The Effect of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers on the Dynamic and Impact Behavior of Glass Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
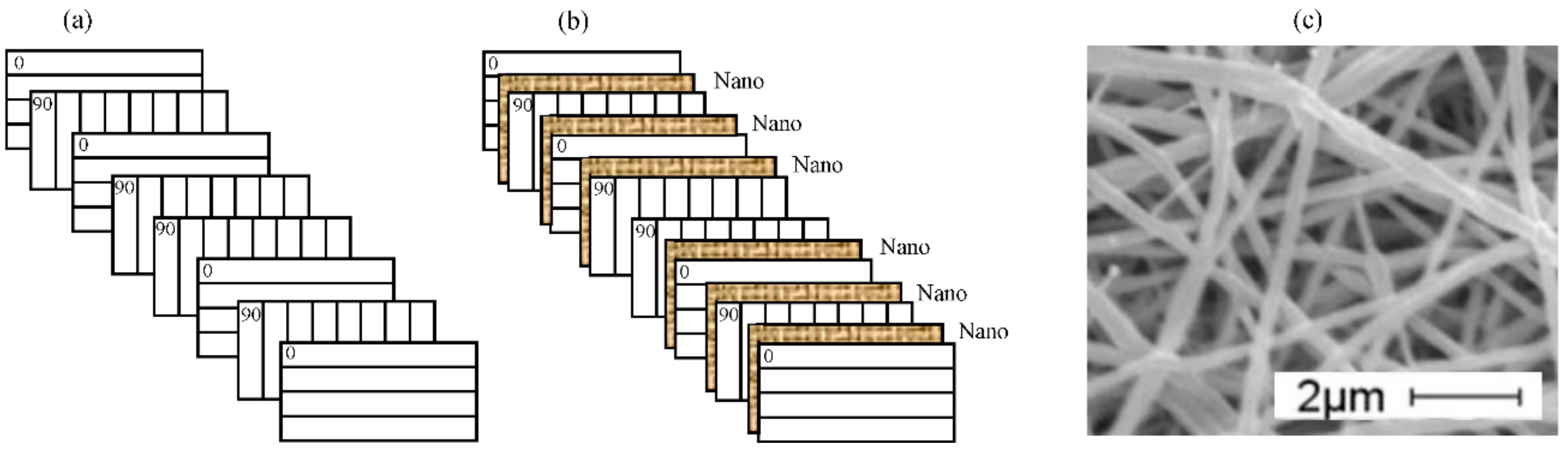
2. Fabrication of Composites with and without Polycaprolactone Nanofibers
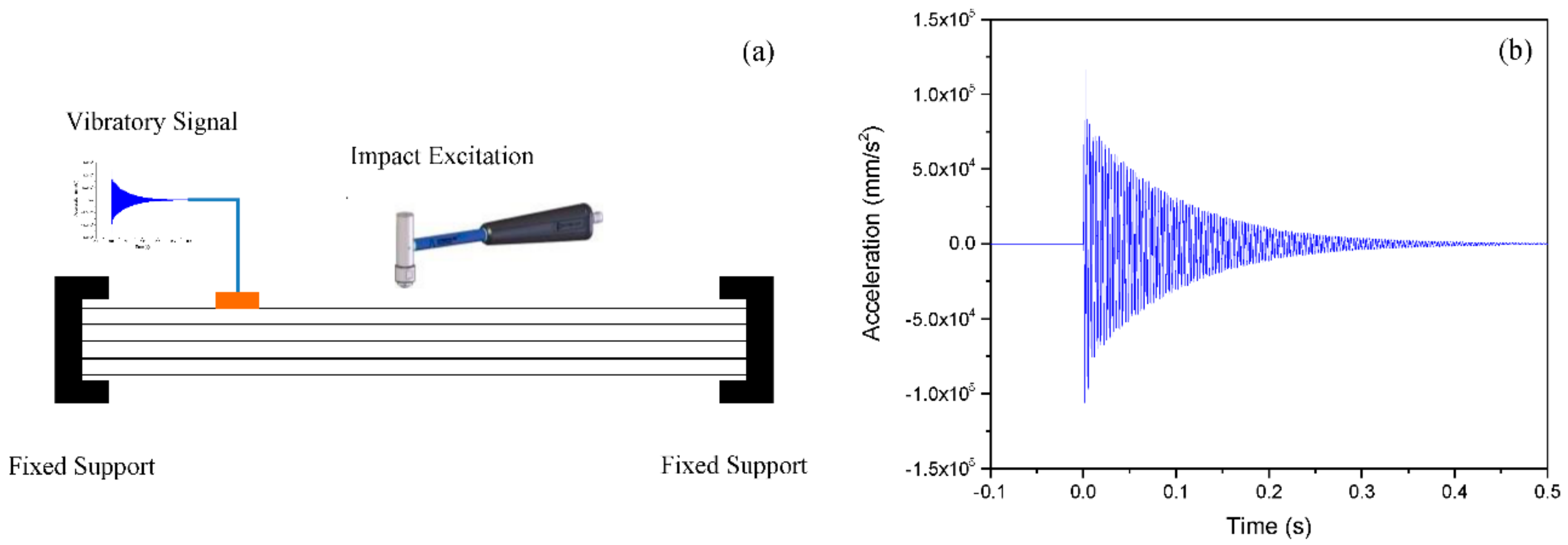
3. Vibratory Behavior of Pristine and Polycaprolactone Nano-Modified Beams
4. Impact Behavior of Pristine and Polycaprolactone Nano-Modified Beams
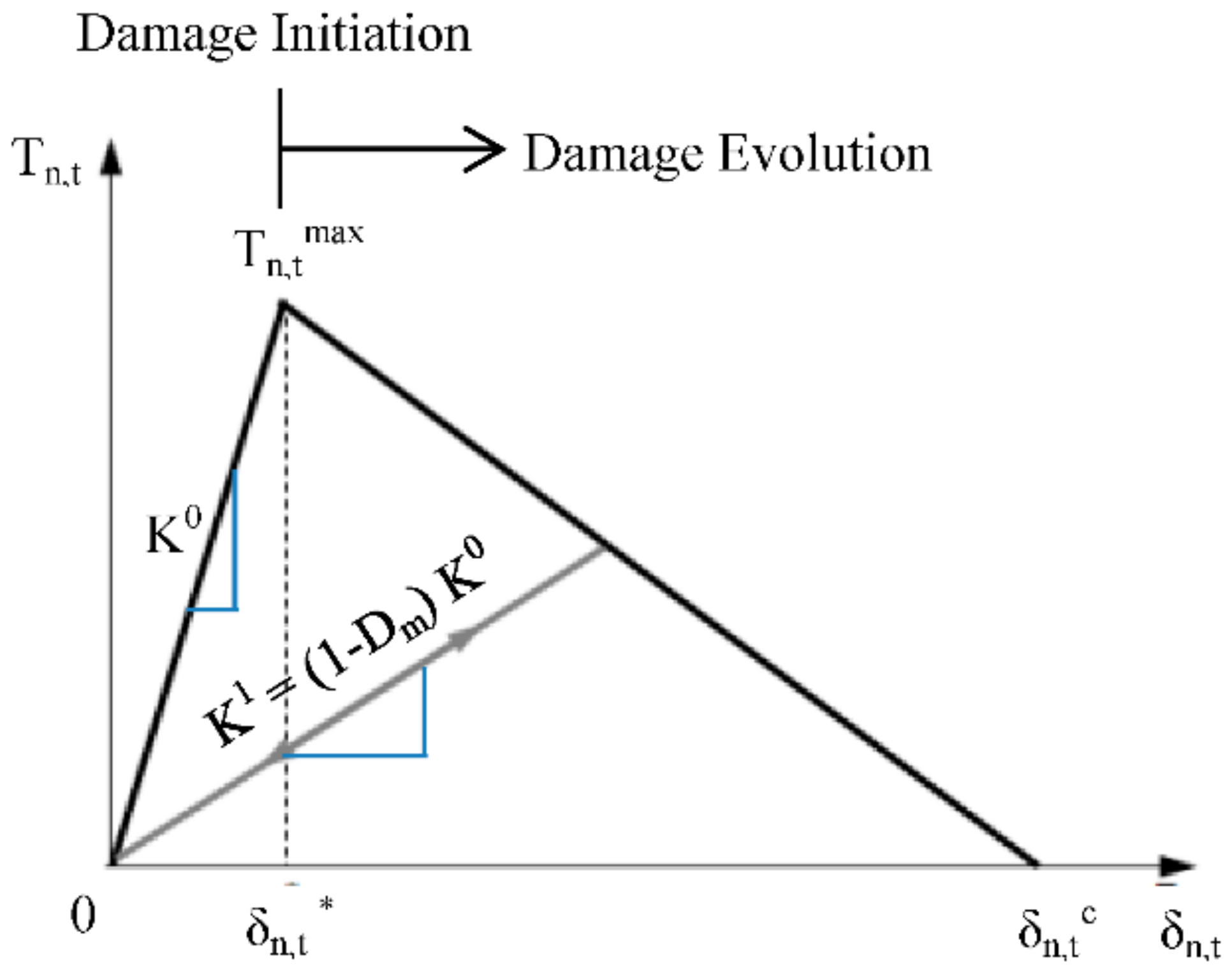
4.1. Numerical (FE) Modelling
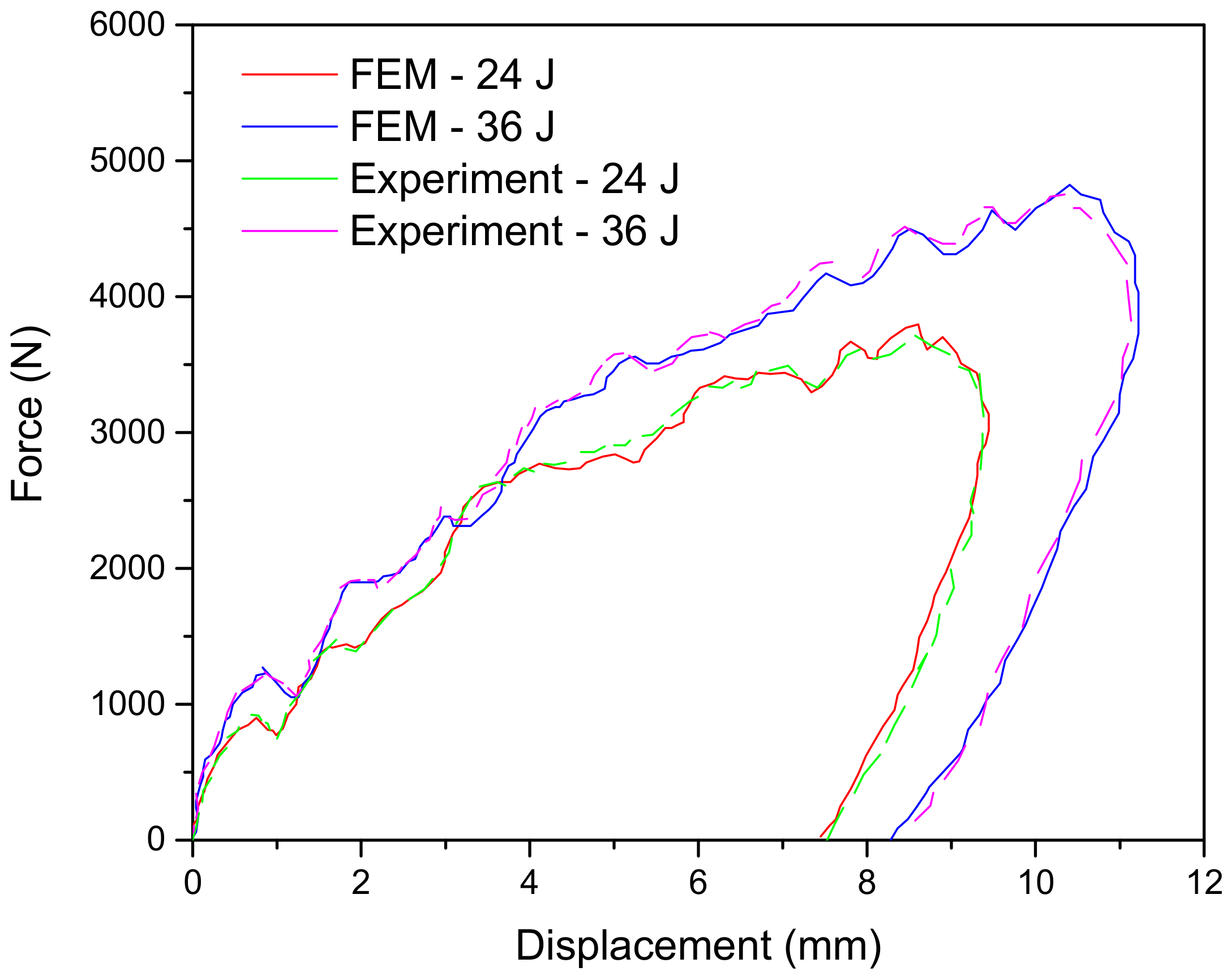
4.2. Model Verification
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Effect of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers on the Natural Frequencies
5.2. Effect of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers on the Damping Ratio
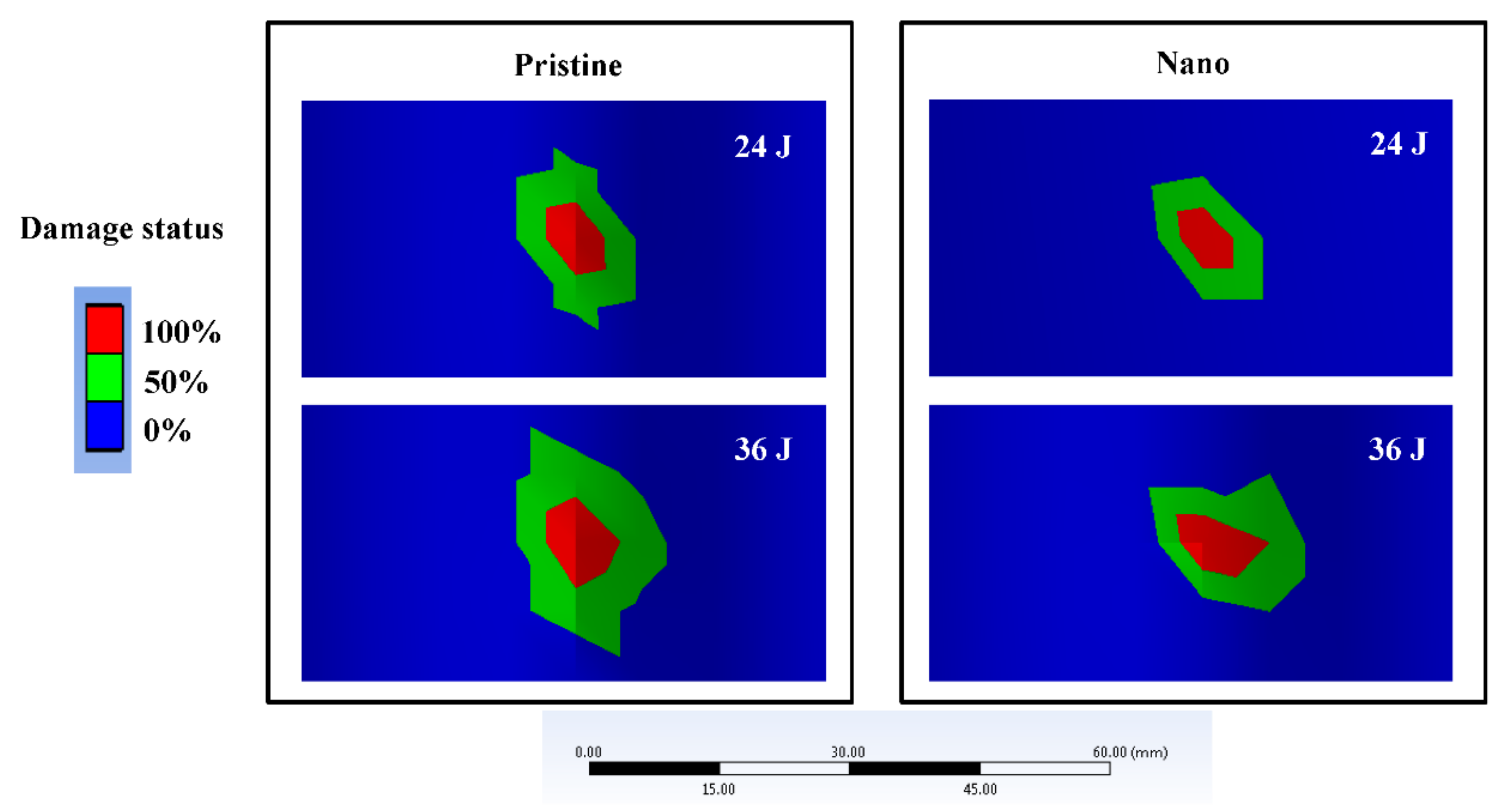
5.3. Effect of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers on the Impact Damage Behaviour
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
| Young’s Modulus X direction | 45 GPa |
| Young’s Modulus Y direction | 10 GPa |
| Young’s Modulus Z direction | 10 GPa |
| Poisson’s Ratio XY | 0.3 |
| Poisson’s Ratio YZ | 0.4 |
| Poisson’s Ratio XZ | 0.3 |
| Shear Modulus XY | 5 GPa |
| Shear Modulus YZ | 3.8 GPa |
| Shear Modulus XZ | 5 GPa |
Appendix B
References
- Daelemans, L.; Vander, H.S.; Baere, I.; Rahier, H.; Paepegem, W.; Clerk, K. Damage resistant composites using electrospun nanofibers: A multiscale analysis of the toughening mechanisms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11806–11818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, D.K.; Kelkar, A.D. Effect of TEOS electrospun nanofiber modified resin on interlaminar shear strength of glass fibre/epoxy composite. Int. J. Mater. Metall. Eng. 2014, 8, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Bielawsky, C.W.; Geng, J. Core-shell structured polyamide 66 nanofibers with enhanced flame retardancy. