Abstract
This study investigates the mechanical, tribological, and electrochemical behaviour of a novel precipitation-hardenable martensitic alloy produced by selective laser melting (SLM). The alloy was specifically engineered with an optimised composition, free from cobalt and molybdenum, and featuring reduced nickel content (7 wt.%) and 8 wt.% chromium. It has been developed as a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to conventional maraging steels, while maintaining high mechanical strength and a refined microstructure tailored to the steep thermal gradients inherent to the SLM process. Several ageing heat treatments were assessed to evaluate their influence on microstructure, hardness, tensile strength, retained austenite content, dislocation density, as well as wear behaviour (pin-on-disc test) and corrosion resistance (polarisation curves in 3.5%NaCl). The results indicate that ageing at 540 °C for 2 h offers an optimal combination of hardness (550–560 HV), tensile strength (~1700 MPa), microstructural stability, and wear resistance, with a 90% improvement compared to the as-built condition. In contrast, ageing at 600 °C for 1 h enhances ductility and corrosion resistance (Rp = 462.2 kΩ; Ecorr = –111.8 mV), at the expense of a higher fraction of reverted austenite (~34%) and reduced hardness (450 HV). This study demonstrates that the mechanical, surface, and electrochemical performance of this novel SLM-produced alloy can be effectively tailored through controlled thermal treatments, offering promising opportunities for demanding applications requiring a customised balance of strength, durability, and corrosion behaviour.
1. Introduction
Additive manufacturing (AM), in particular selective laser melting (SLM), is transforming the production of high-performance metallic components, especially those with complex geometries and demanding functional requirements [1,2]. Among the various metal additive manufacturing (AM) technologies, selective laser melting (SLM) stands out for its ability to produce components with complex geometries, high resolution, and near-full density. Although other techniques such as Directed Energy Deposition (DED) or Electron-Beam Melting (EBM) may be suitable in certain contexts, SLM provides superior surface finishes and finer microstructural control, making it a preferred option for demanding metallic alloys such as stainless steel 316L [3], or—as in the present study—for a novel martensitic steel.
SLM involves the layer-by-layer melting of metal powder using a high-energy laser, which selectively fuses predefined regions from a 3D model and produces parts with high density and geometric accuracy [4,5,6]. The process is carried out under controlled atmospheres, typically argon or nitrogen, to prevent oxidation and contamination. Improper parameterisation can lead to defects such as balling, incomplete fusion, or excessive porosity [5,7]. As-built samples exhibit cellular and columnar microstructures due to the rapid solidification and cooling rates [2,8,9,10]. An example of alloys manufactured using this technology are maraging steels. These are high-strength Fe-Ni alloys originally developed for aerospace and tooling applications [11]. After ageing, cellular structures disappear, transforming into parallel martensitic plates [12]. These steels typically contain high nickel content (~18% Ni) and alloying elements such as molybdenum (Mo), cobalt (Co), titanium (Ti), and aluminium (Al) [13]. These alloys were designed to combine high mechanical strength with excellent wear and corrosion resistance [14,15]. Ageing induces precipitation hardening through the formation of intermetallic compounds of the Ni3(Ti,Mo,V,W) type, along with Laves phases like (Fe,Cr,Ni)2(Ti,Mo) [2,16,17,18].
During ageing, the formation of reverted austenite has been reported, possibly linked to the decomposition of the Ni3(Ti,Mo) phase and the formation of Fe2Mo, which locally enriches the matrix in Ni [11,19,20,21]. Local Ni enrichment following intermetallic dissolution promotes the nucleation of reverted austenite [22]. In the as-built condition, experimental evidence shows segregation of Ti and Mo to cell boundaries [6,9,10], facilitating the formation of a reverted austenite network at these boundaries during ageing [9,23,24]. This phenomenon is favoured by higher ageing temperatures, which may lead to a drop in hardness [10,23,25]. The enrichment of Ti and Mo along cell boundaries enhances the local driving force for austenite reversion [9]. This austenite is generally stable and persists after cooling [24,26]. It has been reported that reverted austenite improves corrosion resistance in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution [22]. However, in the absence of austenite, directly aged samples exhibit worse behaviour due to galvanic coupling between the precipitates and the martensitic matrix, accelerating corrosion in NaCl solution [27].
The extremely high cooling rate of the SLM process—on the order of 106 K/s—far exceeds that of conventional manufacturing methods, producing non-equilibrium microstructures. To reduce the risk of thermal cracking, carbon is often excluded from these alloys [15,28]. The rapid thermal cycling during SLM also induces microstructural anisotropy, which affects the physical, mechanical, and corrosion properties of fabricated parts [29].
Mechanically, these steels reach hardness values around 350 HV in the as-built condition, which can increase to over 550 HV after ageing. Their tensile strength ranges from 800 to 1000 MPa in the as-built state, rising to 1800–2000 MPa after thermal treatment [9,12,20,25,30,31].
To reduce the Ni content and improve microstructural stability, various AM-processable alternative alloys have been developed. One example is NMS steel, with 7% Ni and high Co (18%) and Mo (15%) content, which exceeds 800 HV after ageing at 530 °C [2]. Another is FeCo15Cr14Ni4Mo3 steel with 4% Ni, 14% Cr, and 15% Co, which achieves 1100 MPa in the as-built state and up to 1480 MPa after ageing at 550 °C [32]. CX steel (9% Ni, 12% Cr, 1.5% Mo, and 1.5% Al) [33,34,35] reaches over 1600 MPa tensile strength and 500 HV hardness after ageing [36]. Among the most studied alternatives, 17–4PH martensitic stainless steel is prominent for its excellent corrosion resistance in saline or acidic media and its good mechanical properties. This steel can reach over 1200 MPa tensile strength after direct ageing [37,38,39,40,41,42,43].
Recently, a new cobalt- and molybdenum-free martensitic alloy with 8% Cr and reduced nickel content (7%) has been developed. Its main hardening mechanism is the precipitation of Ni3Ti during ageing [7]. This alloy shows the formation of reverted austenite at ageing temperatures above 540 °C [7]. This novel alloy is specifically tailored for demanding applications across key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, consumer goods, energy, machinery, and transportation, demonstrating both versatility and industrial focus.
Technologically, the development of alloys free from critical elements like cobalt and molybdenum is especially relevant in the current context of sustainability and cost optimisation. However, the influence of direct ageing parameters on the microstructural evolution and functional properties of this new alloy remains insufficiently characterised.
The main objective of this study is to evaluate the response of this SLM-processed martensitic alloy to direct ageing treatments in the temperature range 480–600 °C, with different dwell times. To this end, hardness, tensile, wear, and corrosion tests have been conducted, the latter via linear polarisation in 3.5 wt.% NaCl aqueous solution.
2. Materials and Methods
Table 1 presents the nominal chemical composition of the newly developed steel, as provided by the manufacturer of the powder used for SLM processing.

Table 1.
The chemical composition of the powder used in the SLM process (wt.%).
All specimens were fabricated using a RenAM500Q selective laser melting (SLM) system (Renishaw, Wotton-under Edge, England, UK), operating with a laser power of 250 W, a scanning speed of 1000 mm/s, and a hatch spacing of 80 μm. The layer thickness was set to 50 μm. The mean particle size of the powder used was 32.2 μm, with a D10 of 20 μm and a D90 of 51 μm.
