Structural Nanocomposite Fabrication from Self-Assembled Choline Chloride Modified Kaolinite into Poly(Methylmethacrylate)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Fabrication of Poly(methylmethacrylate)/Choline Chloride Modified Kaolinite PMMA/CCMK Nanocomposite Films
2.2.2. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
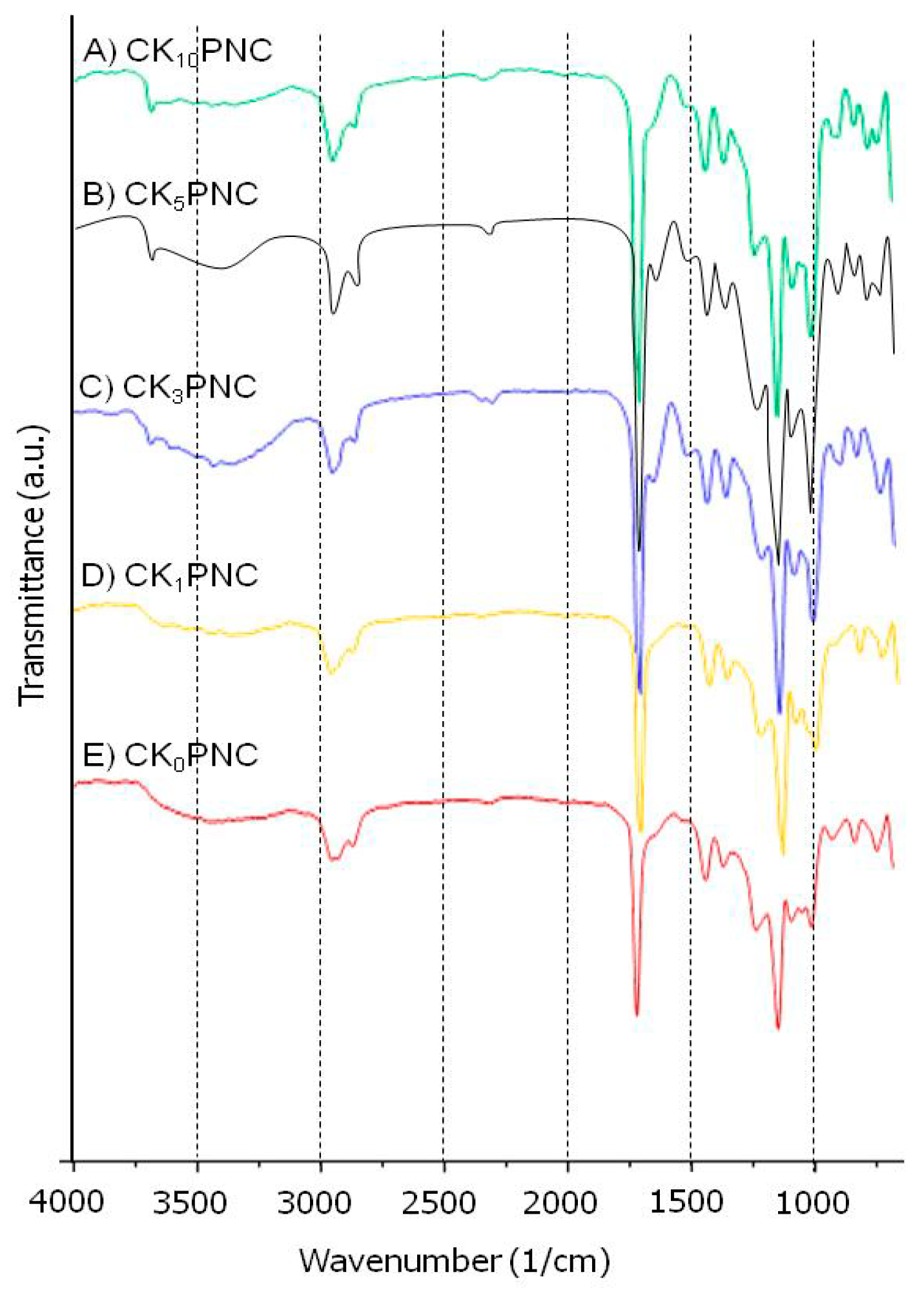
3.1. ATR-IR Spectral Analysis
3.2. XRD Analysis
3.3. Studies of Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposite Films
3.3.1. Stress–Strain Relationship
3.3.2. Tensile Strength Measurement
3.3.3. Elongation at Break
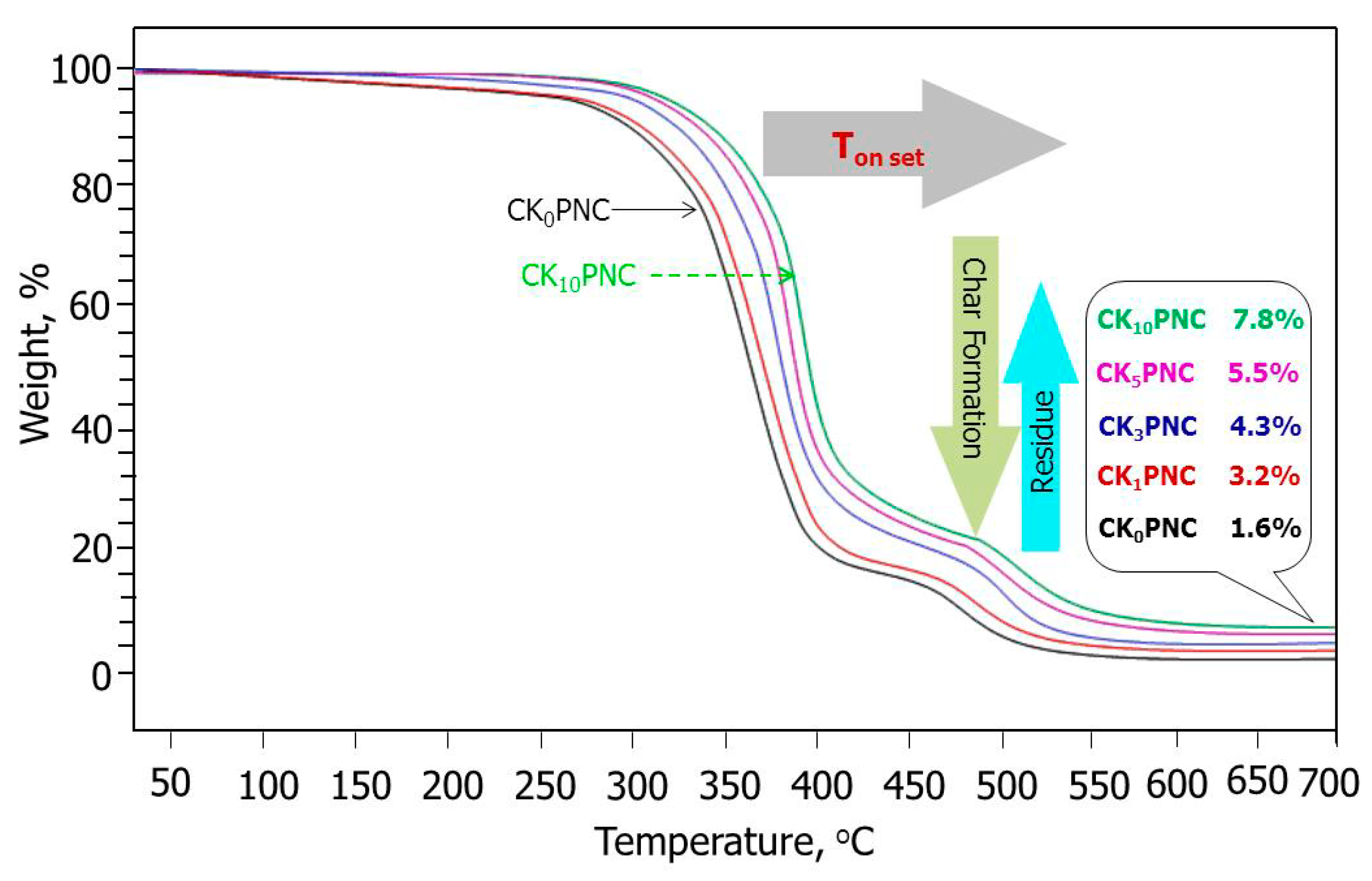
3.4. Thermo Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
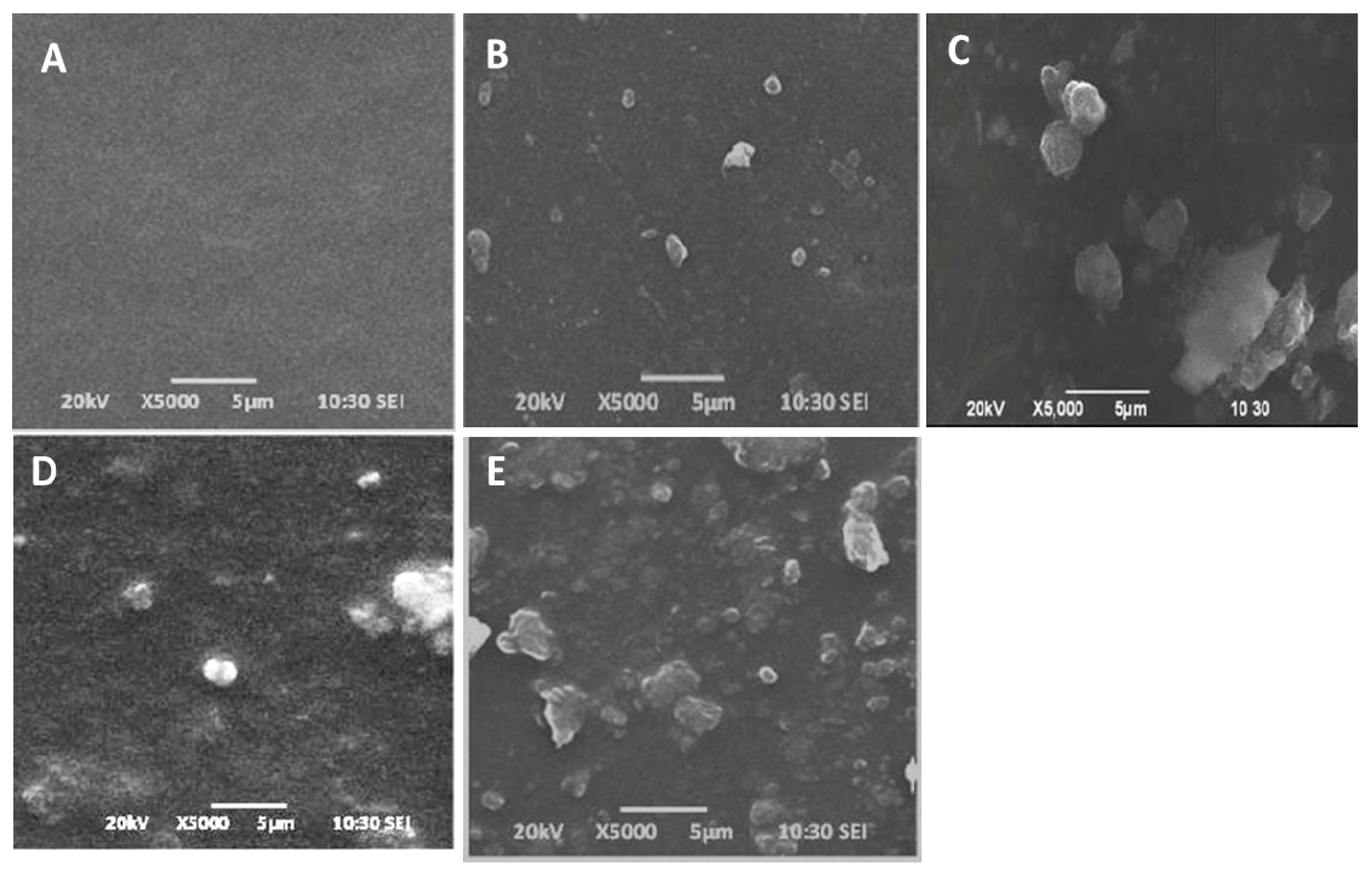
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Morphological Studies of Nanocomposites Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Massaro, M.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Parisi, F.; Riela, S. Biocompatible poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-halloysite nanotubes for thermoresponsive curcumin release. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 8944–8951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrullina, G.I.; Akhatova, F.S.; Lvov, Y.M.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Toxicity of halloysite clay nanotubes In Vivo: A Caenorhabditis elegans study. Environ. Sci.: Nano. 2015, 2, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Konnova, S.; Fakhrullin, R.; Lvov, Y. Composite films of natural clay nanotubes with cellulose and chitosan. Green Mater. 2014, 2, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costache, M.C.; Heidecker, M.; Manias, E.; Wilkie, C.A. Preparation and characterization of poly (ethylene terephthalate)/clay nanocomposites by melt blending using thermally stable surfactants. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2006, 17, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, H.; Carreau, P.J.; Kamal, M.R.; Uribe-Calderon, J. Preparation and characterization of PET/clay nanocomposites by melt compounding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrasi, G.; Pantani, R.; Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. PLA/Halloysite nanocomposite films: Water vapor barrier properties and specific key characteristics. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoretti, A.; Kolarik, J.; Peroni, C.; Migliaresi, C. Recycled poly (ethylene terephthalate)/layered silicate nanocomposites: morphology and tensile mechanical properties. Polymer 2004, 45, 2751–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Ma, Y.; Agarwal, U.S. Study on mechanical properties, thermal stability and crystallization behavior of PET/MMT nanocomposites. Composites Part B 2006, 37, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, H.; Carreau, P.J.; Kamal, M.R.; Tabatabaei, S.H. Properties of PET/clay nanocomposite films. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2012, 52, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, A.; Heuzey, M.C.; Carreau, P.J.; Ton-That, M.T. Morphology and properties of polymer/organoclay nanocomposites based on poly (ethylene terephthalate) and sulfopolyester blends. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnean, Z.Y. Effect of grain and calcinations kaolin additives on some mechanical and physical properties on low densitypolyethylene composites. Al-Khwarizmi Eng. J. 2008, 4, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bergaya, F.; Lagaly, G. Hand Book of Clay Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2006; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Milanova, M.; Warmoeskerken, M.; Dutschk, V. Surface modification of TiO2 nanoparticles with silane coupling agents. In Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects; Gradzielski, M., Miller, R., Starov, V., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2012; Volume 413, pp. 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, B.; Xu, X.; Gao, X.; Ding, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, S.; Yang, M. Highly exfoliated poly (ethylene terephthalate)/clay nanocomposites via melt compounding: Effects of silane grafting. J. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2011, 50, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M.W.; Hunter, D.; Knesek, B.; Paul, D.R. Morphology and properties of polypropylene nanocomposites based on a silanized organoclay. Polymer 2011, 52, 5369–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Shim, J.H.; Woo, J.Y.; Yoo, K.S.; Yoon, J.S. Effect of the silane modification of clay on the tensile properties of nylon 6/clay nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzara, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Abhishek, P.; Fakhrullin, R.; Anna, S.; Vladimir, V.; Yuri, L. An assembly of organic–inorganic composites using halloysite clay