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 2665–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzetti, R.; Zucchelli, A. Electrospun nanofibers as reinforcement for composite laminates materials—A review. Compos. Struct. 2017, 182, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2685–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.; Palazzetti, R.; Trendafilova, I.; Fiorini, C.; Zucchelli, A. Vibration based delamination diagnosis and modelling for composite laminate plates. Compos. Struct. 2015, 130, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.; Tcherniak, D.; Trendafilova, I. Damage Assessment for wind turbine blades based on a multivariate statistical approach. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 1, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Wilson, J.; Trendafilova, I.; Yang, L. Vibratory behaviour of glass fibre reinforced polymer (GFRP) interleaved with nylon nanofibers. Compos. Struct. 2017, 176, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzetti, R.; Zucchelli, A.; Trendafilova, I. The self-reinforcing effect of nylon 6,6 nano-fibres on CFRP laminates subjected to low-velocity impact. Compos. Struct. 2013, 106, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghafi, H.; Palazzetti, R.; Zucchelli, A.; Minak, G. Influence of electrospun nanofibers on the interlaminar properties of unidirectional epoxy resin/glass fiber composite laminates. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzetti, R. Flexural behavior of carbon and glass fiber composite laminates reinforced with nylon 6,6 electrospun nanofibers. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 3407–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beylergil, B.; Tanoglu, M.; Aktaş, E. Enhancement of interlaminar fracture toughness of carbon fiber-epoxy composites using polyamide-6,6 electrospun nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 10, 45244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckermann, G.W.; Pickering, K.L. Mode I and mode II interlaminar fracture toughness of composite laminates interleaved with electrospun nanofiber veils. Compos. Part A 2015, 72, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, K.; Kostakova, E.; Meszaros, L. The effect of needleless electrospun nanofibrous interleaves on mechanical properties of carbon fabrics/epoxy laminates. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manh, C.V.; Choi, H.J. Enhancement of interlaminar fracture toughness of carbon fiber/epoxy composites using silk fibroin electrospun nanofibers. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2016, 55, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akangah, P.; Shivakumar, K. Impact damage resistance and tolerance of polymer nanofiber interleaved composite laminates. In Proceedings of the 53rd AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–26 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Saghafi, H.; Brugo, T.; Minak, G.; Zucchelli, A. Improvement the impact damage resistance of composite materials by interleaving polycaprolactone nanofibers. Eng. Solid Mech. 2015, 3, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueren, L.V.; Schoenmaker, B.; Kalaoglu, O.I.; Clerk, K. An alternative solvent system for the steady state electrospinning of polycaprolactone. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N. An efficient method for frequency calculation of an audio signal. Presidency 2013, 2, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Casiano, M.J. Extracting Damping Ratio from Dynamic Data and Numerical Solutions; Marshal Space Flight Center: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2016; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Alfano, G.; Crisfield, M.A. Finite element interface models for the delamination analysis of laminated composites: Mechanical and computational issues. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2001, 50, 1701–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuschle, H.M.; Puck, A. Application of the Puck failure theory for fibre-reinforced composites under three-dimensional stress: Comparison with experimental results. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 47, 827–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Trendafilova, I.; Zucchelli, A.; Contreras, J. The effect of nylon nanofibers on the dynamic behaviour and the delamination resistance of GFRP composites. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Vibration ICoEV, MATEC Web Conference, Sofia, Bulgaria, 4–7 September 2017; Volume 148, p. 14001. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, J.; O′Braint, S.; Gu, H.; Song, G. Damping augmentation of nanocomposites using carbon nanofiber paper. J. Nanomater. 2006, 2006, 32803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, S.H.; Lai, C.Y. Dynamic behaviour of nanocomposites reinforced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). Materials 2013, 6, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padal, K.T.B.; Ramji, K.; Prasad, V.V.S. Damping behaviour of jute nano fibre reinforced composites. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2014, 4, 753–759. [Google Scholar]
