A Review of Friction Stir Welding of Industrial Alloys: Tool Design and Process Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Aim and Structure of the Review
- Fundamentals of FSW—an overview of the process, alloy selection criteria, and research methodology;
- Process parameters and tool design—a detailed list of tool dimensions and features, and process parameters across different materials;
- Tool design and process windows—an analysis and discussion of tool dimensions, features, materials, and process windows relative to alloy thickness;
- Conclusions and future trends—a summary of findings and identification of promising areas for future research.
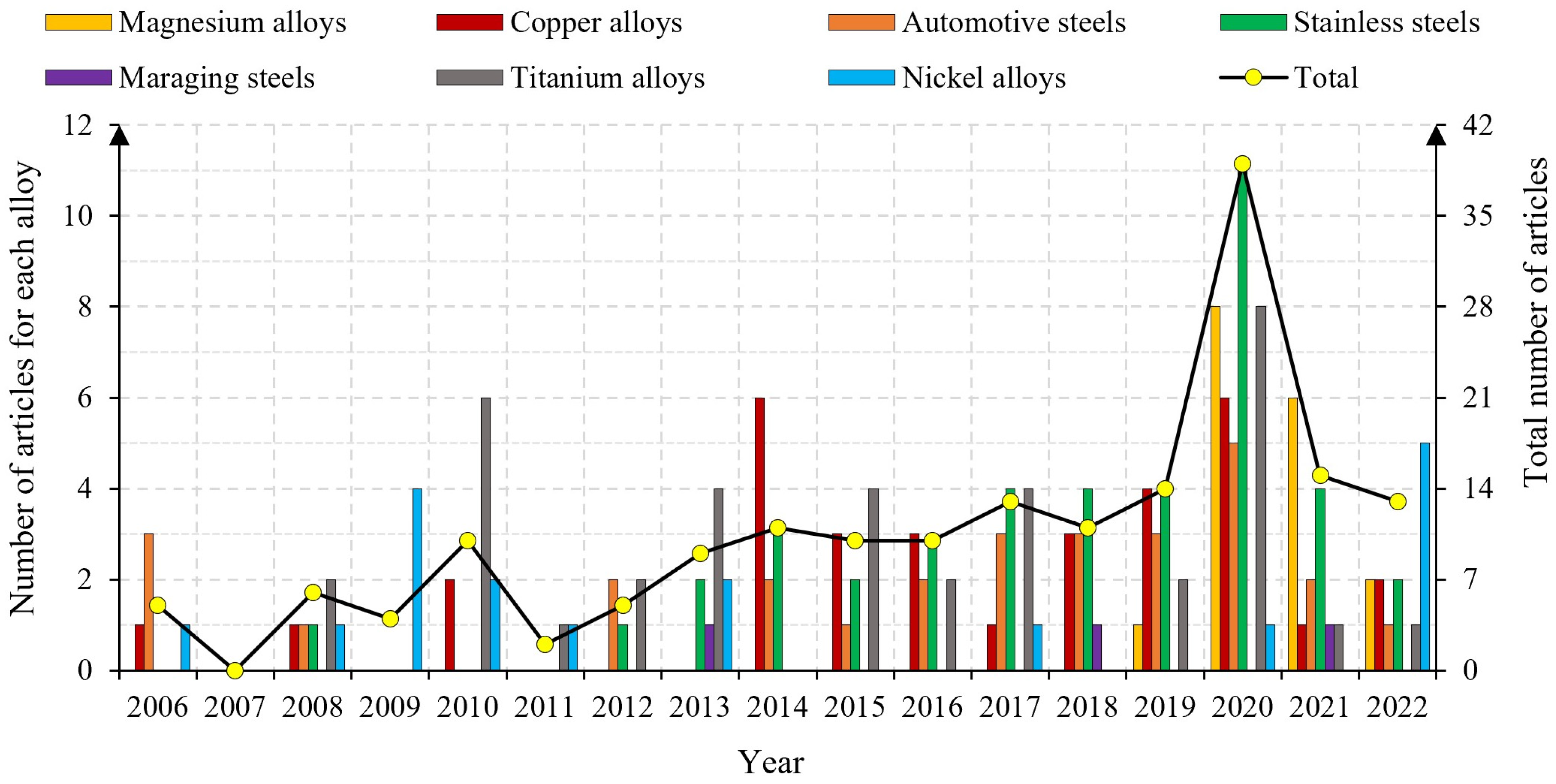
1.2. Review Methodology
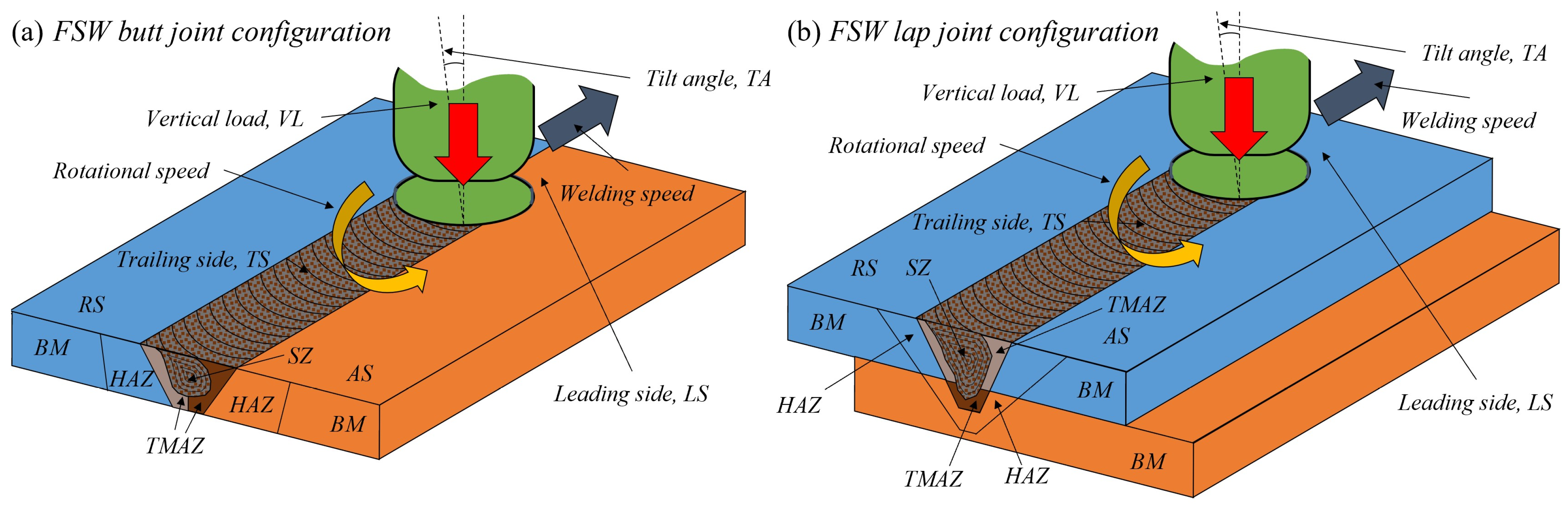
2. Data Inventory: Process Parameters and Tool Design
| Materials, Thick. [mm] | Tool Material | Tool Geometry [mm] | Process Parameters [rpm, mm/min] | Notes | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | Pin | Rotational Speed | Welding Speed | ||||
| Comm. pure, B, 3 | H13 | 15, F | PL: 2.8, BD: 6, Cy | 1700 | 100 | TA: 3 | [18] |
| Comm. pure, B, 5 | N.A. | 16, Co | PL: 4.8, BD: 5, Cy | 1000, 1500 | 200 | TA: 3 | [19] |
| AZ31, B, 2 | N.A. | 13, F, S | PL: 1.8, BD: 5, T, S, TFLA | 2000 | 2000 | TA: 0.5 | [20] |
| AZ31B, B, 4 | H13 | 15, F | PL: 3.8, BD: 5.4, T(24) | 800 | 30 | TA: 2.5, PD: 3.95 | [21] |
| AZ31, B, 4 | HSS | 14, F | PL: 3.8, BD: 4, Cy | 750, 1500 | 47.5 | [22] | |
| AZ31B, B, 5 | N.A. | 15, * | PL: 4.7, BD: 6, T(30), S, TFLA | 1300 | 50 | TA: 2.5, PD: 4.8 | [23] |
| AZ31B, B, 6 | H13 | 18, F, S | PL: 5.7, BD: 10, T(63), S | 800 | 50 | TA: 0, 2 | [24] |
| AZ61A, B, 6 | High C-Cr steel | 24, F | PL: 5.7, BD: ~5, Cy, S | 1600, 1800, 2000 | 20, 40 | [25] | |
| AZ61, AZX612, B, 3 | H13 | 15, T(160) | PL: 2.8, BD: 5, Cy, S | 600 | 500 | TA: 3 | [26] |
| AZ91, B, 4 | H13 | 18, F | PL: 3.8, BD: 6, Cy, S, TFLU | 1400 | 25 | [27] | |
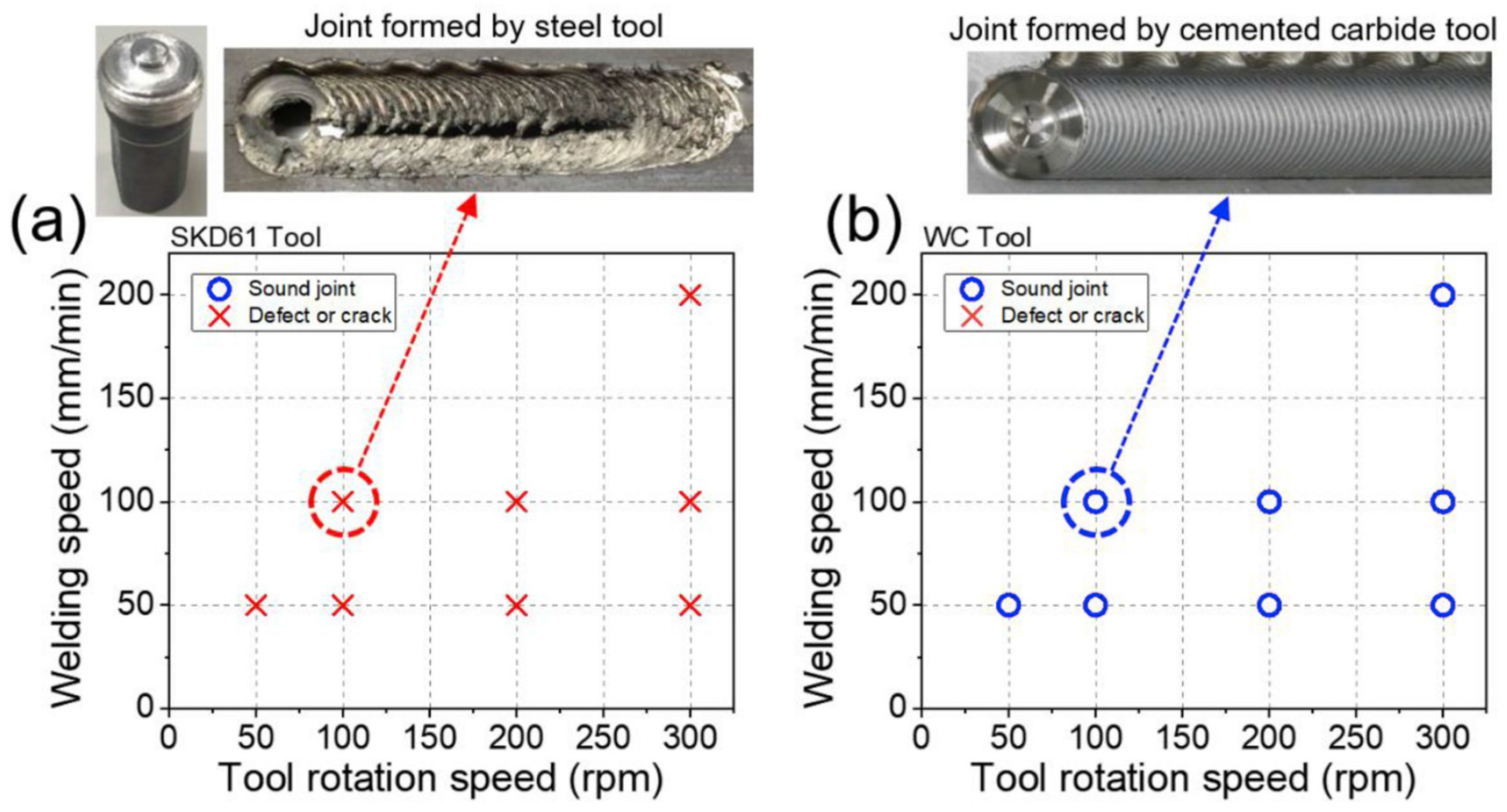
| LZ91, B, 3 | SKD61, WC | 15, F | PL: 2.8, BD: 6, Cy | ∙ 50, † 100, 200, 300, ‡ 300 | ∙ 50, † 50, 100, ‡ 200 | TA: 3 | [28] |
| AM20, B, 4 | H13 | 24, F | PL: 3.5, BD: 6, Cy, S | 600, 815, 1100 | 63 | PD: 3.62 | [29] |
| ZE41, B, 5 | High C steel | 15, F | PL: 4, BD: 5, Cy | 660, 1220 | 40 | TA: 2.5, VL: 5 | [30] |
| AZ31—AM60, B, 5 | N.A. | 15, F | PL: 4.78, BD: 6, T(29), S | ∙ 800, † 1600 | ∙ 100, † 600 | TA: 2.5 | [31,32] |
| AZ80A—AZ91C, B, 5 | HSS | 15, F | PL: 4.75, BD: ~5, T(12) | 500, 750, 1000 | 75 | [33] | |
| AZ31—AZ91, B, 6.35 | H13 | (a) 15, 21, (b) 18, F | PL: ~6, BD: 6, Cy, S | (a) ∙ 850, † 700, 1000, (b) ∙ 700, 1000, † 850 | ∙ 30, 50, † 40 | TA: 2.5 | [34] |
| Materials, Thick. [mm] | Tool Material | Tool Geometry [mm] | Process Parameters [rpm, mm/min] | Notes | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | Pin | Rotational Speed | Welding Speed | ||||
| Comm. pure, B, 2 | WC-Co | 12, F | PL: 1.8, BD: 4, Cy | 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000 | 200 | TA: 3, VL: 15 | [35] |
| Comm. pure (3N), B, 2 | WC | 12, Co | PL: 1.9, BD: 4, Cy | 800 | 150 | TA: 3, VL: 15 | [36] |
| Comm. pure, B, 3 | HSS | 12, Co | PL: 2.85, BD: 3, Cy, S | 600 | 25, 50, 100, 150, 200 | [37] | |
| Comm. pure (DHP), B, 3 | N.A. | 20, F | PL: 2.8, BD: 4, T(20) | ∙ 800, † 1000, ‡ 1200 | ∙ 90, 150, † 90, 120, 150, ‡ 90, 150 | [38] | |
| Comm. pure (C11000), B, 3 | N.A. | 16, F | PL: 2, BD: 3, Cy | 1250, 1600 | 20 | TA: 2.5 | [39] |
| Comm. pure, B, Nu, 3 | WC-Co | 18, F | PL: 2.9, BD: 6.2, T(53) | 1225, 1535, 1842, 2000 | 30 | TA: 0, VL: 5.3 | [40] |
| Comm. pure (C11000), B, 3.1 | HSS | 12, F | PL: 2.8, BD: 3.75, T(15) | ∙ 800, † 900 | ∙ 30, † 50 | PD: 2.85 | [41] |
| Comm. pure, B, Nu, 4 | H13 | 11.5, F | PL: 3.7, BD: 5, Cy, S | 900 | 80, 100, 125, 150 | [42] | |
| Comm. pure, B, 4 | Steel for tools | 12, Co | PL: 1.7, BD: 4, Cy, S | 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 800, 1000 | 120 | TA: 3, PD: 1.75 | [43] |
| Comm. pure, B, 5 | N.A. | 20, F | PL: 4.7, BD: 8, Cy, S | ∙ 500, † 710 | ∙ 56, 112, † 56 | TA: 2.5, PD: 4.9 | [44] |
| Comm. pure (ETP R220), B, 5 | N.A. | 23, Co, S | PL: 4.5, BD: 8, T(32), S | 580 | 40, 60, 80 | TA: 0, PD: 4.8 | [45] |
| 0.7Ni–0.3Cr–0.12Fe–0.04Ti, wt.%, B, 4 | Pin: WC; Shoulder: HSS | 17.8, F | PL: 3.5, BD: 6.5, Cy | ∙ 630, † 710 | ∙ 40, † 40, 63 | TA: 1.5, PD: 3.8 | [46] |
| Brass C44300, B, 2 | N.A. | 12, * | PL: 1.8, BD: 4, * | 800 | 150 | TA: 3, VL: 9.8 | [47] |
| Brass Cu-30Zn, B, N.A. | Steel for tools | 12, Co | PL: 1.7, BD: 4, Cy, S | 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 | 120 | TA: 3, PD: 1.75 | [48] |
| Brass Cu-30Zn, B, 2 | WC | 12, F | PL: 1.9, BD: 4, Cy | 600 | 200 | TA: 3, VL: 15 | [49] |
| Brass Cu-30Zn, B, 2 | WC | 12, Co | PL: 1.9, BD: 4, Cy | 800 | 200 | TA: 3, VL: 8 | [50] |
| Brass Cu-30Zn, B, 2 | WC-Co | 12, F | PL: 1.8, BD: 4, Cy | 600 | 200 | VL: 12 | [51] |
| Brass Cu-30Zn, B, 3 | Steel for tools | 13, F | PL: 2.9, BD: ~5, Cy, S | 2050 | 20, 40, 56, 80, 112, 140 | TA: 0 | [52] |
| Brass Cu-37Zn, B, 2 | H13 | 12, F | PL: 1.75, BD: 3, Cy | ∙ 800, † 800, ‡ 600, 1000, ± 463, 1136 | ∙ 100, † 16, 184, ‡ 50, 150, ± 100 | VL: ∙ 1.7, 2.5, 3.3, † 2.5, ‡ 2, 3, ± 2.5 | [53] |
| Brass Cu-37Zn, B, 4 | Pin: HSS; Shoulder: Steel for tools | 20, F | PL: 3.8, BD: 6, T(30), S | ∙ 750, † 1000 | ∙ 20, † 20, 40, 60 | TA: 2, PD: 4 | [54] |
| Brass Cu-38Zn, B, 5 | N.A. | 18, F | PL: 4.7, BD: 6, Cy, S | 400, 600, 800, 1000 | 100 | TA: 2.5, PD: 4.9 | [55] |
| Brass Cu-40Zn, B, 3 | Steel for tools | 18, F | PL: 2.8, BD: 6, (a) Cy, S, (b) T, S | 450 | 16 | TA: 2.5, PD: 2.95 | [56] |
| Brass α plates, B, 2 | WC-Co | 12, Co | PL: 1.9, BD: 4, Cy | 600 | 200 | TA: 3, VL: 8 | [57] |
| Bronze CuSn6, B, 4 | H13 | 12, Co | PL: 3.8, BD: 3.5, T, S | 800 | 50, 100, 150 | TA: 3, PD: 4 | [58] |
| Bronze CuSn6, B, 4 | H13 | 12, Co | PL: 3.8, BD: 3.5, Cy, S | 400, 600, 800, 1000 | 100 | TA: 3, PD: 4 | [59] |
| AB (C95300), B, 4 | H13 | 16, F | PL: 3.8, BD: 5, T(36), S | ∙ 850, † 1250, 1500 | ∙ 50, † 50, 100 | [60] | |
| NAB (C95800), B, 6 | WC | 24, F | PL: 5.5, BD: 6, Cy | (a) 1200, (b) 1400, (c) 1600 | ∙ 60, † 80, ‡ 100 | VL: (a) ∙ 12, † 14, ‡ 16, (b) ∙ 14, † 16, ‡ 12, (c) ∙ 16, † 12, ‡ 14 | [61] |
| NAB (C95800), B, 6 | WC | 24, F | PL: 5.5, BD: 6, Cy | 1600 | 100 | TA: 0, VL: 12 | [62] |
| NAB (C95800), B, 9 | WC | 16, F | PL: 8.5, BD: 8, T(13), TFLA | ∙ 800, † 1250, 1600 | ∙ 85, 135, † 135, 270 | VL: 4.5 | [63] |
| Comm. pure—Brass Cu-37Zn, B, 0.6 | WC-Co | 6, F | PL: 0.4, BD: 2, T(53) | ∙ 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, † 12 [krpm] | ∙ 240, † 160, 200, 240, 280, 320 | PD: 0.06 | [64] |
| Comm. pure—Brass Cu-37Zn, B, 3 | Steel for tools | 15, F | PL: 2.8, BD: 4, T(20), S | 710, 900, 1120 | 32, 40, 50 | [65] | |
| Comm. pure—Brass Cu-40Zn, B, 6 | H13 | 24, F | PL: 4.5, BD: 6, Cy | 1000, 1200, 1400 | 40 | [66] | |
| Comm. pure—Bronze CuSn1, B, Nu, 6 | H13 | 20, F | Base: PL: 2.7, BD: 6, Cy. Tip: PL: 3, BD: 6, T(37) | 800, 1000, 1200 | 40 | TA: 2.5, VL: 10 | [67] |
| Materials, Thick. [mm] | Tool Material | Tool Geometry [mm] | Process Parameters [rpm, mm/min] | Notes | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | Pin | Rotational Speed | Welding Speed | ||||
| IF, B, 1.6 | WC | 12, F | PL: 1.4, BD: 4, Cy | 400 | 100, 200, 300, 400 | TA: 3 | [68,69,70] |
| DP590, B, 1 | WC-Co (12%wt) | 10, T(172) | PL: 0.85, BD: 3, T(33) | 600 | 240 | TA: 2 | [71] |
| DP590, B, 1.4 | Si3N4 | 11, T(174) | PL: 1.3, BD: 4.7, T(66) | ∙ 600, † 800, ‡ 1000 | ∙ 120, 180, 240, 300, † 180, 240, 300, 360, 420, ‡ 300, 420 | TA: 2 | [72] |
| DP590, B, 1-1.6 | PCBN | 11.8, F | PL: 1.4, BD: N.A., Cy | ∙ 600, † 800 | ∙ 76, 102, † 152, 203 | TA: 2.5 | [73] |
| DP600, B, 1.5 | WC | 14, F | PL: 1.3, BD: 5, T(30) | 1600 | 170 | TA: 2, VL: 6 | [74] |
| DP700, B, 2 | WC-Co | 16, F | PL: 1.8, BD: 6, Cy | ∙ 800, † 600, 800, 1000 | ∙ 100, 150, 200, † 50 | TA: 3 | [75,76,77] |
| DP780, B, 1 | WC-Co (12%wt) | 10, T(172) | PL: 0.85, BD: 3, T(33) | 600 | 240 | TA: 2 | [71] |
| DP980, B, 1 | WC-Co (12%wt) | 10, T(172) | PL: 0.85, BD: 3, T(33) | 600 | 240 | TA: 2 | [71] |
| DP980, B, 1 | N.A. | 10, T(172) | PL: 0.85, BD: 3, T(33) | 600 | 240 | TA: 2, VL: 14 | [78] |
| HSLA, B, 3 | WRe | 18, F | PL: 2.7, BD: 8, T(40) | 500 | 57, 67, 77, 87, 97 | VL: 9 | [79] |
| HSLA, B, 5 | W alloy | 20, 22.5, 25, 27.5, 30, F | PL: 4, BD: 12, T(53) | 600 | 30 | TA: 0 | [80,81] |
| HSLA, B, 6.35 | PCBN | 23.7, Co, S | PL: 5.5, BD: ~8, T(30), S | 400 | ∙ 50, † 100, ‡ 150, ± 200, × 250 | VL: ∙ 35, † 40, ‡ 43, ± 48, × 53 | [82,83] |
| HSLA, B, 6.35 | WRe (25%wt) | 25, Co, S | PL: ~5.5, BD: 8, T, TFLU | 600 | ∙ 50, † 100, ‡ 150, ± 200, × 250, α 300, β 350, π 400, ∞ 450, µ 500 | VL: ∙ 12, † 15, ‡ 18, ± 21, × 23, α 31, β 45, π 45, ∞ 51, µ 55 | [82,83] |
