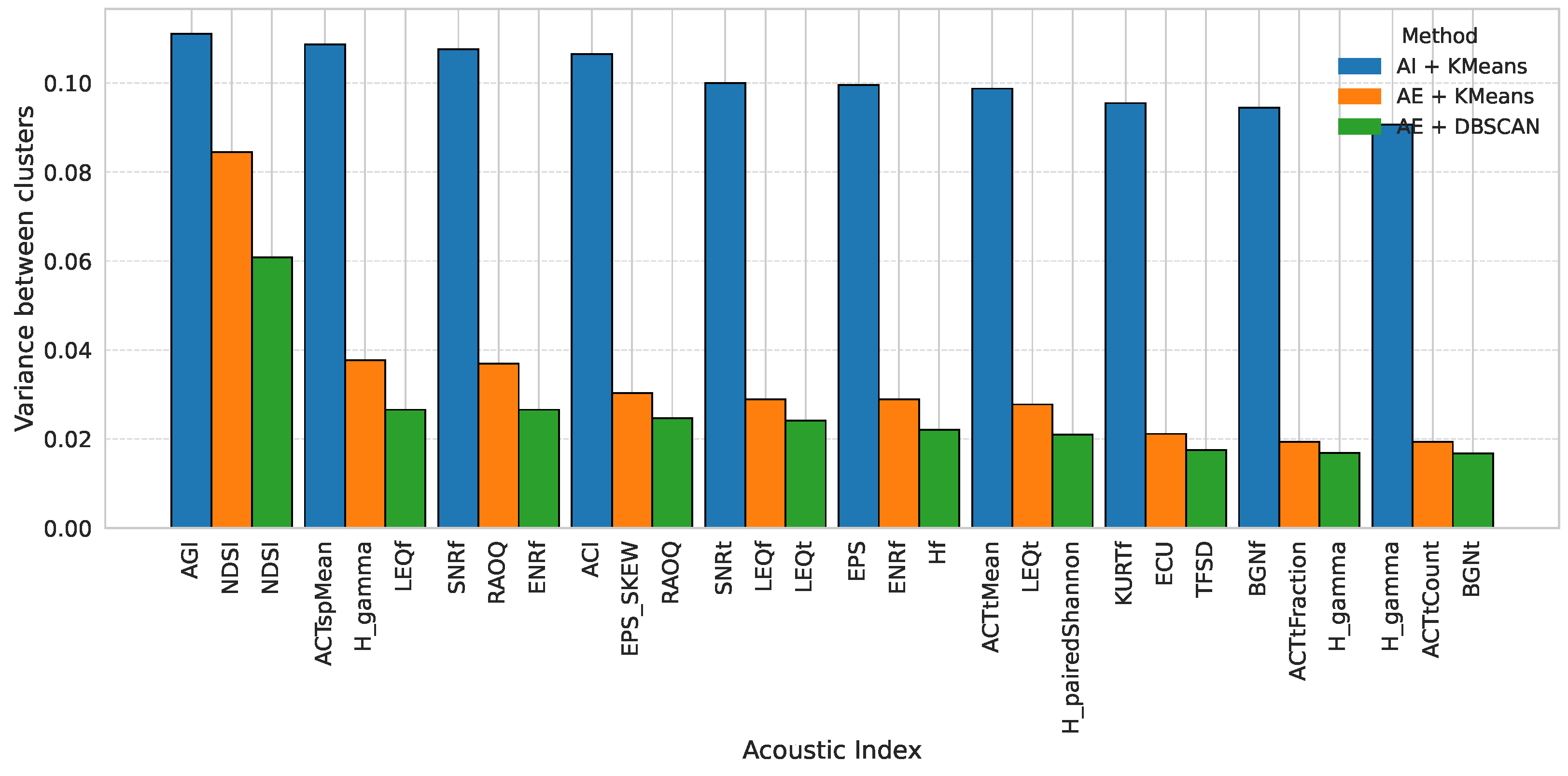
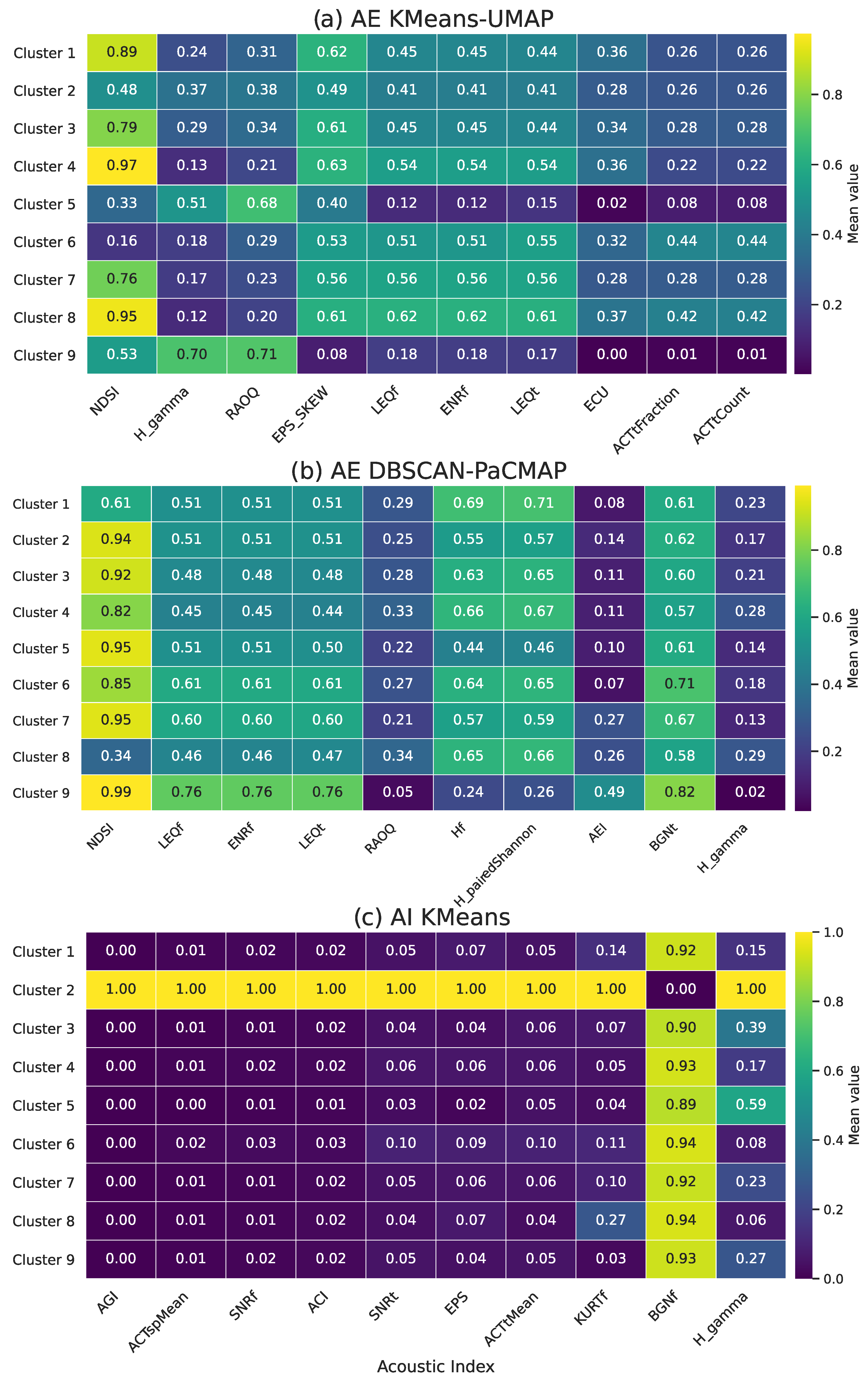
3.4. Acoustic Index Distribution Among Clusters
3.5. Soundscape Connectivity Based on Audio Features
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Abbr. | Full Name | Description (Variants) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACI | Acoustic Complexity Index | Measures variation in intensity over time within frequency bands; reflects biotic activity. Temporal and spectral variants exist. | [61] |
| ACTcount | Active segment count | Count of active segments in time or frequency. | [63] |
| ACTfraction | Active fraction | Proportion of signal above energy threshold. Exists in time and spectral forms. | [63] |
| ACTspMean | Mean active spectral width | Mean bandwidth of active spectral segments. Temporal variant: ACTtMean. | [63] |
| AEI | Acoustic Evenness Index | Energy evenness using Gini index. | [62] |
| AGI | Acoustic Generalized Index | Composite of multiple indices for biodiversity proxy. | [32] |
| BGN | Background noise | Ambient noise level. Estimated in time or frequency. | [57] |
| ECU | Entropy of cumulative spectrum | Cumulative entropy across frequency bins. | [32] |
| ENRF | Spectral energy ratio | Ratio of energy in frequency bands. | [62] |
| EPS | Entropy of power spectrum | Entropy of power spectral density. Variants include EPS_SKEW and EPS_KURT. | [58] |
| H_gamma | Gamma entropy | Entropy modulated by gamma; measures distribution complexity. | [60] |
| H_pairedShannon | Paired Shannon entropy | Shannon entropy for co-occurring components. | [60] |
| Hf | Spectral entropy | Entropy of energy across frequencies. Time-domain variant: Ht. | [60] |
| KURT | Kurtosis | Peakedness of amplitude or frequency distribution. Time and frequency variants. | [32] |
| LEQ | Equivalent continuous level | Averaged sound pressure level. Variants exist in time and frequency. | [58] |
| NDSI | Normalized Difference Soundscape Index | Compares biological vs. anthropogenic energy. Time and frequency variants exist. | [58] |
| RAOQ | Rao’s quadratic entropy | Biodiversity metric accounting for trait dissimilarity. | [59] |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio | Signal vs. noise energy ratio. Temporal and spectral forms exist. | [28] |
References
- Rendon, N.; Rodríguez-Buritica, S.; Sanchez-Giraldo, C.; Daza, J.M.; Isaza, C. Automatic acoustic heterogeneity identification in transformed landscapes from Colombian tropical dry forests. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 109017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, A.E.; Jensen, F.H.; Jarriel, S.D.; Aoki, N.; Ferguson, S.R.; Hyer, M.D.; Apprill, A.; Mooney, T.A. Unsupervised clustering reveals acoustic diversity and niche differentiation in pulsed calls from a coral reef ecosystem. Front. Remote Sens. 2024, 5, 1429227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, A.; Casey, M.; Moscoso, P.; Peck, M. A new method for ecoacoustics? Toward the extraction and evaluation of ecologically-meaningful soundscape components using sparse coding methods. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Ospina, A.E.; Rodríguez-Marín, P.; López, J.D.; Martínez-Vargas, J.D. Leveraging time-based acoustic patterns for ecosystem analysis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 20513–20526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.S.; Jones, N.S.; Fulcher, B.D.; Picinali, L.; Clink, D.J.; Klinck, H.; Orme, C.D.L.; Wrege, P.H.; Ewers, R.M. Characterizing soundscapes across diverse ecosystems using a universal acoustic feature set. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17049–17055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, H.; Mitchell, A.; Aletta, F.; Kang, J.; Botteldooren, D. AI-based soundscape analysis: Jointly identifying sound sources and predicting annoyance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 154, 3145–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, J.G.; Carvalho, J.R.; Rosso, O.A. Estimating ecoacoustic activity in the Amazon rainforest through information theory quantifiers. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, S.; Wood, C.M.; Eibl, M.; Klinck, H. BirdNET: A deep learning solution for avian diversity monitoring. Ecol. Informatics 2021, 61, 101236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sato, K.; Gautam, B.P. A Methodological Literature Review of Acoustic Wildlife Monitoring Using Artificial Intelligence Tools and Techniques. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuia, D.; Kellenberger, B.; Beery, S.; Costelloe, B.R.; Zuffi, S.; Risse, B.; Mathis, A.; Mathis, M.W.; van Langevelde, F.; Burghardt, T.; et al. Perspectives in machine learning for wildlife conservation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Mora, D.A.; Rodríguez-Buritica, S.; Rodríguez-Marín, P.; Martínez-Vargaz, J.D.; Isaza-Narváez, C. Systematic review of machine learning methods applied to ecoacoustics and soundscape monitoring. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, K.A.; Eldridge, A.; Sandom, C.J.; Simpson, I.J. Towards interpretable learned representations for ecoacoustics using variational auto-encoding. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, S.; Axel, A.C.; Tucker, D.; Gage, S.H. Connecting soundscape to landscape: Which acoustic index best describes landscape configuration? Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, N.; Guerrero, M.J.; Sánchez-Giraldo, C.; Martinez-Arias, V.M.; Paniagua-Villada, C.; Bouwmans, T.; Daza, J.M.; Isaza, C. Letting ecosystems speak for themselves: An unsupervised methodology for mapping landscape acoustic heterogeneity. Environ. Model. Softw. 2025, 187, 106373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, M.J.; Sánchez-Giraldo, C.; Uribe, C.A.; Martínez-Arias, V.M.; Isaza, C. Graphical representation of landscape heterogeneity identification through unsupervised acoustic analysis. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2025, 16, 1255–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Guo, C.; Wan, J.; Ren, H. piRNA-disease association prediction based on multi-channel graph variational autoencoder. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiyapuri, T.; Binbusayyis, A. Application of deep autoencoder as an one-class classifier for unsupervised network intrusion detection: A comparative evaluation. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2020, 6, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Zheng, J.; Qu, H. Anomaly detection for blueberry data using sparse autoencoder-support vector machine. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiec, M.L.; Dikow, R.B.; Frandsen, P.B.; McKeeken, A.; Valentini, G.; White, A.E. Deep learning as a tool for ecology and evolution. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 1640–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirn, J.; García, J.E.; Montesinos-Navarro, A.; Sánchez-Martín, R.; Sanz, V.; Verdú, M. A deep Generative Artificial Intelligence system to predict species coexistence patterns. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guei, A.C.; Christin, S.; Lecomte, N.; Hervet, É. ECOGEN: Bird sounds generation using deep learning. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2024, 15, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, B.; Eichinski, P.; Zhang, J.; Roe, P. Acoustic auto-encoders for biodiversity assessment. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 62, 101237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, M.J.; Restrepo, J.; Nieto-Mora, D.A.; Daza, J.M.; Isaza, C. Insights from Deep Learning in Feature Extraction for Non-supervised Multi-species Identification in Soundscapes. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (Incl. Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinform.) 2022, 13788, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casallas-Pabón, D.; Calvo-Roa, N.; Rojas-Robles, R. Seed dispersal by bats over successional gradients in the Colombian orinoquia (San Martin, Meta, Colombia). Acta Biológica Colomb. 