Multi-Scale Experimental Investigation of UHPC Rheology: From Cement Paste to Fiber-Reinforced Mortar Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mixture Proportion and Sample Preparation
2.3. Test Methods
2.3.1. Slump Flow of UHPC at Three Scales
2.3.2. Rheological Properties of the Cement Paste
2.3.3. Rheological Properties of the Binder Paste
2.3.4. Rheological Properties of the Mortar Scale and Fiber-Reinforced Scale (UHPC)
2.3.5. Compressive, Flexural, and Tensile Strengths and the Heat of Hydration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fresh Properties
3.2. Limitation of the Modified Bingham Model
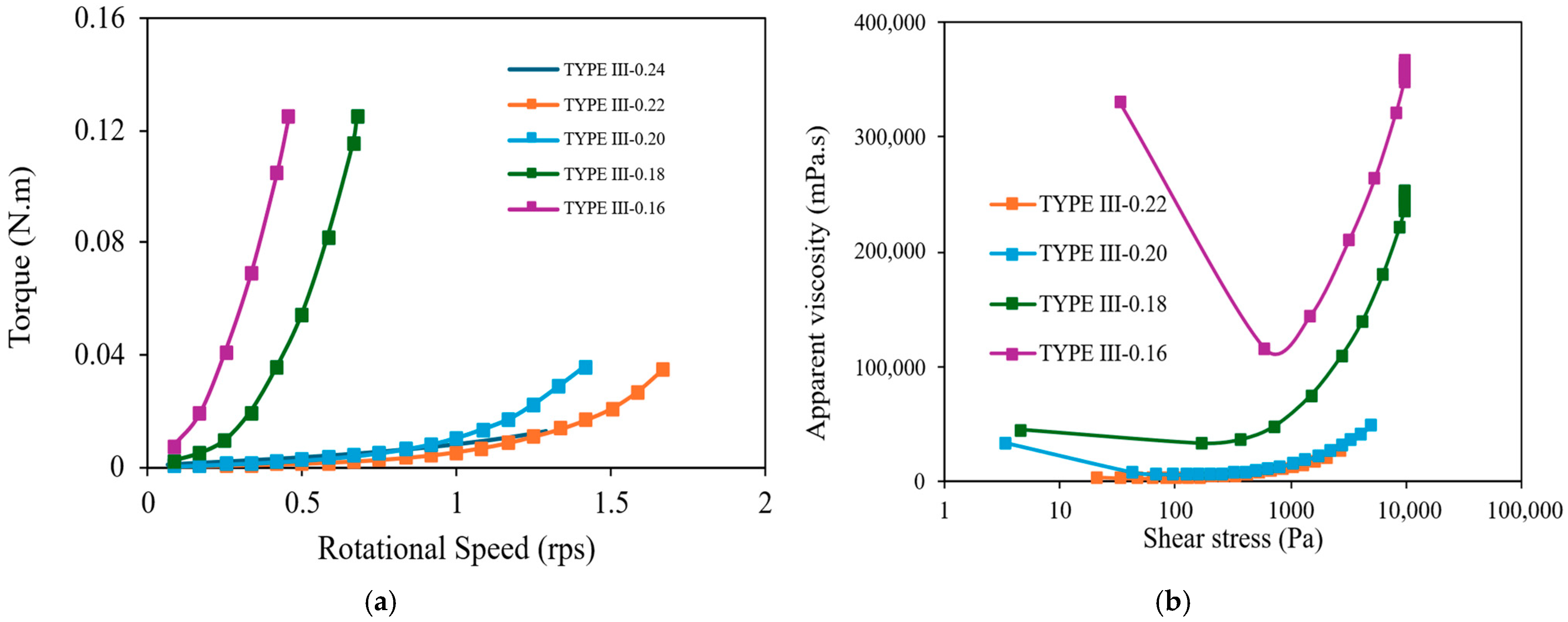
3.3. Effect of Cement Type and w/b on the Thixotropy of the Cement Paste
3.4. Effect of SL and SF on the Rheology of the Binder Paste Mixtures
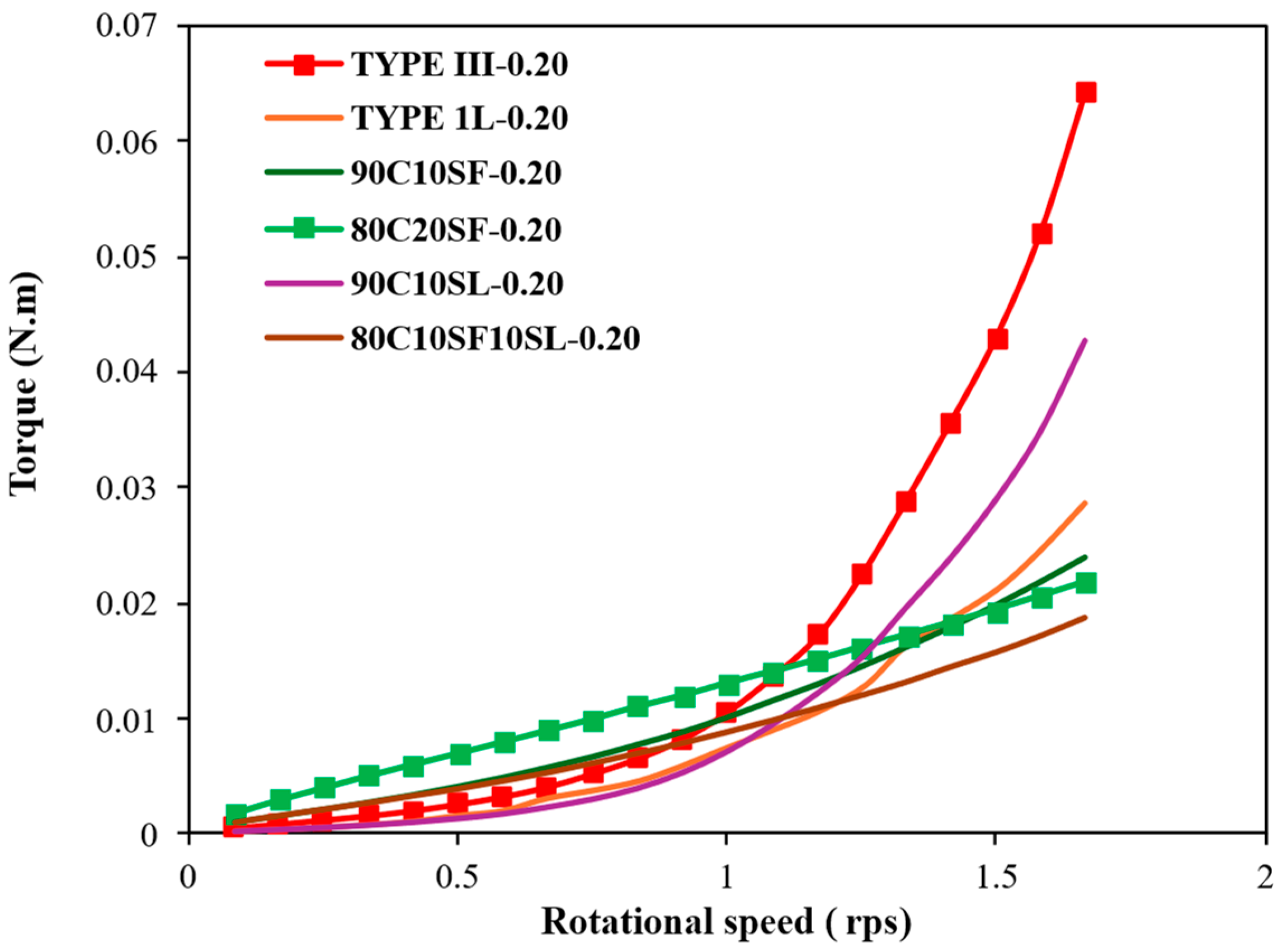
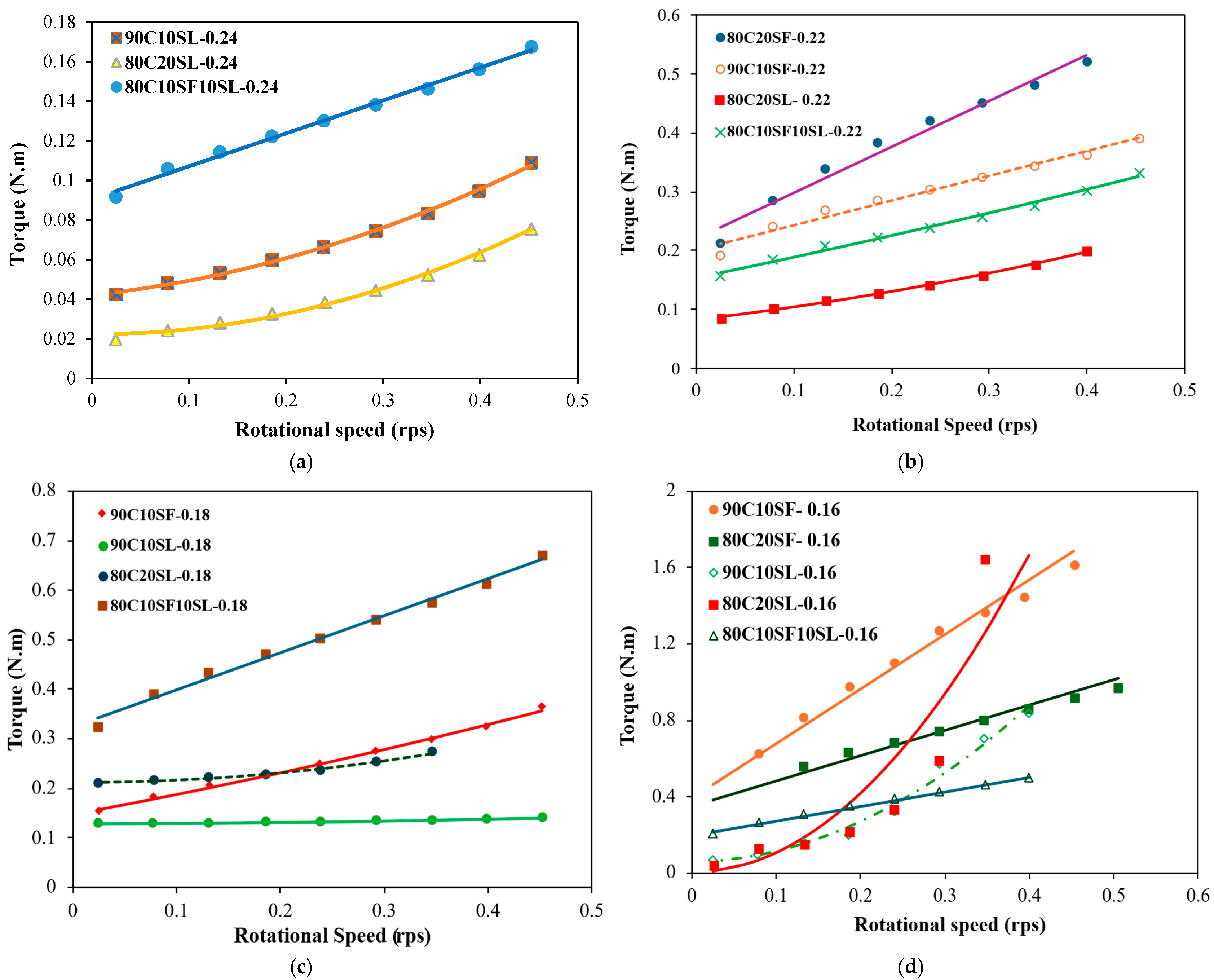
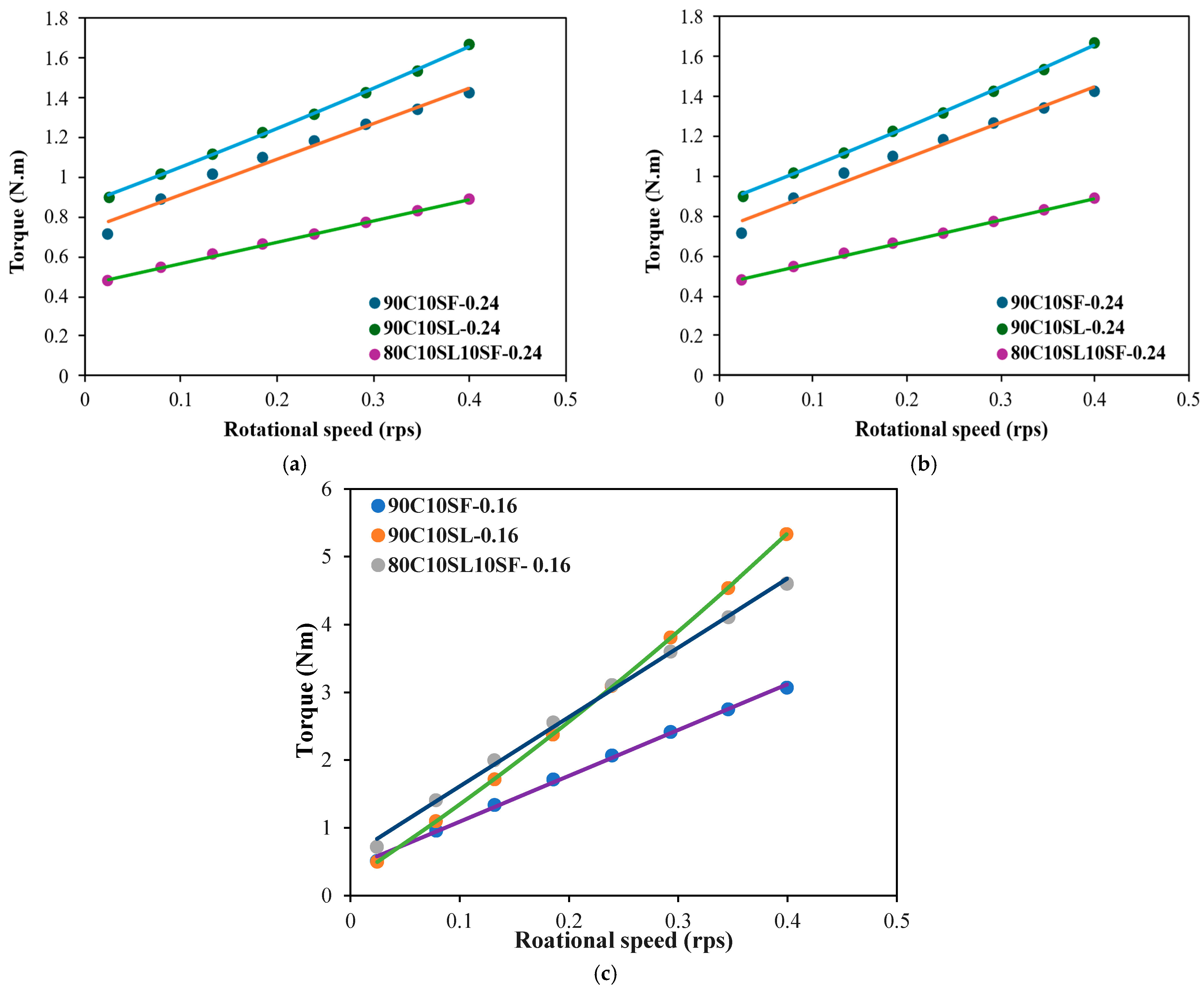
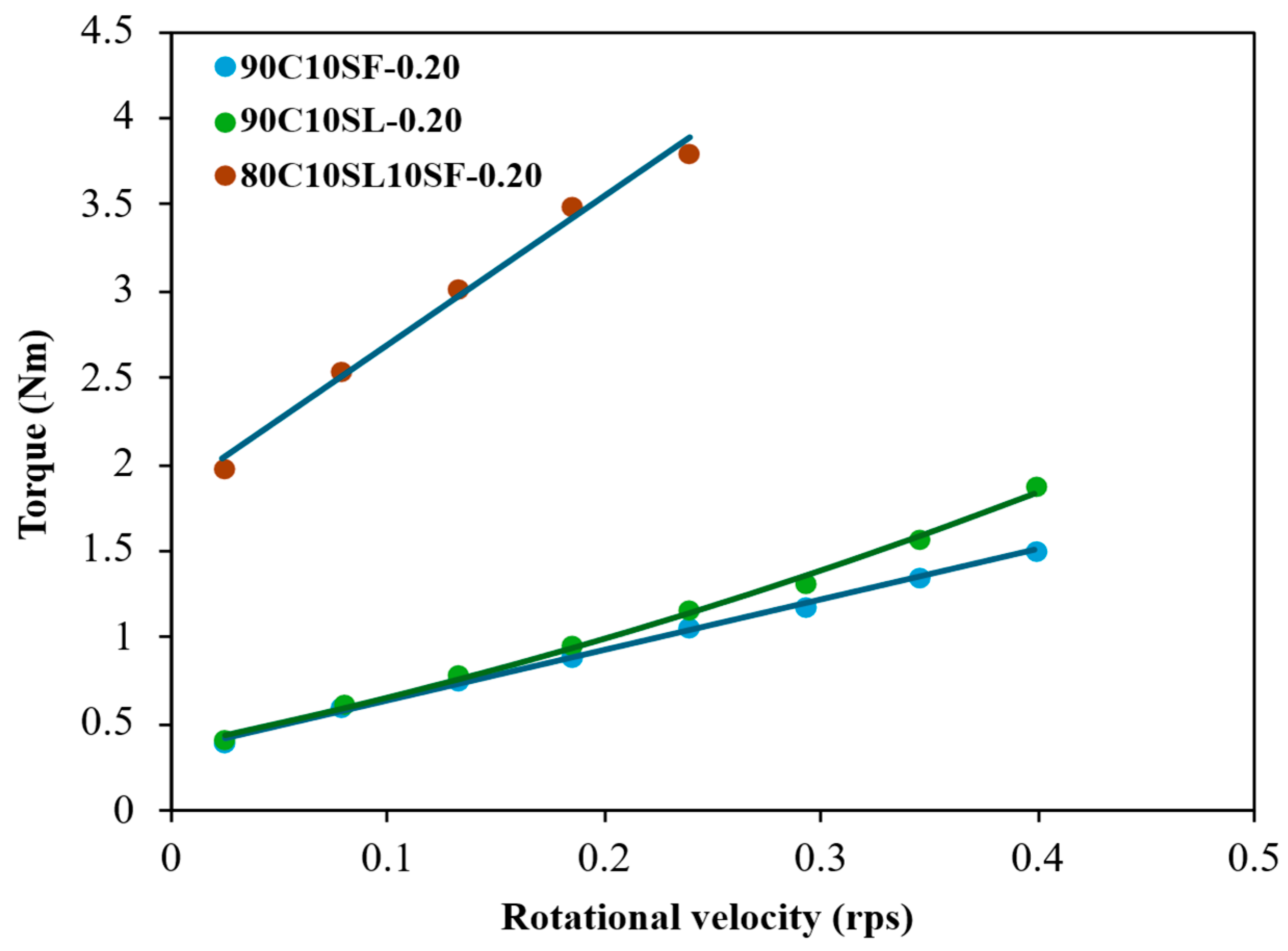
3.5. Rheological Properties of the High-Strength Mortar and UHPC Mixtures
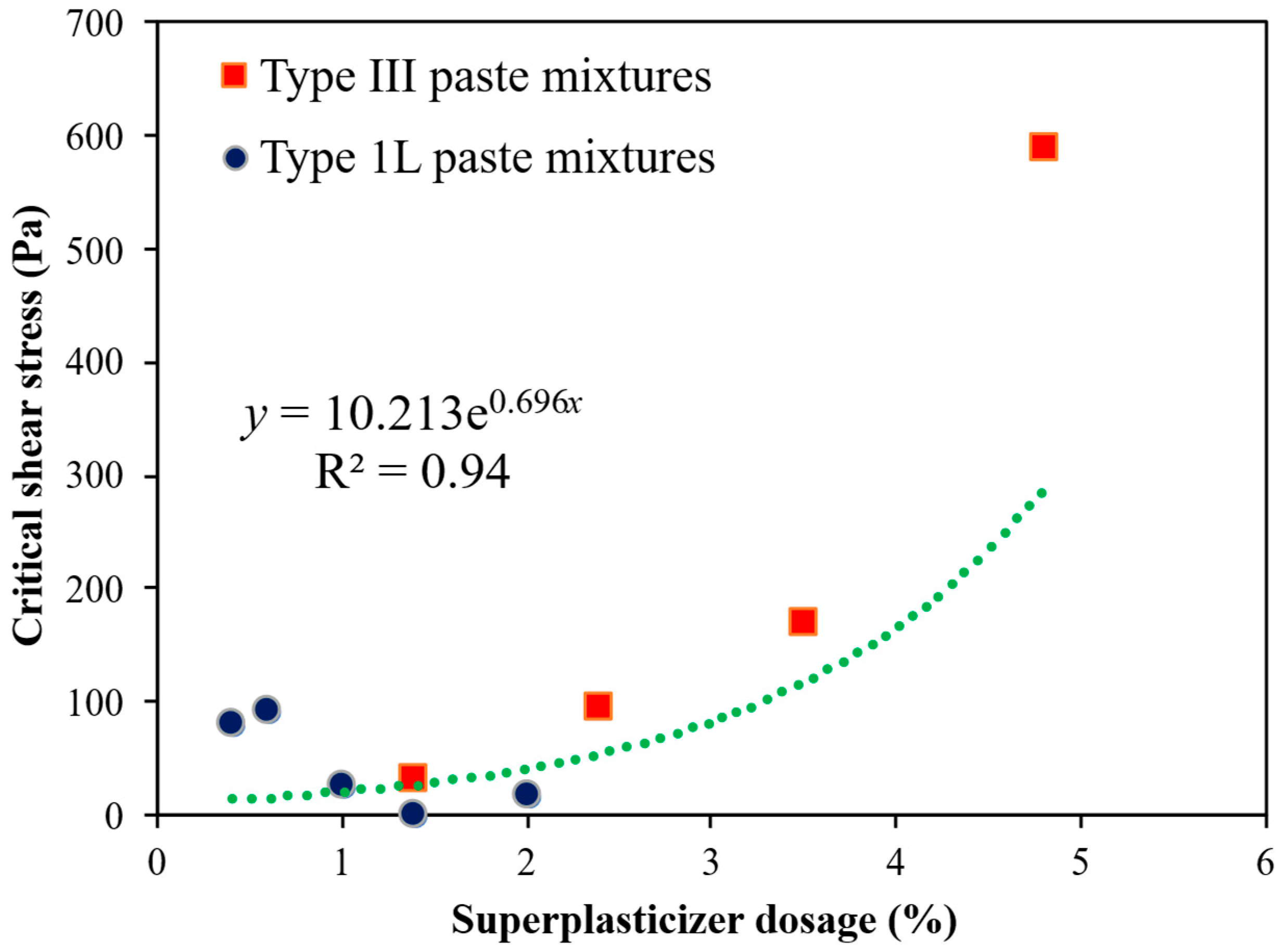
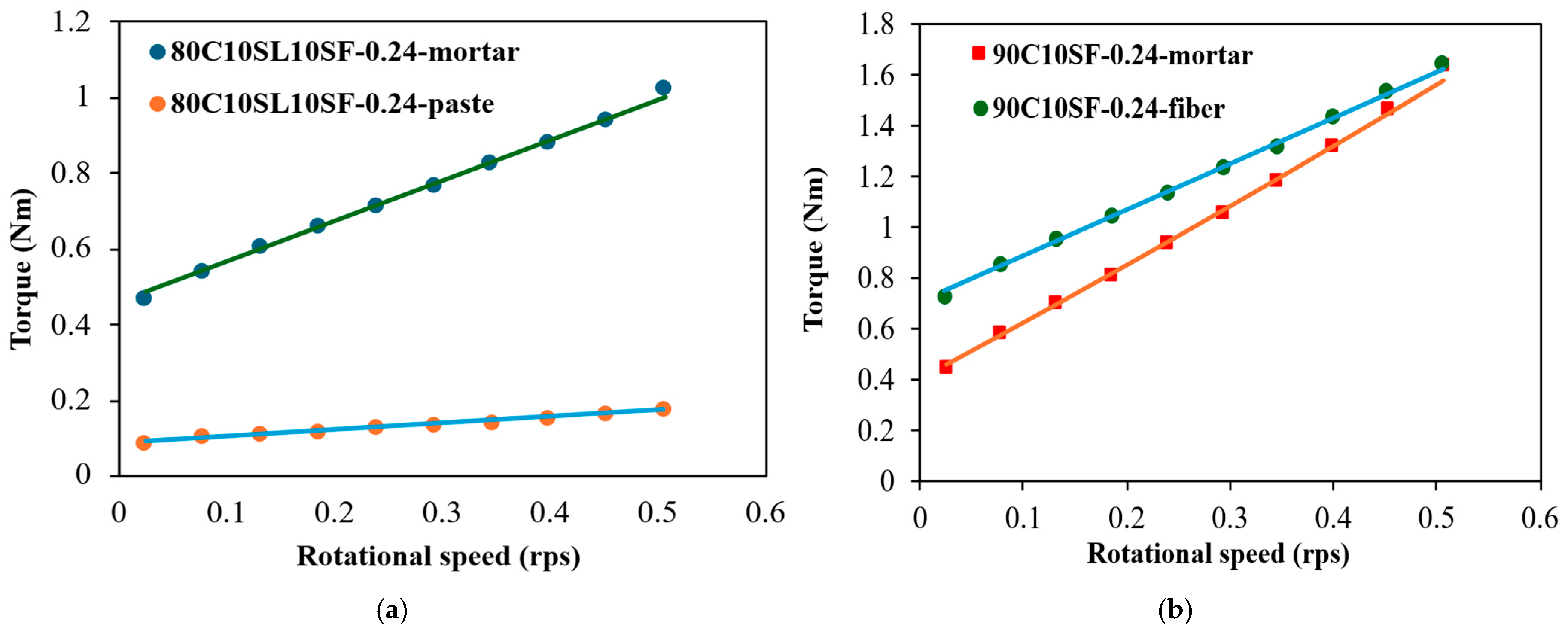
3.6. Relationships Between the Rheologies of the Paste, Mortar, and UHPC Scales
3.7. Isothermal Calorimetry
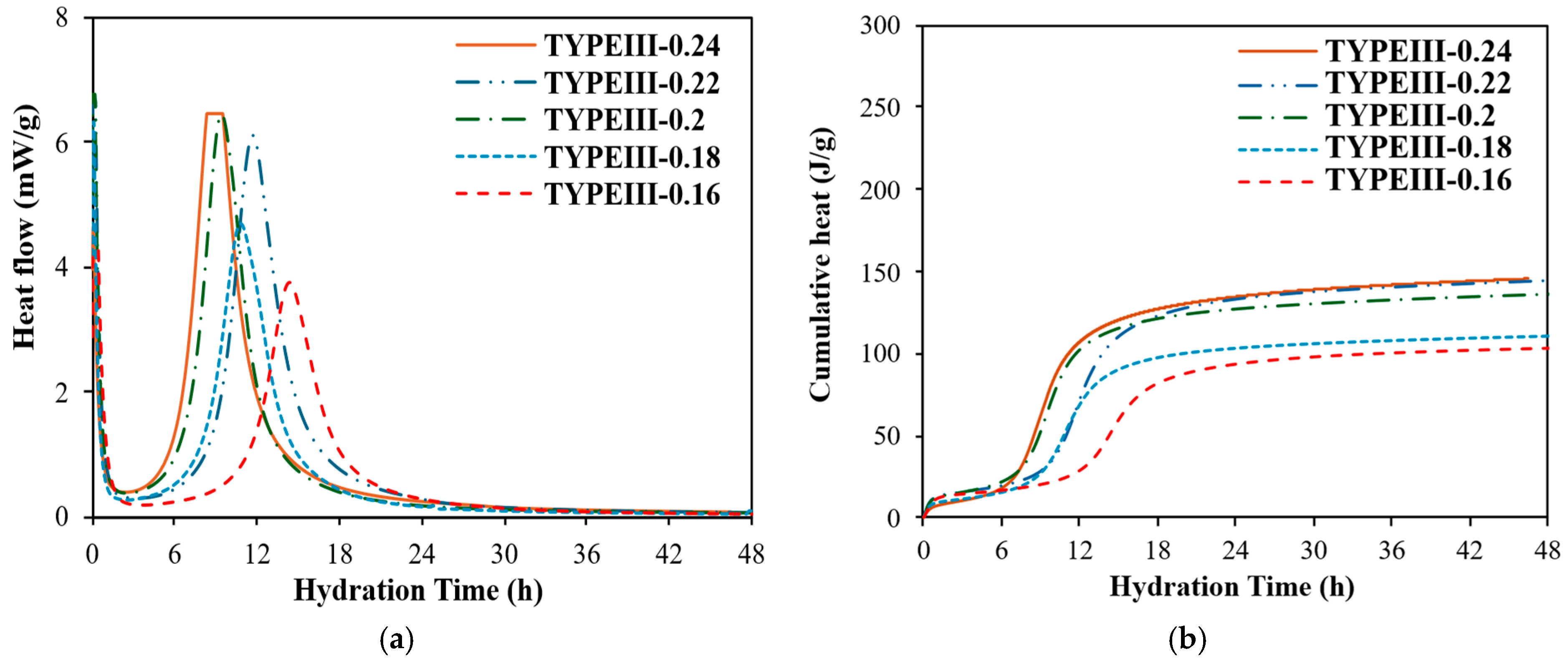
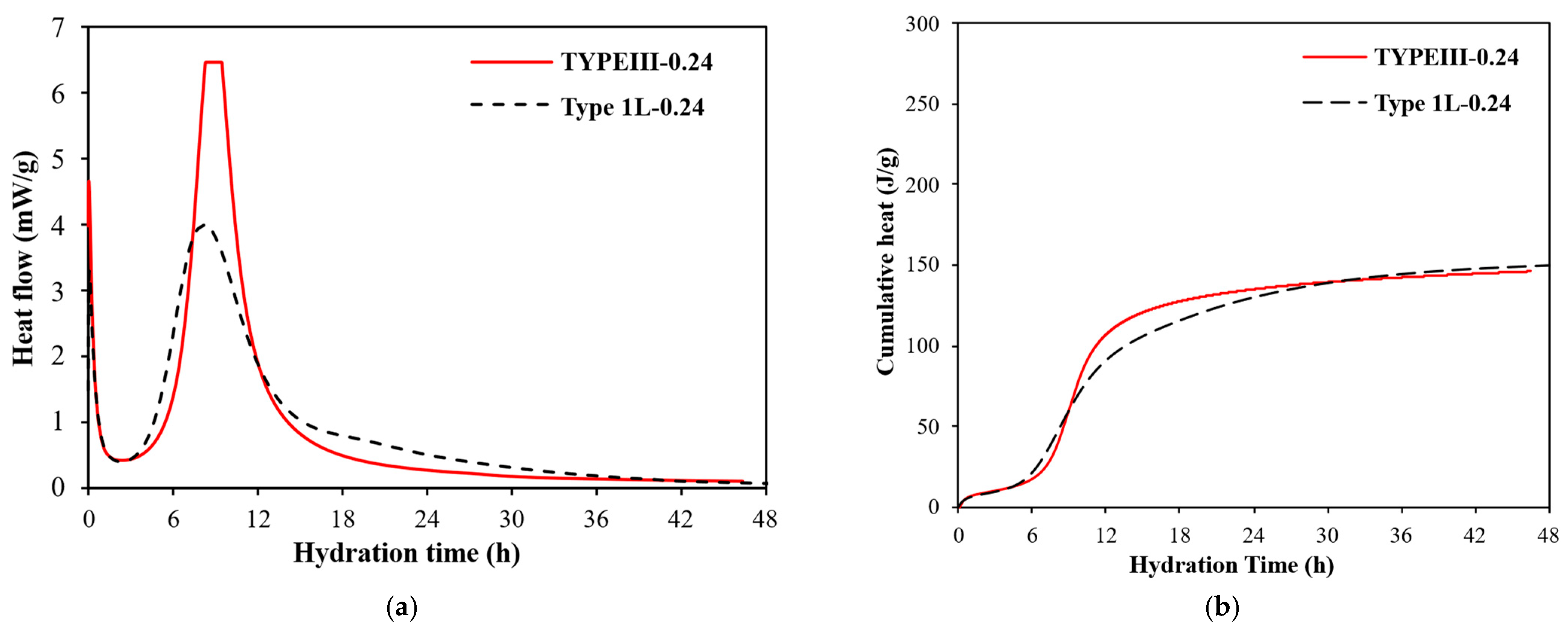
3.7.1. Effect of Cement Type and w/b on Heat of Hydration
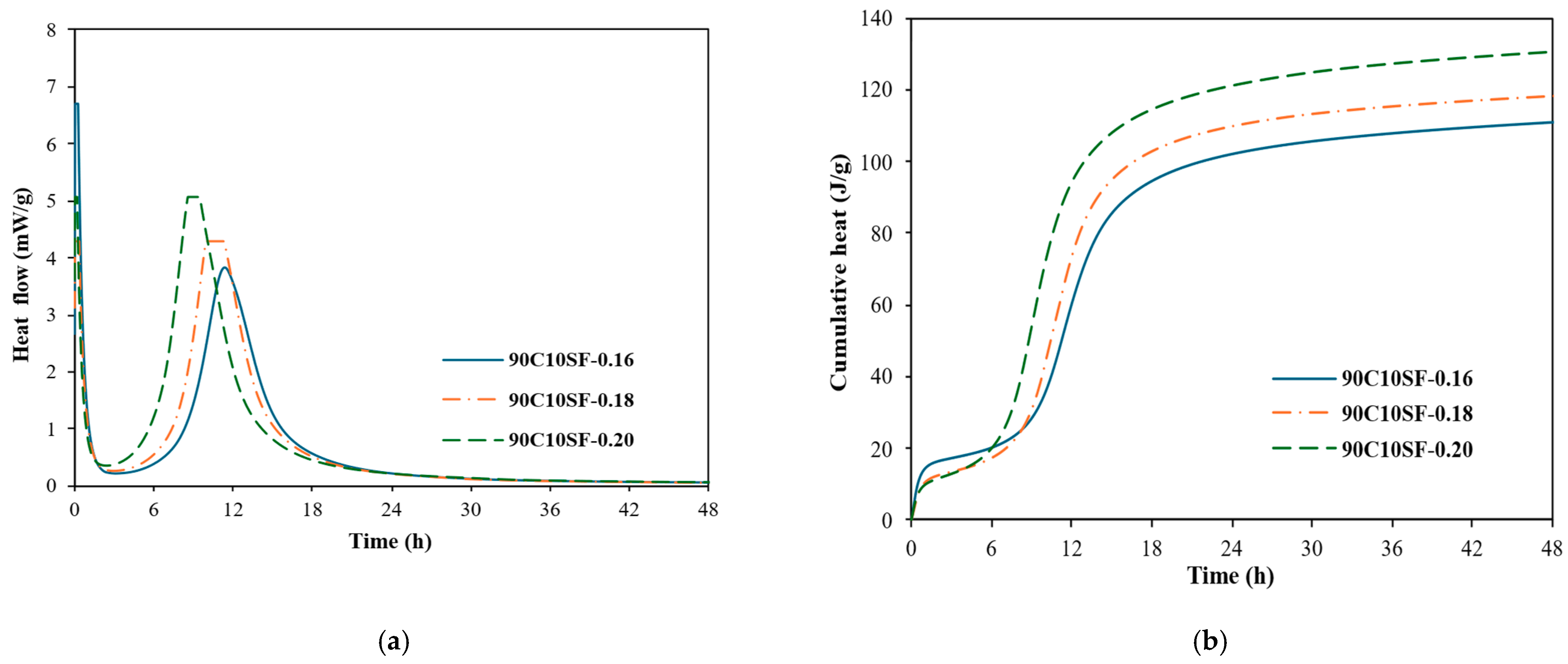
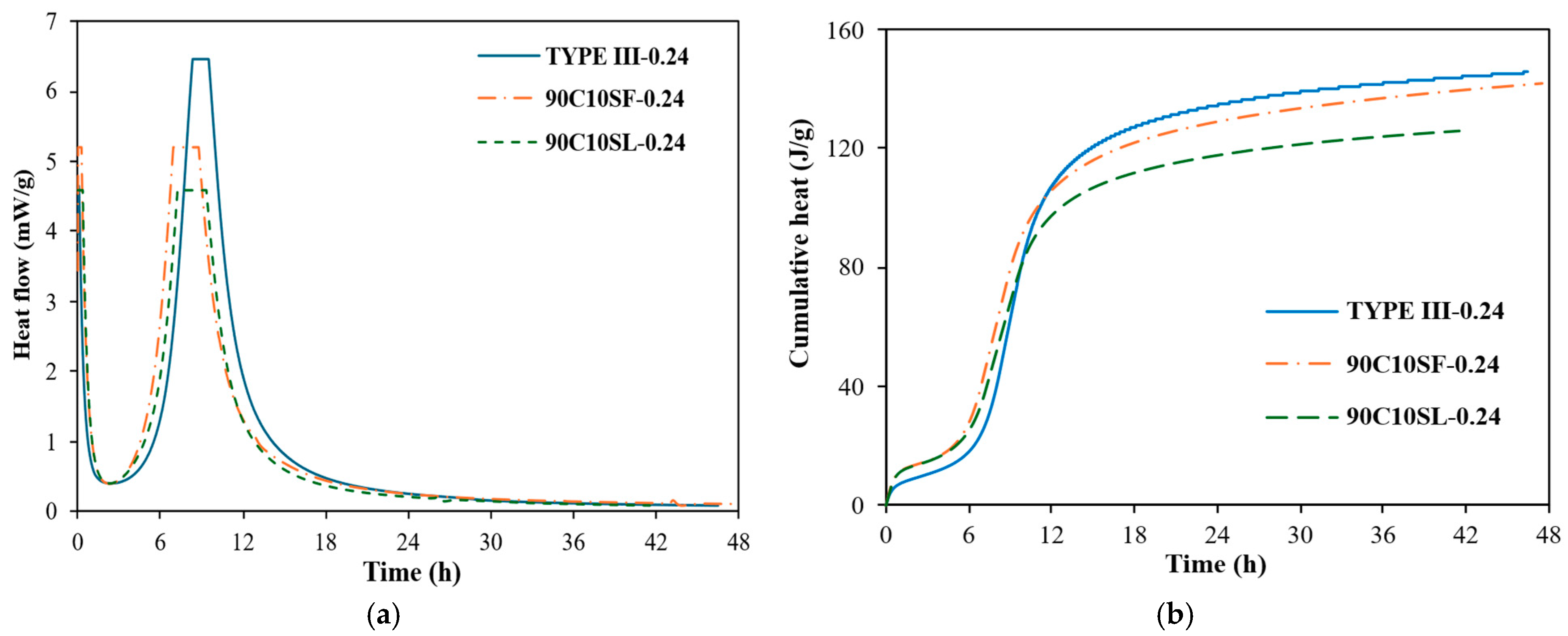
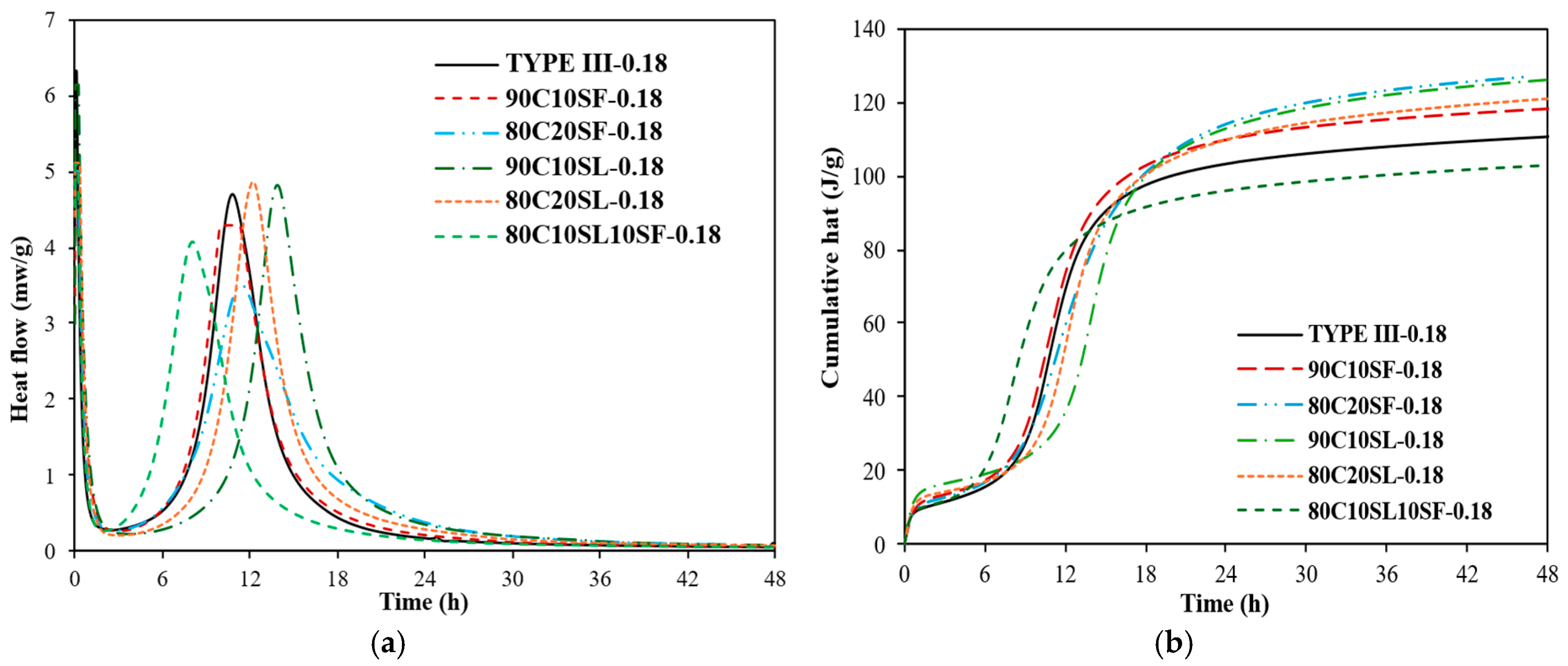
3.7.2. Effect of Slag and Silica Fume on Heat of Hydration
3.8. Mechanical Performance
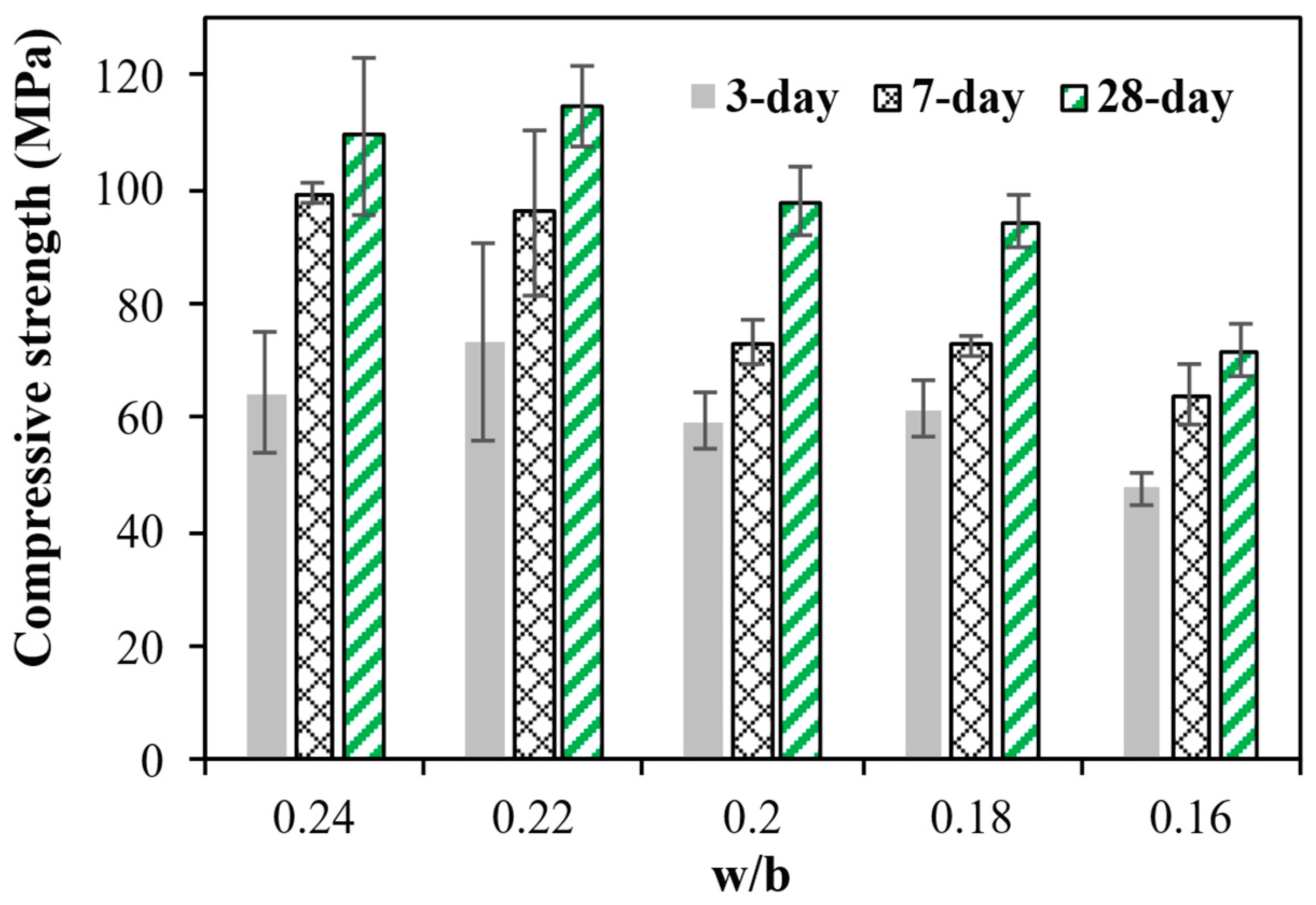
3.8.1. Effect of w/b and Cement Type on the Compressive Strength
3.8.2. Effect of Binder Type on Tensile and Flexural Behavior of UHPC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SCM | Supplementary cementitious material |
| SF | Silica fume |
| SL | Slag |
References
