Fatigue-Damage Evolution of Notched Composite Multilayered Structures under Tensile Loads
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- to demonstrate the failure forms of the plates and cylindrical panels and to confront them with finite element (FE) analysis;
- to compare the experimental results for the hybrid analysis including the infra-red thermography, the SHM and the DIC methods, and to evaluate the effectiveness of these methods for static and fatigue tests.
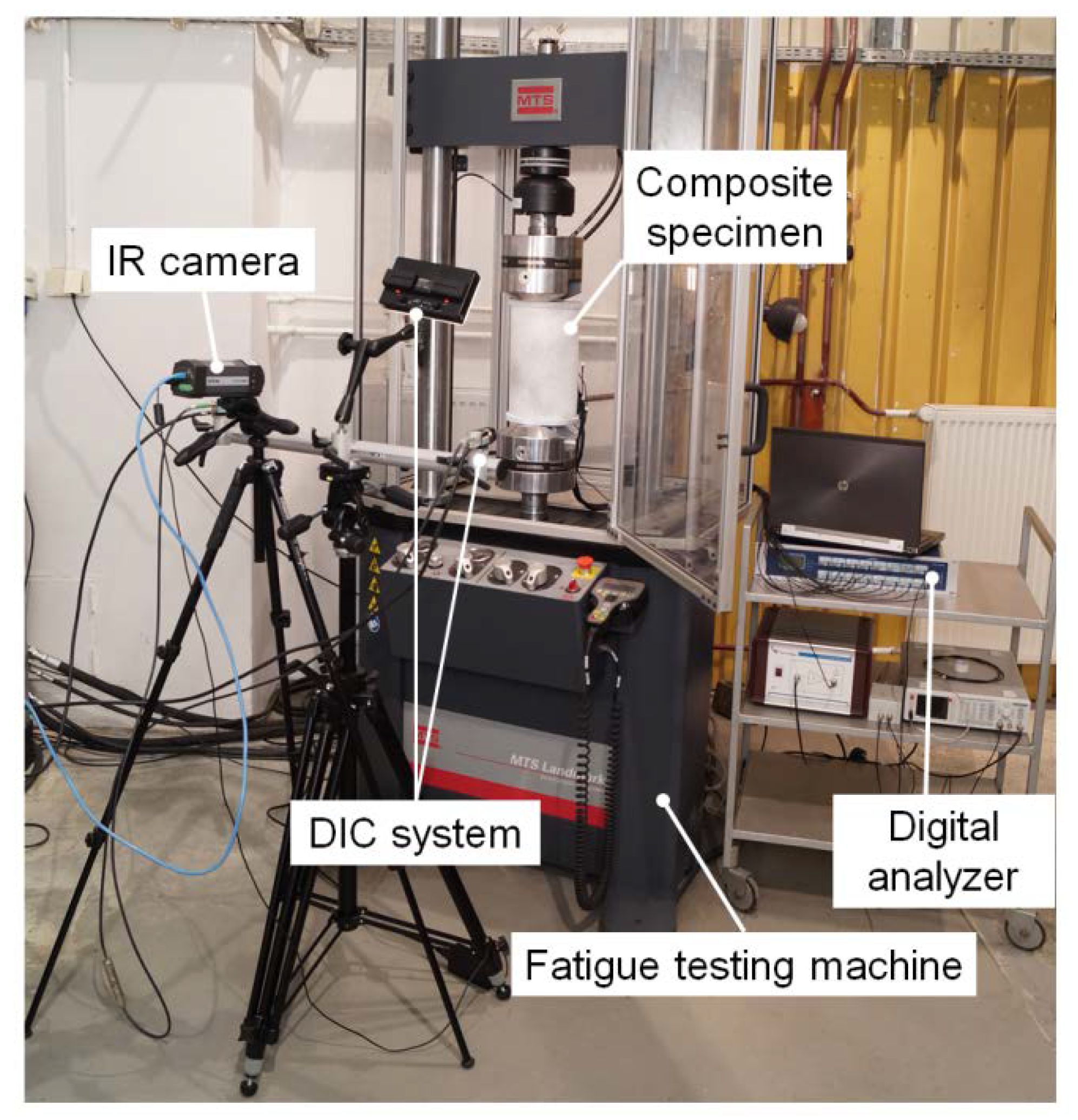
2. Experimental Equipment
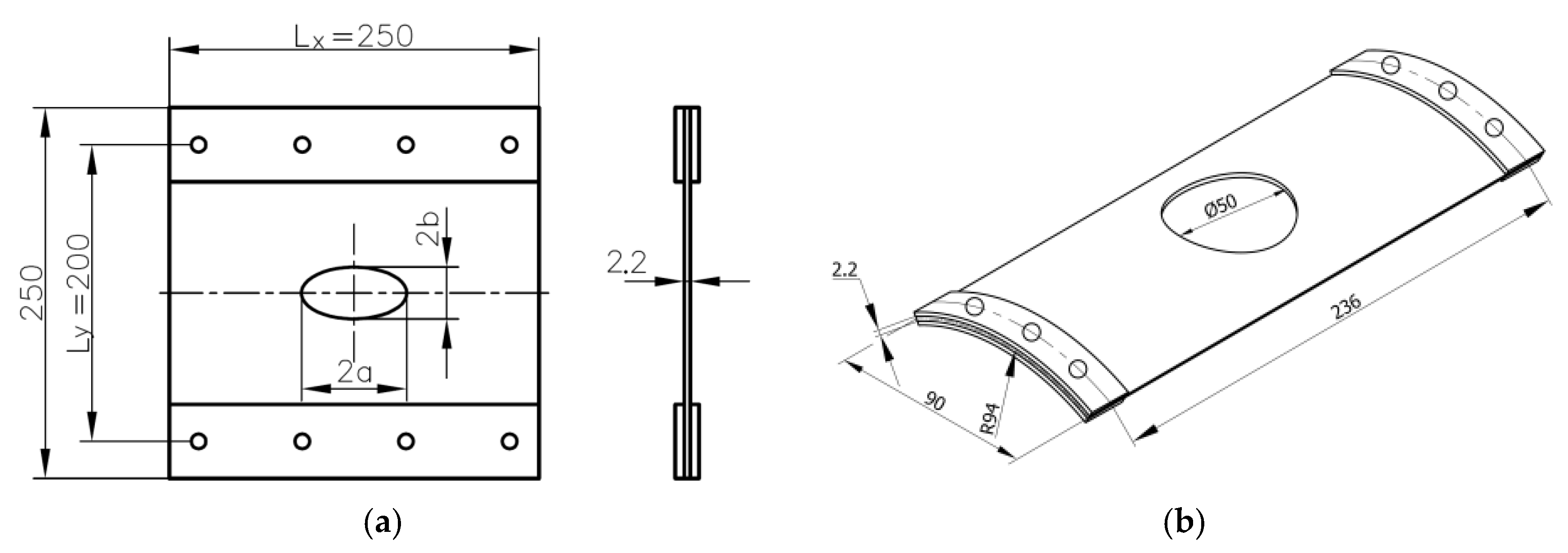
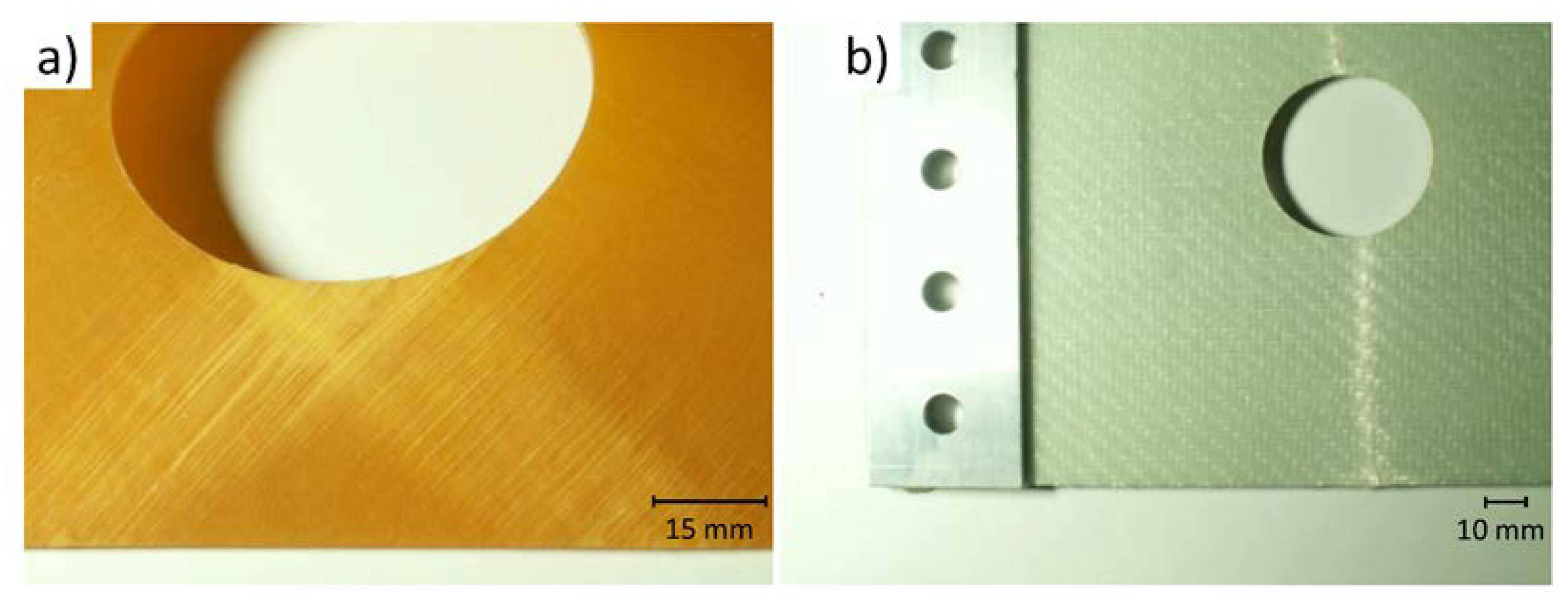
3. Mechanisms of Failure Modes for Multilayered Panels with Open Holes