2017, 22, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez B, H.; Mejía, W.; Barrera Zambrano, V.A. Flora al Interior del Área 1 del Banco de Hábitat del Meta de Terrasos. v2.9; SiB Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Mora, D.A.; Ferreira de Oliveira, M.C.; Sanchez-Giraldo, C.; Duque-Muñoz, L.; Isaza-Narváez, C.; Martínez-Vargas, J.D. Soundscape Characterization Using Autoencoders and Unsupervised Learning. Sensors 2024, 24, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, K.A.; Eldridge, A.; Sandom, C.J.; Simpson, I.J. Towards interpretable learned representations for ecoacoustics using variational auto-encoding. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, Z. Biotic sound SNR influence analysis on acoustic indices. Front. Remote Sens. 2022, 3, 1079223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omprakash, A.; Balakrishnan, R.; Ewers, R.; Sethi, S. Interpretable and Robust Machine Learning for Exploring and Classifying Soundscape Data. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoh, N.; Haley, C.L.; Burivalova, Z. Time series methods for the analysis of soundscapes and other cyclical ecological data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2024, 15, 1158–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowans, A.; Lambin, X.; Hare, D.; Sutherland, C. Improving the integration of artificial intelligence into existing ecological inference workflows. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2024, 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, J.S.; Haupert, S.; Latorre, J.F.; Aubin, T.; Sueur, J. scikit-maad: An open-source and modular toolbox for quantitative soundscape analysis in Python. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, 2334–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmeke, J.F.; Ellis, D.P.W.; Freedman, D.; Jansen, A.; Lawrence, W.; Moore, R.C.; Plakal, M.; Ritter, M. Audio Set: An ontology and human-labeled dataset for audio events. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Ospina, A.E.; Solarte-Sanchez, M.A.; Vega-Escobar, L.S.; Isaza, C.; Martínez-Vargas, J.D. Graph-Based Audio Classification Using Pre-Trained Models and Graph Neural Networks. Sensors 2024, 24, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Melville, J. UMAP: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1802.03426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Rudin, C.; Shaposhnik, Y. Understanding How Dimension Reduction Tools Work : An. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 22, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Venna, J.; Kaski, S. Neighborhood preservation in nonlinear projection methods: An experimental study. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (Incl. Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinform.) 