Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructure, Corrosion Resistance and Wear Behaviour of Bainitic/Martensitic Ductile Iron Under Dry Sliding Friction
Abstract
1. Introduction
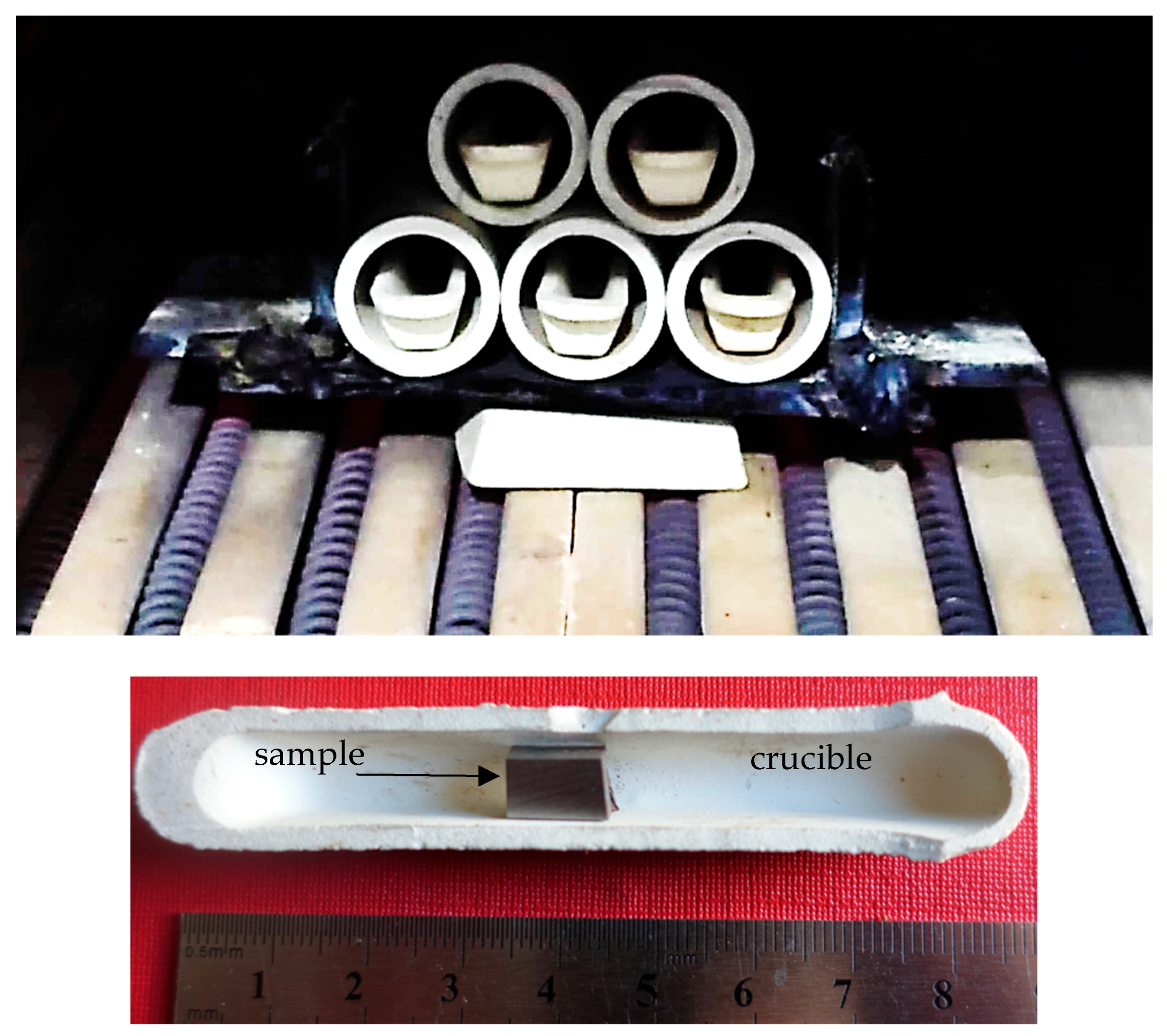
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. Materials
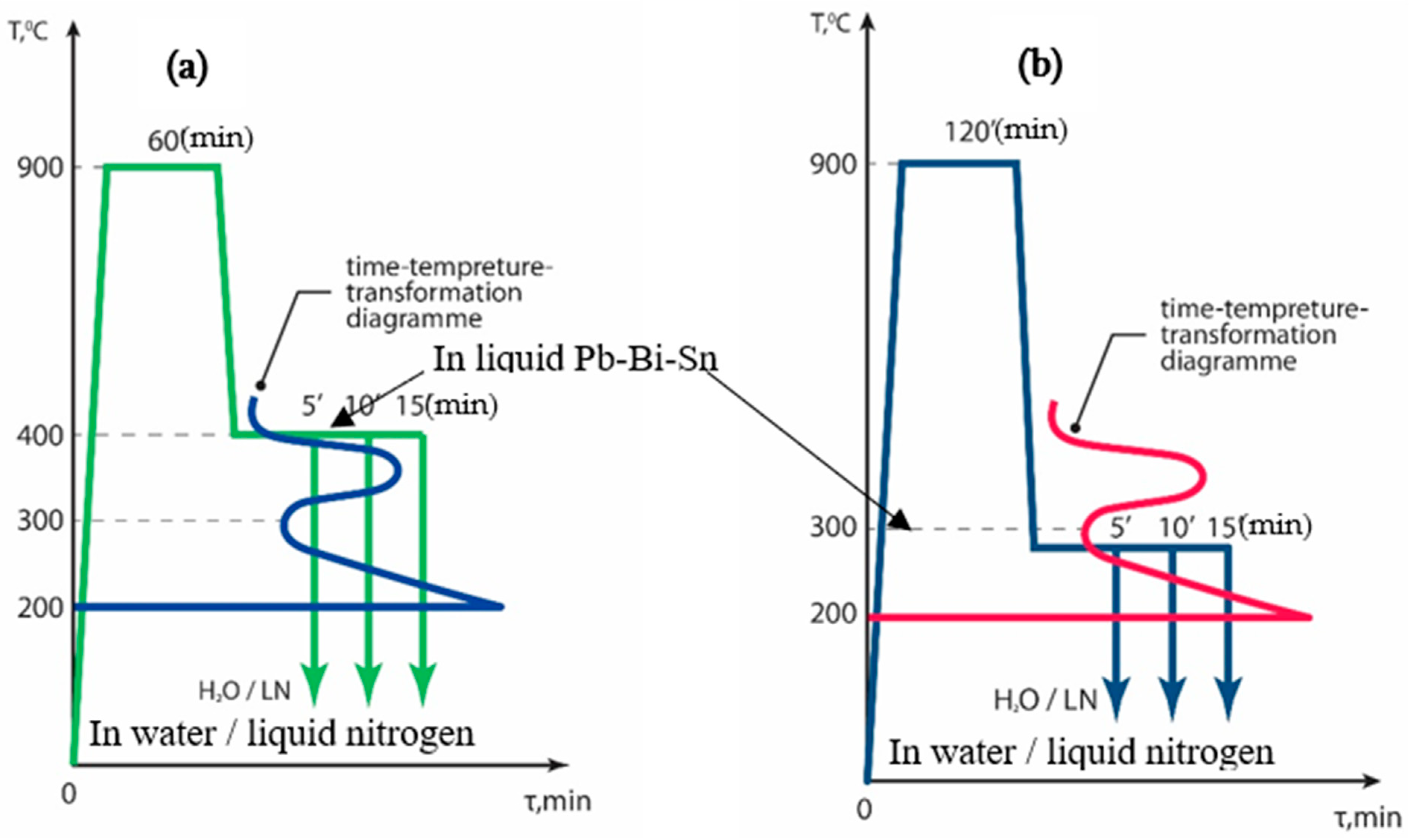
2.2. Heat Treatment Cycles
2.3. Microstructures Examination
2.4. Corrosion Tests
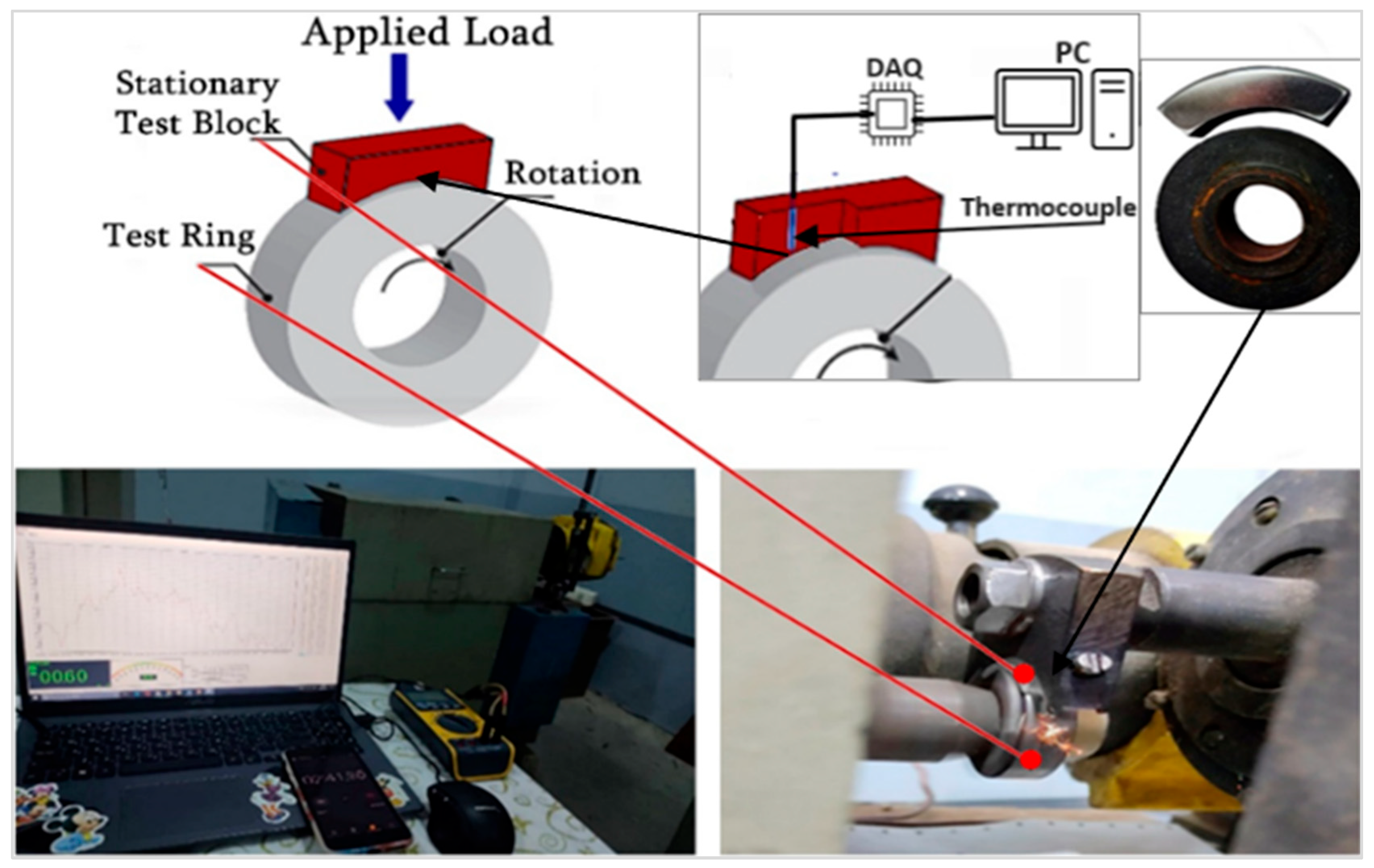
2.5. Wear Tests
3. Results and Discussion
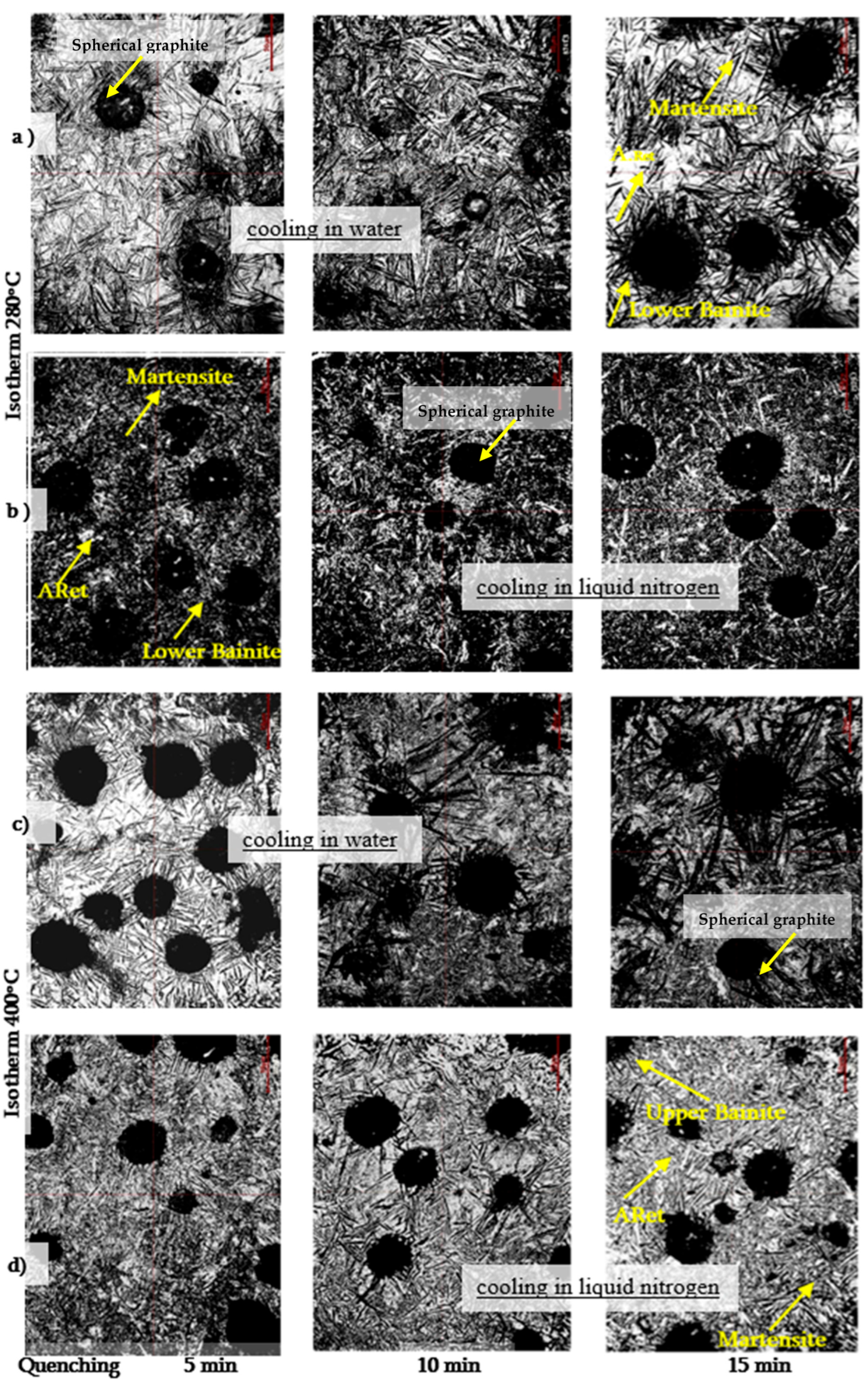
3.1. Microstructural Study
3.2. Hardness Performance
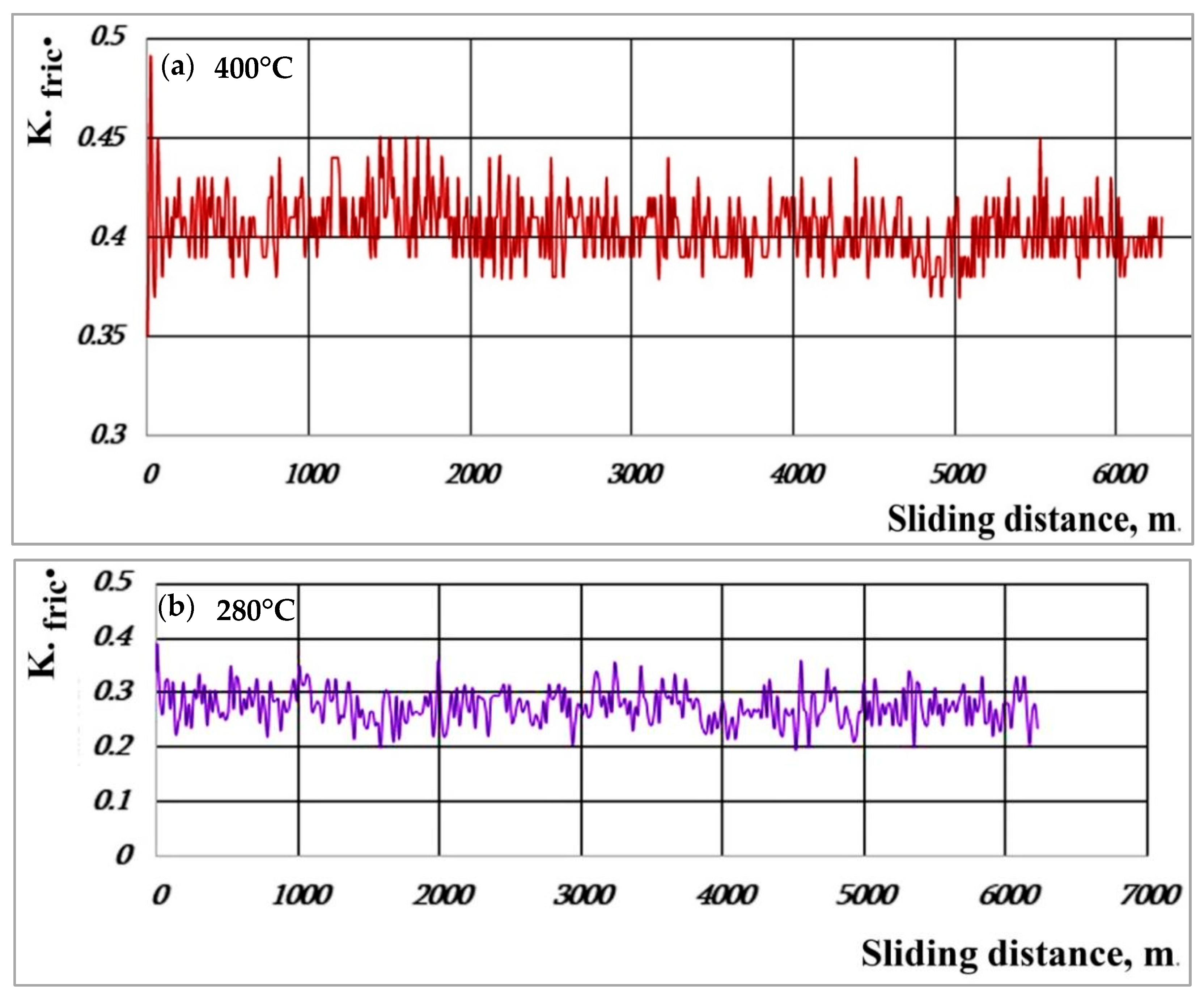
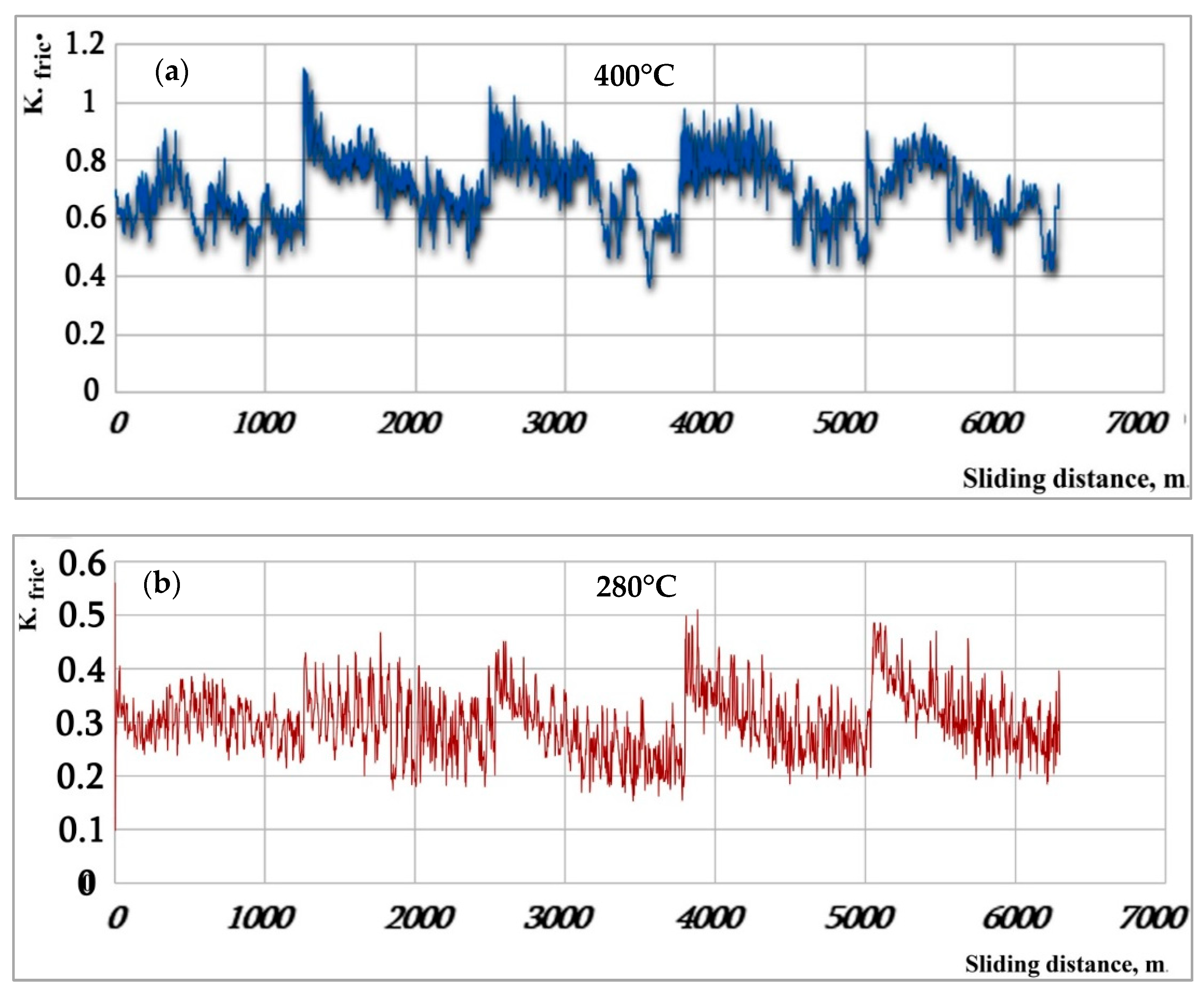
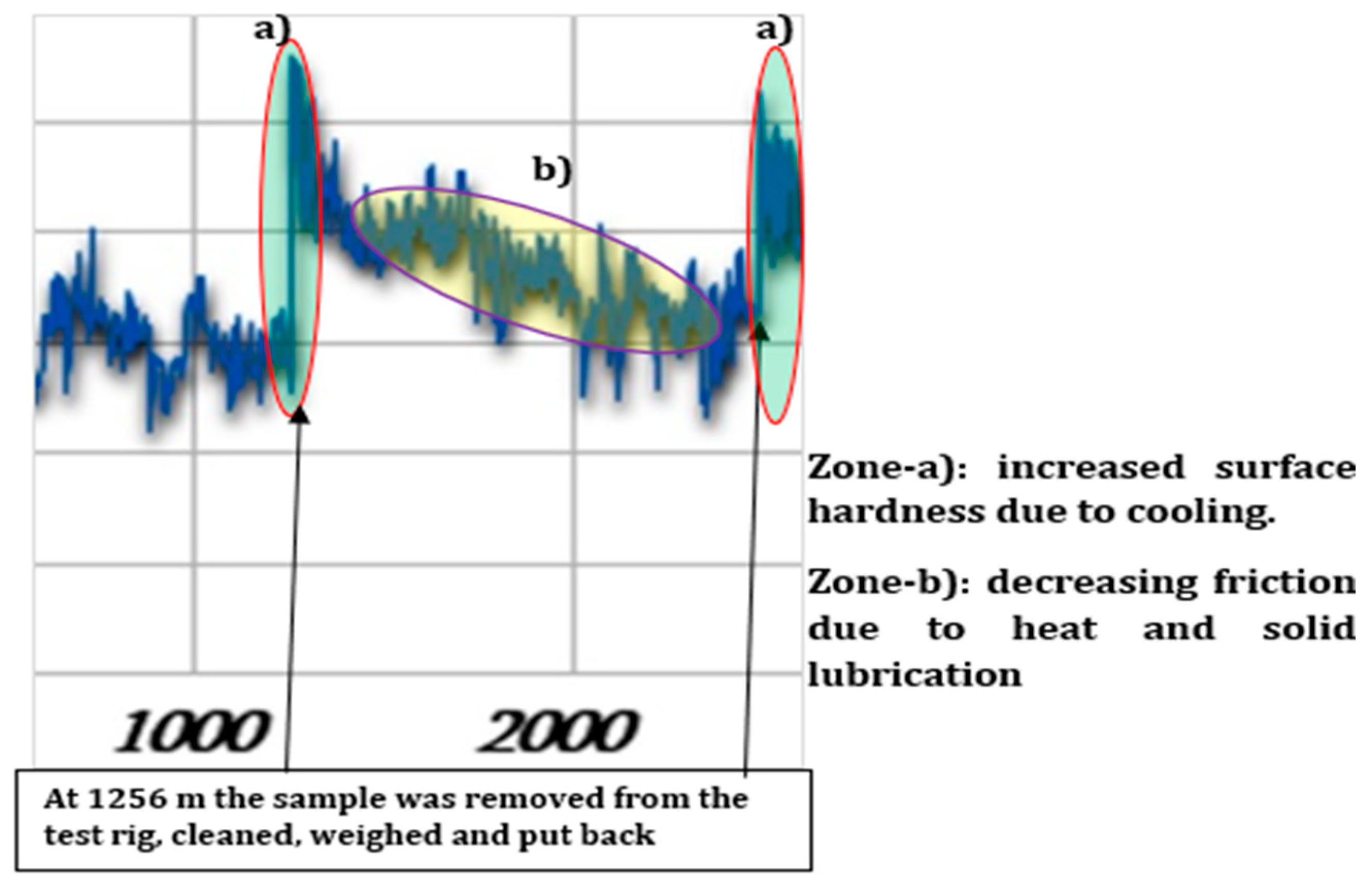
3.3. Friction Coefficient
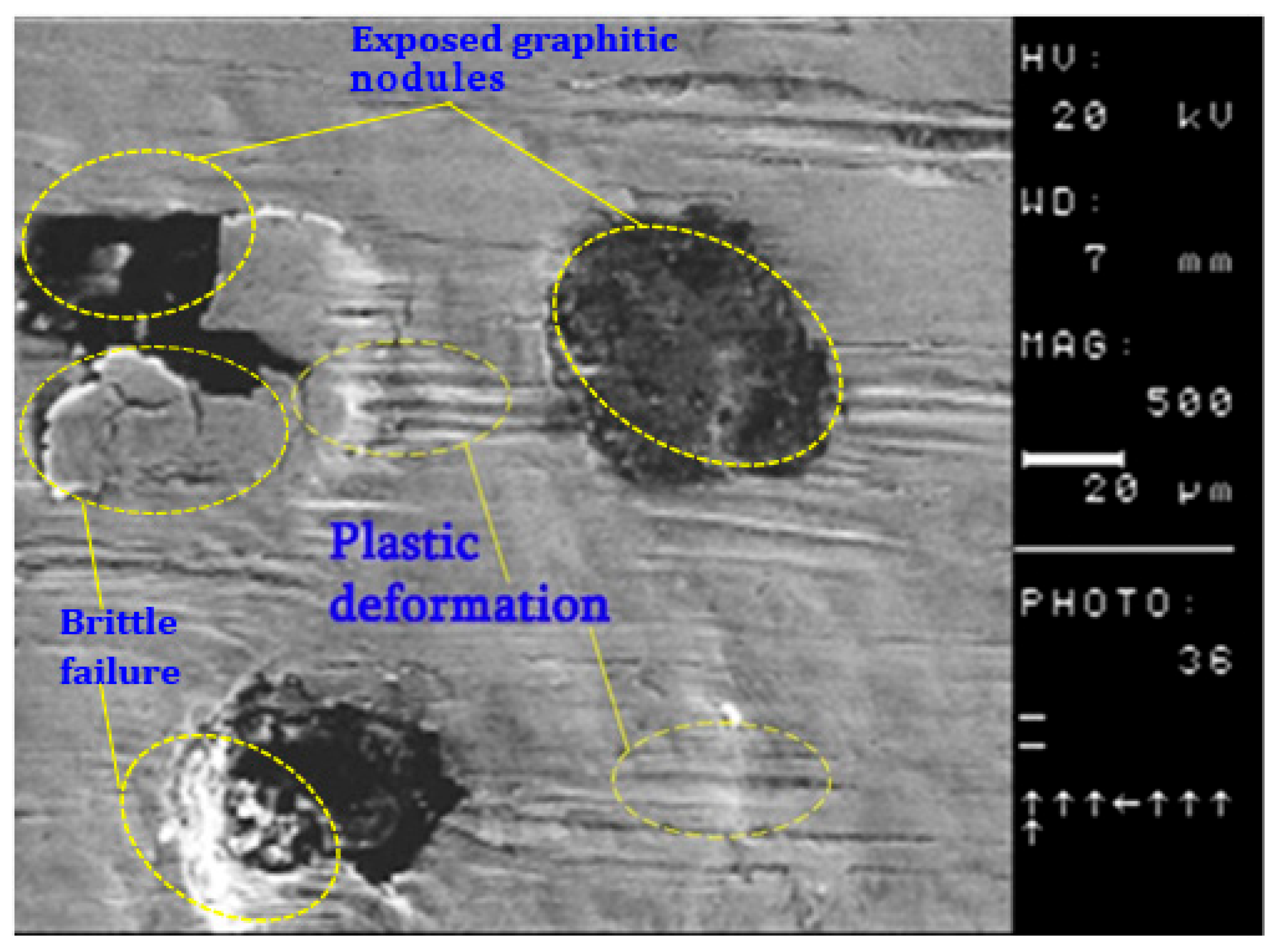
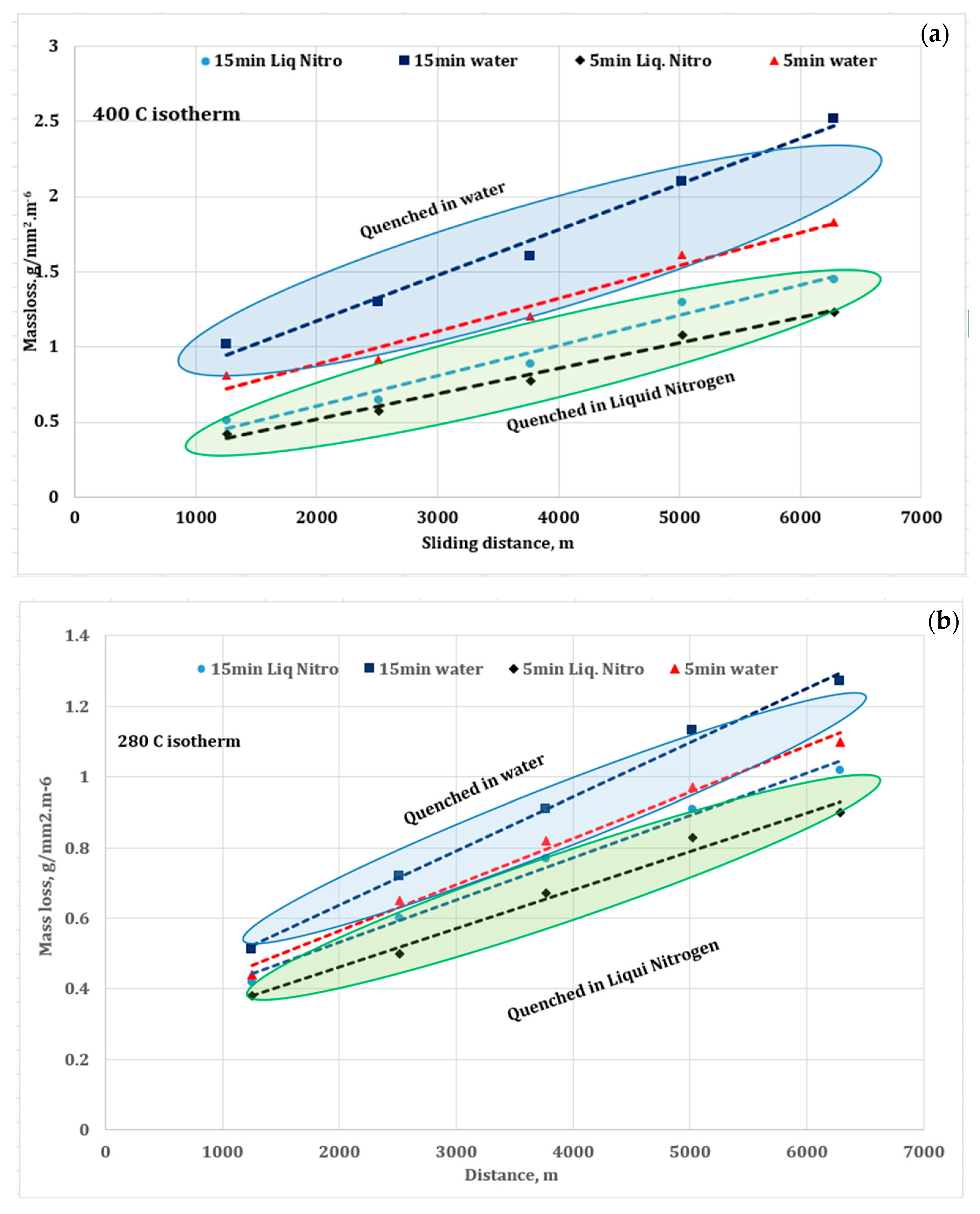
3.4. Wear Performance
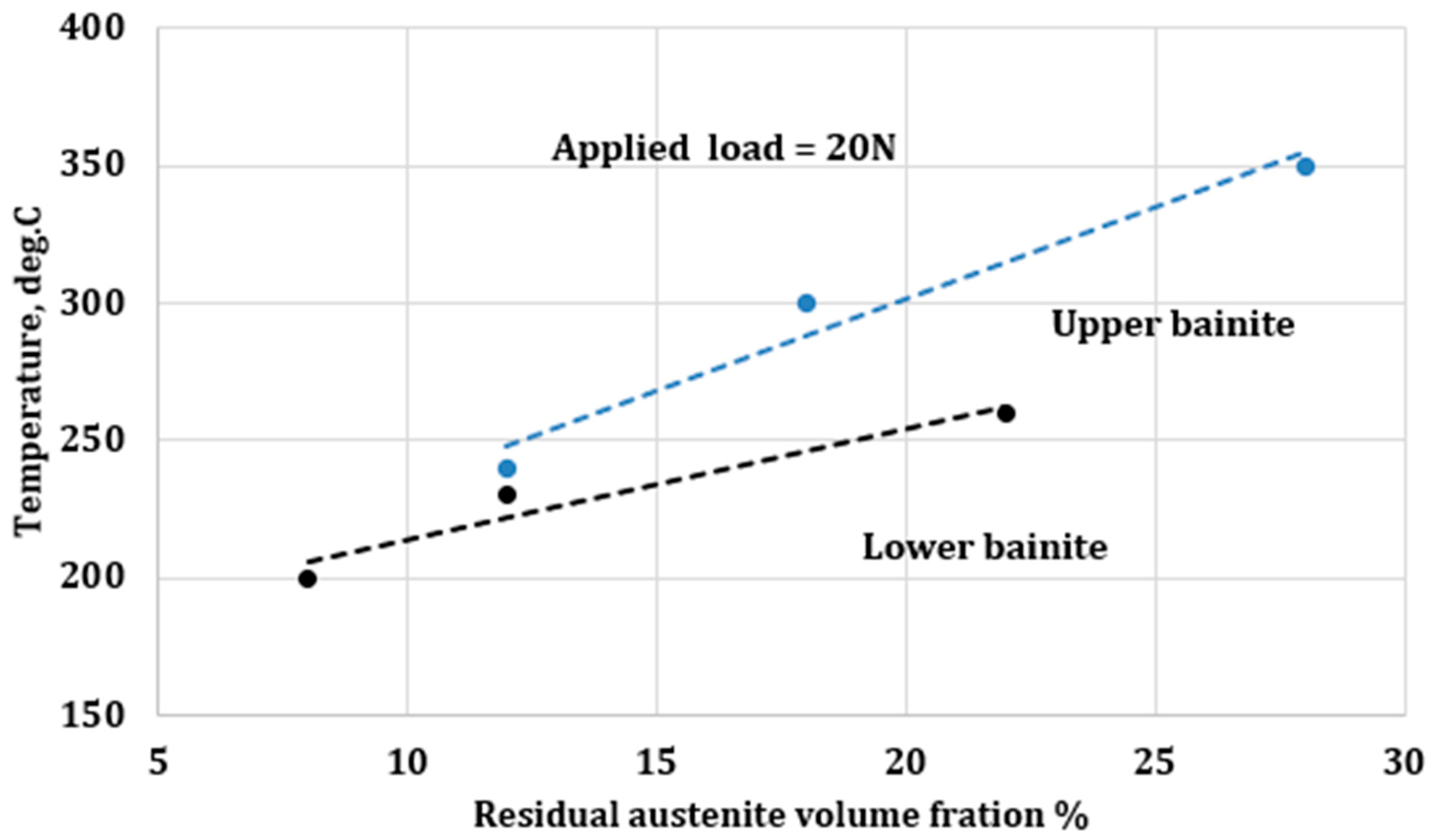
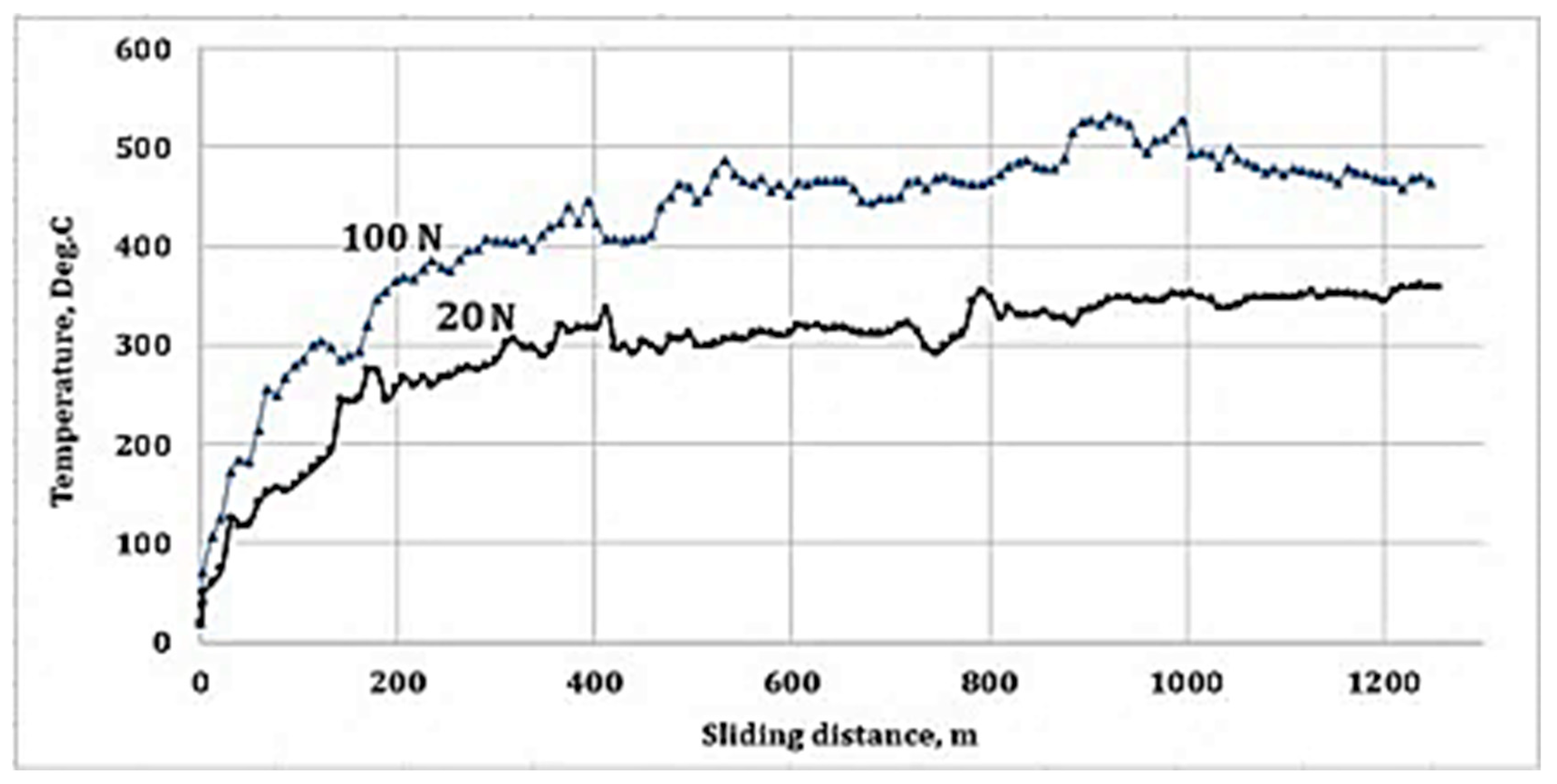
3.5. Process Temperature
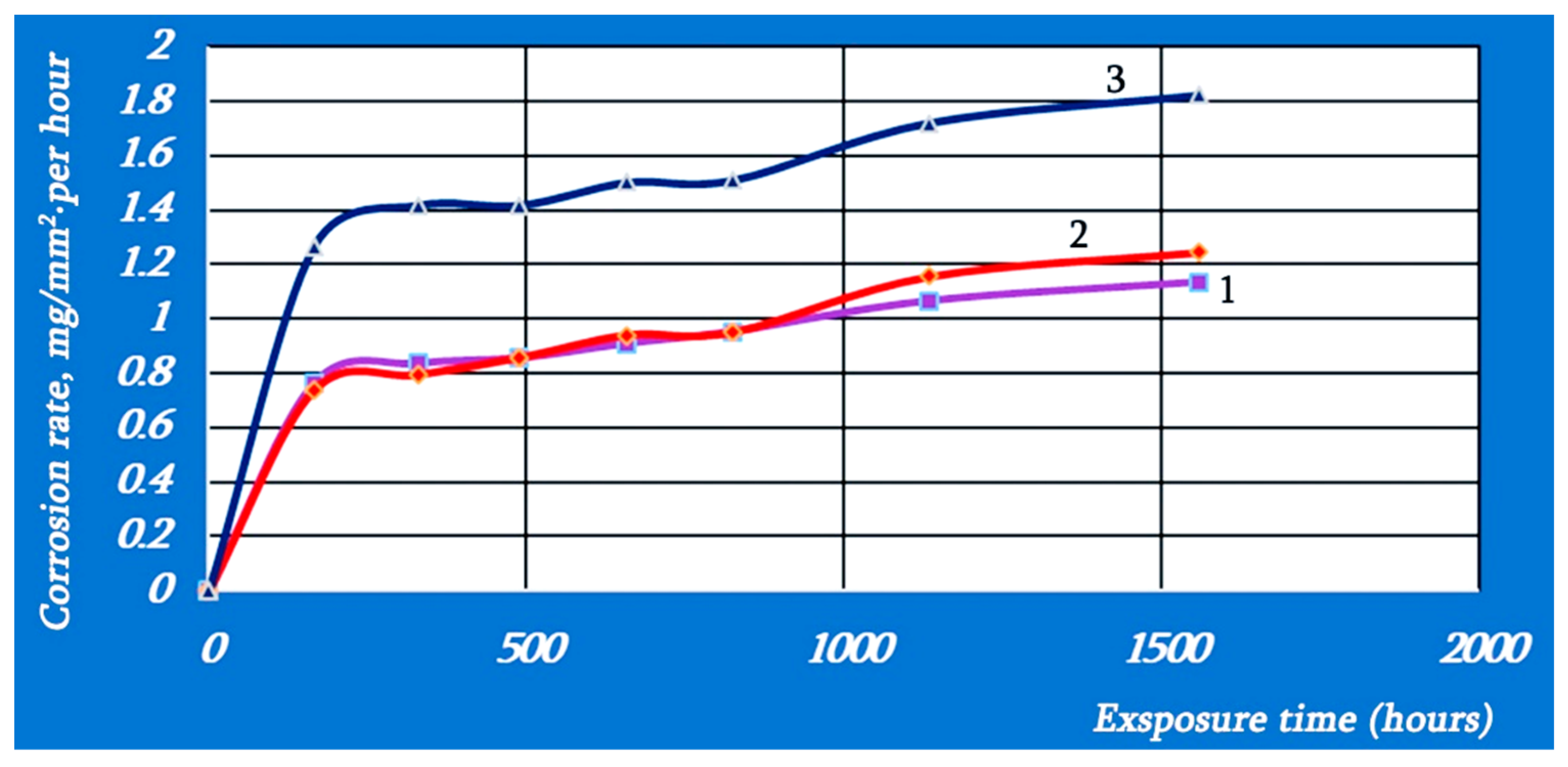
3.6. Corrosion Test
- K—is the corrosion rate, mg/mm2·hours;
- M1—is the mass of the sample after the corrosion test, mg;
- M0—is the initial mass of the sample, mg;
- S—is the area of the sample, mm2;
- τ—duration of the corrosion test.
3.7. Remarks from Wear and Corrosion Test
4. Conclusions
- The technique of micro-alloying with boron and subsequent quenching in a liquid bath of Pb-Bi-Sn alloy allowed the engineering of unique inter-matrix structures in the cast iron to the desired constituents.
- Using liquid nitrogen as a cooling medium is a new first-time approach, quenching a cast iron from 400 °C without cracks, and it proved to be an effective method of targeted restructuring of the developed high-strength cast iron.
- The best frictional performance was achieved in samples with a multiphase structure with a mixture of 10–15% lower bainite, martensite and 10% residual austenite.