- Wu, Z.; Khayat, K.H.; Shi, C. Changes in Rheology and Mechanical Properties of Ultra-High Performance Concrete with Silica Fume Content. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 123, 105786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, K.H.; Meng, W.; Vallurupalli, K.; Teng, L. Rheological Properties of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete—An Overview. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; An, M.; Wang, Y.; Han, S.; Yu, Z. Research on the Relation between Slump Flow and Yield Stress of Ultra-High Performance Concrete Mixtures. Materials 2022, 15, 8104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Yang, J.; He, H.; Wei, J.; Zhu, Y. Influences of Additives on the Rheological Properties of Cement Composites: A Review of Material Impacts. Materials 2025, 18, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Cui, H.; Jiao, D. Experimental Observations on Factors Influencing Shear-Thickening Characteristics of Cement-Based Materials. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 86, 108620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, K.H.; Sayed, M.A. Effect of Supplementary Cementitious Materials on Rheological Properties, Bleeding, and Strength of Structural Grout. ACI Mater. J. 2008, 105, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, I.; Khayat, K.H. Effect of Supplementary Cementitious Material Content and Binder Dispersion on Packing Density and Compressive Strength of Sustainable Cement Paste. ACI Mater. J. 2016, 113, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, K.H.; Feys, D. Design, Production and Placement of Self-Consolidating Concrete. In Proceedings of the SCC2010, Montreal, QC, Canada, 26–29 September 2010; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 1, ISBN 9789048196630. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; De Schutter, G. Enhancing Thixotropy of Fresh Cement Pastes with Nanoclay in Presence of Polycarboxylate Ether Superplasticizer (PCE). Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 111, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, D.; Verhoeven, R.; De Schutter, G. Why Is Fresh Self-Compacting Concrete Shear Thickening? Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 510–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keke, L.; Yong, L.; Liuliu, X.; Junjie, Z.; Kangning, L.; Dingqiang, F.; Rui, Y. Rheological Characteristics of Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) Incorporating Bentonite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 349, 128793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaut, F.; Chateau, X.; Coussot, P.; Ovarlez, G. Yield Stress and Elastic Modulus of Suspensions of Noncolloidal Particles in Yield Stress Fluids. J. Rheol. 