| TRIP1180, B, 1.2 | WC-Co (12%wt) | 10, T(172) | PL: 0.85, BD: 3, T(33) | 600 | 240 | TA: 2 | [71] |
| TRIP, B, 2 | WC-Co | 11.2, * | PL: 1, BD: 2, He | ∙ 400, † 400, 600, 800, 1000 | ∙ 50, † 100 | TA: 2.5, VL: 3 | [84] |
| MS1300, B, 1 | WC-Co (12%wt) | 10, T(172) | PL: 0.85, BD: 3, T(33) | 600 | 240 | TA: 2 | [71] |
| PHS, B, 2 | PCBN | 14.3, Co, S | PL: 2, BD: N.A., T, S | 1200, 1500 | 50 | TA: 2, PD: 1.85 | [85] |
| S12C, B, 1.6 | WC | 12, F | PL: 1.4, BD: 4, Cy | 400 | 100, 200, 300, 400 | TA: 3 | [68,69] |
| S35C, B, 1.6 | WC | 12, F | PL: 1.4, BD: 4, Cy | 400 | 100, 200, 300, 400 | TA: 3 | [68,69] |
| HSLA-TRIP, B, 3.5 | PCBN | 36.8, Co, S | PL: 2, BD: N.A., T, S | 300, 400, 500 | 100 | [86] | |
| HPF1500, B, 1.2 | WC-Co (12%wt) | 10, T(172) | PL: 0.85, BD: 3, T(33) | 600 | 240 | TA: 2 | [71] |
| TWIP, B, 2 | WC | 15, * | PL: 1.8, BD: 6, * | ∙ 120, † 400 | ∙ 100, † 50, 100, 200 | TA: 3 | [87,88,89] |
| DH36, B, 4 | WC-Co (6%wt), WC-Co (10%wt) | 25, F | PL: 3, BD: 10, Cy | ∙ 450, † 300, 450, 600, ‡ 450 | ∙ 90, † 132, ‡ 180 | [90] | |
| DH36, B, Nu, 6 | WRe matrix and PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 5.7, BD: 10, T, S | ∙ 160, † 200, ‡ 300, ± 325, × 500, α 550 | ∙ 100, † 100, ‡ 250, ± 400, × 400, α 400 | VL: ∙ 55, † 58, ‡ 60, ± 64, × 53, α 59–63 | [91,92] |
| DH36, B, Nu, 6 | WRe matrix and PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 5.7, BD: 10, T, S | ∙ 200, † 300, ‡ 400, ± 450, × 600–700 | ∙ 100–156, † 250, ‡ 200–375, ± 350–400, × 500 | [93] | |
| Q&P1180, B, 1.6 | WRe (25%wt) | 11, Co | PL: N.A., BD: 5, * | 450, 600 | 200 | TA: 1.5 | [94,95] |
| Materials, Thick. [mm] | Tool Material | Tool Geometry [mm] | Process Parameters [rpm, mm/min] | Notes | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | Pin | Rotational Speed | Welding Speed | ||||
| AISI 304, B, 1.5 | Ir10Re1Zr (at-%) | 15, T | PL: ~1.4, BD: 6, Cy, He | ∙ 1080, 1332, † 1332, ‡ 1578, ± 1878, 3000 | ∙ 252, 318, 402, † 498, ‡ 498, 630, ± 630, 798 | TA: 3 | [96] |
| AISI 304, B, 2 | WC | 16, * | PL: 1.7, BD: 4.5, T(33) | 400 | 50, 150 | [97] | |
| AISI 304-B4, B, 2 | PCBN | 14.3, Co, S | PL: 2, BD: N.A., T, S | 1000, 1500 | 50, 75 | TA: 2, PD: 1.9 | [98] |
| AISI 304, B, 2.5 | PCBN | 15, F | PL: N.A., BD: 10, Cy | 500, 800 | 120 | TA: 0, PD: 2.4 | [99] |
| AISI 304, B, 2.5 | WRe (25%wt) | 13, F | PL: N.A., BD: 6, T(45) | 400, 600 | 120 | TA: 0, PD: 2.4 | [99] |
| AISI 304, B, 2.95 | WC | (a) 12, (b) 14, (c) 16, F | PL: 2.75, BD: 7, T(45) | (a) ∙ 285, † 355, ‡ 450, (b) ∙ 285, † 355, ‡ 450, (c) ∙ 285, † 355, ‡ 450 | (a) ∙ 53, † 66, ‡ 84, (b) ∙ 84, † 53, ‡ 66, (c) ∙ 66, † 84, ‡ 53 | TA: 1.5 | [100] |
| AISI 304, B, 2.95 | WC | (a) 14, (b) 16, F | PL: 2.75, BD: 7, T(45) | ∙ 355, † 450 | (a) ∙ 66, † 84, (b) ∙ 84, † 66 | TA: 1.5 | [101] |
| AISI 304L, B, 12.7 | PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 3.8, BD: 9, T(55), S | 250 | 100 | VL: 8 | [102,103] |
| AISI 304L, B, 12.7 | PCBN | 36.8, Co, S | PL: 5.7, BD: N.A., T, S | 95–130 | 25.4 | TA: −0.5, VL: 48.9 | [104] |
| AISI 304, L, 0.8 | WC-Co | 16, F | PL: 1.2, BD: 6, Cy | 1200 | 30, 50, 70 | [105] | |
| AISI 316L, B, 3 | WLa2O3 (1%wt) | 18, F | PL: 2.8, BD: 8, T(39) | 600 | ∙ 25, 50, 75, 100, † 45 | TA: ∙ 1.5, † 0, 1.5, 3, VL: ∙ 12, † 11 | [106,107] |
| AISI 316, B, 5 | PCBN | 15, T(160) | PL: 1.8, BD: 5.1, T(70) | 600 | 50 | TA: 3 | [108] |
| AISI 304—AISI 316, B, 2 | WC | 8, F | Pinless | 930, 1100, 1320 | 32 | TA: 0, PD: 1.8 | [109] |
| S32654, B, 2.4 | WRe | 20, Co | PL: 2.3, BD: 8, T(75) | 300, 400 | 100 | TA: 0, VL: 20 | [110,111] |
| AISI 409M, B, 4 | W alloy | ∙ 20, † 16, 24, ‡ 17.2, ± 22.8, F | PL: 3.7, BD: 8, T(30) | ∙ (a) 1000, (b) 800, 1200, † 1000, ‡ (a) 860, (b) 1140, ± (a) 860, (b) 1140 | ∙ (a) 30, 70, 110, (b) 70, † 70, ‡ (a) 42, (b) 98, ± (a) 98, (b) 42 | [112] | |
| T4003 (~AISI 409), B, Nu, ~3.4 | WRe (25%wt) | 15, T(174) | PL: 2.5, BD: 5.1, T(16) | 300 | 120 | TA: 2.5, PD: 2.6 | [113] |
| AISI 410S, B, 4 | PCBN | 25, T | PL: 3.7, BD: 9.2, T, S | ∙ 450, † 800 | 60 | TA: 0, VL: ∙ 10, 15, 20, † 22, 25, 30 | [114] |
| AISI 430M2, B, 0.5 | WC-Co (12%wt) | 6, F | Pinless | ∙ 800, 850, 900, † 300, 450, 900 | ∙ 84, 96, 108, † 300 | TA: 2, PD: 0.2 | [115,116] |
| 1Cr11Ni2W2MoV, B, Nu, 3.8 | WRe (25%wt) | 15, Co, S | PL: 2.95, BD: 7.3, T(69) | 250, 350, 450, 550, 650 | 75 | PD: 3.25 | [117,118] |
| GX2CrNiMoN26-7-4 (Nr 1.4469), B, 5 | PCBN | 23.7, Co, S | PL: 5, BD: 8.9, T, S | 300 | ∙ 100, † 200 | TA:0, VL: ∙ 18, 26, † 26 | [119] |
| Lean S2101, B, 4 | WC | 14, T | PL: 2, BD: 4, T | 710, 900, 1120 | 50 | TA: 3, PD: 4 | [120] |
| S32101, B, 6 | WRe matrix-40% and PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 6, BD: 8, T, S | ∙ 200, † 450 | ∙ 100, † 60 | VL: ∙ 37, † 22 | [121,122] |
| S32205, B, 1.86 | WRe | 12, F | PL: 1.65, BD: 5, T(62) | 300, 350, 400, 450, 500, 600 | 100 | TA: 2, PD: 1.7 | [123] |
| S32205, B, 2 | WC | 16, F | PL: 1.5, BD: 5, Cy | ∙ 400, 600, 800, † 600, 800, ‡ 800 | ∙ 50, 100, 150, † 200, 250, ‡ 300, 350 | TA: 3, PD: 1.7 | [124,125] |
| S32205, B, 4 | N.A. | 20, * | PL: 3.8, BD: N.A., * | 600 | 30, 50, 70 | [126] | |
| S32205, B, 6 | WRe matrix-40% and PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 6, BD: 8, T, S | ∙ 200, † 450 | ∙ 100, † 60 | VL: ∙ 37, † 22 | [121,122,127] |
| S32205, B, 6 | WRe matrix-60% and PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 6, BD: 10, T, S | 200 | 100 | VL: 37 | [128] |
| S32205, B, 6.5 | WC | 20, F | PL: 5.5, BD: 11.4, T(60) | 300 | 25 | TA: 3 | [129] |
| S32707, B, 3 | WRe | 20, Co | PL: 2.8, BD: 8, T(64) | 200, 300, 500 | 100 | TA: 0, VL: 20 | [130] |
| S32750, B, 2 | WC | 16, * | PL: 1.8, BD: 5, * | ∙ 700, † 1000 | ∙ 40, 60, † 60, 80 | TA: 3 | [131] |
| S32750, B, 6 | WRe matrix-40% and PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 6, BD: 8, T, S | ∙ 200, † 450 | ∙ 100, † 60 | VL: ∙ 37, † 22 | [121,122] |
| S32750, B, 6 | WRe matrix-60% and PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 6, BD: 10, T, S | 200 | 100 | VL: 37 | [128] |
| S32760, B, 6 | WRe matrix-40% and PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 6, BD: 8, T, S | ∙ 200, † 450 | ∙ 100, † 60 | VL: ∙ 37, † 22 | [121,122] |
| S32760, B, 6 | WRe matrix-60% and PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 6, BD: 10, T, S | 200 | 100 | VL: 37 | [128] |
| AISI 430—AISI 304L, B, 2 | WC | 16, F | PL: 1.7, BD: 5, T(61) | 450, 560, 710 | 50, 100 | [132] | |
| AISI 430—AISI 304, B, 2.5 | WC | 18, F | PL: 2.2, BD: 7, T(49) | 700, 750, 800, 900 | 30 | TA: 0, PD: 2.3 | [133] |
| AISI 304—S32205, B, 1.89—1.86 | WRe (25%wt) | 12, F | PL: 1.65, BD: 7, T(85) | 400 | 50 | TA: 2, PD: 1.8 | [134,135] |
| S31603—S32750, B, 6 | WRe matrix-40% and PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 6, BD: 8, T, S | ∙ 100, 150, 200, † 300 | 100 | PD: ∙ 5.47, † 5.54 | [136] |
| Materials, Thick. [mm] | Tool Material | Tool Geometry [mm] | Process Parameters [rpm, mm/min] | Notes | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | Pin | Rotational Speed | Welding Speed | ||||
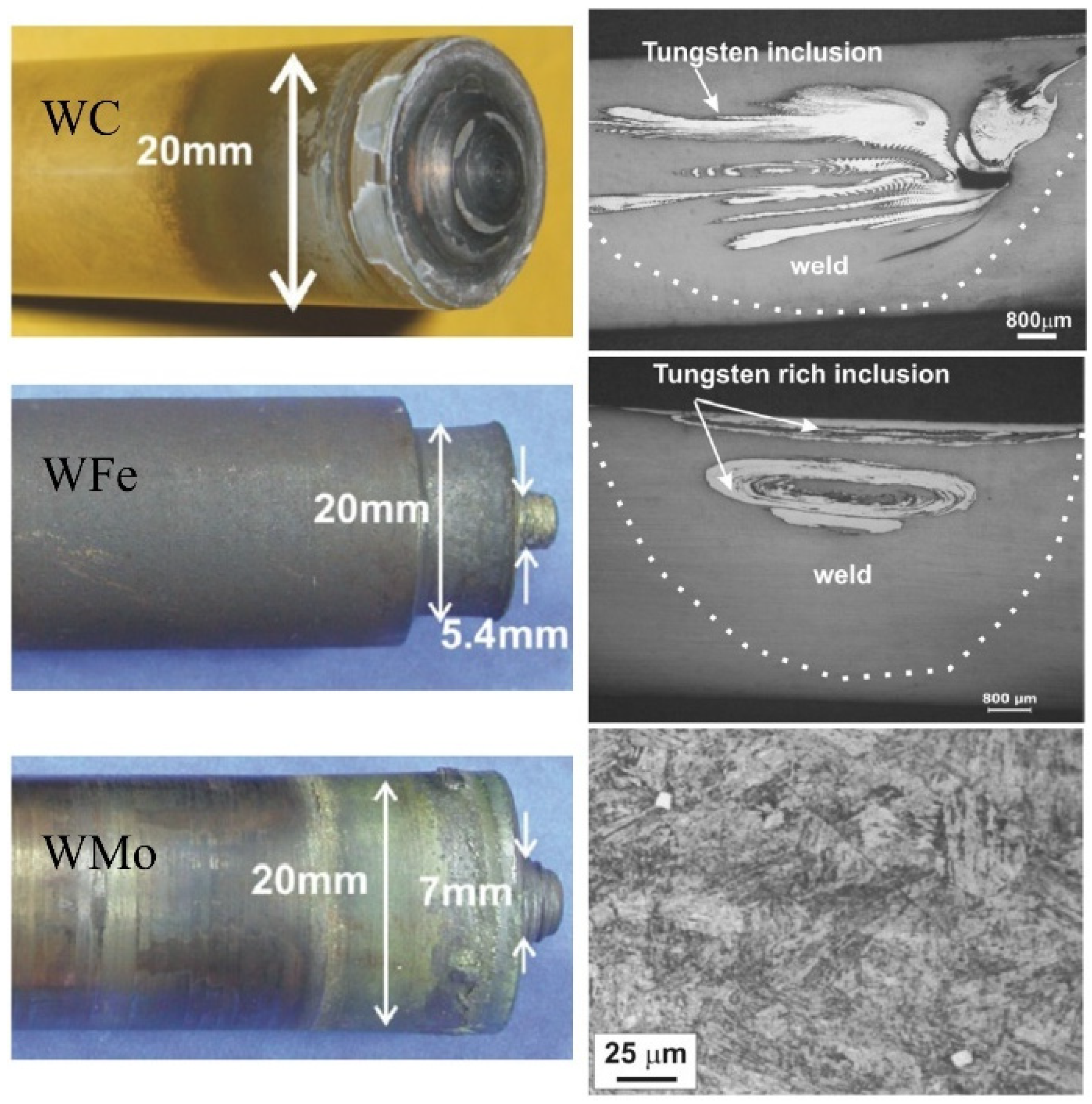
| MDN-250, B, 5.2 | WC, WFe, WMo | 20, F | PL: 5, BD: 12, T(44) | ∙ 250, 450, 650, 850, 1050, † 250 | ∙ 25, † 25, 30, 35, 40 | TA: 2, PD: 5 | [137] |
| MDN-250, B, 5.2 | PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 4.5, BD: 5, T, S | ∙ 250, 450, 650, 850, 1050, † 250 | ∙ 25, † 25, 30, 35, 40 | TA: 2, PD: 5 | [137,138] |
| MDN-250, B, 5.5 | WC, WFe, WMo | 20, F | PL: 5.2, BD: 12, T(42) | 600 | 25 | [139] | |
| Materials, Thick. [mm] | Tool Material | Tool Geometry [mm] | Process Parameters [rpm, mm/min] | Notes | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | Pin | Rotational Speed | Welding Speed | ||||
| Comm. pure, B, 2 | WC | 15, * | PL: 1.8, BD: 6, * | 200 | 50, 100, 200, 300 | [140] | |
| Comm. pure, B, 3 | PCBN | 15, T(166) | PL: 2.2, BD: 6, T(90) | 200 | 50 | PD: 2 | [141] |
| Comm. pure, B, 3 | Pin: HSS or WC; Shoulder: HSS | 18, F | PL: 2.85, BD: 5, Cy, S | 1250 | 32 | TA: 3 | [142] |
| Comm. pure, B, 3 | Pin: WC; Shoulder: W | 18, F | PL: 2.85, BD: 5, Cy | ∙ 1250, † 1500 | ∙ 32, † 60 | TA: ∙ 1, 3, † 1 | [142] |
| Comm. pure, L, 2 | WC-Co | 15, F | PL: 2, BD: 6, Cy | 200–350 | 50–150 | TA: 3, VL: 14.7 | [143] |
| Comm. pure, L, 2 | WC-Co | 15, F | PL: 2, BD: 6, Cy, He | 150–300 | 50–125 | TA: 3, PD: 2.3 | [144] |
| Comm. pure, L, 2 | WC-Co | 15, F | PL: 1.8,2.0,2.2, BD: 6, Cy, He | 200–400 | 60–200 | TA: 3 | [145] |
| Ti4Al0.005B (TA5), Tj, 4.2 | N.A. | 16, F | PL: 4, BD: 9, T(64) | 450, 650, 850 | 50 | TA: 2.5, PD: 4.2 | [146] |
| Ti4Al0.005B (TA5), B, 4 | Co alloy | 18, Co | PL: 3.8, BD: N.A., T | 400 | 40 | TA: 2.5 | [147] |