- The cast irons with a bainite-martensitic matrix structure, however, have a more stable friction coefficient (0.28–0.30) in dry sliding conditions.
- The corrosion resistance of bainite-martensitic samples was increased by 1.5 times with the combination of isothermal holding and cryogenic treatment.
- Treating specimens at 280 °C isotherm with subsequent, direct quenching in nitrogen provided the best performance and opened new opportunities for further investigation aiming at direct industrial applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menga, N.; Bottiglione, F.; Carbone, G. Dynamically induced friction reduction in micro-structured interfaces. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanli, R.; Aliyev, I.; Poladov, N.; Azimova, L.; Tagiyev, T. Isothermal transformations in high-strength cast iron. Sci. Heraldof Uzhhorod Univ. Ser. Phys. 2022, 51, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinribide, O.J.; Ogundare, O.D.; Oluwafemi, O.M.; Ebisike, K.; Nageri, A.K.; Akinwamide, S.O.; Gamaoun, F.; Olubambi, P.A. A Review on Heat Treatment of CastIron: Phase Evolution and Mechanical Characterization. Materials 2022, 15, 7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, A.; Sharma, S.; Hande, R.; Gurumurthy, B.M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of manganese-alloyed austempered ductile iron produced by novel modified austempering process. Cogent Eng. 2022, 9, 2046301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.J.; Liu, C.; Northwood, D.O. Accelerated Nano Super Bainite in Ductile Iron. MRS Adv. 2018, 3, 2789–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A. Phase and Structural Transformations in Metal Alloys: A Textbook; Ural Publishing House, University: Ekaterinburg, Russia, 2018; 316p. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Jing, L.; Gao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Guo, J.; Yan, X. Impact of Cryogenic Treatment Process on the Performance of 51CrV4 Steel. Materials 2023, 16, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, K.; Liu, D.; Jiang, B. Mechanical and tribological behavior of dual-phase ductile iron with different martensite amounts. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 2978–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Cao, W.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y. Effect of tempering temperature on the wear behaviour of martensitic ductile iron. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, X.; Huang, W. Fatigue property and microstructure deformation behavior of multiphase microstructure in a medium-carbon bainite steel under rolling contact condition. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 125, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Lu, C.; Zhou, W.; Northwood, D.O.; Liu, C. Wear behavior of a multiphase ductile iron produced by quenching and partitioning process. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 123, 105290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khidasheli, N.; Gvazava, S.; Batako, A.D.L. Cryogen and heat treatments of boron-lacquered high-strength cast iron. Mater. Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasiak, K.; Węsierska-Hinca, M.; Skołek, E. Effect of a Novel Bainitization Quenching & Partitioning Heat Treatment on Multiphase Microstructure Evolution and Properties of Carburized Cr-Mn-Si Alloyed Steel. SSRN J. 2022, 42. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358688003 (accessed on 2 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, D.; He, K.; Ye, W.; Qu, S.; Shangguan, J. The Role of Bainite in Wear and Friction Behavior of Austempered Ductile Iron. Materials 2019, 12, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yang, C.; Yuan, L.; Northwood, D.O. Role of pre-formed martensite on transformation of austempered ductile iron. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hu, J.; Shan, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Xu, W. Characteristics of bainitic transformation and its effects on the mechanical properties in quenching and partitioning steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 803, 140706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santofimia, M.J.; Van Bohemen, S.M.; Sietsma, J. Combining bainite and martensite in steel microstructures for light weight applications. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2013, 113, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Popelyukh, A.I.; Tyurin, A.G.; Bardin, A.I. Raising the Properties of Steel 30KhGSA by creating a Mixed Martensitic-Austenitic Structure. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2022, 63, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.K.; Mozumder, Y.H.; Shama, S.; Behera, R.K.; Pattaniak, A.; Sindhoora, L.P.; Sen, S. Dry sliding war system response of ferritic and tempered martensitic ductile iron. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 75, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, M.; Tian, J.; Xu, G. Comparison of wear performance of bainitic and martensitic structure with similar fracture toughness and hardness at different wear conditions. Wear 2023, 512–513, 204512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, N.H.K.; Koizumi, K.; Mizuno, K.; Yamada, Y.; Okuyama, T.; Nakayama, M. Role of Matrix Structure on Impact-Wear Resistance of As-Quenched 27%Cr Cast Iron. Mater. Trans. 