- In the fiber direction, the behavior is almost elastic. The damage is observed before the final fracture. Three major intralaminar mechanisms are responsible for all observed non-linearities in the stress–strain curve of a composite lamina: matrix microdamage, matrix macroscopic cracking (modes I and II), and axial fiber failure (mode I).
- In shearing, obtained from a tension test on a ±45° laminate, we can observe a non-linear behavior; there are anelastic strains. We can observe a classical behavior in the form of splitting along the fiber direction (the intralaminar mechanisms) associated with delaminations (the interlaminar mechanism).
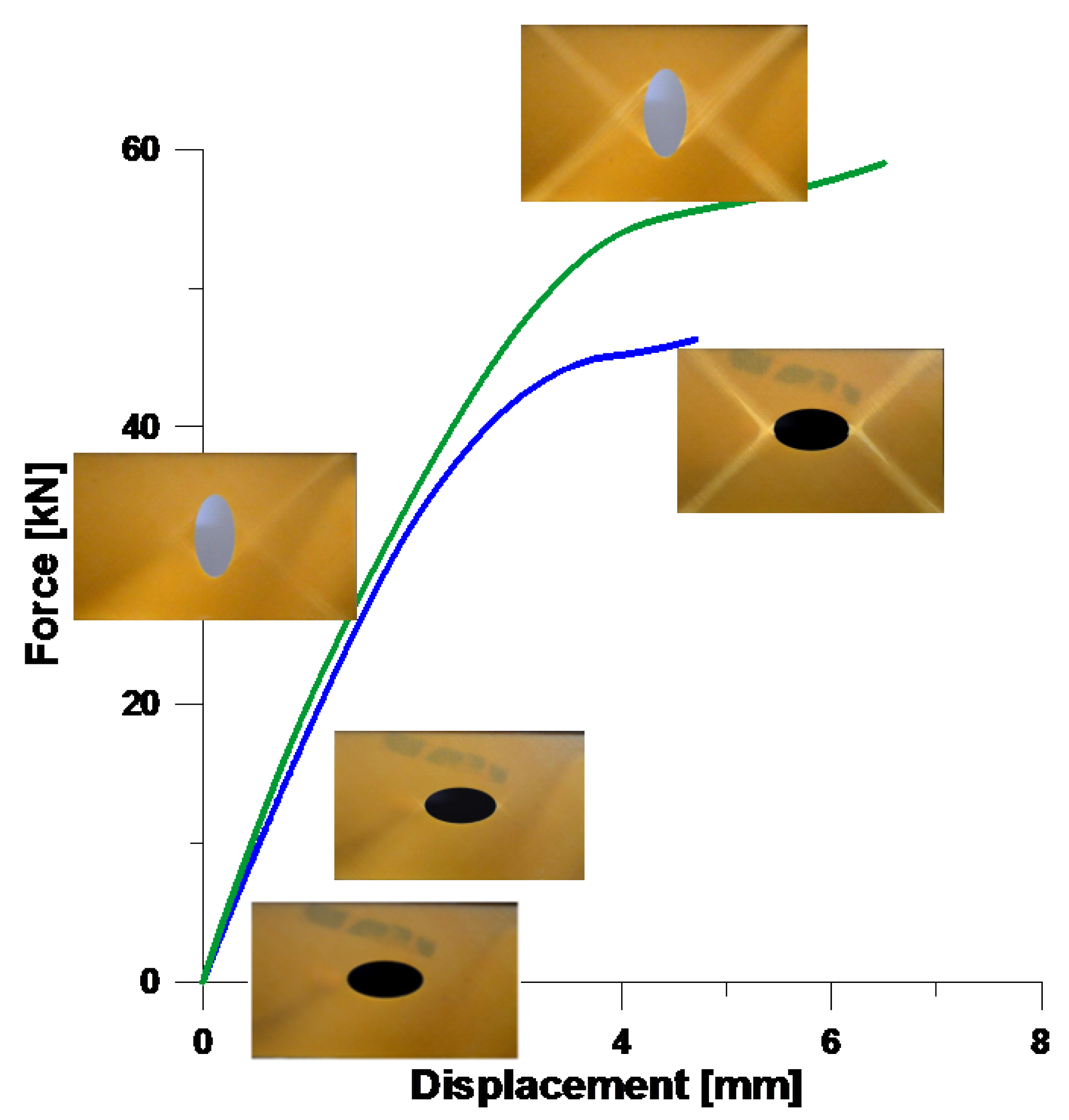