| Ti4Al0.005B (TA5), B, 5 | Co alloy | 18, T(174) | PL: 4.85, BD: 8, T(45) | 250 | 20, 35, 50 | TA: 3, PD: 5 | [148] |
| Ti4Al0.005B (TA5), B, 6 | W alloy | 18, Co | PL: 5.8, BD: N.A., T | 500 | 50 | TA: 2 | [149] |
| Ti1.5Al1Mn, B, 2.5 | ZhS6U | 20, F | PL: 2.4, BD: 5.8, T(60) | ∙ 400, † 450, ‡ 600, ± 950 | ∙ 90, † 90, 95, 100, ‡ 100, ± (a) 130, (b) 140, (c) 150, (d) 180 | VL: ∙ 24–26, † 19–22, ‡ 17, ± (a) 15–17, (b) 10–14, (c)–(d) 9.5 | [150] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 2 | WRe | 11, F | PL: 1.8, BD: 6, T(58) | ∙ 400, † 400, 500, 600 | ∙ 25, 50, 100, † 75 | TA: 2.5, PD: 2 | [151,152] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 2 | WC | 15, F | PL: 1.8, BD: 6, Cy | ∙ 225, 300, † 300, 350, ‡ 400, ± 1000 | ∙ 50, † 25, ‡ 25, 50, 100, ± 400 | TA: 3 | [153,154] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 2 | WRe | 12, T | PL: ~1.9, BD: 7, T(~66), S | 350 | 50 | TA: 2.5 | [155] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, Nu, 2 | WRe | 12, F | PL: 1.7, BD: 8, T(~99) | 120, 300, 350, 375 | 50 | [156] | |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 2 | WC | 15, F | PL: 1.8, BD: 6, T | 1500 | 100 | [157] | |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 2 | Pin: WRe (25%wt); Shoulder: GH4043 | 28, F | PL: 1.9, BD: 16, T(55) | ∙ 700, 800, 900, † 1000, 1100, 1200 | ∙ 20, † 30 | TA: 0, PD: 2 | [158] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 2 | Pin: WRe (25%wt); Shoulder: GH4043 | 26, F | PL: 1.9, BD: 16, T(55) | ∙ 700, 900, 1100, 1300, † 900, 1100 | ∙ 10, 20, † 40, 60 | TA: 0, PD: 2 | [159] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, Nu, 2 | N.A. | 12, F | PL: 1.8, BD: 6, T(58) | 800 | 30 | [160] | |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 2.5 | WRe | 15, T | PL: 2.1, BD: 7.2, T(55), S | 100, 120, 150, 200 | 30 | TA: 2.5, PD: 2.3 | [161] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 2.5 | ZhS6U | 20, F | PL: 2.3, BD: N.A., T | 340, 360, 380 | 86 | TA: 1.5, VL: 45 | [162] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 3 | Mo alloy | 15, Co | PL: N.A., BD: 5.1, T, S | 300, 400, 500, 600 | 60 | PD: 2 | [163] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, Nu, 3 | WC, WRe (25%wt) | 16, F | PL: 2.6, BD: 5, T(30) | 300, 700, 1000 | 35 | TA: 2, PD: 2.8 | [164] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, Nu, 3 | WC | 16, F | PL: 2.6, BD: 5, T(30) | 300, 500, 700, 1000 | 50 | TA: 2, PD: 2.8 | [165] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, Nu, 3 | WRe (25%wt) | 16, F | PL: 2.6, BD: 5, T(30) | 300, 500, 700 | 35, 50 | TA: 0, PD: 2.85 | [166] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 3 | WLa | 19, F | PL: 2.8, BD: ~15, T(~110) | 300 | 75 | [167] | |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 3 | WLa2O3 (1%wt) | 14, F | Pinless | 950 | 55 | TA: 0, 1, 2, PD: 0.15, 0.2, 0.25 | [168] |
| Ti6Al4V (AM), B, 3 | WC-Co (10%wt) | 20, * | PL: 2.6, BD: 7, T(60) | 400, 500, 700 | 45 | TA: 1 | [169] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 5 | Co alloy | 25, F | PL: 4.9, BD: N.A., T | 50, 150 | 10 | TA: 1 | [170,171] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 6 | WLa | 24, F | PL: 5.9, BD: ~19, T(~70) | 280 | 100 | [167] | |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 6 | WLa | 25, F | PL: 5.9, BD: 20, T(~80) | ∙ 200, † 300, ‡ 400 | ∙ 100, † 50, 100, 150, ‡ 100 | TA: 3 | [172] |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 9 | WLa | 24, F | PL: 9.0, BD: ~19, T(~60) | 270 | 65 | [167] | |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 10.3 | WLa2O3 (1%wt) | 25.4, F | PL: 9.91, BD: 15.7, T(30), He | ∙ 120, 150, 200, † 400, ‡ 800 | ∙ 50.8, † 101, ‡ 203 | [173] | |
| Ti6Al4V, B, 12 | WLa | 32, F | PL: 13.3, BD: ~26, T(~60) | 170 | 65 | [167] | |
| Ti6Al4V, L, Nu, 1.25 | WRe (25%wt) | 13, F | PL: 2, BD: 4, T(30) | 300, 500, 700 | 25, 50, 75 | TA: 0, PD: 2.1 | [174] |
| Ti6Al4V, L, 1.8 | WRe | 12, T | PL: 1.9, BD: 6.3, T(55), S | 150, 180 | 30 | PD: 2 | [175] |
| ATI-425—TIMET-54M, B, 4 | WLa | 15.9, F | PL: 1.4, BD: 8.6, T | 300 | 75–100 | TA: 3, PD: 1.6 | [176] |
| Materials, Thick. [mm] | Tool Material | Tool Geometry [mm] | Process Parameters [rpm, mm/min] | Notes | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | Pin | Rotational Speed | Welding Speed | ||||
| Inconel 600, B, 2 | WC | ~16, F | PL: 1.8, BD: 6, Cy | 400 | 100 | TA: 3 | [177] |
| Inconel 600, B, 2 | WC-Co | 15, * | PL: 1.8, BD: 6, * | 400 | 150, 200, 250, 300, 450 | TA: 3, VL: 23 | [178,179,180] |
| Inconel 600, B, 4.8 | PCBN | 25, * | PL: 1.8, BD: N.A., TFLA | 600 | 60 | TA: 3.5 | [181] |
| Inconel 601, B, 2 | WC | 10, * | PL: 1.8, BD: 2, * | 900, 1000, 1100 | 10, 20, 30 | [182] | |
| Inconel 625, B, 2 | WC-Co | 15, * | PL: 1.8, BD: 6, * | 200 | 100 | TA: 3, VL: 42 | [183,184] |
| Inconel 625, B, 3.2 | WRe matrix-30% and PCBN | 25, Co, S | PL: 3, BD: N.A., T, S | ∙ 180, 200, 1000, 1200 † 200, ‡ 500, 600 | ∙ 60, † 90, ‡ 60 | TA: 1.5, VL: ∙ 60, † 60, ‡ 50 | [185] |
| Inconel 718, B, 2 | WC-Co | 15, * | PL: 1.8, BD: 6, * | 200 | 150 | TA: 3, VL: 39 | [186,187] |
| Inconel 718, B, Nu, 3 | WC-Co | 25, F | PL: 2.7, BD: 7, T(40) | ∙ 300, † 450, 600 | ∙ 40, 70, 90, 140, † 90 | TA: 2, PD: 2.9 | [188,189,190,191] |
| Inconel 718, B, 4 | Si3N4 | 20, F | PL: N.A., BD: ~7, TFLA | 400 | 30, 50, 80 | TA: 2, PD: 3.6 | [192] |
| Inconel 825, B, 2 | PCBN | 14.3, Co, S | PL: 2, BD: N.A., * | 2000 | 75 | TA: 2, PD: 1.8 | [193] |
| Monel 400—Inconel 600, L, 2 | WC-Co | 15, * | PL: 2, BD: 6, * | 200 | 100 | TA: 3, VL: 21 | [194] |
3. Discussions
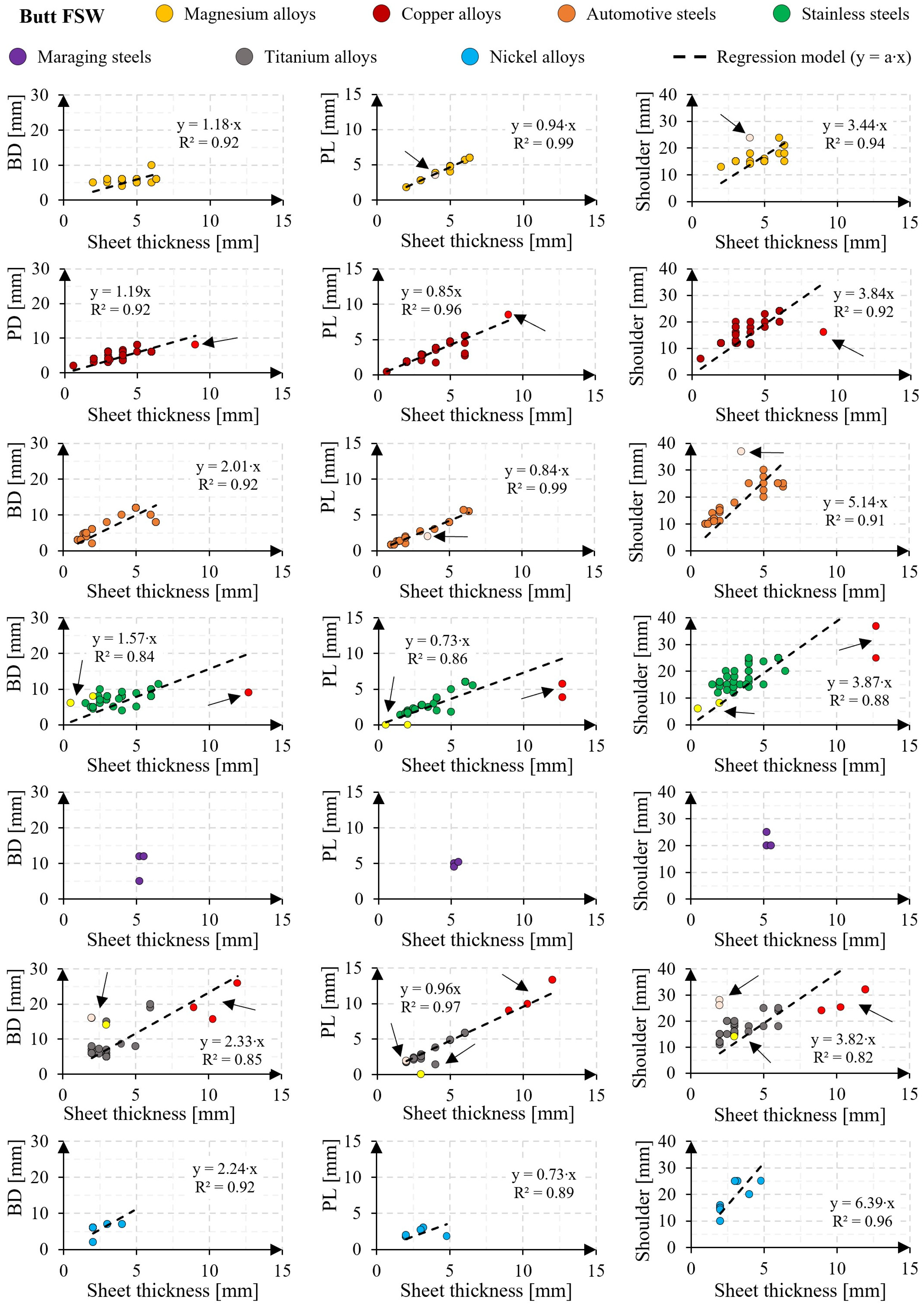
3.1. Tool Dimensions
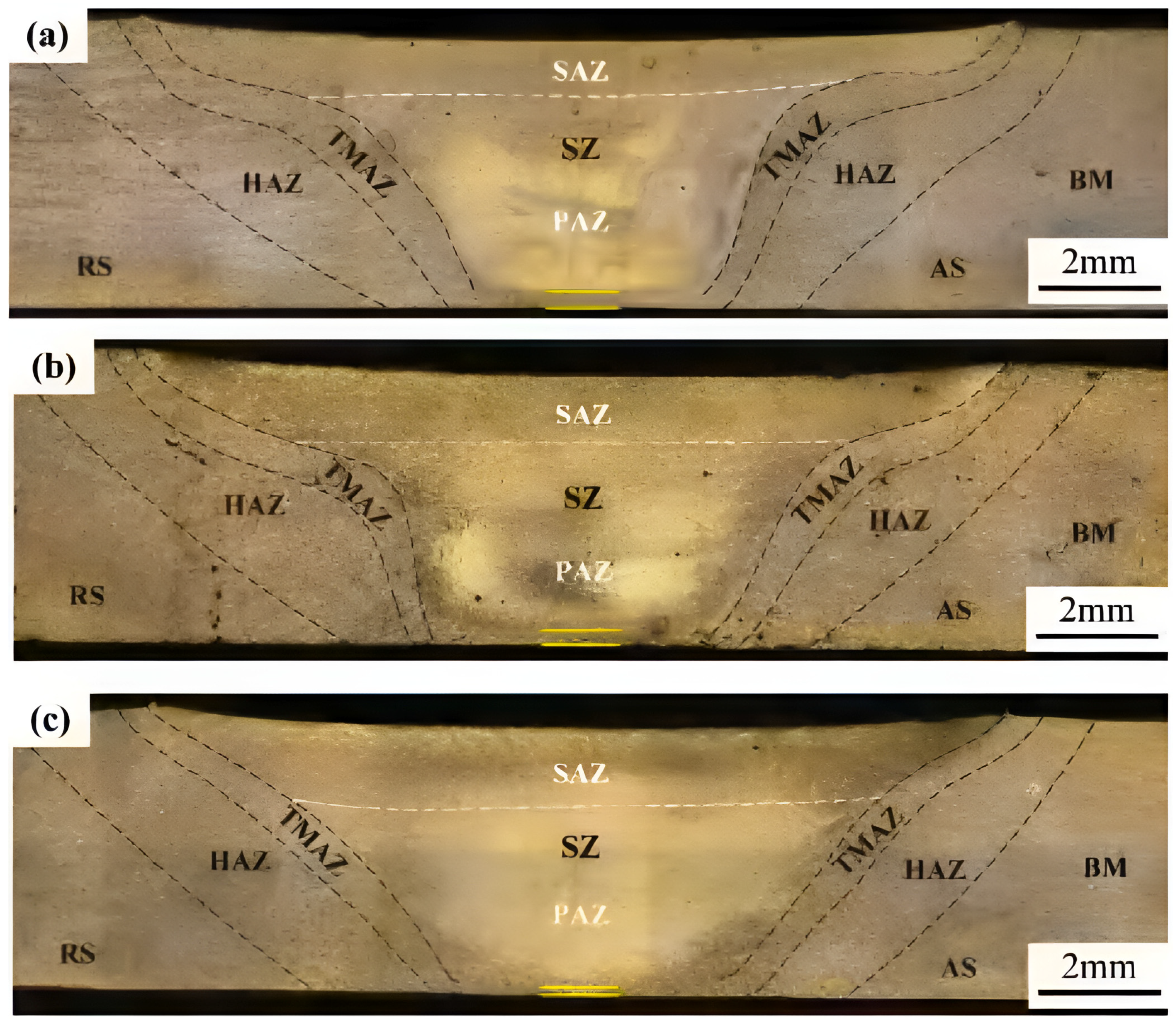
3.2. Tool Features
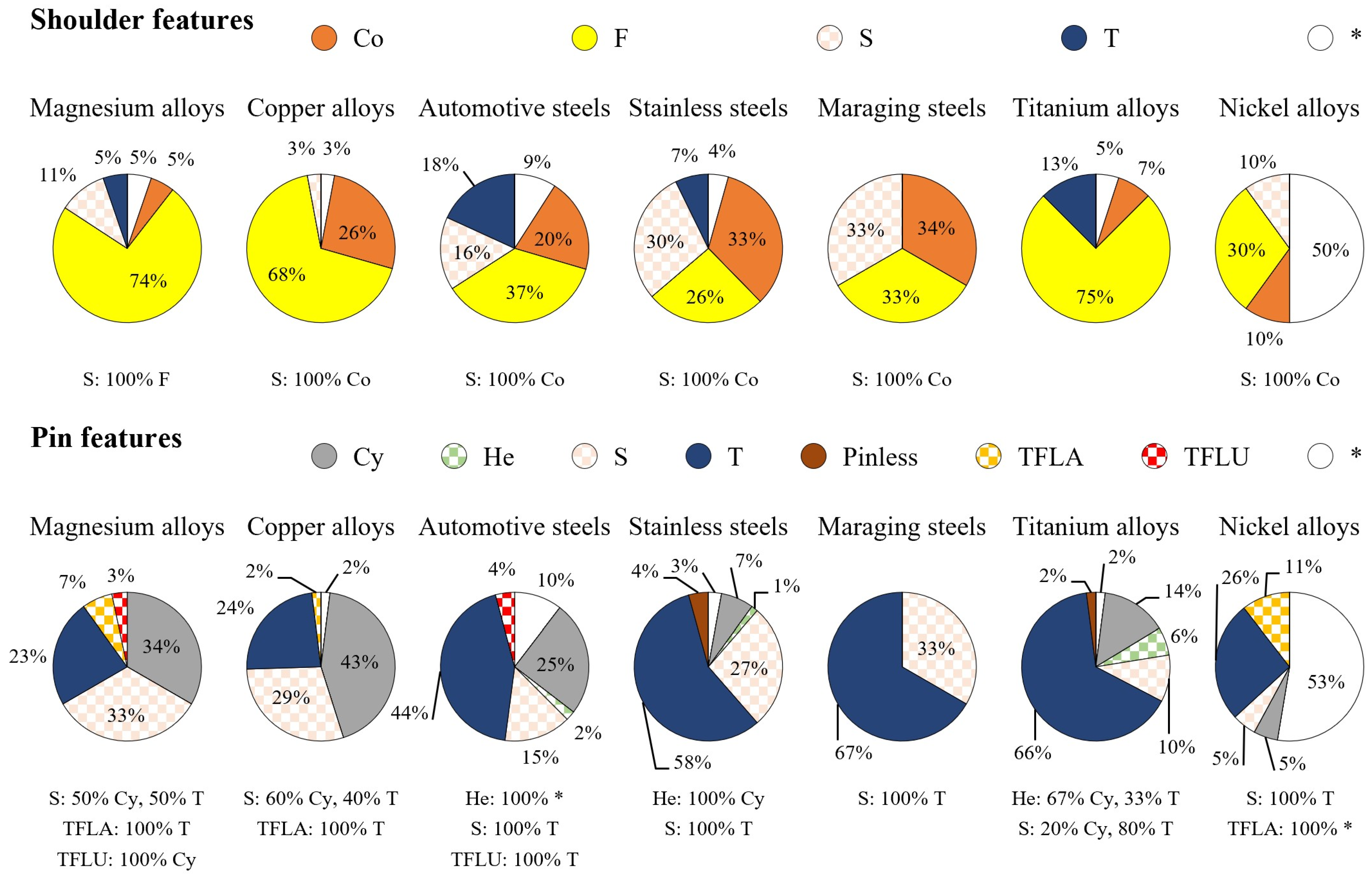
3.2.1. Shoulder Features
3.2.2. Pin Features
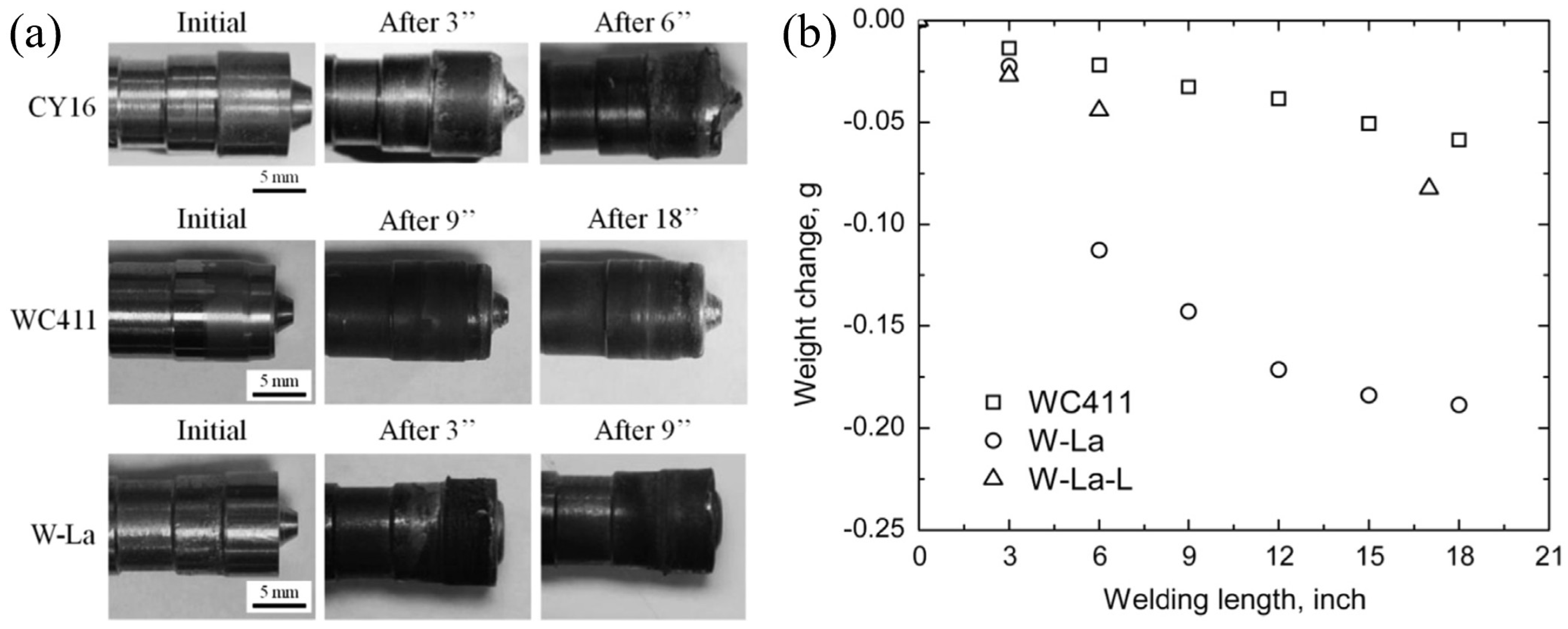
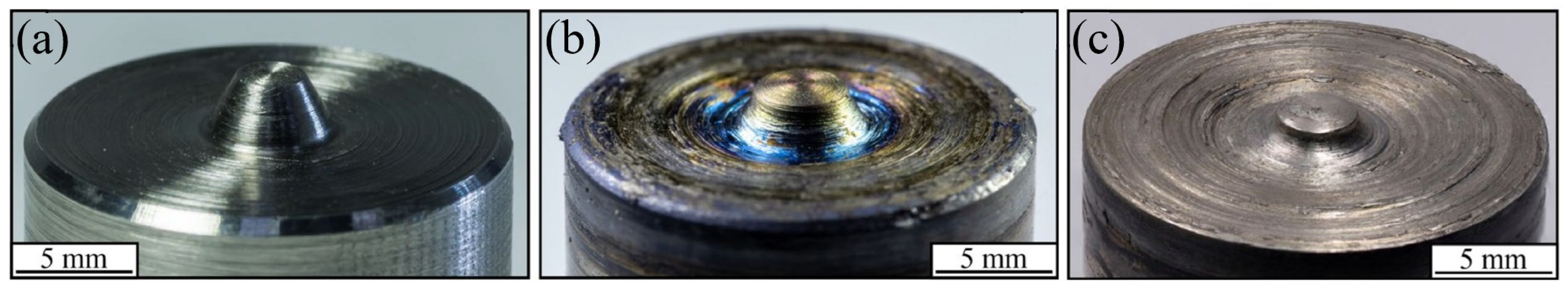
3.3. Tool Materials
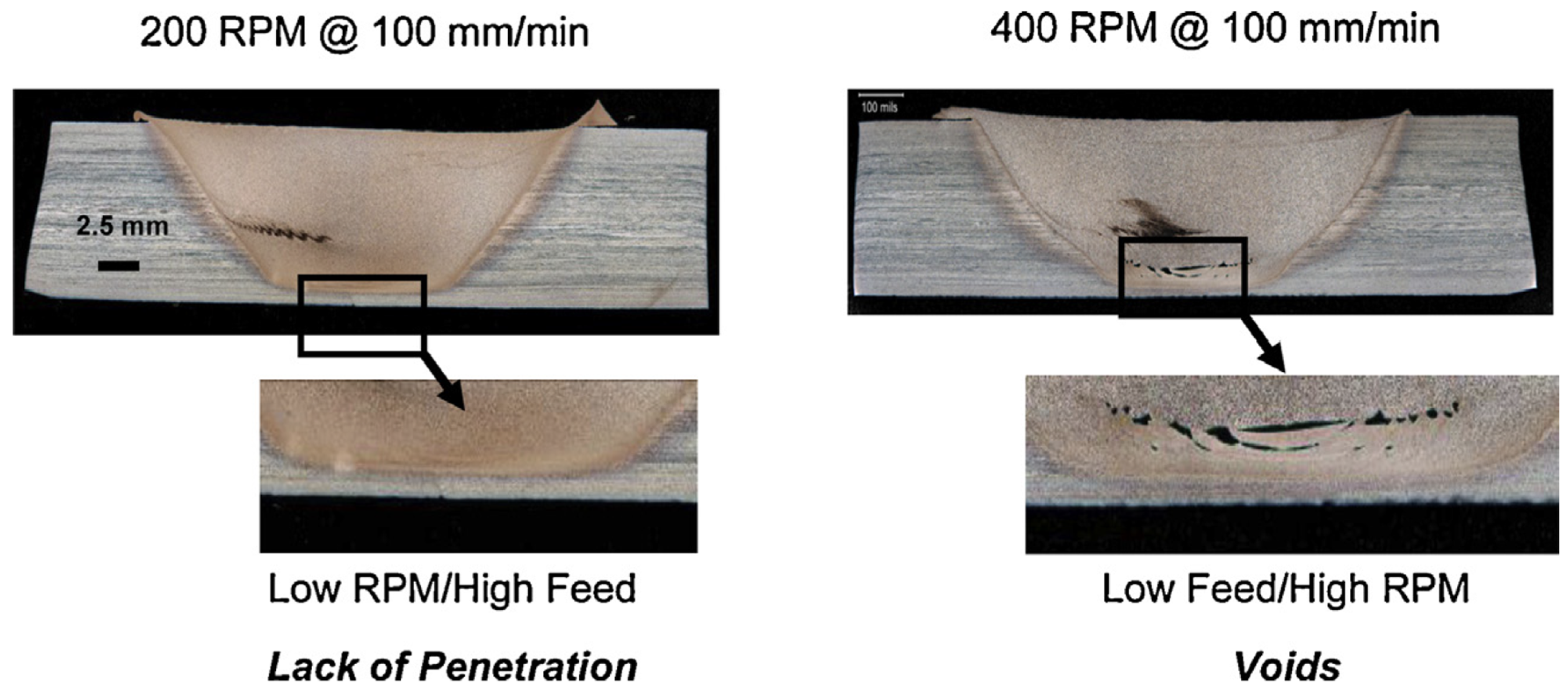
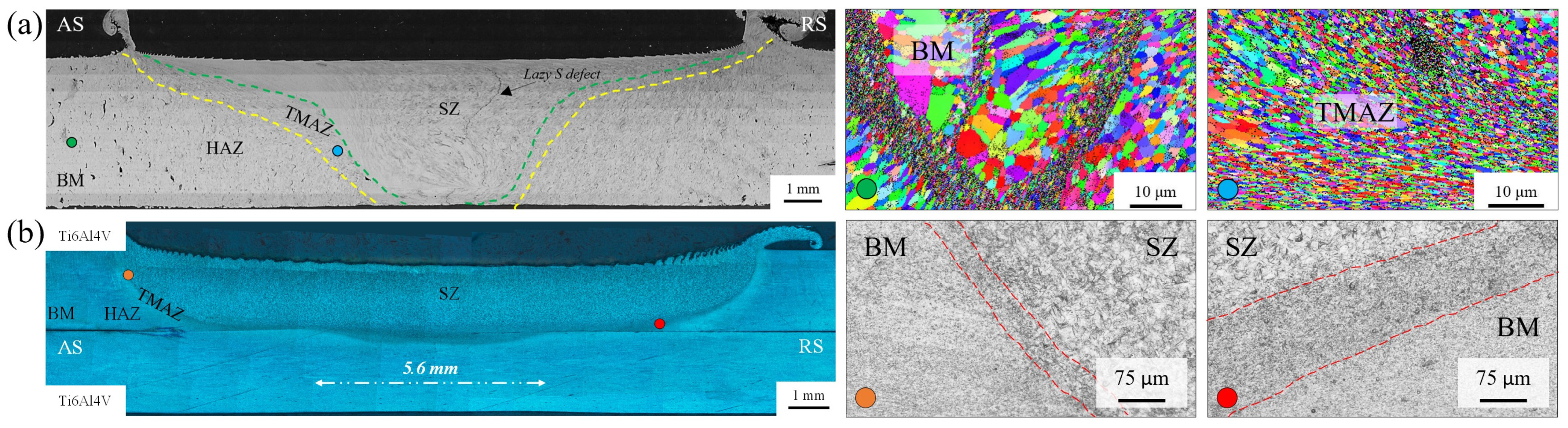
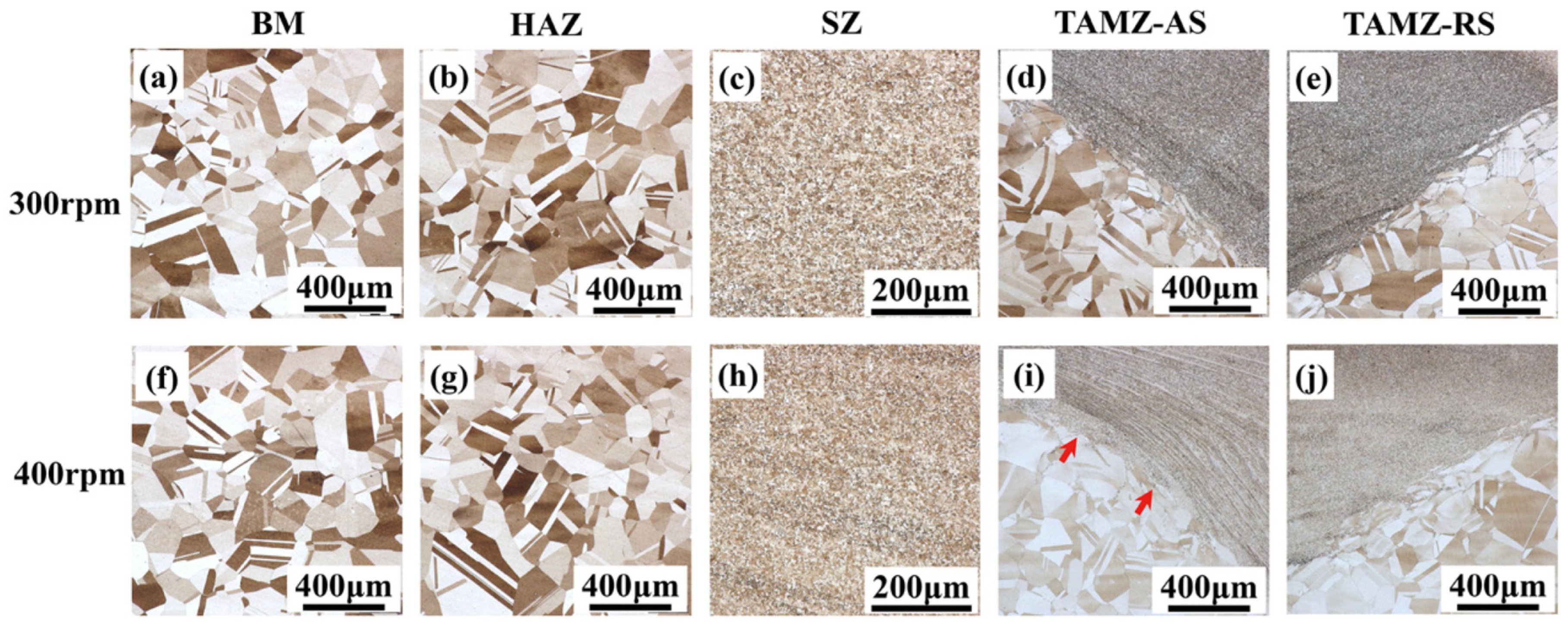
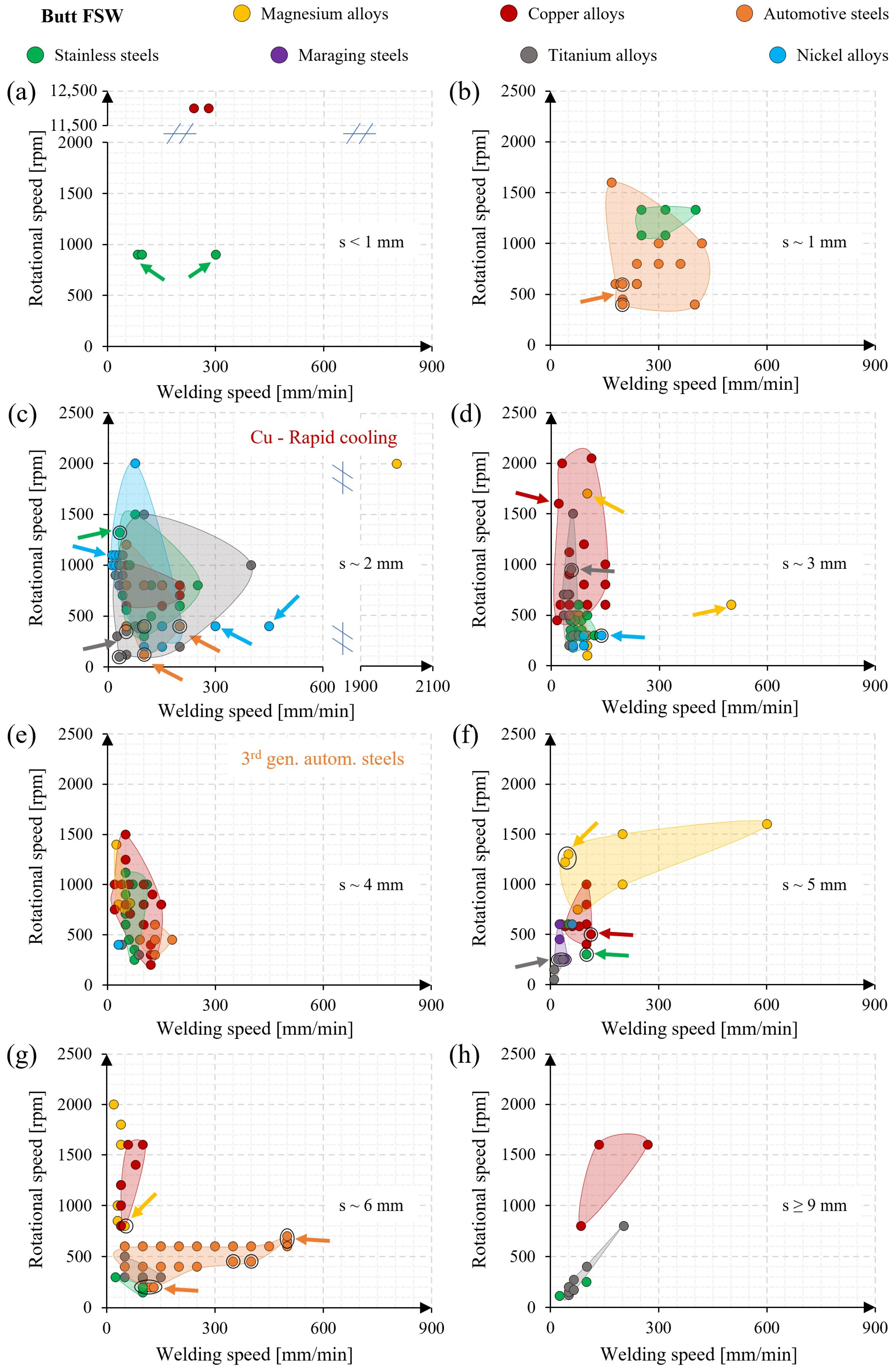
3.4. Process Windows
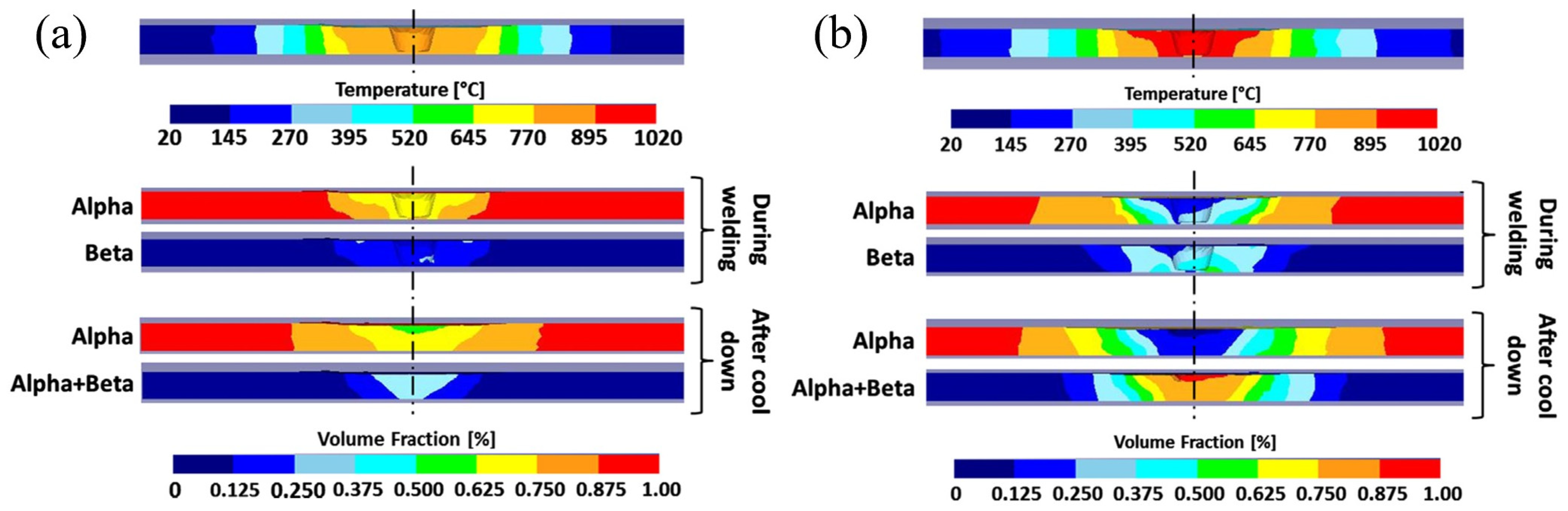
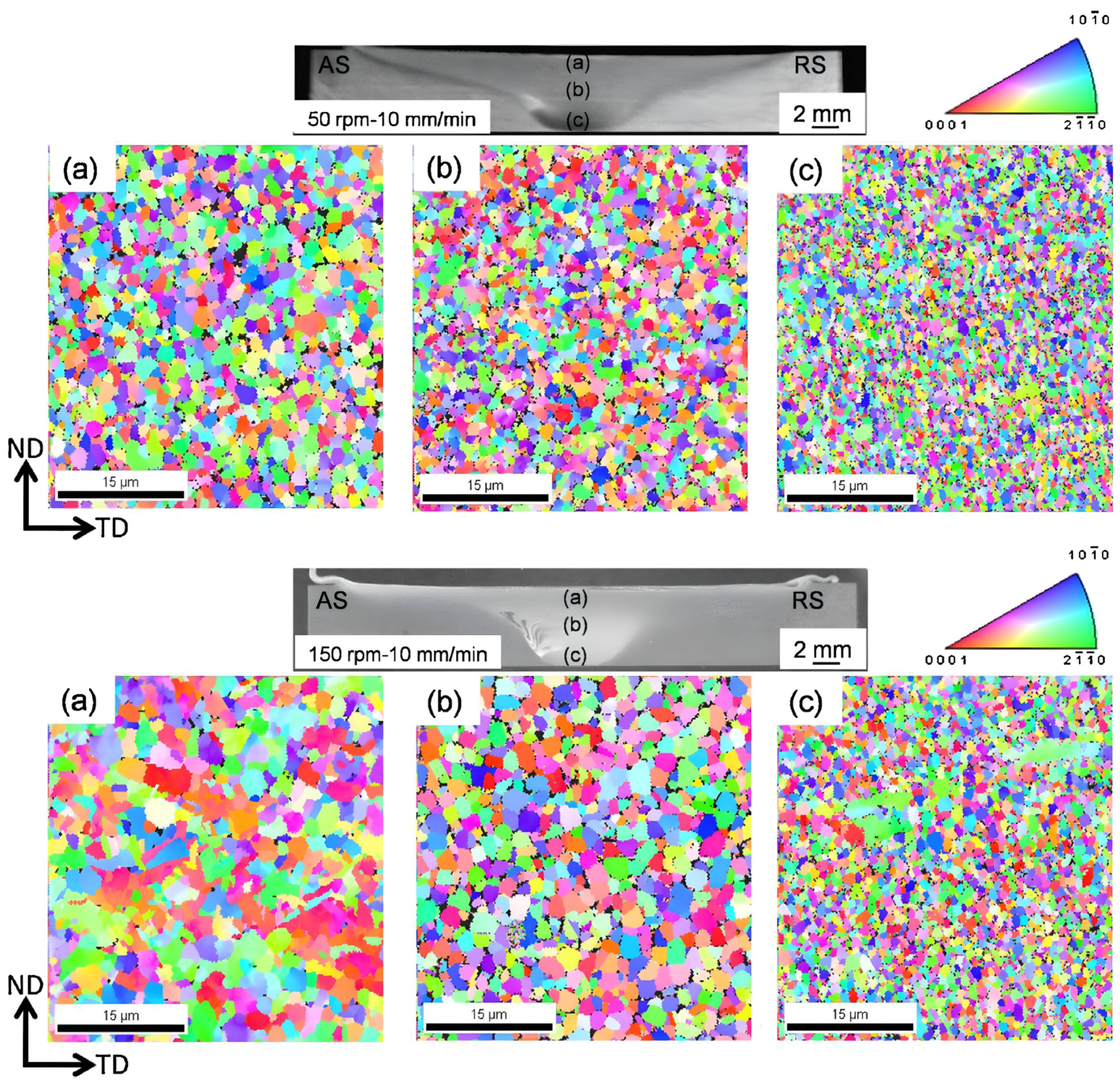
3.4.1. Butt FSW of Magnesium Alloys
3.4.2. Butt FSW of Copper Alloys
3.4.3. Butt FSW of Automotive Steels
3.4.4. Butt FSW of Stainless Steels
3.4.5. Butt FSW of Maraging Steels
3.4.6. Butt FSW of Titanium Alloys
3.4.7. Butt FSW of Nickel Alloys
4. Conclusions
4.1. Advancements in Tool Design and Materials
4.2. Process Parameter Optimization
4.3. Material Flow and Microstructure
4.4. Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wayne, T. Friction Welding. U.S. Patent 5,460,317, 24 October 1995. Available online: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/66/60/ad/5f784d0b8653b7/US5460317.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- The Welding Institute Last Time. Available online: https://www.twi-global.com (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Lunetto, V.; De Maddis, M.; Russo Spena, P. Pre-hole friction stir spot welding of dual-phase steels and comparison with resistance spot welding, conventional and pinless friction stir spot welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 129, 2333–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirandola, P.; Lunetto, V.; Novel, D.; Barozzi, M.; Bellutti, P.; De Maddis, M.; Russo Spena, P. Strength and microstructure of friction stir welded additively manufactured Scalmalloy® in as-welded and heat-treated conditions. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 97, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirandola, P.; Novel, D.; Perini, M.; Benedetti, M.; Lombardi, F.; Lunetto, V.; Spena, P.R. Microstructures and mechanical properties of friction stir welded additively manufactured Scalmalloy®. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 134, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, H.G.; Tufaro, L.N.; Leitão, C.; Rodrigues, D.M. Dissimilar Friction Stir Lap Welding of Aluminium to Steel: Influence of Alloy Type and Sheet Thickness on Strain Distribution and Failure Location. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, Z.; Ji, S.; Song, Q.; Gong, P.; Li, R. Effective joining of Mg/Ti dissimilar alloys by friction stir lap welding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 278, 116483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatsuka, K.; Yoshida, S.; Tsuchiya, A.; Nakata, K. Direct joining of carbon-fiber–reinforced plastic to an aluminum alloy using friction lap joining. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 73, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunetto, V.; Basile, D.; Razza, V.; Russo Spena, P. Active and Passive Filling Stir Repairing of AISI 304 Alloy. Metals 2024, 14, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunetto, V.; Catalano, A.R.; Priarone, P.C.; Settineri, L. Comments About the Human Health Risks Related to Additive Manufacturing. In Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 130, pp. 