Thermal Properties of Multilayer Nanocomposites Based on Halloysite Nanotubes and Biopolymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Multilayer Nanocomposites
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Thermogravimetry
2.3.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3. Results and Discussion
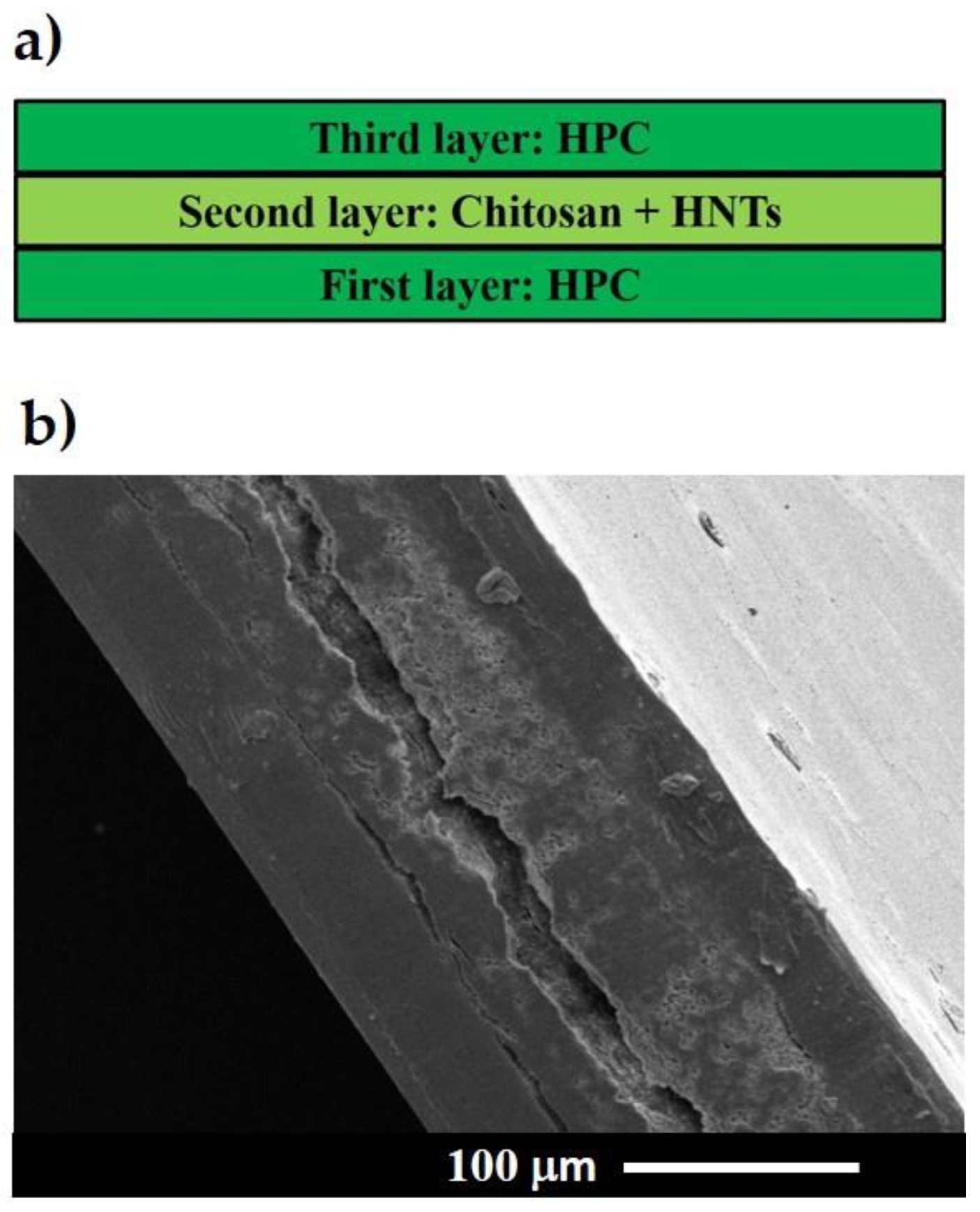
3.1. Multilayer Structure the Nanocomposites
3.2. Thermal Properties of the Nanocomposites
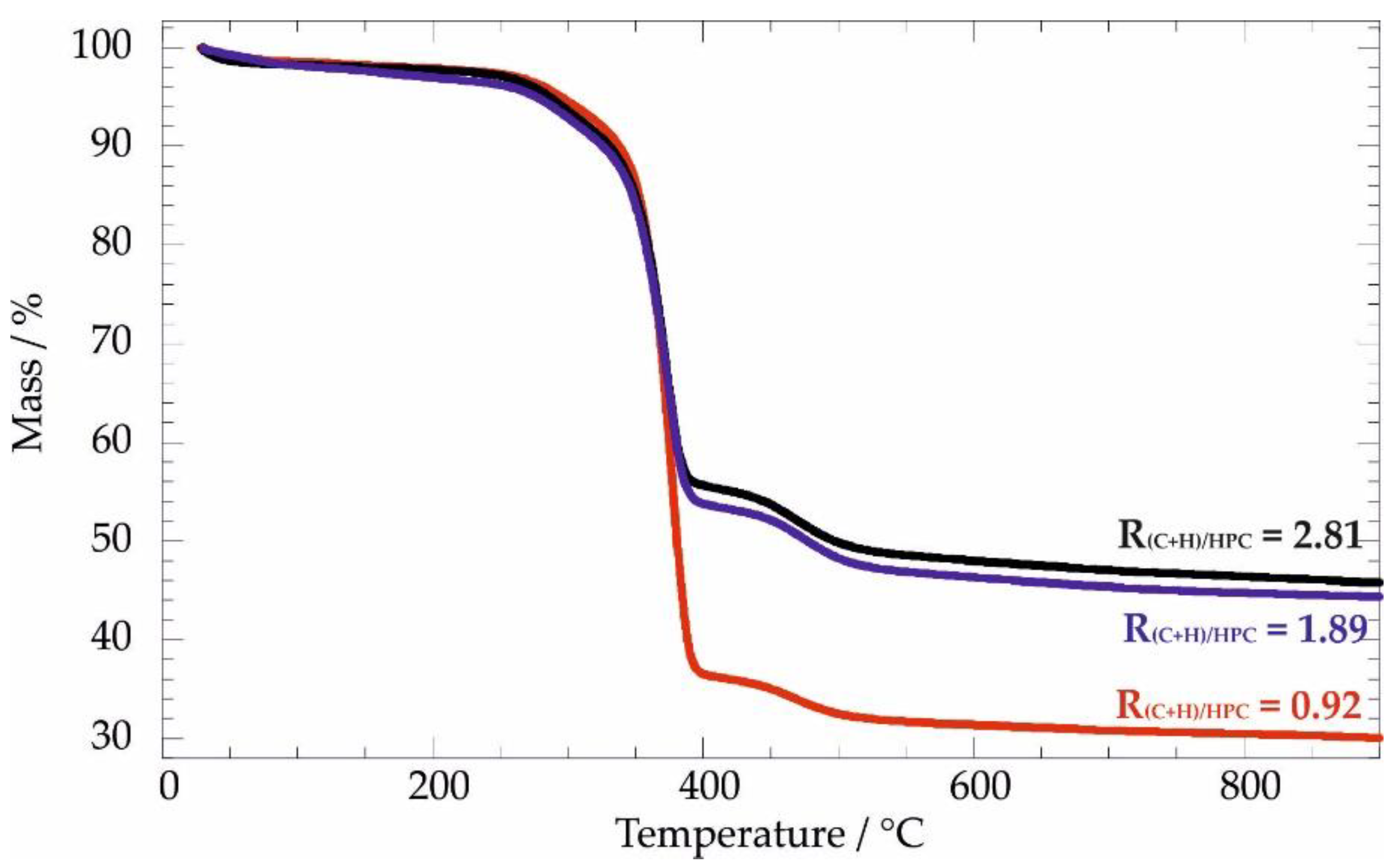
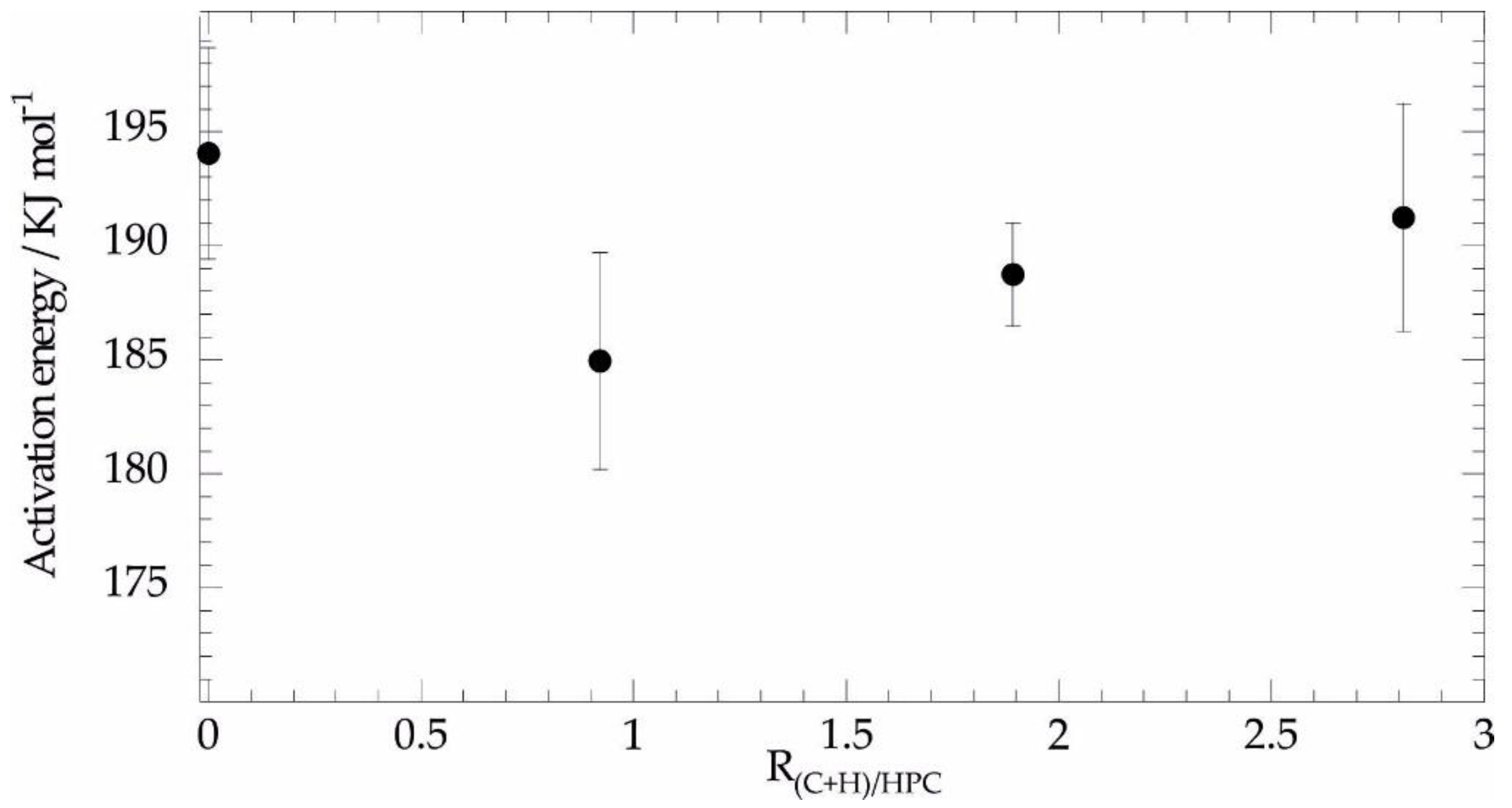
3.2.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis: Thermal Behavior under Inert Atmosphere
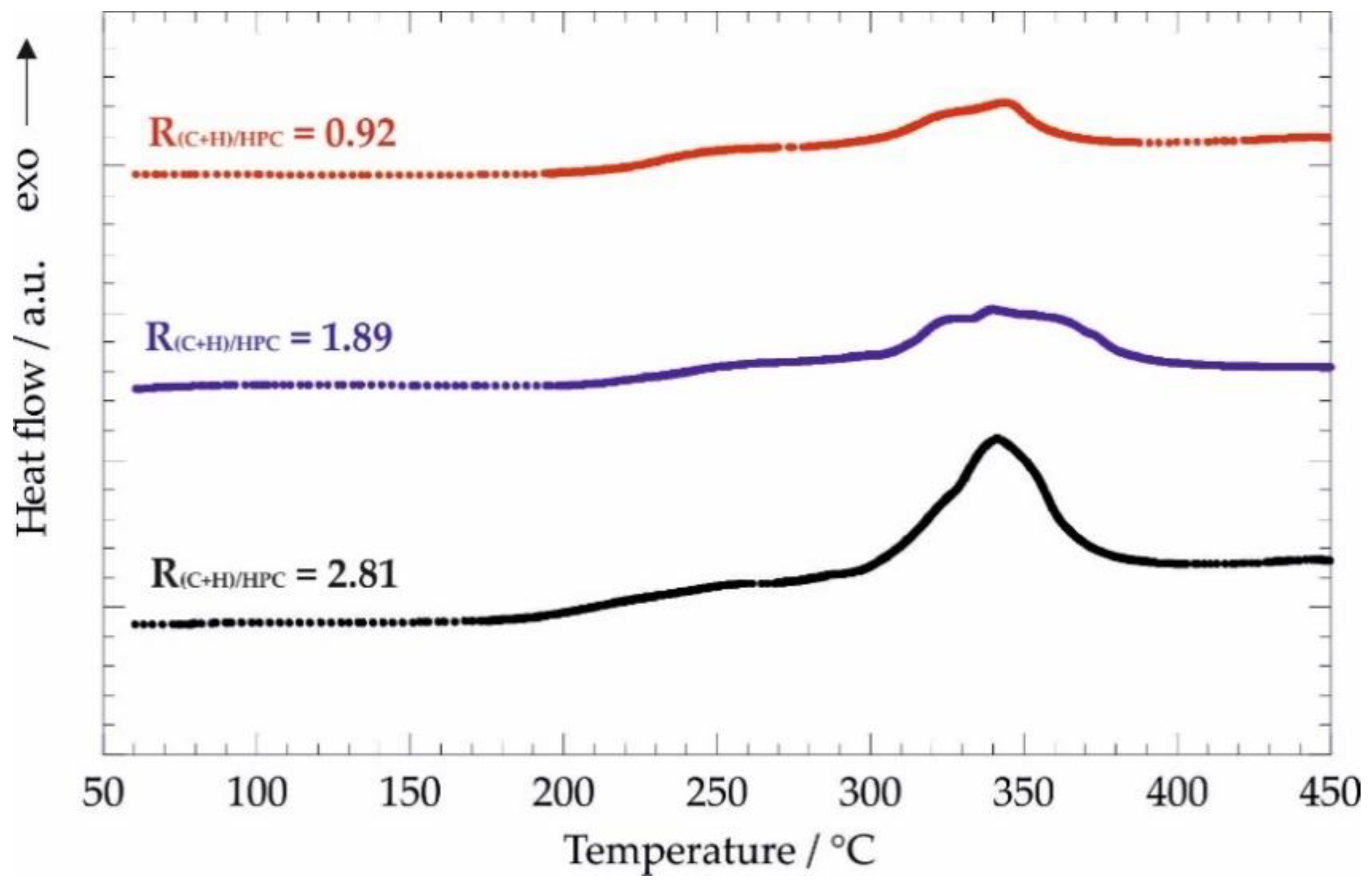
3.2.2. Oxidative Degradation of Nanocomposites by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fix, D.; Andreeva, D.V.; Lvov, Y.M.; Shchukin, D.G.; Möhwald, H. Application of inhibitor-loaded halloysite nanotubes in active anti-corrosive coatings. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Aerov, A.; Fakhrullin, R. Clay nanotube encapsulation for functional biocomposites. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 207, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.; Abdullayev, E.; Vasiliev, A.; Volkova, O.; Lvov, Y. interfacial modification of clay nanotubes for the sustained release of corrosion inhibitors. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7439–7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Donato, D.I.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S. Films of halloysite nanotubes sandwiched between two layers of biopolymer: From the morphology to the dielectric, thermal, transparency, and wettability properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 20491–20498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaremi, M.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Aw, Y.K.; Lee, S.M.; Milioto, S. Effect of morphology and size of halloysite nanotubes on functional pectin bionanocomposites for food packaging applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17476–17488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Jia, D. Newly emerging applications of halloysite nanotubes: A review. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Abdullayev, E.; Vasiliev, A.; Lvov, Y. Halloysite nanotubule clay for efficient water purification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 406, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, P. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue on halloysite nanotubes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 112, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owoseni, O.; Nyankson, E.; Zhang, Y.; Adams, S.J.; He, J.; McPherson, G.L.; Bose, A.; Gupta, R.B.; John, V.T. Release of surfactant cargo from interfacially-active halloysite clay nanotubes for oil spill remediation. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13533–13541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchal, A.; Swientoniewski, L.T.; Omarova, M.; Yu, T.; Zhang, D.; Blake, D.A.; John, V.; Lvov, Y.M. Bacterial proliferation on clay nanotube Pickering emulsions for oil spill bioremediation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 164, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Gianguzza, A.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Piazzese, D. Alginate gel beads filled with halloysite nanotubes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 72, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.-H.; Zhang, B. Polydopamine-coated halloysite nanotubes supported AgPd nanoalloy: An efficient catalyst for hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 2754–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.-H.; Zhang, B. Preparation of bimetallic Cu-Co nanocatalysts on poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) functionalized halloysite nanotubes for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Niu, Y.; Xiang, X.; Chen, R. Fabricating roughened surfaces on halloysite nanotubes via alkali etching for deposition of high-efficiency Pt nanocatalysts. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 3110–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, S.; Hosseinnejad, T.; Malmir, M.; Heravi, M.M. Cu@furfural imine-decorated halloysite as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for promoting ultrasonic-assisted A3 and KA2 coupling reactions: A combination of experimental and computational study. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 13935–13951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; van Spreeuwel, A.; Zhang, C.; Varghese, S. PEG/clay nanocomposite hydrogel: A mechanically robust tissue engineering scaffold. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 5157–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrullin, R.F.; Lvov, Y.M. Halloysite clay nanotubes for tissue engineering. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wu, C.; Jiao, Y.; Xiong, S.; Zhou, C. Chitosan-halloysite nanotubes nanocomposite scaffolds for tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Danilushkina, A.A.; Evtugyn, V.G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Rozhina, E.V.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Halloysite nanotubes: Controlled access and release by smart gates. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Sparacino, V. Thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of beeswax-halloysite nanocomposites for consolidating waterlogged archaeological woods. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 120, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lisi, R.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S. Polyethylene glycol/clay nanotubes composites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 112, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrasi, G.; Bugatti, V.; Vittoria, V. Pectins filled with LDH-antimicrobial molecules: Preparation, characterization and physical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Konnova, S.; Fakhrullin, R.; Lvov, Y. Composite films of natural clay nanotubes with cellulose and chitosan. Green Mater. 2014, 2, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryuchkova, M.; Danilushkina, A.; Lvov, Y.; Fakhrullin, R. Evaluation of toxicity of nanoclays and graphene oxide in vivo: A Paramecium caudatum study. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gong, J.; Rong, R.; Gui, Z.; Hu, T.; Xu, X. Halloysite nanotubes-induced al accumulation and fibrotic response in lung of mice after 30-day repeated oral administration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2925–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lvov, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Fakhrullin, R. Halloysite clay nanotubes for loading and sustained release of functional compounds. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1227–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joussein, E.; Petit, S.; Churchman, G.J.; Theng, B.; Righi, D.; Delvaux, B. Halloysite clay minerals—A review. Clay Miner. 2005, 40, 383–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Chiappisi, L.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Gradzielski, M.; Lazzara, G. A structural comparison of halloysite nanotubes of different origin by Small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and electric birefringence. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F. Biopolymer-targeted adsorption onto halloysite nanotubes in aqueous media. Langmuir 2017, 33, 3317–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalay, S.; Stetsyshyn, Y.; Lobaz, V.; Harhay, K.; Ohar, H.; Çulha, M. Water-dispersed thermo-responsive boron nitride nanotubes: Synthesis and properties. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 035703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Cavallaro, G.; Lvov, Y. Orientation of charged clay nanotubes in evaporating droplet meniscus. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 440, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Huo, Z.; Liu, T.; Shen, Y.; He, R.; Zhou, C. Self-assembling halloysite nanotubes into concentric ring patterns in a sphere-on-flat geometry. Langmuir 2017, 33, 3088–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Grillo, I.; Gradzielski, M.; Lazzara, G. Structure of hybrid materials based on halloysite nanotubes filled with anionic surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 13492–13502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Merli, M.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Sciascia, L. Effect of the biopolymer charge and the nanoclay morphology on nanocomposite materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 7373–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrasi, G. Dispersion of halloysite loaded with natural antimicrobials into pectins: Characterization and controlled release analysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, R.T.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Goh, K.L.; Chai, S.-P.; Ismail, H. Physico-chemical characterisation of chitosan/halloysite composite membranes. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ahmed, S. A review on chitosan and its nanocomposites in drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiong, S.; Zhou, C. Chitosan/halloysite nanotubes bionanocomposites: Structure, mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Liu, M.; Zhou, C. Chitosan composite hydrogels reinforced with natural clay nanotubes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrasi, G.; Pantani, R.; Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. PLA/Halloysite nanocomposite films: water vapor barrier properties and specific key characteristics. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F. Halloysite nanotubes sandwiched between chitosan layers: Novel bionanocomposites with multilayer structures. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 8384–8390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Abdullayev, E. Functional polymer–clay nanotube composites with sustained release of chemical agents. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1690–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terekhova, I.V. Comparative thermodynamic study on complex formation of native and hydroxypropylated cyclodextrins with benzoic acid. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 526, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terekhova, I.V.; Romanova, A.O.; Kumeev, R.S.; Fedorov, M.V. Selective Na+/K+ effects on the formation of α-cyclodextrin complexes with aromatic carboxylic acids: competition for the guest. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 12607–12613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, I.; Abate, L.; Bottino, F.A.; Bottino, P. Thermal behaviour of a series of novel aliphatic bridged polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSSs)/polystyrene (PS) nanocomposites: The influence of the bridge length on the resistance to thermal degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 102, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Jia, D. Thermal stability and flame retardant effects of halloysite nanotubes on poly(propylene). Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, I.; Abate, L.; Bottino, F.A.; Bottino, P. Thermal degradation of hepta cyclopentyl, mono phenyl-polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (hcp-POSS)/polystyrene (PS) nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budrugeac, P.; Cucos, A.; Miu, L. The use of thermal analysis methods for authentication and conservation state determination of historical and/or cultural objects manufactured from leather. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 104, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazovkin, S.; Dranca, I.; Fan, X.; Advincula, R. Degradation and relaxation kinetics of polystyrene—Clay nanocomposite prepared by surface initiated polymerization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 11672–11679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazovkin, S.; Chrissafis, K.; Di Lorenzo, M.L.; Koga, N.; Pijolat, M.; Roduit, B.; Sbirrazzuoli, N.; Suñol, J.J. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for collecting experimental thermal analysis data for kinetic computations. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 590, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, A.; De Gracia, A.; Haurie, L.; Cabeza, L.F.; Fernández, A.I.; Barreneche, C. Study of the thermal properties and the fire performance of flame retardant-organic PCM in bulk form. Materials 2018, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Fasulo, P.D.; Rodgers, W.R.; Paul, D.R. TPO based nanocomposites. Part 2. Thermal expansion behavior. Polymer 2006, 47, 3528–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Material | Solvent | Concentration (wt %) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) | ethanol | 2.01 |
| Chitosan | water (pH = 3.5) | 1.02 |
| R(C+H)/HPC | Amount of HPC Solution (First Layer)/g | Amount of Chitosan/HNTs Dispersion (Second Layer)/g | Amount of HPC Solution (Third Layer)/g |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.92 | 8.18 | 4.96 | 8.02 |
| 1.89 | 8.15 | 10.24 | 8.07 |
| 2.81 | 8.05 | 15.03 | 8.00 |
| R(C+H)/HPC | h(HPC) (First Layer)/μm | h(HPC) (Third Layer)/μm | hC+H (Middle Layer)/μm | Nanocomposite Thickness/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.92 | 71.2 | 69.8 | 2.67 | 144 |
| 1.89 | 70.9 | 70.3 | 5.52 | 147 |
| 2.81 | 70.1 | 69.7 | 8.11 | 149 |
| R(C+H)/HPC | ML150/% | ML400/% | ML600/% | MR900/% | TCHIT/°C | THPC/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.65 | 92.4 | / | 4.07 | 289.2 | 369.7 |
| 0.92 | 1.74 | 61.3 | 4.28 | 30.1 | 290.2 | 376.4 |
| 1.89 | 1.83 | 43.2 | 6.33 | 44.8 | 291.6 | 373.4 |
| 2.81 | 2.31 | 42.1 | 6.49 | 45.8 | 286.5 | 374.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Lazzara, G. Thermal Properties of Multilayer Nanocomposites Based on Halloysite Nanotubes and Biopolymers. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030041
Bertolino V, Cavallaro G, Milioto S, Parisi F, Lazzara G. Thermal Properties of Multilayer Nanocomposites Based on Halloysite Nanotubes and Biopolymers. Journal of Composites Science. 2018; 2(3):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030041
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertolino, Vanessa, Giuseppe Cavallaro, Stefana Milioto, Filippo Parisi, and Giuseppe Lazzara. 2018. "Thermal Properties of Multilayer Nanocomposites Based on Halloysite Nanotubes and Biopolymers" Journal of Composites Science 2, no. 3: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030041
APA StyleBertolino, V., Cavallaro, G., Milioto, S., Parisi, F., & Lazzara, G. (2018). Thermal Properties of Multilayer Nanocomposites Based on Halloysite Nanotubes and Biopolymers. Journal of Composites Science, 2(3), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2030041