2022, 63, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawiec, H.; Lelito, J.; Mróz, M.; Radoń, M. Influence of Heat Treatment Parameters of Austempered Ductile Iron on the Microstructure, Corrosion and Tribological Properties. Materials 2023, 16, 4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eri, O.; Jovanovi, M.; Šidjanin, L.; Rajnovi, D. Microstructure and mechanicalproperties of cunimo austemperedductile iro. J. Min. Metall. 2004, 40, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Medyński, D.; Janus, A. Effect of Cr, Mo and Al on structure and selected mechanical properties of austenitic cast iron. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2019, 19, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Feng, X.; Zhao, A.; Li, Q.; Ma, J. Influence of Prior Martensite on Bainite Transformation, Microstructures, and Mechanical Properties in Ultra-Fine Bainitic Steel. Materials 2019, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Fan, Y.P.; Feng, X.Y.; Li, Q. Ultrafine bainitic steel produced through ausforming-quenching process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 3659–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, H.; Hayashi, K.; Sugiura, N.; Yoshinaga, N.; Takahashi, M. Effect of Martensite in Initial Structure on Bainite Transformation. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 638–642, 3307–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, D.; Zhang, F.; Meng, J. Roles of pre-formed martensite in below-Ms bainite formation, microstructure, strain partitioning and impact absorption energies of low-carbon bainitic steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 96, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulapura, A. Thermodynamic modelling of martensite start temperature in commercial steels. Mater. Sci. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 1–48. Available online: https://kth.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1176624/FULLTEXT02.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Lu, Y.; Yu, H.; Sisson, R.D. The effect of carbon content on the c/a ratio of as-quenched martensite in Fe-C alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 700, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, Y.; Hong, Z.; Du, S.; Ma, T.; Liu, S.; Jin, X. The dominating role of austenite stability and martensite transformation mechanism on the toughness and ductile-to-brittle-transition temperature of a quenched and partitioned steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 820, 141517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, L.F.V.; Bedolla-Jacuinde, A.; Mejía, I.; Zuno, J.; Maldonado, C. Effects of boron addition and austempering time on microstructure, hardness and tensile properties of ductile irons. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 648, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Sundararajan, G. Influence of the pack thickness of the boronizing mixture on the boriding of steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 149, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulana, M.I.; Syahid, A.N.; Elvira, B.R.; Erryani, A.; Thaha, Y.N.; Rokhmanto, F.; Mori, M.; Yamanaka, K.; Korda, A.A.; Kartika, I.; et al. Effect of boron microalloying on the microstructure, mechanical, and corrosion properties of as-cast biomedical Co–Cr–W–Ni-based alloys. J. Mater. Res. 2024, 39, 2272–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokumaci, E.; Özkan, I.; Önay, B. Effect of boronizing on the cyclic oxidation of stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 232, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellamuthu, P.; Samuel, D.; Dinakaran, D.; Premkumar, V.; Li, Z.; Seetharaman, S. Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI): Influence of Austempering Temperature on Microstructure, Mechanical and Wear Properties and Energy Consumption. Metals 2018, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, U.; Ray, S.; Prabhakar, S.R. The Influence of Nickel and Copper on the Austempering of Ductile Iron. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2004, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khidasheli, N.; Gordeziani, G.; Gvazava, S.; Tavadze, G.; Tabidze, R.; Batako, A.D.L. Influence of Structural Parameters on the Wear Resistance of ADI During Dry Sliding Friction. Global Congress on Manufacturing and Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Carbucicchio, M.; Reverberi, R.; Palobarini, G.; Sambogna, G. On the early stages of oxidation of iron borides. Hyperfine Interact. 1989, 46, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitar, M.A.; Scheid, A.; Nayak, U.P.; Nakamura, L.; Ponge, D.; Britz, D.; Mücklich, F. Quantification of the Phase Transformation Kinetics in High Chromium Cast Irons Using Dilatometry and Metallographic Techniques. Metall Mater Trans A 2020, 51, 3789–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazda, A. Determination of the optimal austempering parameters of Ni-Cu (Mo,Mn) ductile iron based on CCT and TTT diagrams. Prace Inst. Odlew. 2016, 56, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Chemical Composition of High-Strength Cast Iron, % | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Si | Mn | S | P | B | Mg | |
| Basic | 3.42 | 2.12 | 0.31 | 0.005 | 0.005 | - | 0.040 |