2008, 52, 287–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hou, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Mechtcherine, V.; Sun, Z. Design of 3D Printable Concrete Based on the Relationship between Flowability of Cement Paste and Optimum Aggregate Content. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 104, 103406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutou, Z.; Roussel, N. Multi Scale Experimental Study of Concrete Rheology: From Water Scale to Gravel Scale. Mater. Struct. 2006, 39, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.C. A Constitutive Equation for Fiber Suspensions in Viscoelastic Media. Phys. Fluid. 2021, 33, 071702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, T. Multiscale Materials Modeling Workshop Summary Report; FHWA-HRT-13-072; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Gao, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, J.; Xu, D.; Hu, Z.; Han, F.; Liu, J. A Review on Multi-Scale Toughening and Regulating Methods for Modern Concrete: From Toughening Theory to Practical Engineering Application. Research 2024, 7, 0518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.; Lu, J.X.; Liu, K.; Ban, J.; Yu, R.; Poon, C.S. Multi-Scale Design of Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) Composites with Centroplasm Theory. Compos. B Eng. 2024, 281, 111562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Addai-Nimoh, A.; Kreiger, E.; Khayat, K.H. Methodology to Design Eco-Friendly Fiber-Reinforced Concrete for 3D Printing. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 147, 105415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaut, F.; Mokéddem, S.; Chateau, X.; Roussel, N.; Ovarlez, G. Effect of Coarse Particle Volume Fraction on the Yield Stress and Thixotropy of Cementitious Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Zhu, J.; Khayat, K.H.; Liu, J. Effect of Welan Gum and Nanoclay on Thixotropy of UHPC. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Valipour, M.; Khayat, K.H. Optimization and Performance of Cost-Effective Ultra-High Performance Concrete. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallevik, O.H.; Feys, D.; Wallevik, J.E.; Khayat, K.H. Avoiding Inaccurate Interpretations of Rheological Measurements for Cement-Based Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, D.G. Minimizing the Negative Effect of Pumping on SCC Freeze-Thaw Durability; Missouri University of Science and Technology: Rolla, MO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Qian, Y.; Kawashima, S. Experimental and Modeling Study on the Non-Linear Structural Build-up of Fresh Cement Pastes Incorporating Viscosity Modifying Admixtures. Cem. Conc.r Res. 2018, 108, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, D.; Riding, K.; Moreno, D.G.; Salinas, A.; Wehar, A. Influence of Casting Conditions on Durability and Structural Performance of HPC-AR: Changes In Workability And Air-Void System Of Concrete Due To Pumping, United States; University Transportation Centers (UTC) Program: Rolla, MO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Feys, D.; Verhoeven, R.; De Schutter, G. Fresh Self Compacting Concrete, a Shear Thickening Material. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C109 Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or Cube Specimens). Annu. Book ASTM Stand. 2016, 4, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Maranzano, B.J.; Wagner, N.J. The Effects of Particle Size on Reversible Shear Thickening of Concentrated Colloidal Dispersions. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 114, 10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, A.; Wille, K. Evaluation of Resonance Acoustic Mixing Technology Using Ultra High Performance Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.J.; Martys, N.; Bergstrom, L. The Rheology of Cementitious Materials. MRS Bull. 2004, 29, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artelt, C.; Garcia, E. Impact of Superplasticizer Concentration and of Ultra-Fine Particles on the Rheological Behaviour of Dense Mortar Suspensions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N. A Thixotropy Model for Fresh Fluid Concretes: Theory, Validation and Applications. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N. Rheological Requirements for Printable Concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 112, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N.; Ovarlez, G.; Garrault, S.; Brumaud, C. The Origins of Thixotropy of Fresh Cement Pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graybeal, B. Design and Construction of Field-Cast UHPC Connections; Federal Highway Administration: McLean, VA, USA, 2014; FHWA-HRT-14-084. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.D.; Guo, L.P.; Fei, X.P.; Lyu, B.C.; Chen, B. Synergistic Effects of Silica Fume and Slag on the Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviors of Ultra-High-Strength and High-Ductility Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
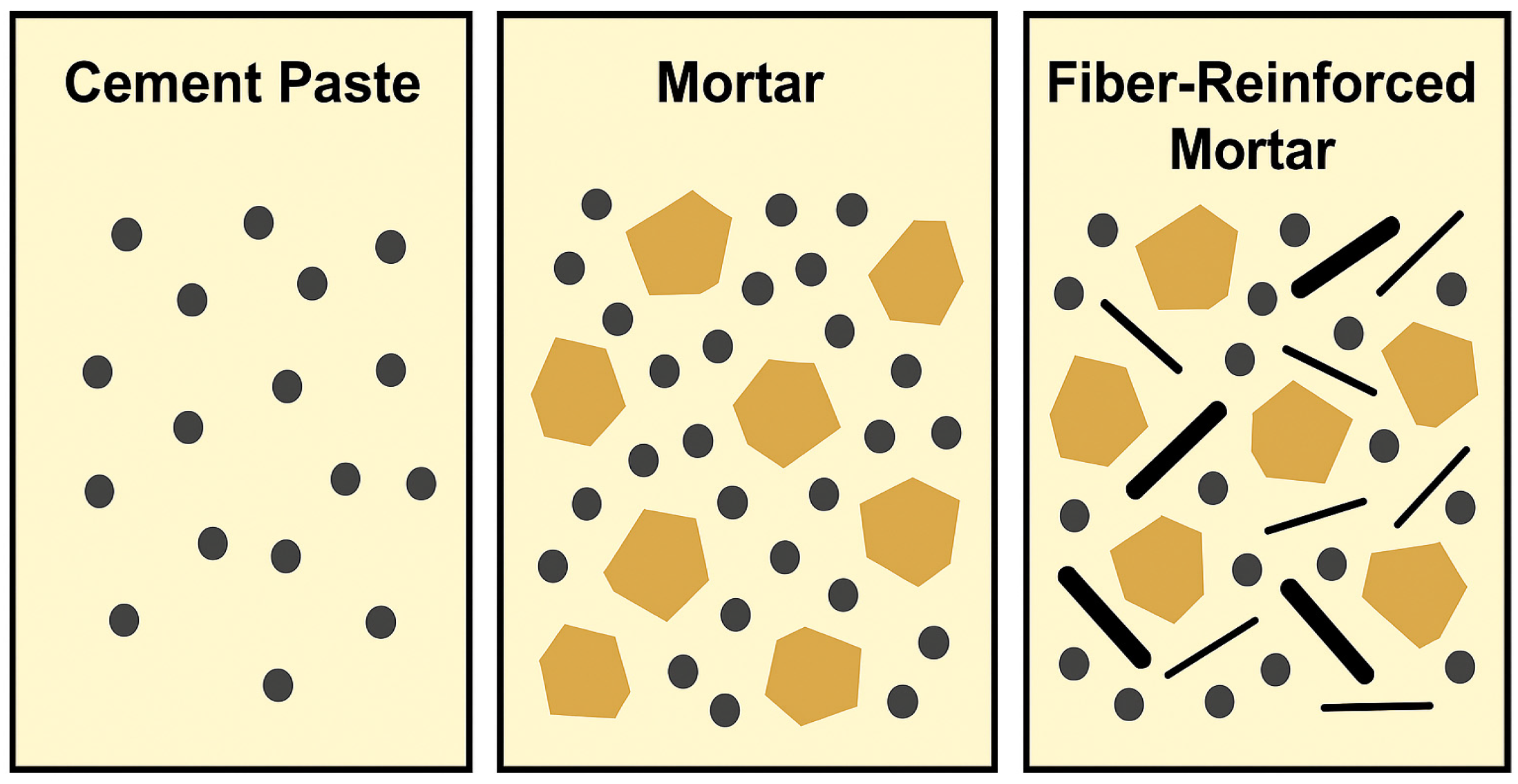
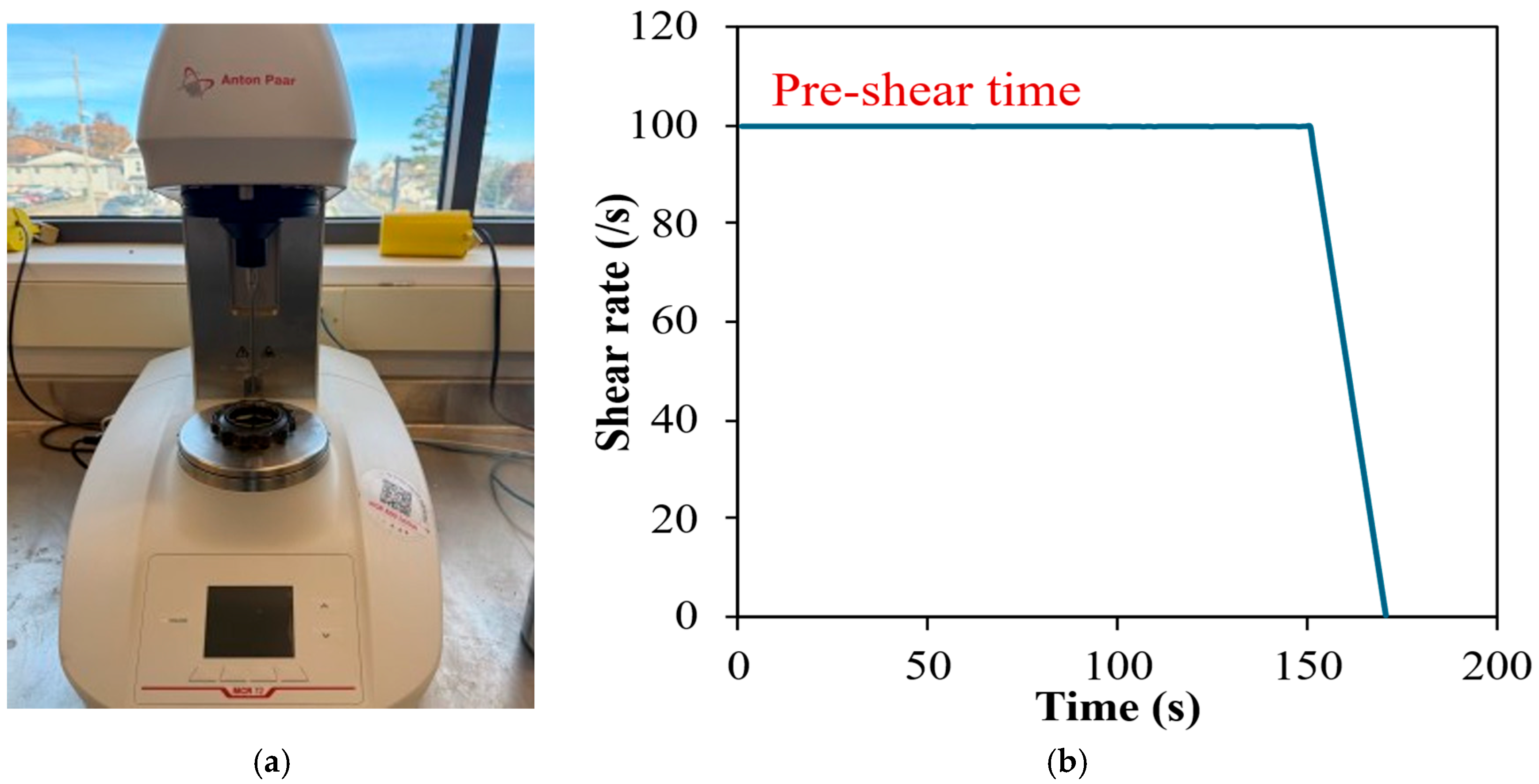
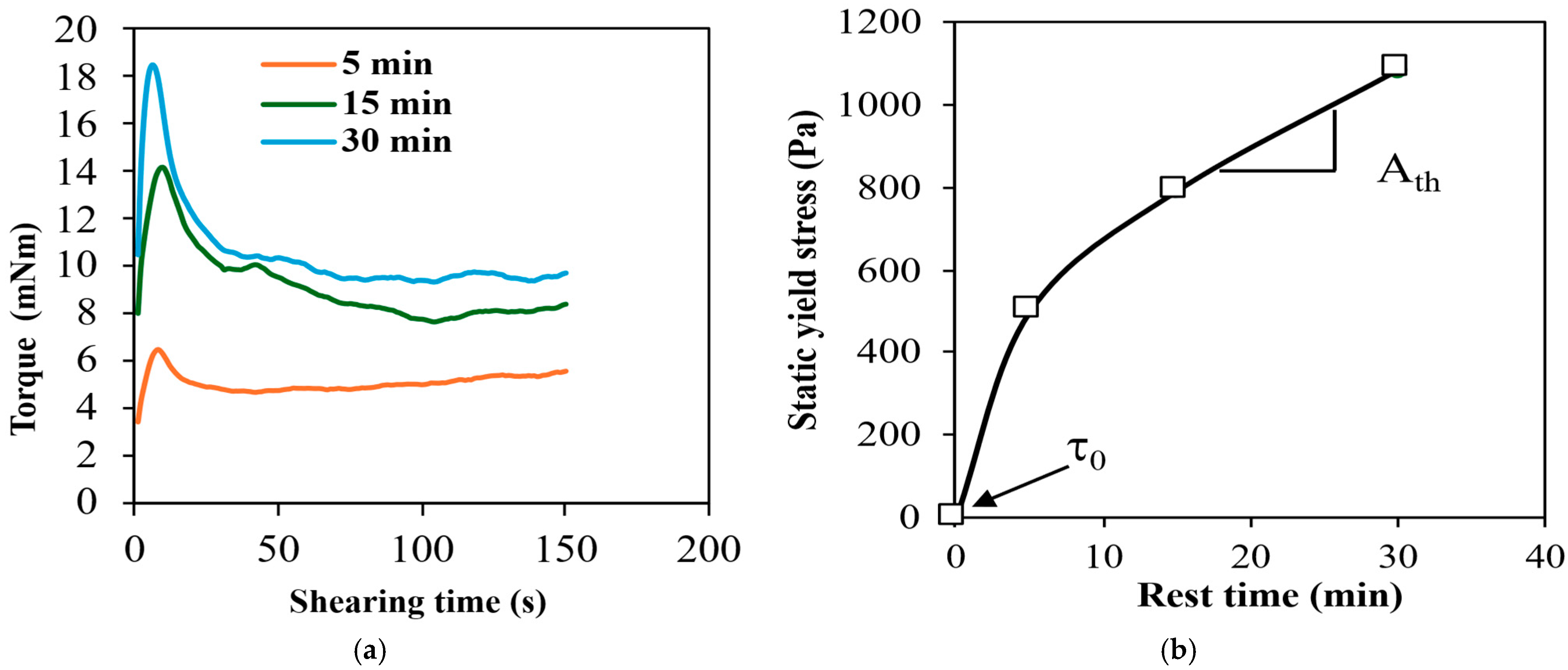
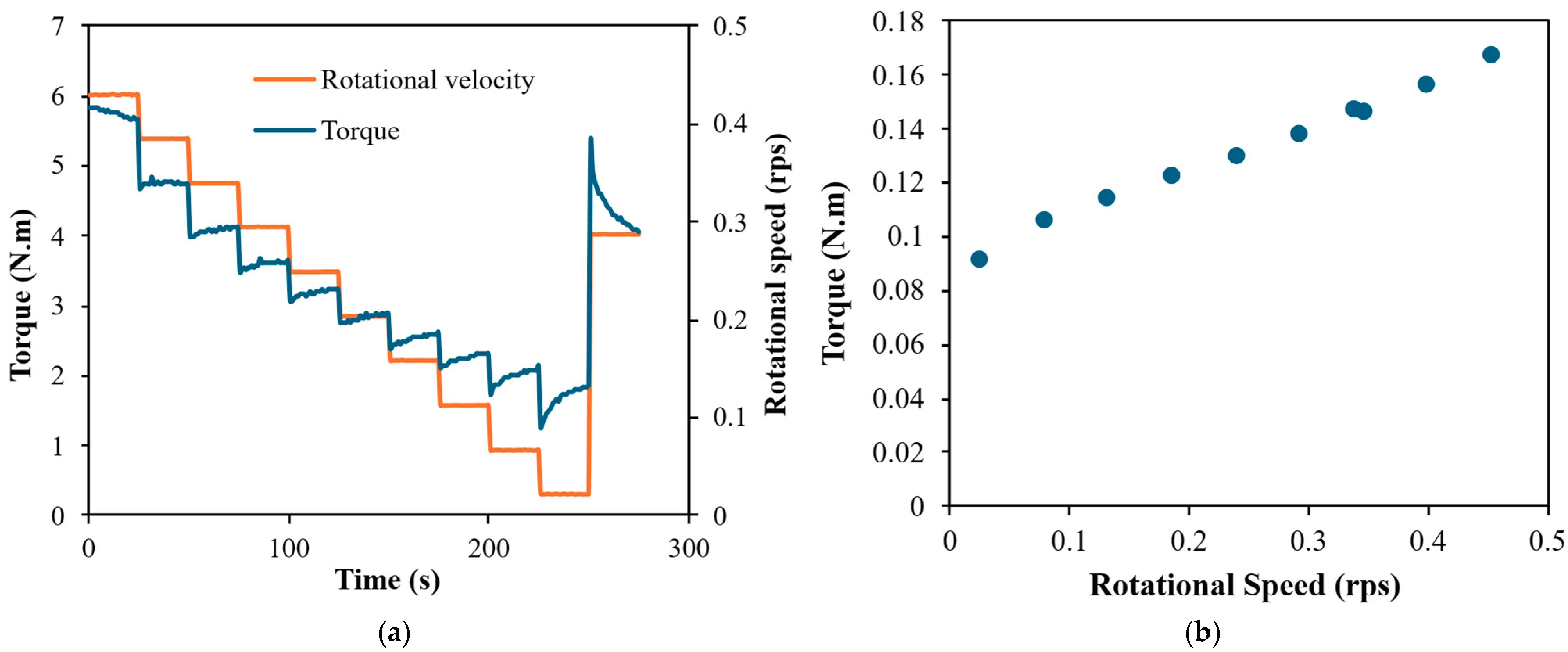
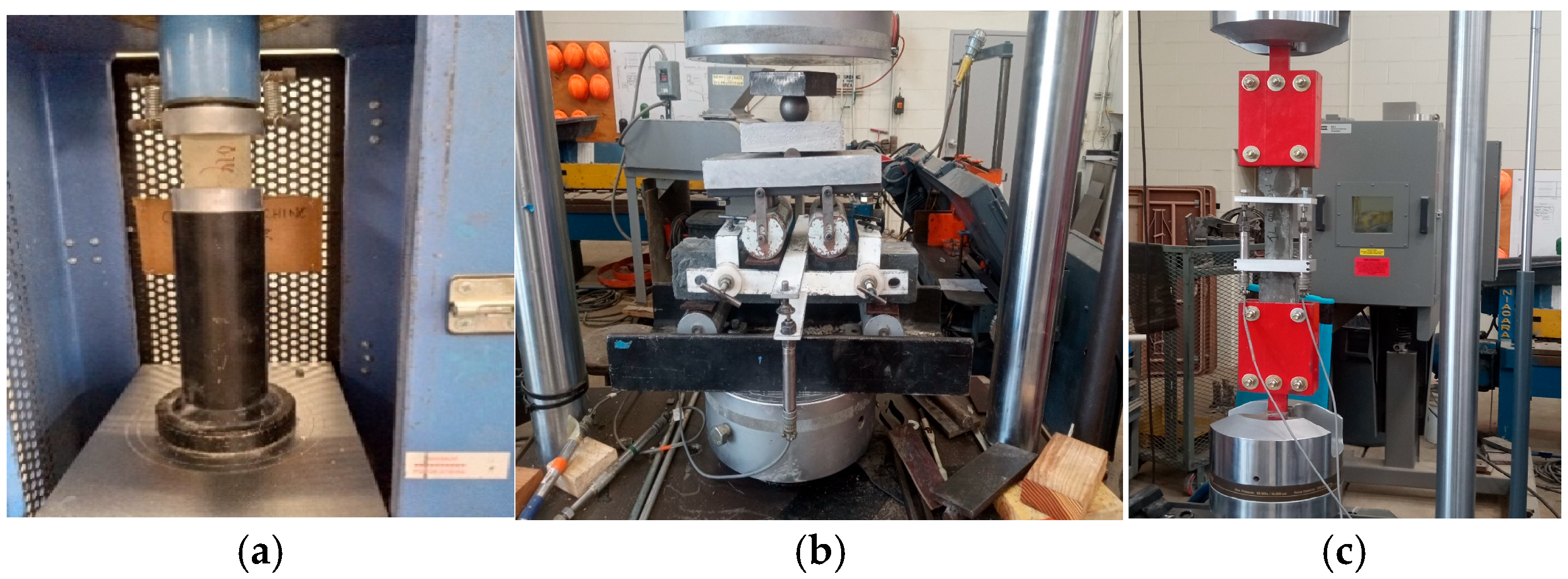



| % | Type III | Type 1L | SF | SL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgO | 2.15 | 2.41 | 0.5 | 9.5 |
| Al2O3 | 4.62 | 3.77 | 0.7 | 9.2 |
| SiO2 | 20.12 | 18.03 | 95.5 | 36.8 |
| P2O5 | 0.06 | 0.08 | - | - |
| SO3 | 2.01 | 2.53 | - | - |
| Cl | 0.05 | 0.06 | - | - |
| K2O | 0.52 | 0.73 | - | - |
| CaO | 65.80 | 68.33 | - | 37.1 |
| TiO2 | 0.20 | 0.27 | - | - |
| Mn2O3 | 0.269 | 0.087 | - | - |
| Fe2O3 | 3.90 | 3.59 | 0.3 | 0.76 |
| MgO | 2.15 | 2.41 | 0.5 | 9.5 |
| Level | Type III | Type 1L | SF | SL | w/b | s/b | Steel Fiber | No. of Mixtures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paste | Type1L | 100 | - | - | 0.16; 0.18; 0.20; 0.22; 0.24 | 0 | 0 | 26 |
| Type III | 100 | - | - | |||||
| 90C10SF | 90 | 10 | - | |||||
| 90C10SL | 90 | - | 10 | |||||
| 80C20SF | 80 | 20 | - | |||||
| 80C20SL | 80 | - | 20 | |||||
| 80C10SF10SL | 80 | 10 | 10 | |||||
| Mortar | 90C10SF | 90 | 10 | - | 0.16; 0.20; 0.24 | 1.2 | 0 | 9 |
| 90C10SL | 90 | - | 10 | |||||
| 80C10SF10SL | 80 | 10 | 10 | |||||
| UHPC | 90C10SF | 90 | 10 | - | 0.20; | 1.2 | 2% | 3 |