2001, 2130, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya, C.; Isaza, C.; Daza, J.M.; López, J.D. Automatic identification of rainfall in acoustic recordings. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco, I.; Singh, S.; Morfi, V.; Lostanlen, V.; Strandburg-Peshkin, A.; Vidaña-Vila, E.; Gill, L.; Pamuła, H.; Whitehead, H.; Kiskin, I.; et al. Learning to detect an animal sound from five examples. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Pieretti, N.; Salutari, P.; Tognari, E.; Lombardi, A. The Application of the Acoustic Complexity Indices (ACI) to Ecoacoustic Event Detection and Identification (EEDI) Modeling. Biosemiotics 2016, 9, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, J.S.; Aubin, T.; Llusia, D.; Courtois, É.A.; Fouquet, A.; Gaucher, P.; Pavoine, S.; Sueur, J. Explosive breeding in tropical anurans: Environmental triggers, community composition and acoustic structure. BMC Ecol. 2019, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dröge, S.; Budi, L.; Muys, B. Acoustic indices as proxies for biodiversity in certified and non-certified cocoa plantations in Indonesia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrity, M.W.; Saunders, L.M.; Queitsch, C.; Fields, S.; Trapnell, C. Dimensionality reduction by UMAP to visualize physical and genetic interactions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poblete, V.; Espejo, D.; Vargas, V.; Otondo, F.; Huijse, P. Characterization of sonic events present in natural-urban hybrid habitats using umap and sednet: The case of the urban wetlands. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Jensen, F.H.; Averly, B.; Demartsev, V.; Manser, M.B.; Sainburg, T.; Roch, M.A.; Strandburg-Peshkin, A. A practical guide for generating unsupervised, spectrogram-based latent space representations of animal vocalizations. J. Anim. Ecol. 2022, 91, 1567–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanju, P. Advancing dimensionality reduction for enhanced visualization and clustering in single-cell transcriptomics. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2025, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueur, J.; Farina, A. Ecoacoustics: The Ecological Investigation and Interpretation of Environmental Sound. Biosemiotics 2015, 8, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Du, Y.; Mao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J. AMD-DBSCAN: An Adaptive Multi-density DBSCAN for datasets of extremely variable density. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 9th International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), Shenzhen, China, 13–16 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, J.; Hassan, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Yang, C.; Zhou, X.; Jia, F. Density peak clustering algorithms: A review on the decade 2014–2023. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 121860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, R.T.; McKenna, M.F.; Clapp, M.; Meyer, E.; Stabenau, E.; Angeloni, L.M.; Crooks, K.; Wittemyer, G. Efficacy of extracting indices from large-scale acoustic recordings to monitor biodiversity. Conserv. Biol. 2018, 32, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.B.; Aguiar, L.; Jones, G. Do acoustic indices reflect the characteristics of bird communities in the savannas of Central Brazil? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradfer-Lawrence, T.; Gardner, N.; Bunnefeld, L.; Bunnefeld, N.; Willis, S.G.; Dent, D.H. Guidelines for the use of acoustic indices in environmental research. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Giraldo, C.; Correa Ayram, C.; Daza, J.M. Environmental sound as a mirror of landscape ecological integrity in monitoring programs. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 19, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Lima, R.S.; Ferreira, L.M.; Oliveira, E.G.; Lopes, L.C.; Brito, M.R.; Baumgarten, J.; Rodrigues, F.H. What do insects, anurans, birds, and mammals have to say about soundscape indices in a tropical savanna. J. Ecoacoust. 2018, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholghi, M.; Phillips, Y.; Towsey, M.; Sitbon, L. Active learning for classifying long-duration audio recordings of the environment. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1948–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradfer-Lawrence, T.; Duthie, B.; Abrahams, C.; Adam, M.; Barnett, R.; Beeston, A.; Darby, J.; Dell, B.; Gardner, N.; Gasc, A.; et al. The Acoustic Index User’s Guide: A practical manual for defining, generating and understanding current and future acoustic indices. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2024, 16, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towsey, M.W. Noise Removal from Wave-Forms and Spectrograms Derived from Natural Recordings of the Environment. Available online: http://eprints.qut.edu.au/61399/ (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Towsey, M.; Wimmer, J.; Williamson, I.; Roe, P. The use of acoustic indices to determine avian species richness in audio-recordings of the environment. Ecol. Inform. 2014, 21, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta-Dukát, Z. Rao’s quadratic entropy as a measure of functional diversity based on multiple traits. J. Veg. Sci. 2005, 16, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, O.; Nunes, C.; Abrahams, C.; Baccaro, F.; Bradfer-Lawrence, T.; Lees, A.; Vale, E.; Barlow, J. The efficacy of acoustic indices for monitoring abundance and diversity in soil soundscapes. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, N.; Farina, A.; Morri, D. A new methodology to infer the singing activity of an avian community: The Acoustic Complexity Index (ACI). Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasten, E.P.; Gage, S.H.; Fox, J.; Joo, W. The remote environmental assessment laboratory’s acoustic library: An archive for studying soundscape ecology. Ecol. Inform. 2012, 12, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijanowski, B.C.; Villanueva-Rivera, L.J.; Dumyahn, S.L.; Farina, A.; Krause, B.L.; Napoletano, B.M.; Gage, S.H.; Pieretti, N. Soundscape ecology: The science of sound in the landscape. BioScience 2011, 61, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, D.; Ryan, S.J.; Beier, P.; Cushman, S.A.; Dieffenbach, F.; Trombulak, S.C. The Role of Landscape Connectivity in Planning and Implementing Conservation and Restoration Priorities; Issues in Ecology; Ecological Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, M.R.; Fortin, M.J. From graphs to spatial graphs. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2010, 41, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, C.A.; Burns, P.; Jantz, P.; Salas, L.; Goetz, S.; Clark, M. Soundscape mapping: Understanding regional spatial and temporal patterns of soundscapes incorporating remotely-sensed predictors and wildfire disturbance. Environ. Res. Ecol. 2024, 3, 25002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertassello, L.E.; Bertuzzo, E.; Botter, G.; Jawitz, J.W.; Aubeneau, A.F.; Hoverman, J.T.; Rinaldo, A.; Rao, P.S. Dynamic spatio-temporal patterns of metapopulation occupancy in patchy habitats. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 201309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbal, E.; Barua, P.D.; Dogan, S.; Tuncer, T.; Acharya, U.R. Explainable automated anuran sound classification using improved one-dimensional local binary pattern and Tunable Q Wavelet Transform techniques. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 225, 120089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, D.; Auer, T.; Johnston, A.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, V.; Hochachka, W.M.; Kelling, S. Modeling avian full annual cycle distribution and population trends with citizen science data. Ecol. Appl. 2020, 30, e02056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


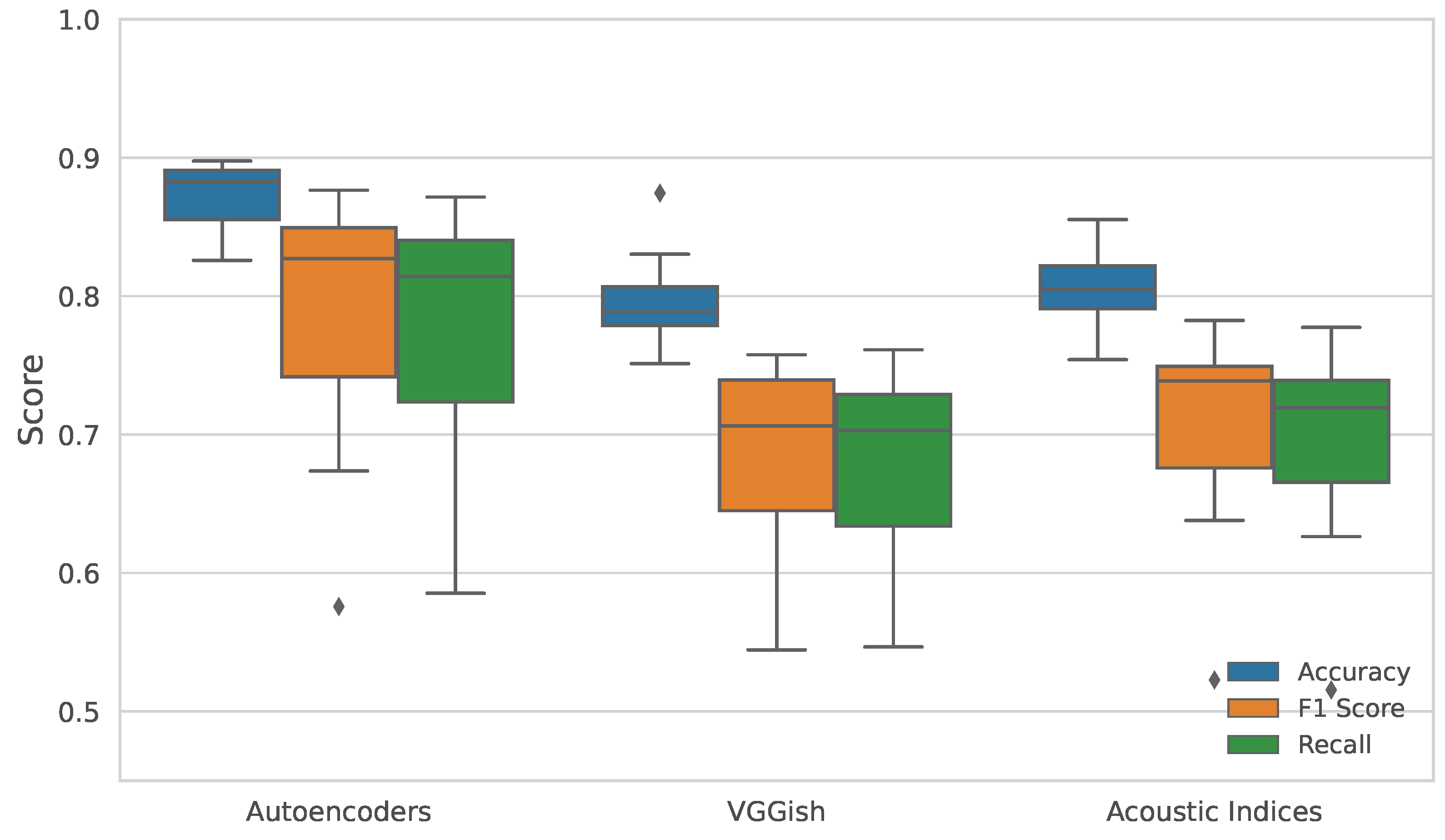

| Metric | Test | Comparison | Statistic | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Friedman | AE, VGG, AI | 20.182 | 0.00004 *** |
