Efficacy of Combined Hyperbaric Oxygen, per Os Steroid, and Prostaglandin E1 Therapy for Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Prognostic Factors for Recovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
- Age ≥ 18 years.
- A diagnosis of unilateral idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss, defined as ≥30 dB sensorineural hearing loss occurring within 72 h in at least three consecutive frequencies, according to our institutional protocol.
- Initiation of treatment at our hospital within 14 days of symptom onset.
- Availability of complete audiometric data at baseline and at least one month post-treatment.
- Brain MRI demonstrating no retrocochlear pathology (e.g., vestibular schwannoma, stroke, demyelinating disease).
- Availability of relevant medical records.
- Receipt of intratympanic corticosteroid therapy.
- History of previous sensorineural hearing loss in the affected ear.
- Identifiable causes of hearing loss (e.g., Ménière’s disease, ototoxic drug exposure, noise-induced trauma).
- Comorbidities contraindicating hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
- Inability to complete the one-month follow-up assessment.
2.2. Treatment
2.3. Patient Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Profiles
3.2. Therapeutic Outcomes
3.3. Prognostic Factors for Hearing Recovery After ISSNHL Treated with a Combination of HBO, SS, and PGE1
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Main Findings
4.2. Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Benefit of HBO
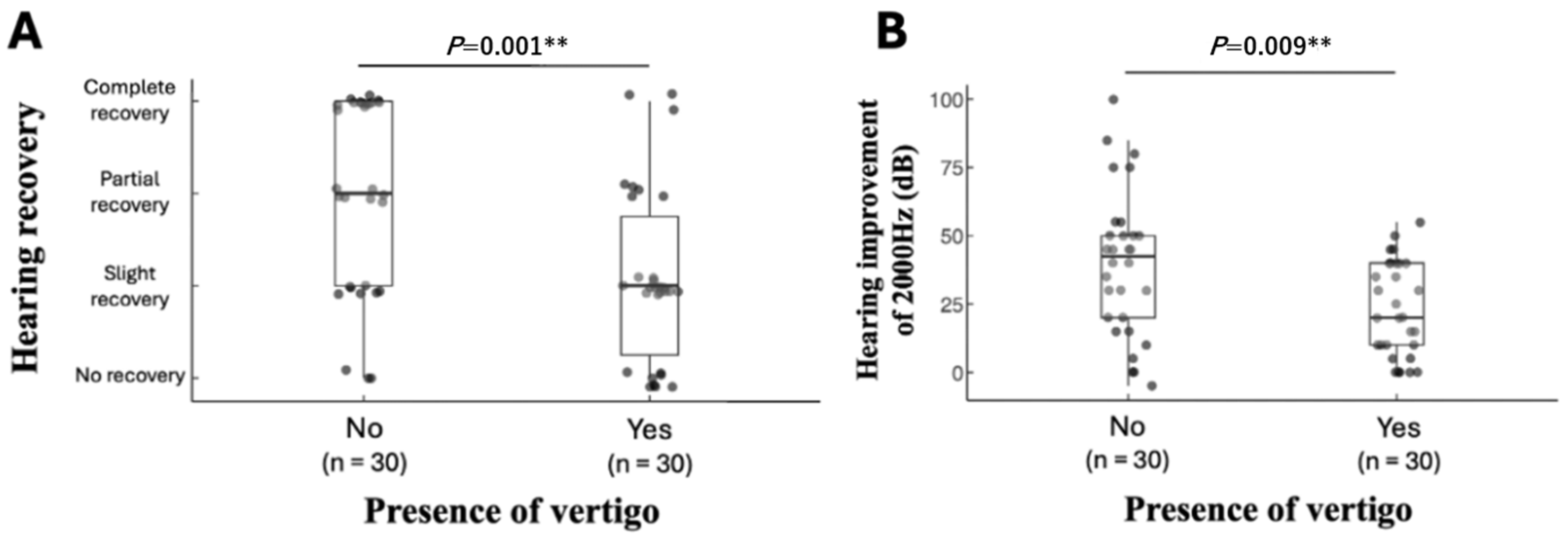
4.3. Prognostic Factors Associated with Hearing Recovery: The Presence of Vertigo
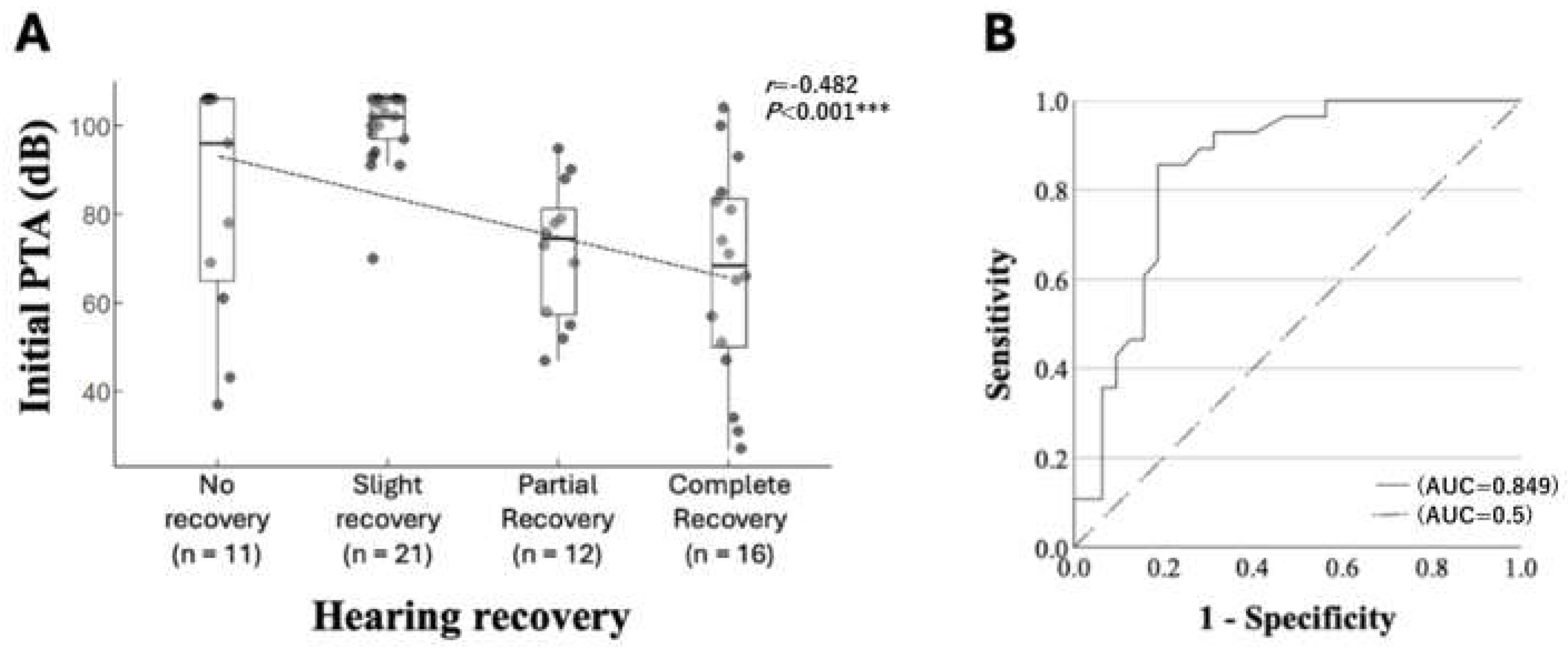
4.4. Prognostic Factors Associated with Hearing Recovery: Initial Hearing Level
4.5. Limitations of the Present Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATA | Atm absolute |
| DL | Dyslipidemia |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| HBO | Hyperbaric oxygen therapy |
| HT | Hypertension |
| ISSNHL | Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss |
| PGE1 | Prostaglandin E1 |
| PTA | Pure tone average |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| SD | Standard deviations |
| SS | Systemic steroids |
References
- Hosokawa, S.; Hosokawa, K.; Takahashi, G.; Sugiyama, K.I.; Nakanishi, H.; Takebayashi, S.; Mineta, H. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as concurrent treatment with systemic steroids for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A comparison of three different steroid treatments. Audiol. Neurootol. 2018, 23, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.H.; Fagan, P.A.; Ryugo, D.K. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A critique on corticosteroid therapy. Hear. Res. 2022, 422, 108565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maihoub, S.; Molnár, A.; Gáborján, A.; Tamás, L.; Szirmai, Á. Comparative study between the auditory and vestibular functions in Ménière’s disease. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022, 101, NP329–NP333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Tsai Do, B.S.; Schwartz, S.R.; Bontempo, L.J.; Faucett, E.A.; Finestone, S.A.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Kelley, D.M.; Kmucha, S.T.; Moonis, G.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Sudden hearing loss (update). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161 (Suppl. 1), S1–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Chen, Y.T.; Chou, S.F.; Lee, L.C.; Wang, J.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Chang, H.T. Effect of the timing of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on the prognosis of patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitoh, R.; Nishio, S.Y.; Sato, H.; Ikezono, T.; Morita, S.; Wada, T.; Usami, S.I. Research Group on Intractable Hearing Disorders and Japan Audiological Society. Clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute sensorineural hearing loss. Auris Nasus Larynx 2024, 51, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamm, C.; Walliser, U.; Schumann, K.; Lamm, K. Sauerstoffpartialdruck-Messungen in der Perilymphe der Scala tympani unter normo- und hyperbaren Bedingungen. Eine tierexperimentelle Studie [Oxygen partial pressure measurements in the perilymph and scala tympani in normo- and hyperbaric conditions. An animal experiment study]. HNO Hals- Nasen- Ohrenärzte 1988, 36, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. Interventions in the management of blood viscosity for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A meta-analysis. J. Health Res. Rev. 2017, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, D.S.; O’Malley, M.; Cohen, S.; Watford, K.; Labadie, R.F. Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Niu, K.; Ku, W.; Xie, W.; Dai, Q.; Hellström, S.; Duan, M. Comparison of therapeutic results with/without additional hyperbaric oxygen therapy in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A randomized prospective study. Audiol. Neurootol. 2021, 26, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, S.; Kusunoki, T.; Honma, H.; Kidokoro, Y.; Ikeda, K. Efficacy of the additional effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in combination of systemic steroid and prostaglandin E1 for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, M.; Younes, E.