- Kordani, N.; Fereidoon, A.; Ashoori, M. Damping augmentation of nanocomposites using carbon nanotube/epoxy. J. Struct. Dyn. 2011, 3, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, T.; Lin, T.; Wang, C.H. Phase morphology of nanofiber interlayers: Critical factor for toughening carbon/epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akangah, P.; Lingaiah, S.; Shivakumar, K. Effect of nylon-66 nano-fiber interleaving on impact damage resistance of epoxy/carbon fiber composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghafi, H. Mechanical Behaviour of Flat and Curved Laminates Interleaved by Electrospun Nanofibers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bologne, Bologne, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Saghafi, H.; Palazzetti, R.; Zucchelli, A.; Minak, G. Impact response of glass/epoxy laminate interleaved with nanofibrous mats. Eng. Solid Mech. 2013, 1, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghafi, H.; Palazzetti, R.; Minak, G.; Zucchelli, A. Effect of PAN nanofiber interleaving on impact damage resistance of GFRP laminates. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Nanomaterials—Research and Application, Brno, Czech Republic, 5–7 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Abreviation | Pristine | Nano | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Normal Traction | Tnmax | 5 | 2.8 | MPa |
| Normal Displacement at Debonding | δnc | 0.27 | 0.35 | mm |
| Maximum Tangential Traction | Ttmax | 5 | 2.8 | MPa |
| Tangential Displacement at Debonding | δtc | 0.27 | 0.35 | mm |
| Ratio | α | 0.02 | 0.015 | Dimensionless |
| Non-Dimensional Parameter Initial Stiffness | β K0n,t | 1 926 | 1 533 | Dimensionless MPa/mm |