| 90C10SL | 90 | - | 10 | |||||
| 80C10SF10SL | 80 | 10 | 10 |
| Level | Cement Type | w/c | SP Dosage (% by Mass of Binder) | Slump Flow Before Jolting (mm) | Slump Flow After Jolting (mm) | Water Temperature (°C) | Temperature After Mixing (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paste | Type III | 0.24 | 1.0 | 170 | 210 | - | - |
| 0.22 | 1.4 | 192 | 250 | 20.3 | 37.3 | ||
| 0.20 | 2.4 | 180 | 230 | 21.7 | 36.5 | ||
| 0.18 | 3.5 | 196 | 245 | 19.9 | 38.7 | ||
| 0.16 | 4.8 | 190 | 252 | 20.6 | 40.0 | ||
| Type 1L | 0.24 | 0.4 | 175 | 240 | 20.2 | 27.3 | |
| 0.22 | 0.6 | 185 | 220 | 29 | 29.9 | ||
| 0.20 | 1.0 | 190 | 240 | 20.3 | 27.9 | ||
| 0.18 | 1.4 | 194 | 246 | - | 28.8 | ||
| 0.16 | 2.0 | 195 | 254 | - | 30.3 |
| Level | Cement | w/c | SP Dosage (% by Mass of Binder) | τ0 (Pa) | µ (Pa·s) | c (Pa·s2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paste | Type III | 0.24 | 1.0 | 23.1 | 0.5 | 0.018 |
| 0.22 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 0.064 | ||
| 0.2 | 2.4 | 0 | 0 | 0.099 | ||
| 0.18 | 3.5 | 0 | 0 | 1.730 | ||
| 0.16 | 4.8 | 52.0 | 2.0 | 1.970 | ||
| Type 1L | 0.24 | 0.4 | 6.8 | 0.8 | 0.013 | |
| 0.22 | 0.6 | 8.0 | 0 | 0.051 | ||
| 0.20 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | 0.064 | ||
| 0.18 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 0.158 | ||
| 0.16 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 0.140 |
| Cement | w/c | R2 (×10−8) |
|---|---|---|
| Type III | 0.24 | 45 |
| 0.22 | 19,992 | |
| 0.2 | 13,409 | |
| 0.18 | 37,328 | |
| 0.16 | 214 | |
| Type 1L | 0.24 | 6 |
| 0.22 | 138 | |
| 0.20 | 3866 | |
| 0.18 | 23,384 | |
| 0.16 | 10,000 |
| Cement | w/b | 5 min | 15 min | 30 min | tfloc (Pa) | Athix (Pa/min) | tfloc × Athix (Pa2/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type III | 0.24 | 878 | 1081 | 1284 | 855 | 13.5 | 11,553 |
| 0.22 | 62 | 121 | 181 | 62 | 4 | 245 | |
| 0.20 | 500 | 794 | 1087 | 500 | 19.6 | 9798 | |
| 0.18 | 133 | 211 | 289 | 133 | 5.2 | 692 | |
| 0.16 | 258 | 355 | 454 | 205 | 6.5 | 1337 | |
| Type 1L | 0.24 | 174 | 373 | 570 | 168 | 13.2 | 2217 |
| 0.22 | 382 | 721 | 1059 | 374 | 22.6 | 8446 | |
| 0.20 | 317 | 621 | 925 | 317 | 20.3 | 6432 | |