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Ito, J.; Plontke, S.; O’Leary, S.; Sterkers, O. International consensus (ICON) on treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2018, 135, S23–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, L.G. The treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 1975, 8, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.A.; Chung, J.H. Contemporary review of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Management and prognosis. J. Audiol. Otol. 2024, 28, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawase, T.; Oshima, T.; Kekehata, S.; Takahashi, S.; Sato, T.; Takasaka, T. Prognosis of sudden deafness with special reference to risk factors of microvascular pathology. Auris Nasus Larynx 1999, 26, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.H.; Kertesz, T.; Yeung, P. Hyperbaric oxygen for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, 1, CD004739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Takei, S.; Inoue, Y.; Kanzaki, J. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A double-blinded clinical study. Otol. Neurotol. 2002, 23, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wan, W.; Jiang, H.; Xiong, Y. Prognosis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: The nomogram perspective. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2023, 132, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Ye, L.; Yu, H.; Li, H. Prognosis of vestibular dysfunction in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vertigo: A prospective cohort study. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 5516–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Han, P.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; et al. The relationship between hearing loss and vestibular dysfunction in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2016, 136, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Choi, H.R.; Choi, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Shin, J.E. Patterns of nystagmus conversion in sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vertigo. Medicine 2018, 97, e12982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Yanagita, N. Outcome of sudden deafness with and without vertigo. Laryngoscope 1993, 103, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, R.H.; Liu, B.; Leng, Y.M.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, D.D.; Zhang, S.L.; Kong, W.J. Assessment of balance and vestibular functions in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2017, 37, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tange, R.A. Vascular inner ear partition: A concept for some forms of sensorineural hearing loss and vertigo. ORL 1998, 60, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.G. Uses and abuses of hearing loss classification. ASHA 1981, 23, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Tabata, T.; Koizumi, H.; Hohchi, N.; Takeuchi, S.; Kitamura, T.; Fujino, Y.; Ohbuchi, T. Prediction of hearing outcomes by multiple regression analysis in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2014, 123, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipo, R.; Attanasio, G.; Viccaro, M.; Russo, F.Y.; Mancini, P.; Rocco, M.; Pietropaoli, P.; Covelli, E. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy with short duration intratympanic steroid therapy for sudden hearing loss. Acta Oto-laryngol. 2012, 132, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | HBO Group (n = 60) | No-HBO Group (n = 56) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male), n (%) | 27 (45.0%) | 31 (55.3%) | 0.26 † |
| Age (years) | 65(56.0–70.5) | 67.5 (58.0–74.0) | 0.09 ‡ |
| Incidence of vertigo, n (%) | 30 (50.0%) | 11 (19.6%) | <0.01 ***,‡ |
| Incidence of DM, n (%) | 20 (33.3%) | 20 (35.7%) | 0.78 ‡ |
| Incidence of HT, n (%) | 18 (30.0%) | 18 (32.1%) | 0.80 ‡ |
| Incidence of DL, n (%) | 10 (16.7%) | 6 (10.7%) | 0.41 ‡ |
| Interval between onset and treatment (days) | 6(4.0–9.0) | 3.0 (2.0–6.0) | 0.13 ‡ |
| Initial hearing level (dB) | |||
| PTA | 90.5(66.7–105) | 73 (52.0–106.0) | 0.11 ‡ |
| 125 Hz | 70(52.5–70.0) | 67.5 (40.0–70.0) | 0.29 ‡ |
| 250 Hz | 90(60.0–90.0) | 95 (55.0–90.0) | 0.25 ‡ |
| 500 Hz | 97.5(70.0–110) | 80 (65.0–110) | 0.23 ‡ |
| 1000 Hz | 90(65.0–110.0) | 77.5 (50.0–110) | 0.14 ‡ |
| 2000 Hz | 85(65.0–110.0) | 70 (50.0–110.0) | 0.065 ‡ |
| 4000 Hz | 92.5(62.5–110) | 72.5 (52.5–110.0) | 0.13 ‡ |
| 8000 Hz | 95(65.0–100.0) | 85 (65.0–100.0) | 0.21 ‡ |
| HBO Group (n = 60) | No-HBO Group (n = 56) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post-therapy PTA | 44 (26.1–68.8) | 50 (30.5–78.0) | 0.39 |
| PTA improvement (dB) | 36.5 (16.5–46.0) | 19.5 (7.0–38.5) | 0.003 ** |
| Hearing improvement of 125 Hz (dB) | 25 (7.5–40.0) | 10 (0–27.5) | 0.005 ** |
| Hearing improvement of 250 Hz (dB) | 35 (15.0–52.5) | 15 (0–40.0) | 0.002 ** |
| Hearing improvement of 500 Hz (dB) | 40 (25.0–60.0) | 30 (10.0–47.5) | 0.001 ** |
| Hearing improvement of 1000 Hz (dB) | 37.5 (20.0–50.0) | 20 (5–40.0) | 0.003 ** |
| Hearing improvement of 2000 Hz (dB) | 30 (10.0–45.0) | 15 (0–35.0) | 0.009 ** |
| Hearing improvement of 4000 Hz (dB) | 20 (5.0–42.5) | 10 (0–30.0) | 0.027 |
| Hearing improvement of 8000 Hz (dB) | 10 (0–20.0) | 5 (0–15.0) | 0.31 |
| Grade of hearing recovery | |||
| Complete recovery | 16 (27%) | 10 (17.9%) | 0.007 ** |
| Partial recovery | 12 (20%) | 11 (19.6%) | |
| Slight recovery | 21 (35%) | 5 (8.9%) | |
| No recovery | 11 (18%) | 30 (53.5%) |
| Univariate Logistic Regression Analysis | ||||||
| Variable | Coefficient (β) | SE | Wald χ2 | p-Value | Odds Ratio | 95% CI |