One of the main objectives of this study was to optimise the direct ageing heat treatment from the as-built condition. To this end, ageing treatments were performed over a wide temperature range, from 480 °C to 600 °C. The material was then characterised using an integrated experimental strategy combining microstructural analysis, mechanical testing, electrochemical characterisation, and tribological evaluation. This approach enables the establishment of correlations between the applied heat-treatment conditions, the resulting microstructure, and the functional properties obtained.
Microstructural observations were performed using LePera’s reagent, prepared by mixing 100 mL of ethanol, 5 g of dry picric acid, 1.5 g of Na2S2O5, and 100 mL of distilled water [44]. The strong colour contrast between ferrite (bronze-brown) and austenite (white, bluish) makes this etchant particularly suitable for identifying austenite when slightly over-etched [45,46,47,48]. Observations were conducted using optical and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). A JEOL JSM-5600 scanning electron microscope (JEOL, Nieuw-Vennep, The Netherlands), equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) system, was used.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to determine the retained austenite content following ASTM E975 [49]. Cr radiation was employed using a Stresstech Xstress 3000 G3R diffractometer (Stresstech Inc., Pittsburgh, PA, USA), assessing the area under the diffraction peaks for ferrite and austenite. Peak detection was carried out at a 45° tilt angle (ψ), measuring 20 different θ positions with the sample in a flat position between −45° and +45°. Four crystallographic planes were examined: two for austenite (130° and 80°) and two for ferrite (156.4° and 106.1°). Gaussian functions were used to fit austenite peaks, while Pearson VII functions were used for ferrite. A linear function was applied to reduce background noise [50,51].
The weight fraction of retained austenite was calculated using the XTronic 1.12.0 software, based on the integrated intensities of the selected austenite and ferrite peaks, following the standard equation provided in ASTM E975 Equation (1) [49]:
where and are constants specific to the measured diffraction planes, and ∑Iα and ∑Iγ represent the integrated intensities (areas under the diffraction peaks) of the ferrite and austenite phases, respectively.
To further characterise the microstructure resulting from different ageing treatments, the dislocation density in the martensitic/ferritic matrix was analysed by X-ray diffraction, given its influence on both mechanical and corrosion behaviour. The Williamson–Hall method was employed to estimate dislocation density, allowing for the separation of contributions from coherent domain size and microstrain to peak broadening [52]. The following equation was applied in Equation (2):
where is the full width at half maximum, corrected for instrumental broadening and expressed in radians; θ is the Bragg angle; λ is the wavelength of the X-ray radiation (0.229 nm for Cr); K is the shape factor (taken as 0.9); D is the coherent domain size; and ε is the microstrain in the crystal lattice due to dislocation density. Three reflections corresponding to characteristic ferrite/martensite planes were used: {110} at 69°, {200} at 106.1°, and {211} at 156.4°.
Dislocation density (ρ) was then calculated using Equation (3):
where k = 14.4 for body-centred cubic metals [53], b is the Burgers vector (b = 0.248 nm) [52], and ε is obtained from the slope of the FWHMcorrected cosθ/λ vs. sinθ/λ plot.
FWHM values were corrected for instrumental broadening based on measurements using NIST-certified silicon standards. The corrected FWHM was calculated using Equation (4) [54]:
Tensile tests were performed according to ASTM E8/E8M [55] using an Instron 5582 testing machine (Instron, Norwood, MA, USA) with a crosshead speed of 5 mm/min and a load limit of 100 kN. The gauge length of the tensile specimens was 34 mm with a square cross-section of 6 mm.
Corrosion resistance was evaluated in a slightly acidic 3.5 wt.% NaCl aqueous solution using the linear polarisation resistance method, following ASTM G59 [56]. Sample surfaces were ground to 800 grit and polished to 1 µm. Electrochemical measurements were conducted using a PalmSens4® potentiostat/galvanostat controlled by PSTrace 5.7 software. A conventional three-electrode electrochemical cell was used, with Ag(s)/AgCl(s) (3M KCl) as the reference electrode and a 150 mm platinum wire as the counter electrode. The samples served as working electrodes. Polarisation measurements were performed at room temperature (~25 °C) over a potential range of ±30 mV around the OCP at a scan rate of 1 mV/s. Open-circuit potential (OCP) was monitored for 5400 s prior to the test to ensure interfacial stability. Tafel slopes were fitted in the range Ecorr ± 10 mV and Ecorr ± 20 mV, and corrosion current (Icorr) was estimated using the Stern–Geary equation.
Following electrochemical characterisation, tribological behaviour was assessed to correlate ageing-induced microstructural changes with wear resistance. Adhesive wear resistance was evaluated via “pin-on-disc” tests according to ASTM G99 using a Micro-Test MT/30/SCM/T tribometer (MicroTest, Madrid, Spain) [57]. Testing speed was 0.27 m/s with a 25 N applied load. The pin consisted of a 5 mm diameter Si3N4 ball with a hardness of 1500–1600 HV. Total sliding distance was 2 km. Test surfaces were kept in their as-built condition, without polishing, to preserve the surface morphology generated during SLM. This approach aimed to reflect real-world service conditions.
Surface topography was characterised using a contact profilometer. Arithmetic roughness (Ra) ranged from 7 to 14 µm, and mean peak-to-valley height (Rz) ranged from 30 to 60 µm. Ra represents the average deviation from the mean line, while Rz captures the maximum peak-valley differences, being more sensitive to local defects. These values are typical for SLM-fabricated surfaces that have not undergone any post-processing. Surface-wear profiles were examined using a Leica M205FA fluorescence stereomicroscope (Leica Microsistemas S.L.U, Hospitalet de Llobregat, Spain).
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 1 shows the characteristic microstructure of the age-hardenable martensitic steel in the as-built condition. Semicylindrical melt pools are visible, corresponding to locally melted and subsequently rapidly solidified regions [58]. In Figure 1a,b, the laser-scanning tracks can be seen, with an approximate width of 80–100 μm. A 90° rotation between layers is evident from the perpendicular distribution of melt pools observed in Figure 1a,b. Figure 1c reveals a higher density of cellular structures near the melt-pool boundary, where thermal gradients are steeper and heat conduction is more anisotropic. These heterogeneous cooling conditions promote variations in cell size. Higher cooling rates promote the formation of finer cellular morphologies [59]. A higher-magnification SEM image is shown in Figure 1d, highlighting well-defined cellular structures at the melt-pool boundaries. A semi-quantitative EDX analysis was performed at selected points both within and along the edges of these cells (Table 2). The results confirm a tendency for Ti to segregate along the cellular boundaries [6,9,10]. Interestingly, a higher Si content was also detected relative to the nominal alloy composition, which may suggest a preferential segregation of Si towards the melt-pool boundaries. However, this hypothesis requires confirmation through follow-up studies employing more advanced characterisation techniques.

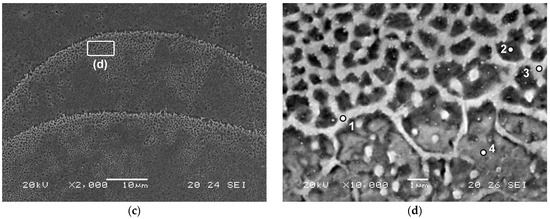
Figure 1.