| 0.18 | 226 | 417 | 607 | 226 | 12.7 | 2873 | |
| 0.16 | 21 | 23 | 25 | 21 | 0.13 | 2.5 |
| Mixture | w/b | SP Dosage (%) | τ0 (Pa) | µ (Pa·s) | c (Pa·s2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90C10SL | 0.24 | 1.3 | 42.7 | 1.8 | 0.24 |
| 80C20SL | 0.9 | 22 | 0.0096 | 0.30 | |
| 80C10SF10SL | 0.8 | 83.2 | 5.2 | 0 | |
| 90C10SF | 0.22 | 1.3 | 200.7 | 11.5 | 0 |
| 80C20SF | 1.7 | 236 | 20 | 0 | |
| 80C20SL | 1.6 | 77.8 | 5.9 | 0.25 | |
| 80C10SF10SL | 1.2 | 142 | 10.6 | 0.089 | |
| 90C10SF | 0.18 | 2.2 | 150.8 | 13.3 | 0.20 |
| 90C10SL | 1.8 | 131 | 0.22 | 0.051 | |
| 80C20SL | 1.8 | 195 | 0 | 0.52 | |
| 80C10SF10SL | 2.2 | 310 | 22.2 | 0 | |
| 90C10SF | 0.16 | 2.6 | 440 | 79 | 0 |
| 80C20SF | 6.7 | 390 | 34 | 0 | |
| 90C10SL | 3.1 | 48 | 3.4 | 5.2 | |
| 80C20SL | 4.2 | 0 | 0 | 11 | |
| 80C10SF10SL | 7.2 | 185 | 18 | 0 |
| Mixture | w/b | SP Dosage (%) | τo | µ | c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type III cement | |||||
| 90C10SF | 0.24 | 2.5 | 255 | 21 | 0 |
| 90C10SL | 2.8 | 259 | 20 | 0.18 | |
| 80C10SF10SL | 1.6 | 128 | 8.8 | 0 | |
| 90C10SF | 0.20 | 3.0 | 161 | 36 | 0 |
| 90C10SL | 3.8 | 109 | 67 | 0 | |
| 80C10SF10SL | 2.1 | 393 | 34 | 0 | |
| Type 1L cement | |||||
| 90C10SF | 0.16 | 5.3 | 140 | 74 | 0 |
| 90C10SL | 6.75 | 60.8 | 105 | 2.05 | |
| 80C10SF10SL | 5.75 | 178 | 101 | 0 | |
| Mixture | w/b | 5 min | 15 min | 30 min | τfloc (Pa) | Athix (Pa/min) | τfloc × Athix (Pa2/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type III | |||||||
| 90C10SF | 0.24 | 546 | 693 | 896 | 291 | 9.8 | 2850 |
| 90C10SL | 344 | 533 | 721 | 70 | 12 | 885 | |
| 80C10SF10SL | 270 | 421 | 572 | 142 | 10 | 1429 | |
| 90C10SF | 0.20 | 508 | 823 | 1138 | 348 | 21 | 7285 |
| 90C10SL | 681 | 1051 | 1422 | 572 | 24 | 14,125 | |
| 80C10SF10SL | 1290 | 1766 | 1940 | 950 | 21 | 20,597 | |
| Type 1L | |||||||
| 90C10SF | 0.16 | 368 | 476 | 583 | 228 | 7.2 | 1639 |
| 90C10SL | 324 | 399 | 497 | 259 | 5.78 | 1500 | |
| 80C10SF10SL | 444 | 551 | 657 | 266 | 7.0 | 1889 | |
| Mixture | w/c | SP Dosage (%) | τo | µ | c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90C10SF | 0.20 | 1.5 | 39 | 19 | 0 |
| 90C10SL | 1.2 | 52.7 | 23.4 | 1.62 | |