| Age | 0.008 | 0.013 | 0.360 | 0.548 | 1.008 | 0.982–1.034 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | −0.071 | 0.376 | 0.035 | 0.851 | 0.932 | 0.446–1.947 |
| HBO (yes vs. no) | 0.377 | 0.378 | 0.994 | 0.319 | 1.458 | 0.695–3.061 |
| Vertigo | −1.030 | 0.421 | 5.974 | 0.015 * | 0.357 | 0.156–0.815 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.172 | 0.394 | 0.190 | 0.663 | 1.188 | 0.548–2.572 |
| Hypertension | 0.622 | 0.406 | 2.348 | 0.125 | 1.863 | 0.841–4.128 |
| Dyslipidemia | 0.018 | 0.544 | 0.001 | 0.973 | 1.019 | 0.351–2.958 |
| Interval between onset and treatment (days) | −0.018 | 0.025 | 0.539 | 0.463 | 0.982 | 0.935–1.031 |
| Initial PTA (dB) | −0.035 | 0.009 | 15.926 | <0.001 *** | 0.965 | 0.949–0.982 |
| Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis | ||||||
| Variable | Coefficient (β) | SE | Wald χ2 | p-Value | Odds Ratio | 95% CI |
| Intercept | 2.271 | 0.729 | ||||
| HBO (yes vs. no) | 1.124 | 0.477 | 5.549 | 0.018 * | 3.076 | 1.208–7.834 |
| Vertigo | −1.111 | 0.500 | 4.934 | 0.026 * | 0.329 | 0.124–0.877 |
| Initial PTA (dB) | −0.036 | 0.010 | 14.46263 | <0.001 *** | 0.960 | 0.939–0.981 |
| Characteristics | Outcomes | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Recovery (n = 11) | Slight Recovery (n = 21) | Partial Recovery (n = 12) | Complete Recovery (n = 16) | |||
| Sex | Male (n = 27) | 5 (19%) | 8 (30%) | 5 (19%) | 9 (33%) | 0.463 † |
| Female (n = 33) | 6 (18%) | 13 (39%) | 7 (21%) | 7 (21%) | ||
| Age | 66 (45.5–75.5) | 59 (42.0–75.0) | 66 (61.0–69.5) | 64 (61.5–67.5) | 0.884 ‡ | |
| ≥60 years (n = 19) | 7 (17%) | 10 (24%) | 11 (27%) | 13 (32%) | 0.052 † | |
| <60 years (n = 41) | 4 (21%) | 11 (58%) | 1 (15) | 3 (16%) | ||
| Interval between onset and treatment (days) | 4.0 (2.1–6.0) | 4.0 (2.7–8.3) | 4.5 (2.4–7.1) | 2.5 (2.1–5.6) | 0.588 ‡ | |
| Incidence of vertigo, n (%) | Yes (n = 30) | 8 (27%) | 14 (47%) | 5 (17%) | 3 (10%) | 0.001 ** † |
| No (n = 30) | 3 (10%) | 7 (23%) | 7 (23%) | 13 (43%) | ||
| Incidence of DM, n (%) | Yes (n = 20) | 3 (15%) | 6 (30%) | 7 (35%) | 4 (20%) | 0.750 † |
| No (n = 40) | 8 (20%) | 15 (38%) | 5 (13%) | 12 (30%) | ||
| Incidence of HT, n (%) | Yes (n = 18) | 4 (22%) | 4 (22%) | 7 (39%) | 3 (10%) | 0.867 † |
| No (n = 42) | 7 (17%) | 17 (41%) | 5 (12%) | 13 (31%) | ||
| Incidence of DL, n (%) | Yes (n = 10) | 2 (20%) | 2 (20%) | 3 (30%) | 3 (30%) | 0.620 † |
| No (n = 50) | 9 (18%) | 19 (38%) | 9 (18%) | 13 (26%) | ||
| Initial PTA (dB) | 96 (65.0–106.0) | 102 (97.0–106) | 74.5 (56.5–3.5) | 68.5 (49.0–84.5) | <0.001 ***,‡ | |
| Number of HBO sessions | 7 (6.0–9.5) | 6 (4.0–8.0) | 6.5 (4.5–9.5) | 5 (3.5–7.5) | 0.173 ‡ | |
| Univariate Logistic Regression Analysis | ||||||
| Variable | Coefficient (β) | SE | Wald χ2 | p-Value | Odds Ratio | 95% CI |