4. Fatigue Analysis—Experimental Results
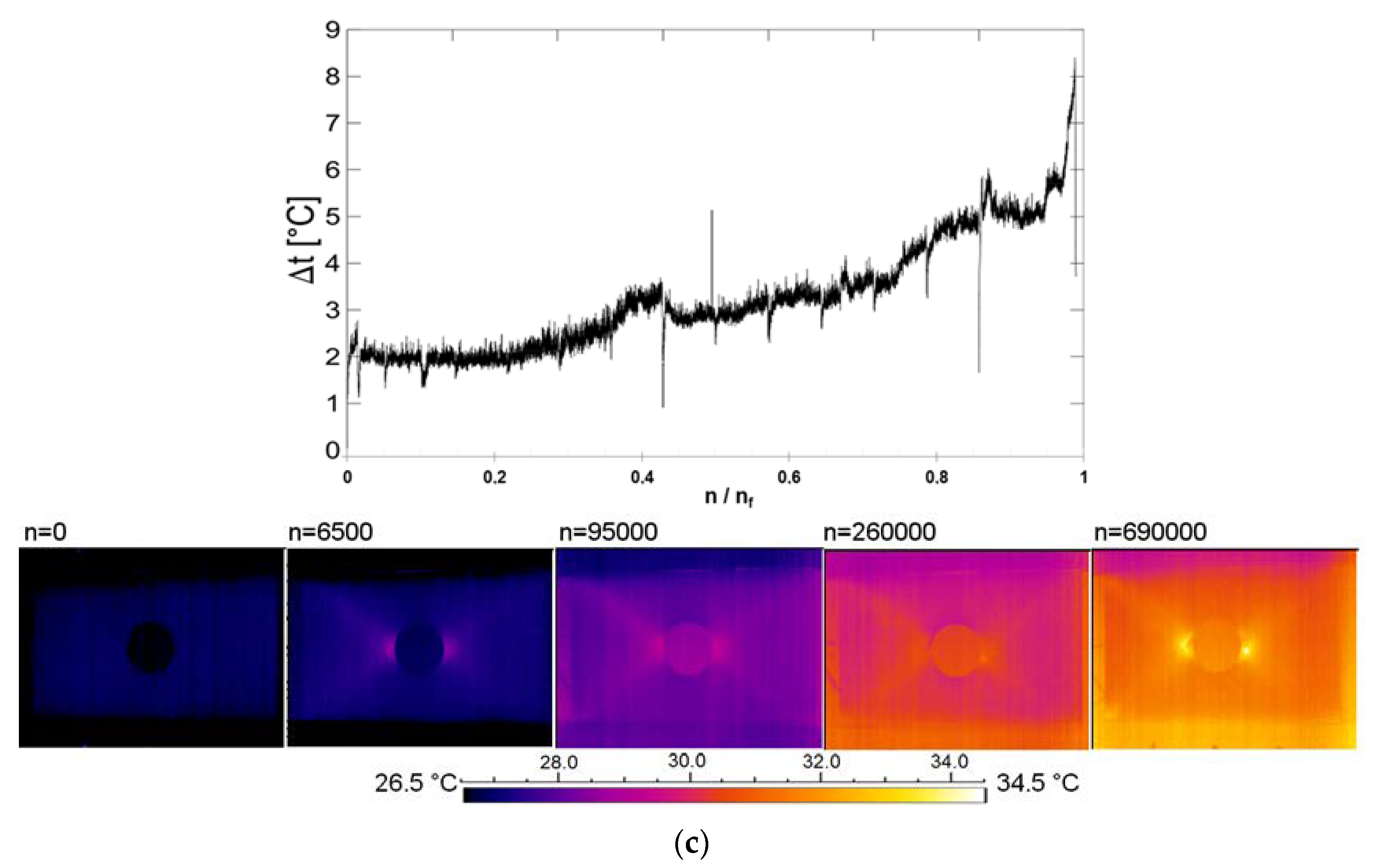
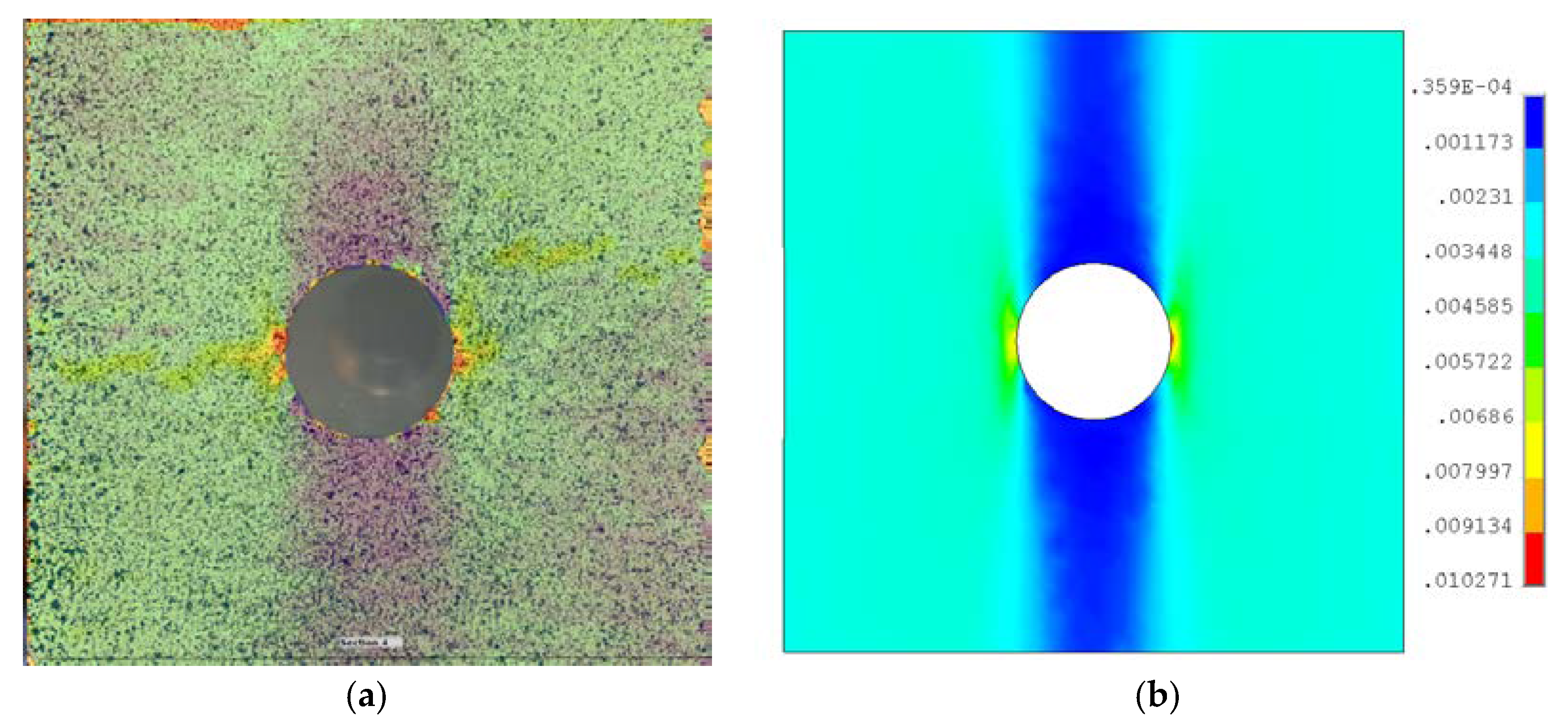
4.1. Infra-Red Thermography (Passive)
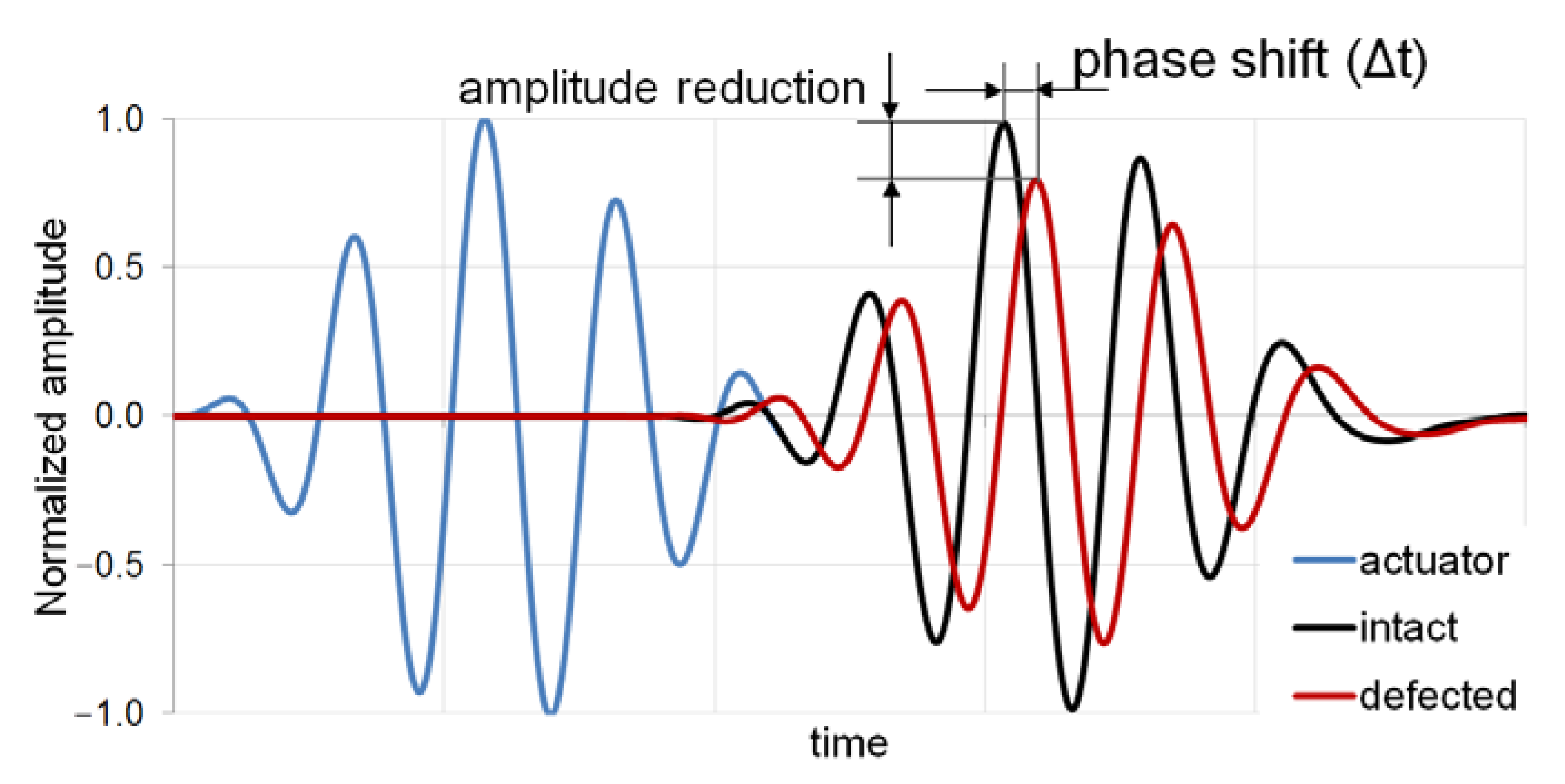
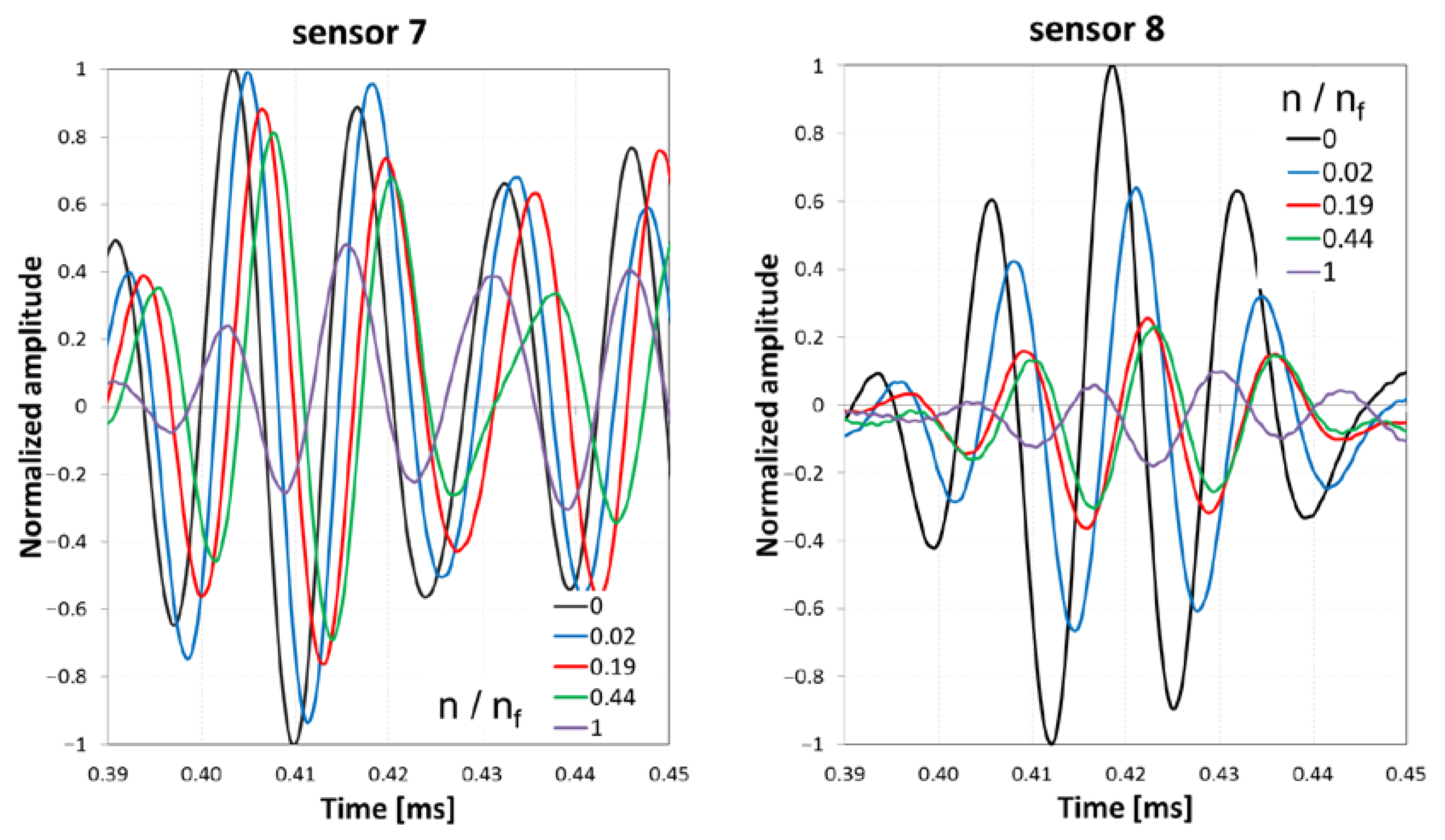
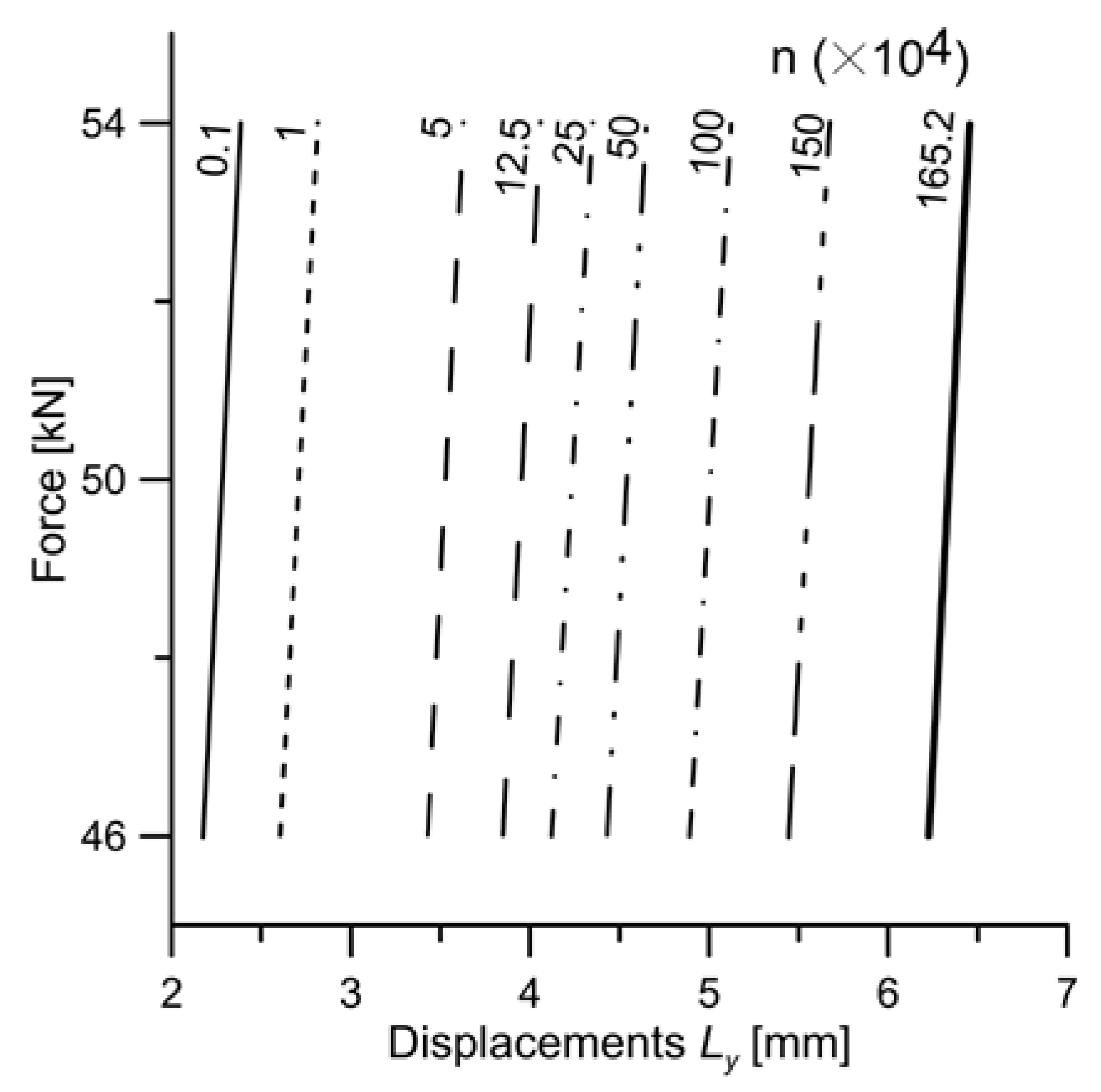
4.2. Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) Method (Active)