| Accuracy | Wilcoxon | AE vs. VGG | 0.000 | 0.0010 *** |
| Accuracy | Wilcoxon | AE vs. AI | 1.000 | 0.0020 ** |
| Accuracy | Wilcoxon | VGG vs. AI | 0.000 | 0.0010 *** |
| F1 Score | Friedman | AE, VGG, AI | 20.182 | 0.00004 *** |
| F1 Score | Wilcoxon | AE vs. VGG | 0.000 | 0.0010 *** |
| F1 Score | Wilcoxon | AE vs. AI | 1.000 | 0.0020 ** |
| F1 Score | Wilcoxon | VGG vs. AI | 0.000 | 0.0010 *** |
| Recall | Friedman | AE, VGG, AI | 20.182 | 0.00004 *** |
| Recall | Wilcoxon | AE vs. VGG | 0.000 | 0.0010 *** |
| Recall | Wilcoxon | AE vs. AI | 1.000 | 0.0020 ** |
| Recall | Wilcoxon | VGG vs. AI | 0.000 | 0.0010 *** |
| Metric | Test | Comparison | Statistic | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Friedman | AE, VGG, AI | 16.909 | 0.0002 *** |
| Accuracy | Wilcoxon | AE vs. VGG | 0.000 | 0.0010 *** |
| Accuracy | Wilcoxon | AE vs. AI | 0.000 | 0.0010 *** |
| Accuracy | Wilcoxon | VGG vs. AI | 20.000 | 0.2783 |
| F1 Score | Friedman | AE, VGG, AI | 15.273 | 0.0005 *** |
| F1 Score | Wilcoxon | AE vs. VGG | 0.000 | 0.0010 *** |
| F1 Score | Wilcoxon | AE vs. AI | 1.000 | 0.0020 ** |
| F1 Score | Wilcoxon | VGG vs. AI | 13.000 | 0.0830 |
| Recall | Friedman | AE, VGG, AI | 14.364 | 0.0008 *** |
| Recall | Wilcoxon | AE vs. VGG | 0.000 | 0.0010 *** |
| Recall | Wilcoxon | AE vs. AI | 1.000 | 0.0020 ** |
| Recall | Wilcoxon | VGG vs. AI | 18.000 | 0.2061 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nieto Mora, D.A.; Duque-Muñoz, L.; Martínez Vargas, J.D. Enhancing Soundscape Characterization and Pattern Analysis Using Low-Dimensional Deep Embeddings on a Large-Scale Dataset. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2025, 7, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7040109
Nieto Mora DA, Duque-Muñoz L, Martínez Vargas JD. Enhancing Soundscape Characterization and Pattern Analysis Using Low-Dimensional Deep Embeddings on a Large-Scale Dataset. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction. 2025; 7(4):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7040109
Chicago/Turabian StyleNieto Mora, Daniel Alexis, Leonardo Duque-Muñoz, and Juan David Martínez Vargas. 2025. "Enhancing Soundscape Characterization and Pattern Analysis Using Low-Dimensional Deep Embeddings on a Large-Scale Dataset" Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 7, no. 4: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7040109
APA StyleNieto Mora, D. A., Duque-Muñoz, L., & Martínez Vargas, J. D. (2025). Enhancing Soundscape Characterization and Pattern Analysis Using Low-Dimensional Deep Embeddings on a Large-Scale Dataset. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 7(4), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/make7040109