As-built microstructure of the newly developed age-hardenable martensitic steel. (a) Optical micrograph showing semicylindrical melt pools generated by the laser-scanning process; (b) a higher-magnification view highlighting laser-scanning tracks (~80–100 μm width); (c) SEM image showing a dense cellular structure near the melt-pool boundaries; (d) cellular structure at the melt-pool boundaries. The marked points indicate the locations selected for semiquantitative EDX analysis.

Table 2.
Semiquantitative EDX analysis of the points marked in Figure 1d (wt.%).
Figure 2 shows the evolution of Vickers hardness as a function of direct ageing treatment applied at different temperatures (480–600 °C) and dwell times (1 to 3 h). A marked increase in hardness is observed compared to the as-built condition, reaching maximum values close to 570 HV for treatments at 520–540 °C, which suggests the effective precipitation of hardening phases such as Ni3Ti. At higher temperatures (≥ 560 °C), hardness tends to decrease, particularly for extended ageing times, which may be attributed to overageing phenomena and/or the formation of reverted austenite.
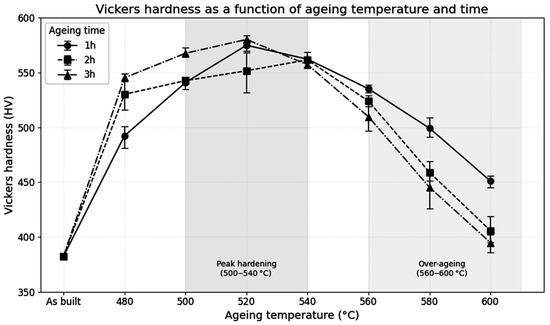
Figure 2.
Evolution of Vickers hardness after direct ageing treatments at different temperatures (480–600 °C) and dwell times (1–3 h). Error bars indicate the full range (minimum to maximum) observed across ten hardness indentations performed for each condition.
Following the hardness evaluation of the heat-treated samples, their overall mechanical strength was assessed via tensile testing, aiming to identify potential correlations with the microstructure resulting from thermal treatment. Figure 3 illustrates the evolution of the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) in the as-built condition and after different direct ageing treatments. The as-built condition exhibits a strength close to 1000 MPa, which decreases sharply after ageing at 480 °C, particularly for short dwell times (1 h). With increasing temperature, the strength progressively rises, reaching a maximum of approximately 1650 MPa after 2 h at 540 °C. This improvement is attributed to the optimal precipitation of strengthening Ni3Ti particles during intermediate thermal exposure, along with a low fraction of retained austenite. In contrast, above this temperature, strength decreases, particularly at 600 °C, where overageing and the formation of reverted austenite likely reduce the effectiveness of precipitation hardening.
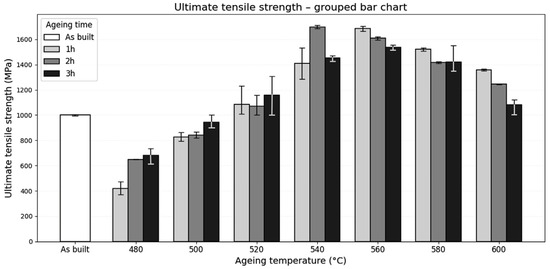
Figure 3.
Evolution of ultimate tensile strength (UTS) after direct ageing treatments at different temperatures (480–600 °C) and dwell times (1–3 h). Error bars indicate the full range (minimum to maximum) obtained from three tensile tests performed for each condition.
Interestingly, the highest hardness was achieved at 520 °C, whereas the tensile strength remained relatively low at this temperature. This apparent contradiction may be explained by the evolution of residual stresses generated during the SLM process, which inherently induces significant tensile and compressive stresses due to rapid thermal cycling and solidification. These stresses are not fully relieved until ageing temperatures exceed 540 °C. As a result, such residual stresses may promote brittle fracture under tensile loading, thereby limiting the UTS. Meanwhile, structural hardening precipitates are likely to begin forming at 520 °C, contributing to a local increase in hardness [60,61].
The decrease in ultimate tensile strength observed after ageing at 480 °C, alongside an increase in hardness, can be attributed to the combined effects of unrelieved residual stresses and the early-stage formation of strengthening precipitates that are not yet effective at the macroscopic scale. The hardening sequence begins with the nucleation of coherent or semi-coherent metastable intermetallic precipitates within the martensitic/ferritic matrix. Although this precipitation process is already underway at 480 °C, its beneficial effects on tensile strength may not be fully realised until residual stresses are sufficiently relieved at higher ageing temperatures. This interpretation is, however, limited by the absence of residual stress measurements, which would be required for a quantitative assessment of their influence.
Figure 4 shows the evolution of ultimate tensile strength as a function of ageing time. At lower temperatures (480–520 °C), strength progressively increases with time, although without reaching high values, indicating slow precipitation kinetics. In contrast, at 540 °C, strength peaks at 2 h, suggesting optimal precipitation of the Ni3Ti-strengthening phase. At 560 °C, strength is already high after 1 h but tends to decrease with longer durations, indicating the onset of overageing. At 600 °C, strength decreases with increasing time. Nevertheless, the strength obtained after 1 h of ageing at 600 °C remains acceptable. The shaded area in Figure 4 highlights the range of highest tensile strength values, which corresponds to ageing temperatures between 540 and 580 °C. The 600 °C (1 h) condition may also be considered within this range.
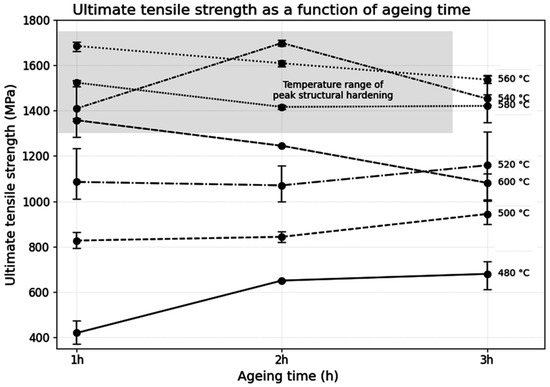
Figure 4.
Evolution of ultimate tensile strength (UTS) as a function of ageing time. The shaded area corresponds to the temperature range (540–580 °C) where the highest strength values were achieved. Error bars indicate the full range (minimum to maximum) obtained from three tensile tests performed for each condition.
It should be noted that most aged specimens fractured within the elastic regime, without exhibiting measurable plastic deformation. Consequently, the yield strength (YS) could not be determined. Only the as-built samples and those aged above 540 °C—or at this temperature for extended times (2–3 h)—showed plastic deformation prior to fracture.
Figure 5 shows the evolution of the maximum uniform elongation as a measure of ductility after different ageing treatments. The temperatures at which fracture occurs with plastic deformation are highlighted by shaded areas. For ageing treatments at 540 °C (1 h) or below, the maximum uniform elongation coincides with the fracture strain.
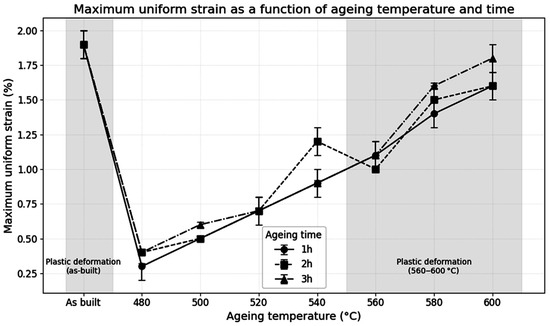
Figure 5.