nanotubes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 35, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, T.P.; Kanny, K. Effects of synthetic and processing methods on dispersion characteristics of nanoclay in polypropylene polymer matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2011, 2, 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Danilushkina, A.A.; Evtugyn, V.G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Rozhina, E.V.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Halloysite nanotubes: Controlled access and release by smart gates. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, A.; Kawasumi, M.; Usuki, A.; Kojima, Y.; Kurauchi, T.; Kamigaito, O. Synthesis and properties of Nylon-6/Clay hybrids. Polym. Based Mol. Compos. 1990, 171, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Pegoretti, A.; Dorigato, A.; Penati, A. Tensile mechanical response of polyethylene-clay nanocomposites. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2007, 1, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agubra, V.; Owuor, P.; Hosur, M. Influence of nanoclay dispersion methods on the mechanical behavior of E-glass/epoxy nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, T.S.; Asha Krishnan, K.; Anjana, R.; George, K.E. Studies on nano kaolin clay reinforced PS-HDPE nanocomposites. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 2013, 1, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Anjana, R.; George, K. Reinforcing effect of nano kaolin clay on PP/HDPE blends. Int. J. Eng. Res. Ind. Appl. 2012, 2, 868–872. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, S.N. Effect of kaolin on the mechanical properties of polypropylene/polyethylene composite material. Diyala J. Eng. Sci. 2012, 5, 162–178. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A. Nano-clay particle as textile coating. Int. J. Eng. Technol. IJET-IJENS 2011, 11, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, R. Advances in application of natural clay and its composites in removal of biological, organic, and inorganic contaminants from drinking water. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 2011, 872531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bashir, S.M.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Al-Faifi, F.; Alenazi, W.K. Spectral properties of PMMA films doped by perylene dyestuffs for photoselective greenhouse cladding applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Brittain, W.J. Synthesis and characterization of PMMA nanocomposites by suspension and emulsion polymerization. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 3255–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Wilkie, C.A. Exfoliated poly (methyl methacrylate) and polystyrene nanocomposites occur when the clay cation contains a vinyl monomer. J. Poym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2003, 41, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.M.; Liou, S.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Cheng, C.Y.; Chang, Y.W.; Lee, K.R. Anticorrosively enhanced PMMA−clay nanocomposite materials with quaternary alkylphosphonium salt as an intercalating agent. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Arun, S.; Upadhyaya, P.; Pugazhenthi, G. Properties of PMMA/clay nanocomposites prepared using various compatibilizers. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2015, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabirqudri, S.A.M.; Roy, A.S.; Prasad, M.A. Electrical and mechanical properties of free-standing PMMA–MMT clay composites. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 29, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, C.; Fu, J.; Naguib, H.E. Constitutive modeling for intercalated PMMA/clay nanocomposite foams. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, S.K.; Mandal, A.; Chakrabarty, D. Studies on synthesis and characterization of poly (methyl methacrylate)-bentonite clay composite by emulsion polymerization and simultaneous in situ clay incorporation. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V. Polymer layered silicate nanocomposites: a review. Materials 2009, 2, 992–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, H.S.; Milewki, J.V. Handbook of Fillers and Reinforcements for Plastics; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, A.; Yang, X.; Lu, L.; Wang, X. Preparation and characterization of mesoporous zirconia made by using a poly (methyl methacrylate) template. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Malhat, F.; Hakim, A.A.; Dekany, I. Synthesis and utilization of poly (methylmethacrylate) nanocomposites based on modified montmorillonite. Arabian J. Chem. 2017, 10, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.K.; Soga, K. Fundamentals of Soil Behavior; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyemo, A.A.; Adeoye, I.O.; Bello, O.S. Adsorption of dyes using different types of clay: a review. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriol, M.; Gentilhomme, A.; Cochez, M.; Oget, N.; Mieloszynski, J. Thermal degradation of poly (methyl methacrylate)(PMMA): Modelling of DTG and TG curves. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 79, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Viswanath, D.S. Degradation of poly (methyl methacrylate)(PMMA) with aluminum nitride and alumina. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2000, 40, 2332–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Composite Identity | PMMA % (w/w) | CCMK % (w/w) | PMMA:CCMK |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK0PNC | 100 | 0 | 100:0 |
| CK1PNC | 99 | 1 | 99:01 |
| CK3PNC | 97 | 3 | 97:03 |
| CK5PNC | 95 | 5 | 95:05 |
| CK10PNC | 90 | 10 | 90:10 |
| Composites | Decomposition Starts at °C | Char Formation at °C | Decomposition Ends at °C | Residue% (w/w), at 700 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK0PNC | 280 | 450 | 562 | 1.6 |
| CK1PNC | 288 | 460 | 565 | 3.2 |
| CK3PNC | 300 | 470 | 570 | 4.3 |
| CK5PNC | 312 | 482 | 585 | 5.5 |
| CK10PNC | 315 | 487 | 590 | 7.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saha, D.; Majumdar, M.K.; Das, A.K.; Chowdhury, A.M.S.; Ashaduzzaman, M. Structural Nanocomposite Fabrication from Self-Assembled Choline Chloride Modified Kaolinite into Poly(Methylmethacrylate). J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs3030083
Saha D, Majumdar MK, Das AK, Chowdhury AMS, Ashaduzzaman M. Structural Nanocomposite Fabrication from Self-Assembled Choline Chloride Modified Kaolinite into Poly(Methylmethacrylate). Journal of Composites Science. 2019; 3(3):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs3030083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaha, Dipti, Mithun Kumar Majumdar, Ajoy Kumar Das, A.M. Sarwaruddin Chowdhury, and Md. Ashaduzzaman. 2019. "Structural Nanocomposite Fabrication from Self-Assembled Choline Chloride Modified Kaolinite into Poly(Methylmethacrylate)" Journal of Composites Science 3, no. 3: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs3030083
APA StyleSaha, D., Majumdar, M. K., Das, A. K., Chowdhury, A. M. S., & Ashaduzzaman, M. (2019). Structural Nanocomposite Fabrication from Self-Assembled Choline Chloride Modified Kaolinite into Poly(Methylmethacrylate). Journal of Composites Science, 3(3), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs3030083