| Boron alloyed | 3.45 | 2.20 | 0.25 | 0.003 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.045 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khidasheli, N.; Gvazava, S.; Zakharov, G.; Chikhradze, M.; Batako, A.D.L.; Ahuir-Torres, J.I.; Pazhani, A.; Xavior, M.A. Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructure, Corrosion Resistance and Wear Behaviour of Bainitic/Martensitic Ductile Iron Under Dry Sliding Friction. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9050145
Khidasheli N, Gvazava S, Zakharov G, Chikhradze M, Batako ADL, Ahuir-Torres JI, Pazhani A, Xavior MA. Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructure, Corrosion Resistance and Wear Behaviour of Bainitic/Martensitic Ductile Iron Under Dry Sliding Friction. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2025; 9(5):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9050145
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhidasheli, Nugzar, Salome Gvazava, Garegin Zakharov, Mikheil Chikhradze, Andre Danonu Lignamnateh Batako, Juan Ignacio Ahuir-Torres, Ashwath Pazhani, and Micheal Anthony Xavior. 2025. "Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructure, Corrosion Resistance and Wear Behaviour of Bainitic/Martensitic Ductile Iron Under Dry Sliding Friction" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 9, no. 5: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9050145
APA StyleKhidasheli, N., Gvazava, S., Zakharov, G., Chikhradze, M., Batako, A. D. L., Ahuir-Torres, J. I., Pazhani, A., & Xavior, M. A. (2025). Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructure, Corrosion Resistance and Wear Behaviour of Bainitic/Martensitic Ductile Iron Under Dry Sliding Friction. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 9(5), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9050145