Evolution of maximum uniform elongation as a function of ageing temperature and dwell time. Error bars indicate the full range (minimum to maximum) obtained from three tensile tests performed for each condition.
Figure 6 presents the engineering stress–strain curves obtained from tensile tests conducted under three representative conditions: as-built, aged at 540 °C for 2 h, and aged at 600 °C for 1 h. As previously stated, three tensile tests were performed for each heat treatment condition. Ageing at 540 °C for 2 h produced the highest tensile strength, reaching nearly 1700 MPa, although it exhibited limited uniform elongation of approximately 1%. In contrast, ageing at 600 °C for 1 h resulted in a lower strength of around 1400 MPa, but with a notable improvement in ductility, reaching 2%. This gain in deformability may be associated with the formation of reverted austenite, which could promote a more stable deformation mechanism. The as-built condition, while exhibiting lower strength (~1000 MPa), retained the highest plastic deformability (2.5–3%). The observed behaviour suggests that ageing at 600 °C for 1 h offers an optimal compromise between strength and ductility.
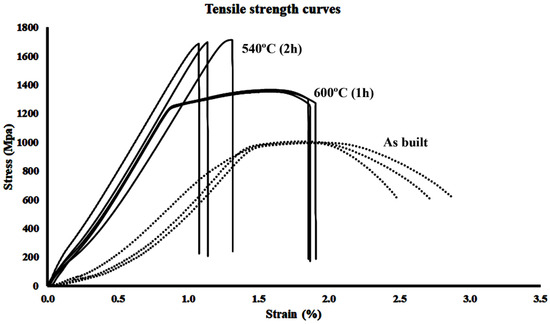
Figure 6.
Representative stress–strain curves for the alloy in the as-built condition and after ageing at 540 °C (2 h) and 600 °C (1 h). The selected conditions correspond, respectively, to the treatment yielding the highest tensile strength (540 °C, 2 h) and to the one offering the best balance between strength and deformability (600 °C, 1 h).
Figure 7 shows the weight percentage of austenite measured in the as-built condition and after direct ageing treatments at 540 °C (2 h) and 600 °C (1 h). A significant increase in austenite content is observed at 600 °C, consistent with the transformation of martensite into reverted austenite. The sharp increase in austenite content observed after ageing at 600 °C for 1 h can be attributed to the onset of austenite reversion, as reported in previous studies [6,10,11,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. This phenomenon is associated with the local enrichment of Ni in the matrix following the partial dissolution of intermetallic phases such as Ni3(Ti,Mo) and the formation of Fe2Mo. Additionally, the segregation of Ti and Mo to the cell boundaries in the as-built microstructure enhances the local driving force for austenite reversion in these regions. The reverted austenite formed under these conditions is generally stable and persists after cooling. It should be noted that the detection limit of XRD for retained austenite is approximately 2–3 wt.%, which may influence the accuracy at low austenite levels.
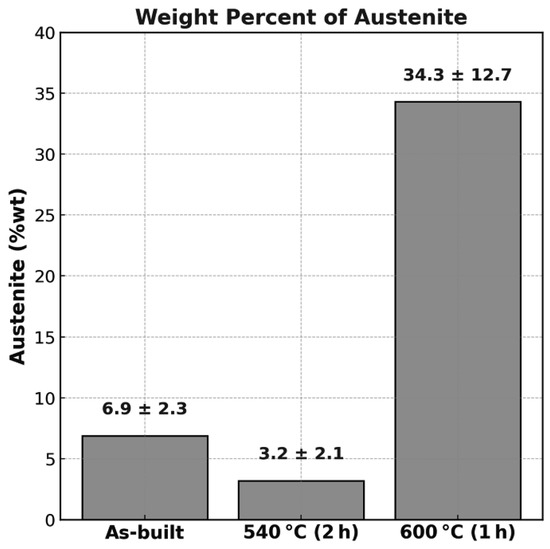
Figure 7.
Weight percentage of austenite in the as-built condition and after direct ageing treatments at 540 °C (2 h) and 600 °C (1 h). Values are expressed as mean ± experimental error.
Figure 8 shows the microstructure of the alloy in the as-built condition and after direct ageing at 540 °C (2 h) and 600 °C (1 h). Whitish-blue regions indicate the presence of fine austenitic areas, typically smaller than 1 μm. In the as-built condition, retained austenite is primarily located along the melt-pool boundaries, as shown in Figure 8a. During direct ageing, this austenite appears to partially transform, although it remains observable at the melt-pool boundaries after ageing at 540 °C (2 h). After ageing at 600 °C (1 h), and in agreement with the XRD results, a greater amount of austenite is detected. This austenite, likely reverted, appears uniformly distributed within the ferritic matrix, while residual retained austenite may still persist along the melt-pool boundaries. It should be noted that austenite identification based on colour contrast using LePera’s reagent is qualitative and dependent on etching conditions and operator interpretation.
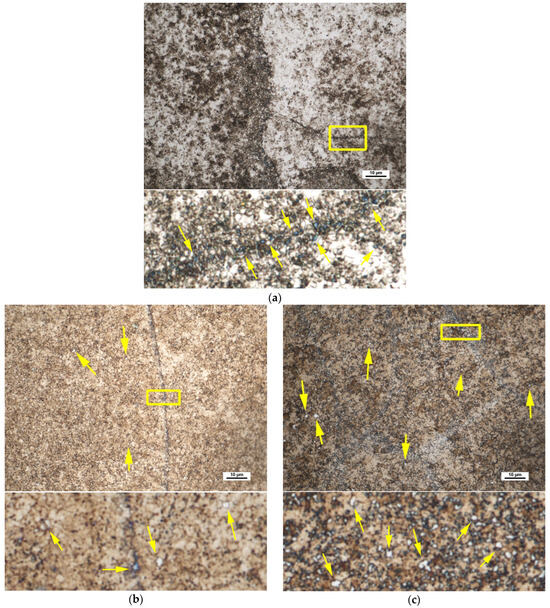
Figure 8.
Presence of austenite in the as-built condition and after direct ageing. Yellow arrows indicate examples of austenite pools. (a) Retained austenite predominantly located at the boundaries of the weld tracks in the as-built condition; (b) remnants of retained austenite at the weld-track boundaries and some reverted austenite within the tracks after ageing at 540 °C (2 h); (c) reverted austenite uniformly distributed within a ferritic/martensitic matrix after ageing at 600 °C (1 h). Note: scale bars are only shown in the main micrographs. Enlarged views were digitally magnified and are presented without scale bars for clarity.
Figure 9 presents the polarisation curves obtained in a 3.5 wt.% NaCl aqueous solution for the as-built condition and after ageing at 540 °C (2 h) and 600 °C (1 h). The curve in Figure 9a, corresponding to the as-built condition, exhibits a corrosion potential (Ecorr) of −132.6 mV and a polarisation resistance (Rp) of 314.8 kΩ. After ageing at 540 °C, Figure 9b shows a shift in Ecorr towards more noble values (−119.1 mV), although Rp decreases to 240.1 kΩ, suggesting a slight reduction in corrosion resistance. In contrast, the treatment at 600 °C, shown in Figure 9c, leads to a marked increase in Rp (462.2 kΩ) and the most noble Ecorr value recorded (−111.8 mV), indicating improved passivation behaviour. Figure 9d provides a comparative view of the three conditions, confirming that although the anodic and cathodic slopes remain similar, the treatment at 600 °C enhances the electrochemical stability in chloride-containing environments, possibly due to a favourable redistribution of alloying elements such as Cr and Ni, or the presence of more stable reverted austenite.