| Age | 0.030 | 0.020 | 2.238 | 0.135 | 1.030 | 0.991–1.071 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | −0.379 | 0.522 | 0.529 | 0.467 | 0.684 | 0.246–1.903 |
| Vertigo | −1.705 | 0.566 | 9.069 | 0.003 * | 0.182 | 0.060–0.551 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.503 | 0.552 | 0.831 | 0.362 | 1.654 | 0.561–4.875 |
| Hypertension | 0.511 | 0.568 | 0.810 | 0.368 | 1.667 | 0.548–5.070 |
| Dyslipidemia | 0.647 | 0.706 | 0.840 | 0.359 | 1.909 | 0.479–7.610 |
| Interval between onset and treatment (days) | −0.041 | 0.063 | 0.414 | 0.520 | 0.960 | 0.849–1.086 |
| Initial PTA (dB) | −0.062 | 0.017 | 13.461 | <0.001 *** | 0.940 | 0.909–0.972 |
| Number of HBO sessions | −0.040 | 0.055 | 0.520 | 0.471 | 0.961 | 0.863–1.071 |
| Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis | ||||||
| Variable | Coefficient (β) | SE | Wald χ2 | p-Value | Odds Ratio | 95% CI |
| Intercept | 5.353 | 1.520 | ||||
| Vertigo | −1.536 | 0.662 | 5.389 | 0.020 * | 0.215 | 0.059–0.787 |
| Initial PTA (dB) | −0.057 | 0.017 | 11.350 | <0.001 *** | 0.944 | 0.913–0.976 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakayama, T.; Hara, S.; Kusunoki, T.; Takata, Y.; Honma, H.; Anzai, T.; Kidokoro, Y.; Yoshikawa, A.; Matsumoto, F. Efficacy of Combined Hyperbaric Oxygen, per Os Steroid, and Prostaglandin E1 Therapy for Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Prognostic Factors for Recovery. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2025, 6, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020025
Nakayama T, Hara S, Kusunoki T, Takata Y, Honma H, Anzai T, Kidokoro Y, Yoshikawa A, Matsumoto F. Efficacy of Combined Hyperbaric Oxygen, per Os Steroid, and Prostaglandin E1 Therapy for Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Prognostic Factors for Recovery. Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine. 2025; 6(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakayama, Takumi, Satoshi Hara, Takeshi Kusunoki, Yusuke Takata, Hirotomo Honma, Takashi Anzai, Yoshinobu Kidokoro, Akihisa Yoshikawa, and Fumihiko Matsumoto. 2025. "Efficacy of Combined Hyperbaric Oxygen, per Os Steroid, and Prostaglandin E1 Therapy for Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Prognostic Factors for Recovery" Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine 6, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020025
APA StyleNakayama, T., Hara, S., Kusunoki, T., Takata, Y., Honma, H., Anzai, T., Kidokoro, Y., Yoshikawa, A., & Matsumoto, F. (2025). Efficacy of Combined Hyperbaric Oxygen, per Os Steroid, and Prostaglandin E1 Therapy for Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Prognostic Factors for Recovery. Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine, 6(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020025