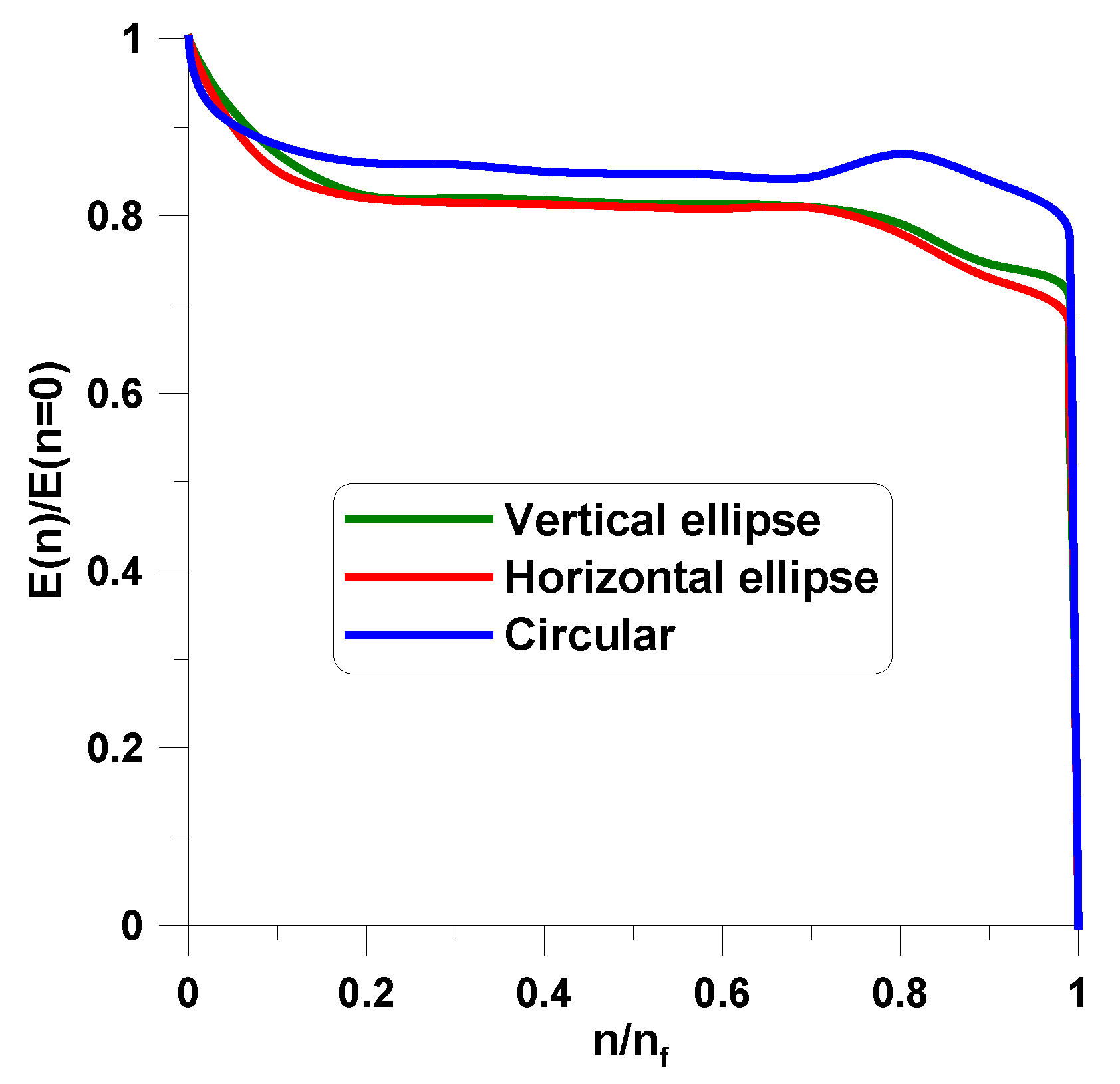
4.3. Digital-Image Correlation (DIC) Method and the Damage Variable
5. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McLaughlin, P.V., Jr.; Kulkarni, S.V.; Huang, S.N.; Walter Rosen, B. Fatigue of Notched Fiber Composite Laminates: Part 1. Analytical Model; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1975.