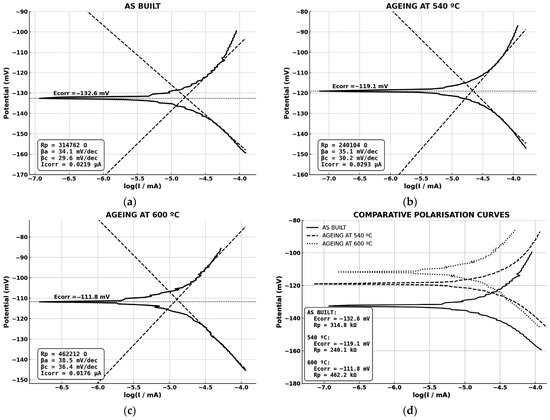
Figure 9.
Polarisation curves. (a) As-built condition; (b) after direct ageing at 540 °C (2 h); (c) after direct ageing at 600 °C (1 h); (d) superimposed curves showing the trend of increasing Ecorr with higher ageing temperatures.
Figure 10 compares the corrosion potential and polarisation resistance of the new age-hardenable martensitic steel in the as-built condition and after direct ageing at 540 °C (2 h) and 600 °C (1 h). The results indicate that ageing at 600 °C (1 h) leads to a marked increase in polarisation resistance, suggesting a significant improvement in the material’s passivation behaviour. This enhancement may be linked to the higher fraction of reverted austenite, whose more noble electrochemical nature could contribute to an improved corrosion response. In contrast, ageing at 540 °C (2 h) does not appear to offer clear advantages in terms of corrosion resistance, displaying a lower Rp value than the as-built condition. This could be attributed to galvanic coupling between the precipitated phase and the martensitic matrix.
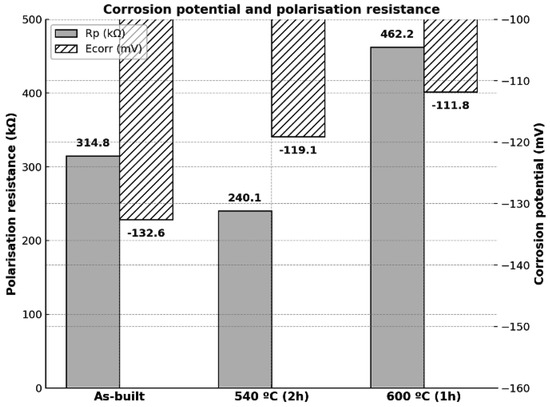
Figure 10.
Corrosion potential (Ecorr) and polarisation resistance (Rp). Values shown above the bars correspond to the average measurements obtained from the polarisation curves.
Figure 11 shows the plot of FWHMcorrected cos(θ)/λ versus sin(θ)/λ, obtained from three 2θ angles corresponding to characteristic diffraction planes of martensite. From the slope of the fitted lines, it is possible to estimate the dislocation density present in the martensitic/ferritic phase [53,54].
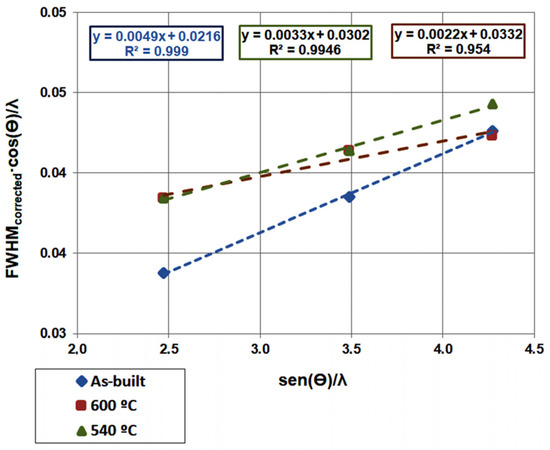
Figure 11.
FWHMcorrected cos(θ)/λ versus sin(θ)/λ, considering the three 2θ angles associated with the characteristic martensite diffraction planes: {110}, {200}, and {211}.
This estimation was carried out by analysing the broadening of the diffraction peaks using the Williamson–Hall method described in the experimental section. The resulting values are shown in Figure 12, with the y-axis presented on a logarithmic scale. As observed, dislocation density significantly decreases after thermal ageing. The high density found in the as-built state is attributed to the rapid cooling rates associated with the additive manufacturing process, consistent with findings for martensitic steels produced under similar conditions [58]. The measured value, in the order of 1015 m−2, aligns with previously reported values for other martensitic steels [62]. Moreover, this high dislocation density may favour the heterogeneous nucleation of the precipitates responsible for hardening during ageing.
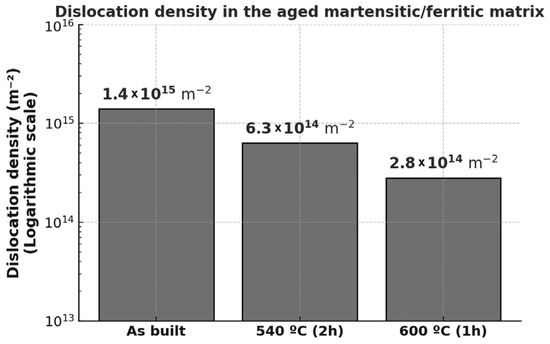
Figure 12.
Dislocation density in the martensitic/ferritic matrix.
As reported for other SLM-processed martensitic steels, dislocations tend to annihilate during ageing, leading to a reduction in density as the heat-treatment temperature increases [62].
These preliminary results suggest that the reduction in dislocation density induced by ageing could be associated with a slight ennoblement of the corrosion potential. However, the evolution of polarisation resistance does not follow a similar trend, indicating that other microstructural factors—such as the amount of reverted austenite—may play a more decisive role. This hypothesis, however, requires further validation in future studies using more specific methodologies.
In addition to corrosion resistance, wear resistance is another critical property in structural applications, particularly under dry friction conditions as simulated in this study. To characterise the tribological performance of the age-hardenable martensitic steel, both mass loss and the coefficient of friction (COF) were assessed using adhesive wear tests (pin-on-disc). Figure 13 shows the influence of heat treatment on both parameters. Ageing at 540 °C for 2 h—which provided the highest hardness and tensile strength—also resulted in the lowest wear and the lowest coefficient of friction.
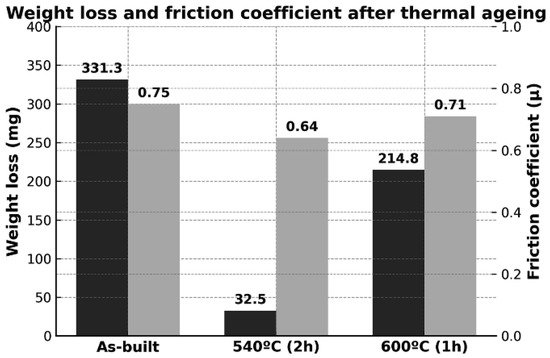
Figure 13.