| Energy | Sample | Experimental [17] | Numerical |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 J | Pristine Nano | 170 mm2 125 mm2 | 175 mm2 126 mm2 |
| 36 J | Pristine Nano | 260 mm2 197 mm2 | 275 mm2 196 mm2 |
| Frequency (f) | Pristine (Hz) | Nano (Hz) | Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| First | 484.5 | 461.5 | 4.7 |
| Second | 930.9 | 923.2 | 0.8 |
| Third | 1373.8 | 1369.8 | 0.3 |
| Fourth | 1857.5 | 1843.2 | 0.8 |
| Fifth | 2303.8 | 2278.0 | 1.2 |
| Pristine (Dimensionless) | Nano (Dimensionless) | Variation (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damping | 0.01208 | 0.01277 | 5.7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, C.; Trendafilova, I.; Zucchelli, A. The Effect of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers on the Dynamic and Impact Behavior of Glass Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030043
Garcia C, Trendafilova I, Zucchelli A. The Effect of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers on the Dynamic and Impact Behavior of Glass Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites. Journal of Composites Science. 2018; 2(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Cristobal, Irina Trendafilova, and Andrea Zucchelli. 2018. "The Effect of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers on the Dynamic and Impact Behavior of Glass Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites" Journal of Composites Science 2, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030043
APA StyleGarcia, C., Trendafilova, I., & Zucchelli, A. (2018). The Effect of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers on the Dynamic and Impact Behavior of Glass Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites. Journal of Composites Science, 2(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030043