| 80C10SL10SF | 1.2 | 292.9 | 66.8 | 0 |
| Mixture | w/c | τs at 5 min | τs at 15 min | τs at 30 min | τfloc (Pa) | Athix (Pa/min) | τfloc × Athix (Pa2/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90C10SF | 0.20 | 171 | 257 | 342 | 133 | 5.7 | 755 |
| 90C10SL | 333 | 589 | 799 | 288 | 15.5 | 4473 | |
| 80C10SL10SF | 825 | 1054 | 1338 | 523 | 17.1 | 8939 |
| UHPC | w/c | 3-d, MPa | Avg, MPa (COV., %) | 7-d, MPa | Avg, MPa (COV.,%) | 28-d, MPa | Avg, MPa (COV.,%) | 56-d, MPa | Avg, MPa (COV,%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1L cement | |||||||||
| 90C10SF | 0.2 | 104.7 | 111.1 (5) | 129.6 | 132.1 (3.8) | 139 | 136.6 (2.15) | 114.4 | 116.3 (1.9) |
| 113.9 | 128.8 | 135 | 118.8 | ||||||
| 114.8 | 137.8 | 134 | 115.8 | ||||||
| 90C10SL | 100.0 | 103.3 (2.9) | 74.5 | 76.3 (3.9) | 85.3 | 89.7 (5.0) | 107.4 | 107.9 (2.9) | |
| 105.9 | 74.5 | 89.6 | 110.3 | ||||||
| 104.0 | 79.7 | 94.3 | 105.9 | ||||||
| 80C10SF10SL | 93.9 | 99.2 (5.2) | 108.5 | 113.9 (5) | 119.0 | 116.6 (3.1) | 136.9 | 131.4 (4.2) | |
| 99.7 | 113.5 | 118.4 | 127.5 | ||||||
| 104.0 | 119.8 | 112.5 | 129.8 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Addai-Nimoh, A.; Wei, J.; Khayat, K.H. Multi-Scale Experimental Investigation of UHPC Rheology: From Cement Paste to Fiber-Reinforced Mortar Scale. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110638
Addai-Nimoh A, Wei J, Khayat KH. Multi-Scale Experimental Investigation of UHPC Rheology: From Cement Paste to Fiber-Reinforced Mortar Scale. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(11):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110638
Chicago/Turabian StyleAddai-Nimoh, Alfred, Jingjie Wei, and Kamal H. Khayat. 2025. "Multi-Scale Experimental Investigation of UHPC Rheology: From Cement Paste to Fiber-Reinforced Mortar Scale" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 11: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110638
APA StyleAddai-Nimoh, A., Wei, J., & Khayat, K. H. (2025). Multi-Scale Experimental Investigation of UHPC Rheology: From Cement Paste to Fiber-Reinforced Mortar Scale. Journal of Composites Science, 9(11), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9110638