Weight loss and average coefficient of friction from adhesive wear tests (pin-on-disc) in the as-built condition and after heat treatments at 540 °C (2 h) and 600 °C (1 h).
Figure 14 displays the wear track topography obtained from pin-on-disc tests under the three thermal conditions examined. Figure 14a,c,e show three-dimensional reconstructions of the wear scars, while Figure 14b,d,f present the corresponding two-dimensional profiles. In the as-built condition, a deep and rough wear scar is observed, with pronounced striations aligned tangentially to the sliding direction. The wear track exhibits an oval-shaped profile, with a maximum depth of 378 µm and a width of 3.3 mm, indicating a high wear rate consistent with the recorded mass loss (331.3 mg).
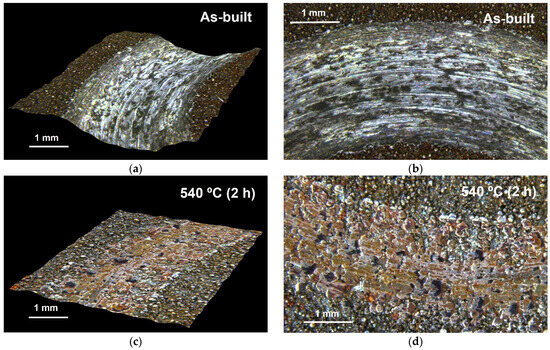
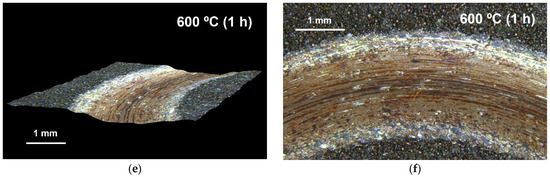
Figure 14.
Wear-track topography. (a,b) Specimen in the as-built condition; (c,d) specimen aged at 540 °C for 2 h; (e,f) specimen aged at 600 °C for 1 h.
After ageing at 540 °C for 2 h, the wear scar becomes significantly shallower and narrower, with a maximum depth of only 25 µm and a width below 2 mm. This morphology suggests reduced abrasive interaction with the pin, which is consistent with the drastic reduction in mass loss (32.5 mg). The wear pattern also suggests that the Si3N4 counterbody may have experienced progressive flattening due to material removal, implying partial wear transfer. However, this hypothesis requires further validation through complementary characterisation.
The sample aged at 600 °C for 1 h exhibits an intermediate topography, with a maximum depth of 213 µm and a width of 2.8 mm, corresponding to a moderate mass loss (214.8 mg).
Overall, the wear profiles obtained by optical profilometry confirm the evolution of wear resistance as a function of the applied heat treatment.
Figure 15 shows SEM images illustrating the morphology of the wear surface after testing. In the as-built condition, the surface appears rough with detached material fragments, suggesting that the predominant wear mechanism was abrasive in nature [63]. In contrast, the thermally aged samples exhibit a different surface morphology.
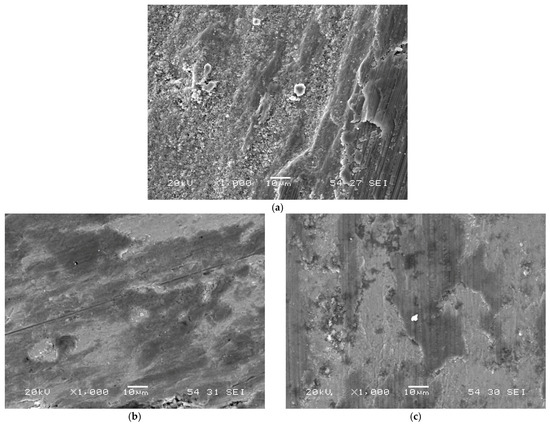
Figure 15.
SEM images showing the morphology of the wear surface. (a) Specimen in the as-built condition; (b) specimen aged at 540 °C (2 h); (c) specimen aged at 600 °C (1 h).
The specimen aged at 540 °C presents a smoother surface, with no evidence of abrasive wear, which, combined with the low recorded coefficient of friction, indicates a predominantly adhesive wear mechanism. Furthermore, the flat wear-track profile observed in this sample suggests that the Si3N4 pin may have experienced significant wear, progressively flattening the contact surface. The sample aged at 600 °C displays similar behaviour, although with a slightly rougher surface and occasional presence of small detached fragments generated during the test.
4. Conclusions
This study evaluated the influence of various direct ageing treatments on the mechanical, tribological, and electrochemical properties of a new cobalt- and molybdenum-free maraging martensitic steel, containing 8 wt.% Cr and a reduced nickel content (7 wt.%), fabricated via SLM. The conclusions below are based on the specific test conditions described and should not be extrapolated without appropriate validation. The following findings were established:
- Ageing treatments had a substantial impact on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and tribological and electrochemical performance of the SLM-processed maraging martensitic steel. These treatments enable property tailoring according to specific application requirements.
- In the as-built condition, the alloy exhibited a hardness of 360 HV, high tensile strength (~1000 MPa), and elevated dislocation density (1.4 × 1015 m−2), associated with a predominantly martensitic microstructure containing ~6.9 wt.% retained austenite.
- Tensile specimens in the as-built state and those aged above 540 °C fractured with measurable plastic deformation, whereas all other conditions exhibited brittle fracture.
- Ageing at 540 °C for 2 h yielded an especially favourable combination of hardness (550–560 HV), tensile strength (~1700 MPa), low retained austenite content (~3.2 wt.%), and excellent wear resistance, achieving a 90% reduction in mass loss compared to the as-built condition.
- Ageing at 600 °C for 1 h is a viable alternative when moderate ductility is required, achieving good tensile strength (~1350 MPa), outstanding corrosion resistance (Ecorr = –111.8 mV; Rp = 462.2 kΩ), moderate hardness (∼450 HV), and a high content of reverted austenite (~34.3 wt.%). Compared to the as-built condition, this treatment improved wear resistance, reducing mass loss by over 35%.
- Dislocation density progressively decreased with thermal exposure, a trend that appears to correlate with an increase in corrosion potential. Electrochemical behaviour may also be influenced by the austenite content. However, the presence of nanoscale strengthening precipitates such as Ni3Ti could generate local galvanic cells affecting the electrochemical response.
- The morphology and topography of worn surfaces revealed a transition in the dominant wear mechanism: from abrasive wear in the as-built condition to predominantly adhesive wear after ageing. In particular, the flatter wear tracks observed in specimens aged at 540 °C for 2 h—with lower track depth and a reduced coefficient of friction (COF = 0.64)—suggest possible additional wear of the Si3N4 counterbody.