- T’ Hart, W.G.J. Residual Strength of (0, ±45)S And (±45, 0)S Carbon/Epoxy Laminates; Nationaal Lucht- en Ruimtevaartlaboratorium: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Shokrieh, M.M. Failure of Laminated Composite Pinned Connections. M.Sc. Thesis, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Shokrieh, M.M.; Yazdi, M.H. A simplified approach to fatigue damage modelling of composite laminates with stress concentration: Regional elements model. Iran. Polym. J. 2009, 18, 233–246. [Google Scholar]
- Muc, A.; Romanowicz, P. Effect of notch on static and fatigue performance of multilayered composite structures under tensile loads. Compos. Struct. 2017, 178, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Venkataram, S.; Miller, I. Predicting fatigue damage of composites using strength degradation and cumulative damage model. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Venkataraman, S.; Miller, I. Fatigue failure predictions of laminated composites using mechanical properties degradation and continuum damage models. In Proceedings of the AIAA/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Degrieck, J.; Van Paepegem, W. Fatigue damage modelling of fibre-reinforced composite materials: Review. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2001, 54, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, A.; Yang, L. Cumulative fatigue damage and life prediction theories: A survey of the state of the art for homogeneous materials. Int. J. Fatigue 1998, 20, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, H.; Rolfes, R. A physically based fatigue damage model for fibre-reinforced plastics under plane loading. Int. J. Fatigue 2015, 70, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, G.D. Fatigue test methods, problems and standards. In Fatigue in Composites; Harris, B., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2003; pp. 36–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, E.; Valot, E.; Herve, P. A comparison between thermosonics and thermography for delamination detection in polymer matrix laminates. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordatos, E.Z.; Aggelis, D.G.; Matikas, T.E. Monitoring mechanical damage in structural materials using complimentary NDE techniques based on thermography and acoustic emission. Compos. Part B 2012, 43, 2676–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalameda, J.N.; Burke, E.R.; Horne, M.R.; Madaras, E.I. Large area nondestructive evaluation of a fatigue loaded composite structure. In Residual Stress, Thermomechanics & Infrared Imaging, Hybrid Techniques and Inverse Problems; Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series; Quinn, S., Balandraud, X., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Maldague, X. Theory and Practice of Infrared Technology for Non Destructive Testing; John-Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vavilov, V. Nondestructive testing handbook. In Book 1: Thermal/Infrared Testing; Spektr Publishing House: Moscow, Russia, 2009; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Meola, C.; Boccardi, S.; Carlomagno, G.M. Infrared Thermography in the Evaluation of Aerospace Composite Materials; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Duxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pastuszak, P.D.; Muc, A.; Barski, M. Methods of infrared non-destructive techniques: Review and experimental studies. In Advanced Materials in Machine Design; Muc, A., Barski, M., Kędziora, P., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Giurgiutiu, V. SHM of fatigue degradation and other in-service damage of aerospace composites. In Structural Health Monitoring of Aerospace Composites; Elsevier: London, UK, 2016; pp. 395–434. [Google Scholar]
- Muc, A.; Stawiarski, A. Identification of damages in composite multilayered cylindrical panels with delaminations. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Orteu, J.-J.; Schreier, H.W. Image Correlation for Shape, Motion and Deformation Measurements; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.I. Progressive Failure Analysis of Laminated Composite Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Virgiia Tech., Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tohgo, K.; Wang, A.S.D.; Chou, T.-W. A criterion for splitting crack initiation in unidirectional fiber-reinforced composites. J. Compos. Mater. 1993, 27, 1054–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhenov, S.L. Longitudinal splitting in unidirectional fibre-reinforced composites with an open hole. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1998, 58, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, H.; Liu, P.; Zou, P.; Song, D. Stress analysis and damage evolution in individual plies of notched composite laminates subjected to in-plane loads. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2017, 30, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achard, V.; Bouvet, C.; Castanié, B.; Chirol, C. Discrete ply modelling of open hole tensile tests. Compos. Struct. 2014, 113, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kremer, T.; Schurmann, H. Buckling of tension-loaded thin-walled composite plates with cut-outs. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 68, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstulović-Opara, L.; Klarin, B.; Neves, P.; Domazet, Ž. Thermal imaging and thermoelastic stress analysis of impact damage of composite materials. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2011, 18, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesinak, J.R.; Boyce, B.R.; Howenwater, G. Thermoelastic measurement under random loading. In Proceedings of the SEM Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 8 June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dulieu-Barton, J.M.; Quinn, S. Thermoelastic stress analysis of oblique holes in flat plates. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1999, 41, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindal, V.N. Transducers for Ultrasonic Flaw Detection; Narosa Press: New Delhi, India, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Ran, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Guan, X. A fatigue crack size evaluation method based on lamb wave simulation and limited experimental data. Sensors 2017, 17, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambu, R.; Aymerich, F.; Bertolino, F. Investigation of the effect of damage on the strength of notched composite laminates by digital image correlation. J. Strain Anal. 2005, 40, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, J.; Kurts, S. Digital image correlation-based experimental stress analysis of reinforced concrete beams, strengthened using carbon composites. SPIE-IS&T 2005, 5665, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lagattu, F.; Brillaud, J.; Lafarie-Frenot, M.-C. High strain gradient measurements by using digital image correlation technique. Mater. Charact. 2004, 53, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lomov, S.V.; Verpoest, I.; Daggumati, S.; Van Paepegem, W.; Degrieck, J. A comparative study of twill weave reinforced composites under tension–tension fatigue loading: Experiments and meso-modelling. Compos. Struct. 2016, 135, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durchlaub, E.C.; Freeman, R.B. Design Data for Composite Structure Safe life Prediction; Technical Report AFML-TR-73–225; Air Force Materials Laboratory: Dayton, OH, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Hallett, S.R.; Jiang, W.-G.; Khan, B.; Wisnom, M.R. Modelling the interaction between matrix cracks and delamination damage in scaled quasi-isotopic specimens. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanowicz, P.; Składanowska, K.; Muc, A. Fracture strength of multi-layered composite plates with circular delamination. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Automation (ICEEA 2016), Xiamen, China, 18–19 December 2016. [Google Scholar]

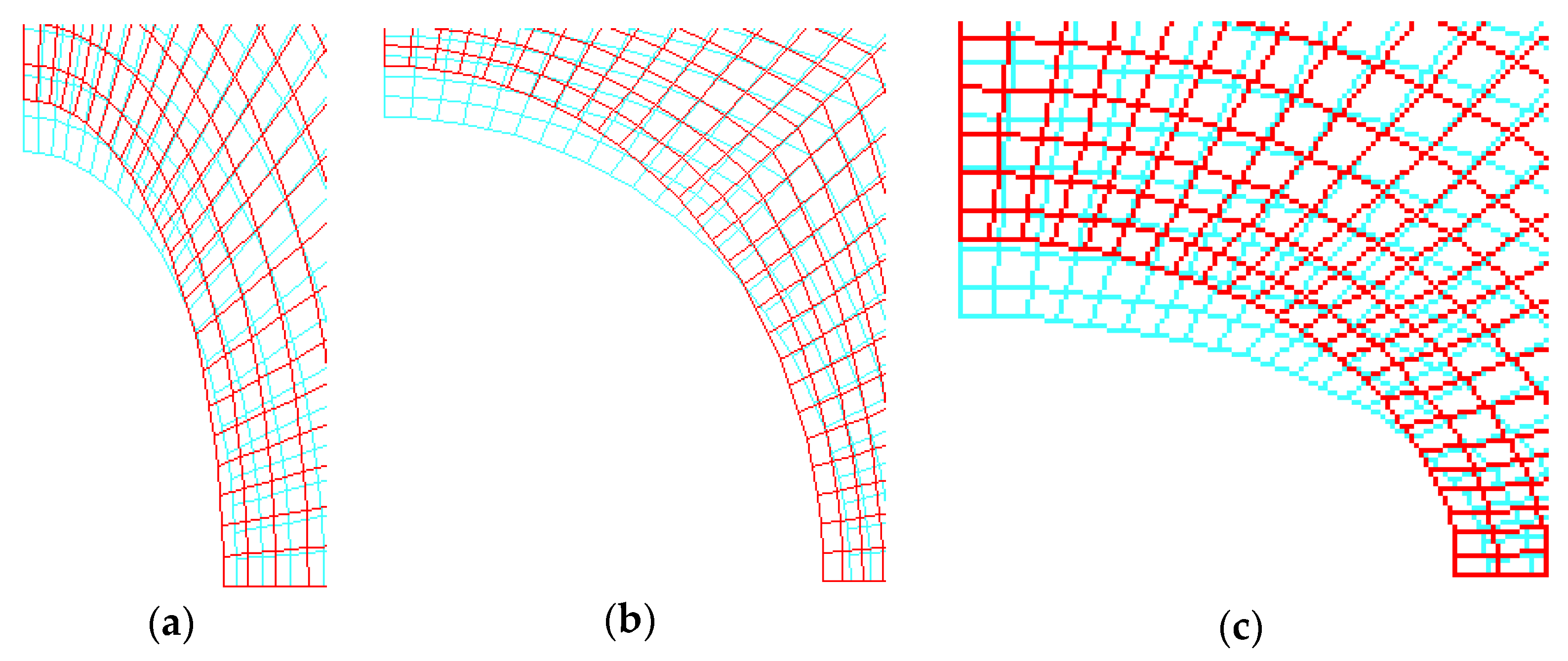

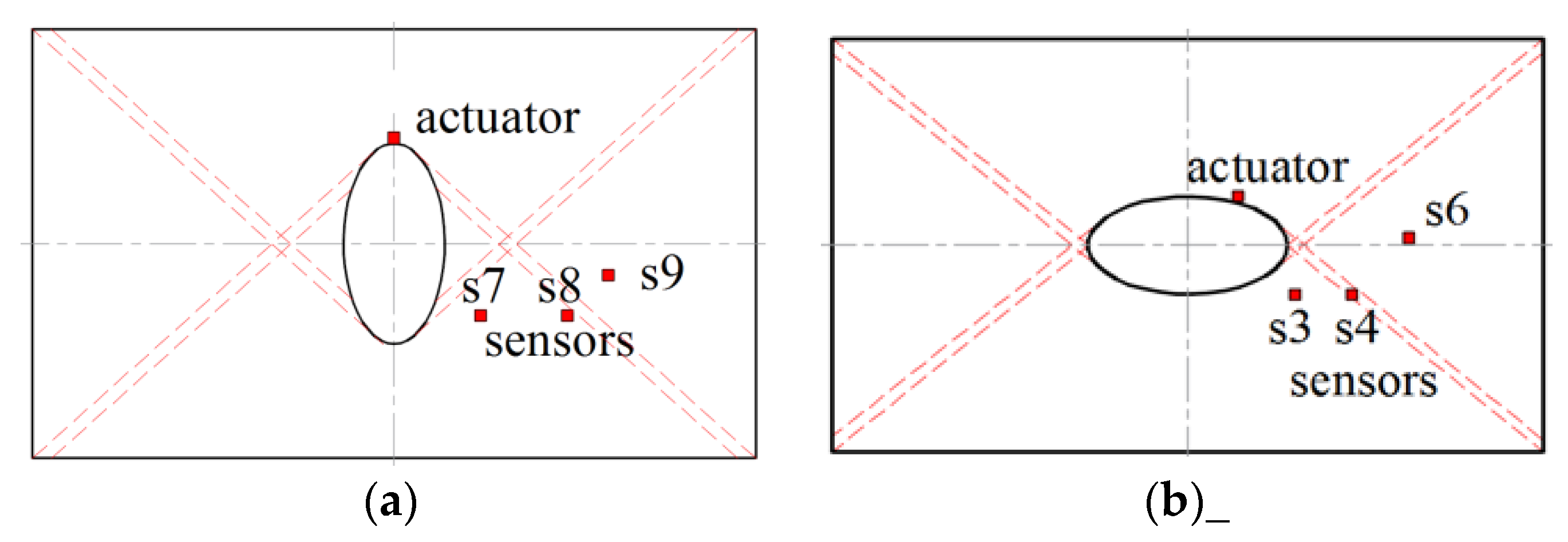



| Hole | Circular a = b = 25 mm | Circular a = b = 25 mm | Elliptical Vertical a = 17.5, b = 35.7 mm | Elliptical Horizontal a = 35.7, b = 17.5 mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Woven-roving glass/epoxy | Unidirectional glass/epoxy | ||
| Stress ratio | 0.818 | 0.833 | 0.852 | 0.810 |
| Frequency (Hz) | 15 | 15 | 30 | 30 |
| Mean load (kN) | 40 | 44 | 50 | 38 |
| Amplitude (kN) | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Materials | Fiber Direction | E1 (GPa) | E2 (GPa) | G12 (GPa) | ν12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unidirectional glass/epoxy | ±45° | 46.4 | 14.9 | 5.2 | 0.27 |
| Woven-roving fabric glass/epoxy | 0° | 62 | 62 | 7.8 | 0.26 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muc, A.; Chwał, M.; Romanowicz, P.; Stawiarski, A. Fatigue-Damage Evolution of Notched Composite Multilayered Structures under Tensile Loads. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020027
Muc A, Chwał M, Romanowicz P, Stawiarski A. Fatigue-Damage Evolution of Notched Composite Multilayered Structures under Tensile Loads. Journal of Composites Science. 2018; 2(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuc, Aleksander, Małgorzata Chwał, Paweł Romanowicz, and Adam Stawiarski. 2018. "Fatigue-Damage Evolution of Notched Composite Multilayered Structures under Tensile Loads" Journal of Composites Science 2, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020027
APA StyleMuc, A., Chwał, M., Romanowicz, P., & Stawiarski, A. (2018). Fatigue-Damage Evolution of Notched Composite Multilayered Structures under Tensile Loads. Journal of Composites Science, 2(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020027