Overall, the results demonstrate the potential of this new SLM-processed maraging martensitic alloy as a versatile material, whose mechanical, tribological, and electrochemical performance can be effectively tuned by direct ageing. However, the numerical values obtained should be interpreted in the context of the specific experimental conditions employed, and further validation is required before extrapolating to other loading conditions, geometries, or environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.A.-A. and A.G.-P.; methodology, F.A.-A. and A.G.-P.; software, F.A.-A. and A.G.-P.; validation, F.A.-A., A.G.-P. and L.B.P.-M.; formal analysis, F.A.-A., A.G.-P. and L.B.P.-M.; investigation, F.A.-A., A.G.-P., L.B.P.-M. and I.P.-G.; resources, F.A.-A., A.G.-P. and I.P.-G.; data curation, F.A.-A., A.G.-P. and L.B.P.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, F.A.-A.; writing—review and editing, A.G.-P.; visualisation, F.A.-A. and A.G.-P.; supervision, F.A.-A. and A.G.-P.; project administration, F.A.-A. and A.G.-P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Başcı, Ü.G.; Avcu, E.; Kıraç, M.; Sever, A.; Gökalp, İ.; Yavuz, H.İ.; Oktay, S.; Abakay, E.; Yıldıran Avcu, Y.; Yamanoğlu, R. Microstructural, Mechanical, and Tribological Properties of Selective Laser Melted Inconel 718 Alloy: The Influences of Heat Treatment. Crystals 2025, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xu, T.Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.L.; Zhang, C.H.; Sun, X.Y.; Chen, H.T.; Chen, J. Effect of Aging Treatment on the Microstructure and Tribological Properties of a New Maraging Steel Manufactured by Laser Directed Energy Deposition. Mater. Charact. 2024, 209, 113767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, U.; McAfee, M.; Manolakis, I.; Timmons, N.; Tormey, D. A Review of Optimization of Additively Manufactured 316/316L Stainless Steel Process Parameters, Post-Processing Strategies, and Defect Mitigation. Materials 2025, 18, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirgazi, H.; Sanjari, M.; Tamimi, S.; Shalchi Amirkhiz, B.; Kestens, L.A.I.; Mohammadi, M. Texture Evolution in Selective Laser Melted Maraging Stainless Steel CX with Martensitic Transformation. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M.; Vural, M.; Raja, S.; Bilal Naim Shaikh, M. Finite Element Analysis of Thermal Behavior in Maraging Steel during SLM Process. Optik 2020, 208, 164128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Ding, M.; Wang, P.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Rao, J.H.; Gong, X.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Z.; et al. Design of New 18Ni-xTi Maraging Steel Harnessing Intrinsic Heat Treatment Effect of Additive Manufacturing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2025, 20, e2499926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gonzalo, I.; González-Pociño, A.; Alvarez-Antolin, F.; del Rio-Fernández, L. The Effect of Selective Laser Melting Fabrication Parameters on the Tensile Strength of an Aged New Maraging Steel Alloy with 8% Cr, Reduced Ni Content (7%), and No Co or Mo. Materials 2023, 16, 7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Tang, Q.; Feng, Q.; Ma, S.; Setchi, R.; Liu, Y.; Han, Q.; Fan, X.; Zhang, M. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviours of 18Ni-300 Maraging Steel Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 120, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Fan, L.; Ding, R.; Franke, C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, T.; Chen, H. On the Role of Cellular Microstructure in Austenite Reversion in Selective Laser Melted Maraging Steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 184, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Khosravifard, A.; Järvenpää, A.; Kömi, J.; Hamada, A. Optimizing Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Additively Manufactured 18Ni (300) Maraging Steel by Controlling Strengthening Agents. Mater. Des. 2025, 254, 114114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, R.; Lemke, J.N.; Tuissi, A.; Vedani, M. Aging Behaviour and Mechanical Performance of 18-Ni 300 Steel Processed by Selective Laser Melting. Metals 2016, 6, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, J. Influence of Layer Thickness and Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of Selective Laser Melted Maraging Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 3911–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seikh, A.H.; Halfa, H.; Soliman, M.S. Effect of Molybdenum Content on the Corrosion and Microstructure of Low-Ni, Co-Free Maraging Steels. Metals 2021, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolomy, S.; Sedlak, J.; Zouhar, J.; Slany, M.; Benc, M.; Dobrocky, D.; Barenyi, I.; Majerik, J. Influence of Aging Temperature on Mechanical Properties and Structure of M300 Maraging Steel Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2023, 16, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovski, I.F.; Rabelo, A.; Bodziak, S.; Milan, J.C.G.; Lafratta, F.H.; Parucker, V.L.S.; Duarte, D.A. Effect of the Plasma Nitriding on the Mechanical Properties of the 18Ni300 Steel Obtained by Selective Laser Melting. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 466, 129688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfa, H.H.; Seikh, A.; Soliman, M.S. Effect of Heat Treatment on Tensile Properties and Microstructure of Co-Free, Low Ni-10 Mo-1.2 Ti Maraging Steel. Materials 2022, 15, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habassi, F.; Houria, M.; Barka, N.; Jahazi, M. Influence of Post-Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Additively Manufactured C300 Maraging Steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 202, 112980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Ruan, H.; Ding, Z.; Kong, L.B. A Novel Maraging Stainless Steel Ultra-High-Strengthened by Multi-Nanoprecipitations. Scr. Mater. 2023, 226, 115224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancey-Rocchi, S.; Vidal, V.; Poulain, T.; Billot, T.; Bechet, D.; Binot, N.; Huleux, V.; Dehmas, M.; Delagnes, D. Influence of Austenitization Parameters on the Precipitation Sequence and the Chemical Homogenization of Austenite in a High-Performance Fe–Ni–Cr–Al–Ti–Mo Stainless Maraging Steel. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2021, 52, 4623–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gonzalo, I.; González-Pociño, A.; Alvarez-Antolin, F.; del Rio-Fernández, L. Analysis of a Double Aging Process in a Maraging 300 Steel Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting, Using the Design of Experiments Technique. Metals 2023, 13, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, C.; Chang, C.; Dong, D.; Zhao, R.; Jenkins, R.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z.; Liu, M.; Liao, H.; et al. Study of the Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of C-X Stainless Steel Processed by Selective Laser Melting (SLM). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 781, 139227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood Khan, H.; Özer, G.; Safa Yilmaz, M.; Tarakci, G. Improvement of Corrosion Resistance of Maraging Steel Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting Through Intercritical Heat Treatment. Corrosion 2022, 78, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Fu, L.; Qin, D.; Ye, C.; Ma, S.; Wen, M.; Shan, A. Effect of Annealing Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Heavy Cold-Rolled Custom 465 Maraging Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 936, 148443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, A.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Z.; Liang, J.; Su, J.; Ge, Q. Effect of Aging on Transformation Behavior of Reverted Austenite and Toughness in Co-Free Maraging Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 9850–9863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Meng, X.; Ou, B.; Xie, Y.; Cai, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, S. Dependence of Microstructure and Properties in Additive Manufactured 18Ni300 on Heat Treatment and Surface Enhancement. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H. Abnormal Thermal Expansion Behaviour and Phase Transition of Laser Powder Bed Fusion Maraging Steel with Different Thermal Histories during Continuous Heating. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 53, 102712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, C.; Zhang, M. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Properties of a High Alloying Maraging Steel Fabricated by Laser Metal Deposition. Met. Mater. Int. 2023, 29, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chales, R.; Cardoso, A.d.S.M.; Garcia, P.S.P.; da Igreja, H.R.; de Almeida, B.B.; Noris, L.F.; Pardal, J.M.; Tavares, S.S.M.; da Silva, M.M. Behavior of Constitutive Models from Slow Strain Rate Test of Maraging 300 and 350 Steels Performed in Several Environmental Conditions. Int. J. Fract. 2022, 234, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoop, S.; Venugopal, A.; Dineshraj, S.; Murty, S.V.S.N.; Pant, B. Stress Corrosion Cracking Behavior of Selective Laser-Melted M300 Maraging Steel in 3.5 Wt.% NaCl Solution. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 6568–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlapudy, S.P.; Nancharaiah, T.; Subba Rao, V.V. Experimental Optimization on Mechanical Properties of 18Ni-300 Maraging Steel Produced by Direct Metal Laser Sintering. Eng. Res. Express 2023, 5, 015073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.V.; Mohanty, C.P.; Prashanth, K.G. Parametric Optimization of Selective Laser Melted 13Ni400 Maraging Steel by Taguchi Method. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Sun, S.; Du, X.; Tang, Q.; Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Qiu, J. Microstructural Evolution of a FeCo15Cr14Ni4Mo3 Maraging Steel with High Ductility Prepared by Selective Laser Melting. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Niu, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z. Effect of Process Parameters and Heat Treatment on the Properties of Stainless Steel CX Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 877, 160062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wu, S.; Xing, S.; Wang, T.; Hou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Corrosion Behavior of Selective Laser Melted CX Stainless Steel. Metals 2025, 15, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, M.-H.; Ku, S.-W.; Li, C.-L.; Chang, S.-H.; Wu, M.-W. The Effects of Heat Treatment on the Impact Toughness and Fracture of Selective Laser-Melted Corrax Maraging Stainless Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, K.; Gao, Y.; Wang, D. Influence of Microdefect on Mechanical Behaviors of CX Stainless Steel Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Met. Mater. Int. 2025, 31, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashgari, H.R.; Adabifiroozjaei, E.; Kong, C.; Molina-Luna, L.; Li, S. Heat Treatment Response of Additively Manufactured 17-4PH Stainless Steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 197, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aripin, M.A.; Sajuri, Z.; Jamadon, N.H.; Baghdadi, A.H.; Syarif, J.; Mohamed, I.F.; Aziz, A.M. Effects of Build Orientations on Microstructure Evolution, Porosity Formation, and Mechanical Performance of Selective Laser Melted 17-4 PH Stainless Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steponavičiūtė, A.; Stravinskas, K.; Selskienė, A.; Tretjakovas, J.; Petkus, R.; Mordas, G. Mechnical Properties of 17-4PH Stainless-Steel at Various Laser Sintering Process Parameters. Lith. J. Phys. 2024, 64, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cabezon, C.; Castro-Sastre, M.A.; Fernandez-Abia, A.I.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; Martin-Pedrosa, F. Microstructure–Hardness–Corrosion Performance of 17-4 Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steels Processed by Selective Laser Melting in Comparison with Commercial Alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 2022, 28, 2652–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olugbade, T.O.; Oladapo, B.I.; Omiyale, B.O. Electrochemical and Microstructural Characterization of a Precipitation Hardened 17-4 Steel in Different Environments. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 706, 135795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, L.; Nitheesh Kumar, R.; Prashanth, K.G.; Sivaprasad, K. Electrochemical Analysis of Friction Welded 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Components Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2025, 19, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Tovar, J.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Lara-Banda, M.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Baltazar-Zamora, M.A.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Olguin-Coca, J.; Estupiñan-Lopez, F.; Almeraya-Calderón, F. Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Passivated Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steels for Aerospace Applications. Metals 2023, 13, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.K.; Jang, J.H.; Tiwari, S.; Bae, H.J.; Sung, H.K.; Kim, J.G.; Seol, J.B. Quantitative Analysis of Retained Austenite in Nb Added Fe-Based Alloy. Appl. Microsc. 2022, 52, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santofimia, M.J.; Zhao, L.; Petrov, R.; Sietsma, J. Characterization of the Microstructure Obtained by the Quenching and Partitioning Process in a Low-Carbon Steel. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Faria Neto, A.d.R.; Fukugauchi, C.S.; dos Santos Pereira, M. Using Design of Experiments in the Evaluation of the Microstructural Characterization Parameters with the LePera Reagent in a Multiphase Steel. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 086522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichkina, A.A.; Matrosov, M.Y.; Éfron, L.I.; Ringinen, D.A.; Il’inskii, V.I.; Lyasotskii, I.V.; Shul’ga, E.V. M/A-Constituent in Bainitic Low-Carbon High-Strength Steel Structure. Part 2. Metallurgist 2020, 63, 1266–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashangeh, S.; Karimi Zarchi, H.R.; Ghasemi Banadkouki, S.S.; Somani, M.C. Detection and Estimation of Retained Austenite in a High Strength Si-Bearing Bainite-Martensite-Retained Austenite Micro-Composite Steel after Quenching and Bainitic Holding (Q&B). Metals 2019, 9, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E975; Standard Practice for X-Ray Determination of Retained Austenite in Steel with Near Random Crystallographic Orientation. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Su, Y.Y.; Chiu, L.H.; Chuang, T.L.; Huang, C.L.; Wu, C.Y.; Liao, K.C. Retained Austenite Amount Determination Comparison in JIS SKD11 Steel Using Quantitative Metallography and X-Ray Diffraction Methods. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 482–484, 1165–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.B.; Karlsson, B.; Vuoristo, T.; Dalaei, K. Determination of Stresses and Retained Austenite in Carbon Steels by X-Rays—A Round Robin Study. Exp. Mech. 2011, 51, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.K.; Hall, W.H. X-Ray Line Broadening from Filed Aluminium and Wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.K.; Smallman, R.E., III. Dislocation Densities in Some Annealed and Cold-Worked Metals from Measurements on the X-Ray Debye-Scherrer Spectrum. Philos. Mag. A J. Theor. Exp. Appl. Phys. 1956, 1, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoozbashi, M.N.; Yazdani, S. XRD and TEM Study of Bainitic Ferrite Plate Thickness in Nanostructured, Carbide Free Bainitic Steels. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 160, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. Available online: https://store.astm.org/e0008_e0008m-24.html (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Standard Test Method for Conducting Potentiodynamic Polarization Resistance Measurements. Available online: https://store.astm.org/g0059-23.html (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Standard Test Method for Wear and Friction Testing with a Pin-on-Disk or Ball-on-Disk Apparatus. Available online: https://store.astm.org/g0099-23.html (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Takata, N.; Nishida, R.; Suzuki, A.; Kobashi, M.; Kato, M. Crystallographic Features of Microstructure in Maraging Steel Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Metals 2018, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M. Influence Mechanism of Parameters Process and Mechanical Properties Evolution Mechanism of Maraging Steel 300 by Selective Laser Melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 703, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, P.; Jammal, A.; Xu, K.; Ye, F.; Zhao, N.; Song, Y. A Review of the Evolution of Residual Stresses in Additive Manufacturing during Selective Laser Melting Technology. Materials 2025, 18, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, N.; Jahan, M.P.; Rangasamy, N.; Rakurty, C.S. A Review of the Residual Stress Generation in Metal Additive Manufacturing: Analysis of Cause, Measurement, Effects, and Prevention. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnajjar, M.; Christien, F.; Bosch, C.; Wolski, K.; Fortes, A.D.; Telling, M. In-Situ Neutron Diffraction Study of Wrought and Selective Laser Melted Maraging Stainless Steels. Mater. Charact. 2021, 172, 110840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Chen, C.; Yan, X.; Feng, X.; Jenkins, R.; O’Reilly, P.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; Lupoi, R. The Influence of Aging Temperature and Aging Time on the Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Selective Laser Melted Maraging 18Ni-300 Steel. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).