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, A.R.; Lunetto, V.; Priarone, P.C.; Settineri, L. A Survey on Energy Efficiency in Metal Wire Deposition Processes. In Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 155, pp. 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunnapu, C.; Kolli, M. Tool shoulder and pin geometry’s effect on friction stir welding: A study of literature. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 39, 1565–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunetto, V.; De Maddis, M.; Russo Spena, P. Similar and dissimilar lap friction stir welding of titanium alloys: On the elimination of the hook defect. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 3417–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abankar, M.; Lunetto, V.; De Maddis, M.; Russo Spena, P. Friction stir welding of additively manufactured A20X aluminum alloy: Welding process, mechanical properties, and microstructure. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 135, 4635–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, M.; De Maddis, M.; Razza, V.; Lunetto, V. Non-destructive detection and analysis of weld defects in dissimilar pulsed GMAW and FSW joints of aluminium castings and plates through 3D X-ray computed tomography. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 132, 2957–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, G.V.B.; Hanke, S.; Dos Santos, J.F.; Bergmann, L.; Reguly, A.; Strohaecker, T.R. Progress in friction stir welding of Ni alloys. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2017, 22, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, M.A.; Khan, Z.A.; Siddiquee, A.N. Review on underwater friction stir welding: A variant of friction stir welding with great potential of improving joint properties. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2018, 28, 193–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengran, Z.; Yufeng, S.; Yoshiaki, M.; Kohsaku, U.; Hidetoshi, F. Quasi-in-situ investigation into the microstructure and texture evolution of pure magnesium during friction stir welding. J. Magnes. Alloys 2020, 8, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ding, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Strain Accumulation and Microstructural Evolution During Friction Stir Welding of Pure Magnesium. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 603464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiuzuli, F.R.; Batistão, B.F.; Bergmann, L.A.; de Alcântara, N.G.; dos Santos, J.F.; Klusemann, B.; Gargarella, P. Effect of the gap width in AZ31 magnesium alloy joints obtained by friction stir welding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 5297–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wu, C.; Shi, L. Multiphase field simulation of dynamic recrystallization during friction stir welding of AZ31 magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 20764–20779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Han, P.; Qiao, K.; Li, T.; Wang, K.; Cai, J.; Wang, L. Effect of the rotation rate on the low-cycle fatigue behavior of friction-stir welded AZ31 magnesium alloy. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 228, 106925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jiang, X.; Chen, S.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, H.; Bai, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Li, X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of electrically assisted friction stir welded AZ31B alloy joints. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 43, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Sharma, V.; Bhadauria, S.S. Effect of tool tilt angle on weld joint strength and microstructural characterization of double-sided friction stir welding of AZ31B magnesium alloy. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Chohan, J.S.; Boparai, K.S. Evaluating the microstructural characteristics in friction stir welding of magnesium AZ61a alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 48, 1762–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Morisada, Y.; Fujii, H. Effect of Ca addition on the microstructure and the mechanical properties of asymmetric double-sided friction stir welded AZ61 magnesium alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2020, 8, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Singh, G.; Singh, H. Microstructural and Mechanical Behaviour Evaluation of Mg-Al-Zn Alloy Friction Stir Welded Joint. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 2020, 17, 8150–8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Morisada, Y.; Fujii, H.; Wang, J.-Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded duplex Mg–Li alloy LZ91. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 773, 138730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.K.; Pal, S.; Das, B.; Shi, Q. Fabrication and effect of Mg–Zn solid solution via Zn foil interlayer alloying in FSW process of magnesium alloy. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2020, 20, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyril Joseph Daniel, S.; Lakshminarayanan, A.K. Comparative Study of Friction Stir Welding and Underwater Friction Stir Welding on Magnesium ZE41 Alloy; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Xia, D.; Huang, G.; Tang, A.; Jiang, B.; Pan, F. Improving performance of friction stir welded AZ31/AM60 dissimilar joint by adjusting texture distribution and microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 778, 139088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, B.; Tang, A.; Pan, F. Characterization of newly developed friction stir-arc welding method for AM60/AZ31 dissimilar Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 800, 140320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthapandian, M.; Pugazhenhi, R.; Gnanavel, C. Study the impaction tool speed on the friction stir welding of magnesium alloys plates. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 69, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.K.; Dubey, A.K. Study of Weld Characteristics in Friction Stir Welding of Dissimilar Mg-Al-Zn Magnesium Alloys under Varying Welding Conditions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 7690–7703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Feng, R.-N.; Guo, W.-F.; Song, Q.-N.; Bao, Y.-F. Effect of Zener–Hollomon Parameter on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Copper Subjected to Friction Stir Welding. Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett. 2020, 33, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ueji, R.; Fujii, H. Dynamic and static change of grain size and texture of copper during friction stir welding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 232, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.J.; Liu, H.J.; Cui, F. Effect of welding speed on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded copper. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 3937–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, M.A.; Nitu, E.L.; Iordache, D.M.; Badulescu, C. Study on the influence of technological parameters on the friction stir butt welding process of pure copper plates. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 968, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubi, M.A.; Anjabin, N. Friction stir welding of severely deformed copper sheets: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlot, P.; Singh, A.K.; Badheka, V.J.; Arora, A. Friction Stir Welding of Copper: Numerical Modeling and Validation. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.M.; Fan, P.L.; Lin, C.H. Experimental study on Friction Stir Welding of copper metals. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 1667–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrar, G.; Shuaib, A.N.; Al-Badour, F.A.; Merah, N.; Mahgoub, A.K. Friction Stir Butt Welding of Commercially Pure Copper Plates. In Proceedings of the ASME 2014 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–20 November 2014; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 2A Advanced Manufacturing, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, S.; Inagaki, K.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Microstructural evolution of pure copper during friction-stir welding. Philos. Mag. 2015, 95, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, A.A.; Shirazi, A. Effects of different friction stir welding conditions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of copper plates. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2016, 23, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machniewicz, T.; Nosal, P.; Korbel, A.; Hebda, M. Effect of FSW Traverse Speed on Mechanical Properties of Copper Plate Joints. Materials 2020, 13, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashazadeh, H.; Teimournezhad, J.; Masoumi, A. Numerical investigation on the mechanical, thermal, metallurgical and material flow characteristics in friction stir welding of copper sheets with experimental verification. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Song, Q.-N.; Bao, Y.-F. Improvement of microstructure and mechanical properties of C44300 tin brass subjected to double-pass rapid cooling friction stir welding. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 834, 155052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, S.; Inagaki, K.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Development of grain structure during friction-stir welding of Cu–30Zn brass. Philos. Mag. 2014, 94, 3137–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ueji, R.; Fujii, H. Enhanced mechanical properties of 70/30 brass joint by rapid cooling friction stir welding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 610, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ueji, R.; Fujii, H. Enhanced mechanical properties of 70/30 brass joint by multi-pass friction stir welding with rapid cooling. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2015, 20, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Chen, L.; Feng, R.N.; Song, Q.N.; Bao, Y.F. Recrystallization of Cu-30Zn brass during friction stir welding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 3746–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meran, C. The joint properties of brass plates by friction stir welding. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarzadeh, A.; Barenji, R.V.; Khalili, V.; Güleryüz, G. Optimizing the friction stir welding of the α/β brass plates to obtain the highest strength and elongation. Vacuum 2019, 159, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, A.; Sik, A.; Cevik, B.; Ozer, M. The effect of friction stir welding parameters on microstructure and fatigue strength of CuZn37 brass alloys. Met. Mater. 2017, 55, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xie, G.M.; Ma, Z.Y.; Geng, L. Effects of Friction Stir Welding Parameters on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Brass Joints. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamikhah, A.; Abbasi, A.; Atefat, A.; Givi, M.K.B. Effect of tool pin profile on friction stir butt welding of high-zinc brass (CuZn40). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 71, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Chen, L.; Gu, B.; Ren, Z.; Song, Q.; Bao, Y. Heterogeneous structure-induced strength and ductility synergy of α-brass subjected to rapid cooling friction stir welding. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2021, 31, 3785–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, F.; Yu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, D.; He, W.; Huang, Y. Microstructural Characteristics and Mechanical Properties of Friction-Stir-Welded CuSn6 Tin Bronze. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 4477–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Jiang, Z.H.; Zhao, D.G.; Yu, M.R.; Zhao, H.Y.; Huang, Y.X.; Song, X.G. Effect of Rotation Speed on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction-Stir-Welded CuSn6 Tin Bronze. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 5581–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizi, M.S.; Kokabi, A.H. Microstructure evolution and microhardness of friction stir welded cast aluminum bronze. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, S.; Senthamaraikannan, S.; Jayaprakasham, S.; Madiq, A.R. Effect of Process Parameters on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Cast Nickel Aluminum Bronze Alloy (C95800). Mater. Res. 2018, 21, 139277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; Sampathkumar, S.; Sudha, J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Exothermic-Reaction-Assisted Friction-Stir-Welded Nickel-Aluminum Bronze Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 2256–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükömeroğlu, T.; Şentürk, E.; Kara, L.; İpekoğlu, G.; Çam, G. Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Nickel-Aluminum Bronze (NAB) Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Qin, Z.; Rong, C.; Shi, W.; Wang, S. The Preliminary Exploration of Micro-Friction Stir Welding Process and Material Flow of Copper and Brass Ultra-Thin Sheets. Materials 2020, 13, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, M. Investigation of structure and mechanical properties of copper-brass plates joined by friction stir welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, C.; Tharwan, M.; Kumar, P.M.; Gebreyohannes, D.T. Microstructural and Mechanical Characteristics of Pure-Cu/brass Dissimilar Joints Welded by Friction Stir Welding Using Various Process Parameters. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2234352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, R.; Thirumalaisamy, N. Experimental and numerical analysis of friction stir welded dissimilar copper and bronze plates. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Cui, L.; Tsuji, N.; Maeda, M.; Nakata, K.; Nogi, K. Friction stir welding of carbon steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 429, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Cui, L.; Nakata, K.; Nogi, K. Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Carbon Steel Joints—Friction Stir Welding with and without Transformation. Weld. World 2008, 52, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Ueji, R.; Takada, Y.; Kitahara, H.; Tsuji, N.; Nakata, K.; Nogi, K. Friction Stir Welding of Ultrafine Grained Interstitial Free Steels. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Kang, M.; Yi, S.; Hyun, S.; Kim, C. Comprehensive Analysis of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction-Stir-Welded Low-Carbon High-Strength Steels with Tensile Strengths Ranging from 590 MPa to 1.5 GPa. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, I.J. Effect of process parameters on optimum welding condition of DP590 steel by friction stir welding. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2014, 28, 5143–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, M.P.; Pew, J.; Nelson, T.W.; Li, M. Comparison of formability of friction stir welded and laser welded dual phase 590 steel sheets. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2006, 11, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükömeroğlu, T.; Aktarer, S.M.; Çam, G. Investigation of mechanical and microstructural properties of friction stir welded dual phase (DP) steel. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 629, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudiniya, M.; Kokabi, A.H.; Kheirandish, S.; Kestens, L.A.I. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded ferrite-martensite DP700 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 737, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudiniya, M.; Kokabi, A.H.; Goodarzi, M.; Kestens, L.A.I. Friction stir welding of advanced high strength dual phase steel: Microstructure, mechanical properties and fracture behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 769, 138490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudiniya, M.; Kokabi, A.H.; Goodarzi, M.; Kestens, L.A.I. The Effect of Improved Cooling on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir-Welded Advanced High-Strength Dual-Phase Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 92, 2000253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, C.; Song, J. An Evaluation of Global and Local Tensile Properties of Friction-Stir Welded DP980 Dual-Phase Steel Joints Using a Digital Image Correlation Method. Materials 2015, 8, 8424–8436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, R.; Dinaharan, I.; Kumar, R.; Akinlabi, E.T. Microstructure and mechanical characterization of friction stir welded high strength low alloy steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 687, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragu Nathan, S.; Balasubramanian, V.; Malarvizhi, S.; Rao, A.G. Effect of Tool Shoulder Diameter on Stir Zone Characteristics of Friction Stir Welded HSLA Steel Joints. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2016, 69, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragu Nathan, S.; Balasubramanian, V.; Malarvizhi, S.; Rao, A. Effect of D/T P ratio on stir zone characteristics of friction stir-welded high-strength low-alloy steel plates. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2018, 232, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.J.; Bhatti, A.R.; Steuwer, A.; Johnson, R.; Altenkirch, J.; Withers, P.J. Friction Stir Welding in HSLA-65 Steel: Part I. Influence of Weld Speed and Tool Material on Microstructural Development. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 2342–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuwer, A.; Barnes, S.J.; Altenkirch, J.; Johnson, R.; Withers, P.J. Friction Stir Welding of HSLA-65 Steel: Part II. The Influence of Weld Speed and Tool Material on the Residual Stress Distribution and Tool Wear. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 2356–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaysultanov, D.; Raimov, K.; Stepanov, N.; Zherebtsov, S. Friction Stir Welding of a TRIP Fe49Mn30Cr10Co10C1 High Entropy Alloy. Metals 2020, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.; Mondal, M.; Hong, S.-T.; Lee, K.-J.; Chattopadhyay, K. Microstructure and mechanical properties evaluation of friction stir welded boron steel. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzolin, R.H.; Francisco, B.R.; da Silva, E.P.; Pereira, V.F.; Ramirez Londono, A.J.; Maluf, O.; Pinto, H.C. Dissimilar Friction Stir Welding of HSLA Steel to Austenitic High-Mn TRIP Steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 879, 2306–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Fujii, H.; Lee, S.-J. Corrosion Behavior and Microstructure of Stir Zone in Fe-30Mn-3Al-3Si Twinning-Induced Plasticity Steel after Friction Stir Welding. Metals 2020, 10, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Ushioda, K.; Fujii, H. Evaluation of stacking-fault energy in Fe-Mn based twinning-induced plasticity steels after friction stir welding. Mater. Charact. 2019, 147, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Sun, Y.; Fujii, H. Stacking-fault energy, mechanical twinning and strain hardening of Fe-18Mn-0.6C-(0, 1.5)Al twinning-induced plasticity steels during friction stir welding. Acta Mater. 2018, 148, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Pankaj, P.; Biswas, P.; Kore, S.D.; Rao, A.G. Tool performance evaluation of friction stir welded shipbuilding grade DH36 steel butt joints. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 1989–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoussawi, M.; Smith, A.J.; Faraji, M.; Cater, S. Segregation of Mn, Si, Al, and Oxygen During the Friction Stir Welding of DH36 Steel. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2017, 6, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-moussawi, M.; Smith, A.J.; Young, A.; Cater, S.; Faraji, M. Modelling of friction stir welding of DH36 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toumpis, A.; Galloway, A.; Cater, S.; McPherson, N. Development of a process envelope for friction stir welding of DH36 steel—A step change. Mater. Des. 2014, 62, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, J.F.; Xie, G.M.; Wu, L.H.; Zhang, H.; Xue, P.; Ni, D.R.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Evolution mechanisms of microstructure and mechanical properties in a friction stir welded ultrahigh-strength quenching and partitioning steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 102, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, H.; An, X.H.; Wu, L.H.; Xue, P.; Zhang, Q.C.; Ni, D.R.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Achieving equal strength joint to parent metal in a friction stir welded ultra-high strength quenching and partitioning steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 793, 139979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, T.; Iwamoto, Y.; Maruko, T.; Fujii, H. Friction stir welding of 304 stainless steel using Ir based alloy tool. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2012, 17, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh, M.; Emami, S.; Saeid, T. Influence of welding speed on microstructure formation in friction-stir-welded 304 austenitic stainless steels. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.; Das, C.R.; Divya, M.; Albert, S.K.; Pal, T.K. Friction Stir Welding: A Solution to Avoid Weld Cracking in Borated Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 7765–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaine, A.H.; de Alcântara, N.G. Prediction of Friction Stir Welding defect-free joints of AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel through axial force profile understanding. Mater. Res. 2014, 17, 1324–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiquee, A.N.; Pandey, S. Experimental investigation on deformation and wear of WC tool during friction stir welding (FSW) of stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 73, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiquee, A.N.; Pandey, S.; Khan, N.Z. Friction Stir Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel: A Study on Microstructure and Effect of Parameters on Tensile Strength. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.C.; Nelson, T.W. In-situ material flow pattern around probe during friction stir welding of austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.C.; Nelson, T.W. In-situ grain structure and texture evolution during friction stir welding of austenite stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2017, 115, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naskar, A.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Raja, K.S.; Charit, I.; Darsell, J.; Jana, S. Room temperature corrosion behaviour of plastically deformed AISI 304 stainless steel by friction stir welding in neutral and acidified chloride solutions. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Shen, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhang, W.; Guan, W. Microstructures and mechanical properties of thin 304 stainless steel sheets by friction stir welding. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashi Kumar, S.; Murugan, N.; Ramachandran, K.K. Effect of friction stir welding on mechanical and microstructural properties of AISI 316L stainless steel butt joints. Weld. World 2019, 63, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Murugan, N.; Ramachandran, K.K. Effect of tool tilt angle on weld joint properties of friction stir welded AISI 316L stainless steel sheets. Measurement 2020, 150, 107083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.J.; Mironov, S.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H.; Park, S.H.C.; Hirano, S. Grain Structure Development During Friction Stir Welding of Single-Crystal Austenitic Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 3157–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethiraj, N.; Sivabalan, T.; Sivakumar, B.; Vignesh Amar, S.; Vengadeswaran, N.; Vetrivel, K. Effect of Tool Rotational Speed on the Tensile and Microstructural Properties of Friction Stir Welded Different Grades of Stainless Steel Joints. Int. J. Eng. 2020, 33, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Dou, W.; Pittman, C.C.; Zhou, E.; Xu, D.; Li, H.; Lekbach, Y.; Wang, F. Microbiologically influenced corrosion behavior of friction stir welded S32654 super austenitic stainless steel in the presence of Acidithiobacillus caldus SM-1 biofilm. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Feng, H.; Han, P.; Li, J. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of friction stir welding super-austenitic stainless steel S32654. Mater. Des. 2017, 118, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayanan, A.K.; Balasubramanian, V. Process Parameters Optimisation for Friction Stir Welding of AISI 409M Grade Ferritic Stainless Steel. Exp. Tech. 2013, 37, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Du, B.; Li, H. Numerical and experimental investigation on friction stir welding of Ti- and Nb-modified 12% Cr ferritic stainless steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 59, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, G.d.Q.; Silva, C.C.; Motta, M.F.; Miranda, H.C.; Farias, J.P.; Bergmann, L.A.; dos Santos, J.F. Influence of rotation speed and axial force on the friction stir welding of AISI 410S ferritic stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 262, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Bang, H.S.; Bang, H.S.; Kaplan, A.F.H. Joint properties of ultra thin 430M2 ferritic stainless steel sheets by friction stir welding using pinless tool. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 243, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Bang, H.-S.; Ro, C.-S.; Bang, H.-S. Influence of preheating source on mechanical properties and welding residual stress characteristics in ultra thin ferritic stainless steel hybrid friction stir welded joints. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 4, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, M.; Liu, H.; Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Yang, G.-J.; Lou, Z.-J.; Mehboob, G. Microstructure evolution during friction stir welding of 1Cr11Ni2W2MoV martensitic stainless steel at different tool rotation rates. Mater. Charact. 2021, 182, 111561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, M.; Liu, H.; Yang, G.J.; Ahmed, M.M.Z. Friction stir welding of 1cr11ni2w2mov martensitic stainless steel: Numerical simulation based on coupled eulerian lagrangian approach supported with experimentalwork. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, A.I.; García, M.; Pena, G.; Sotelo, J.; Verdera, D. Evaluation of an induction-assisted friction stir welding technique for super duplex stainless steels. Surf. Interface Anal. 2014, 46, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammood, A.S.; Esmailzadeh, M.; Hosseini, S.N.; Karimi, S.; Calliari, I.; Pezzato, L.; Brittain, R. Effect of Friction Stir Welding Parameters on Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of 2101 Duplex Stainless Steel in Simulated Body Fluid. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 10, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.F.d.A.; López, E.A.T.; da Fonseca, E.B.; Ramirez, A.J. Friction stir welding of duplex and superduplex stainless steels and some aspects of microstructural characterization and mechanical performance. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.F.d.A.; Torres, E.A.; Ramirez, A.J. Friction stir welding of duplex stainless steels. Weld. Int. 2018, 32, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, H. Effect of Rotation Speed on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction-Stir-Welded 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5176536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.; Saeid, T.; Abdollah-zadeh, A. Effect of friction stir welding parameters on the microstructure and microtexture evolution of SAF 2205 stainless steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 810, 151797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeid, T.; Abdollah-zadeh, A.; Assadi, H.; Malek Ghaini, F. Effect of friction stir welding speed on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 496, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, C.; Miao, S.; Wang, C.; Yi, Y. The influence of welding speed on friction stir welded of duplex stainless steel. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 677, 022124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca, E.B.; Santos, T.F.A.; Button, S.T.; Ramirez, A.J. Physical Simulation of a Duplex Stainless Steel Friction Stir Welding by the Numerical and Experimental Analysis of Hot Torsion Tests. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 4543–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, I.J.; Silva, F.J.; Santos, T.F.A. Rapid precipitation of intermetallic phases during isothermal treatment of duplex stainless steel joints produced by friction stir welding. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 820, 153170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Abdelazem, K.A.; El-Sayed Seleman, M.M.; Alzahrani, B.; Touileb, K.; Jouini, N.; El-Batanony, I.G.; Abd El-Aziz, H.M. Friction Stir Welding of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel: Feasibility of Butt Joint Groove Filling in Comparison to Gas Tungsten Arc Welding. Materials 2021, 14, 4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Han, P. Effect of the Rotation Speed during Friction Stir Welding on the Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of SAF 2707 Hyper Duplex Stainless Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2018, 89, 1700425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahl Sarmadi, M.; Shamanian, M.; Edris, H.; Behjat, A.; Mohtadi-Bonab, M.A.; Szpunar, J. Effect of Friction Stir Welding on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2021, 10, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.; Sadeghi-Kanani, S.; Saeid, T.; Khan, F. Dissimilar friction stir welding of AISI 430 ferritic and AISI 304L austenitic stainless steels. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2020, 20, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Shen, Y. Friction stir welding of dissimilar stainless steels: Evaluation of flow pattern, microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 056510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, H. Dissimilar Friction Stir Welding of Austenitic and Duplex Stainless Steel: Effect of Material Position and Tool Offset. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 91, 2000156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir welds in austenitic-duplex stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 787, 139499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoro, M.C.; Pereira, V.F.; Mei, P.R.; Ramirez, A.J. Dissimilar Friction Stir Welding Between UNS S31603 Austenitic Stainless Steel and UNS S32750 Superduplex Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, S.D.; Reddy, G.M.; Pandey, S. Effect of tool material and process parameters on friction stir weld formation of maraging steel. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 8, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, S.D.; Paradkar, A.G.; Reddy, G.M.; Pandey, S. Stress corrosion cracking behaviour of gas tungsten arc and friction stir maraging steel welds. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 26968–26973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, S.D.; Madhusudhan Reddy, G.; Pandey, S. Friction stir welding of maraging steel (Grade-250). Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Sun, Y.; Kato, H.; Nakata, K. Investigation of welding parameter dependent microstructure and mechanical properties in friction stir welded pure Ti joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3386–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H.; Park, S.H.C.; Hirano, S. Stir zone microstructure of commercial purity titanium friction stir welded using pcBN tool. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 488, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshad Seighalani, K.; Besharati Givi, M.K.; Nasiri, A.M.; Bahemmat, P. Investigations on the Effects of the Tool Material, Geometry, and Tilt Angle on Friction Stir Welding of Pure Titanium. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2010, 19, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Nakata, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Liao, J. Friction stir welding of pure titanium lap joint. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2010, 15, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Nakata, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Liao, J. Grain Orientation and Texture Evolution in Pure Titanium Lap Joint Produced by Friction Stir Welding. Mater. Trans. 2010, 51, 2063–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.C.; Liu, H.; Nakata, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Liao, J. Investigation on friction stir welding parameter design for lap joining of pure titanium. In Proceedings of the 1st International Joint Symposium on Joining and Welding, Osaka, Japan, 6–8 November 2013; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Gao, F.; Yu, Y.; Vairis, A. Strengthening mechanism of friction stir welded alpha titanium alloy specially designed T-joints. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 55, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Guo, Y.; Yang, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, W. Fatigue properties of friction stir welded joint of titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 793, 139819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Liu, H.; Jiang, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, L. Eliminating the cavity defect and improving mechanical properties of TA5 alloy joint by titanium alloy supporting friction stir welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 69, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, W. Fracture toughness of friction stir welded TA5 titanium alloy joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 776, 138962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirov, A.I.; Eliseev, A.A.; Beloborodov, V.A.; Chumaevskii, A.V.; Gurianov, D.A. Formation of α’ titanium welds by friction stir welding. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1611, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, H.J.; Liu, Q.W. Effect of process parameters on stir zone microstructure in Ti–6Al–4V friction stir welds. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, H.J.; Liu, Q.W. Effect of rotation speed on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V friction stir welded joints. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 2631–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Fujii, H.; Iwata, Y.; Sun, Y.S.; Morisada, Y. Flexible control of the microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded Ti–6Al–4V joints. Mater. Des. 2013, 46, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Ueji, R.; Fujii, H. Effect of rotation rate on microstructure and texture evolution during friction stir welding of Ti–6Al–4V plates. Mater. Charact. 2015, 106, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Eliminating the tearing defect in Ti-6Al-4V alloy joint by back heating assisted friction stir welding. Mater. Lett. 2017, 188, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wen, Q.; Ji, S.; Ma, L.; Lv, Z. Effect of Temperature Field on Formation of Friction Stir Welding Joints of Ti–6Al–4V Titanium Alloy. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2017, 36, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, A.; Monajati, H.; Khodabandeh, A.; Fesharaki, M.H.; Champliaud, H.; Jahazi, M. Local mechanical properties, microstructure, and microtexture in friction stir welded Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 749, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shen, Y.; Hou, W.; Qi, Y. Friction stir welding of Ti-6Al-4V alloy: Friction tool, microstructure, and mechanical properties. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 58, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, F.; Shen, Y. Effect of Welding Parameters on Friction Stir Welded Ti–6Al–4V Joints: Temperature, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Metals 2020, 10, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Li, J.; Shen, Y.; Hou, W. Simulation and Experimental Study on Temperature and Flow Field in Friction Stir Welding of TC4 Titanium Alloy Process. Mater. Trans. 2020, 61, 2378–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L. Joint formation and mechanical properties of back heating assisted friction stir welded Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 113, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, S.; Amirov, A.; Chumaevskiy, A.; Savchenko, N.; Rubtsov, V.E.; Ivanov, A.; Moskvichev, E.; Kolubaev, E. Friction Stir Welding of Ti-6Al-4V Using a Liquid-Cooled Nickel Superalloy Tool. Technologies 2022, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H.; Park, S.H.C.; Hirano, S. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V friction stir welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 485, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffa, G.; Fratini, L.; Micari, F.; Settineri, L. On the choice of tool material in friction stir welding of titanium alloys. Proc. NAMRI/SME 2012, 40, 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Buffa, G.; Fratini, L.; Micari, F. Mechanical and microstructural properties prediction by artificial neural networks in FSW processes of dual phase titanium alloys. J. Manuf. Process. 2012, 14, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffa, G.; Ducato, A.; Fratini, L. FEM based prediction of phase transformations during Friction Stir Welding of Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 581, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.; Ramulu, M. Surface Residual Stresses in Ti-6Al-4V Friction Stir Welds: Pre- and Post-Thermal Stress Relief. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 3263–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gili, A.B.; Hattingh, D.G.; Bernard, D. Relationship between tool tilt angle, shoulder plunge depth and process energy input for pin-less friction stir welded thin Ti-6Al-4V sheets. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 655, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kumar, B.; Jha, K.; Astarita, A.; Squillace, A.; Franchitti, S.; Arora, A. Friction stir welding of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V: Microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 277, 116433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Ueji, R.; Fujii, H. Effect of initial microstructure on Ti–6Al–4V joint by friction stir welding. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Ueji, R.; Fujii, H. Microstructure and texture distribution of Ti–6Al–4V alloy joints friction stir welded below β-transus temperature. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 229, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.D.; Ramulu, M. Material flow during friction stir welding of Ti-6Al-4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 218, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilchak, A.L.; Tang, W.; Sahiner, H.; Reynolds, A.P.; Williams, J.C. Microstructure Evolution during Friction Stir Welding of Mill-Annealed Ti-6Al-4V. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffa, G.; Fratini, L.; Schneider, M.; Merklein, M. Micro and macro mechanical characterization of friction stir welded Ti–6Al–4V lap joints through experiments and numerical simulation. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 2312–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Li, Z. Reducing the Hook Defect of Friction Stir Lap Welded Ti-6Al-4V Alloy by Slightly Penetrating into the Lower Sheet. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, K.; Ramulu, M.; Cantrell, A.; Sanders, D. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Dissimilar Titanium Alloys: TIMET-54M and ATI-425. Metals 2016, 6, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Fujii, H.; Tsumura, T.; Nakata, K. Friction stir welding of Inconel alloy 600. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 5376–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Tsumura, T.; Nakata, K. Development of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Laser-FSW Hybrid Welded Inconel 600. Mater. Trans. 2009, 50, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Fujii, H.; Nakata, K. Effect of welding speed on microstructural and mechanical properties of friction stir welded Inconel 600. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3972–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Fujii, H.; Nakata, K. Evaluation of Grain Refinement and Mechanical Property on Friction Stir Welded Inconel 600. Mater. Trans. 2009, 50, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.S.; Arkom, P.; Kokawa, H.; Nelson, T.W.; Steel, R.J. Effect of microstructure on properties of friction stir welded Inconel Alloy 600. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 477, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, K.; Chowdhury, I.; Banerjee, A.; Mondal, A.K.; Bose, D. Analysis of suitability of WC tool for joining Inconel 601 alloy by electric assisted friction stir welding. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 60, 2093–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Nakata, K. Mechanical Properties of Friction-Stir-Welded Inconel 625 Alloy. Mater. Trans. 2009, 50, 2498–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Nakata, K. Effect of precipitation on post-heat-treated Inconel 625 alloy after friction stir welding. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 2942–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, S.; Lemos, G.V.B.; Bergmann, L.; Martinazzi, D.; dos Santos, J.F.; Strohaecker, T.R. Degradation mechanisms of pcBN tool material during Friction Stir Welding of Ni-base alloy 625. Wear 2017, 376–377, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Nakata, K. Microstructural and mechanical properties of friction-stir-welded and post-heat-treated Inconel 718 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 505, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, W.Y. Precipitates formation and its impact in friction stir welded and post-heat-treated Inconel 718 alloy. MRS Proc. 2011, 1363, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Pankaj, P.; Biswas, P. Friction Stir Welding of Inconel-718 Alloy Using a Tungsten Carbide Tool. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 2086–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Biswas, P. High-Frequency Induction-Assisted Hybrid Friction Stir Welding of Inconel 718 Plates. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2022, 144, 041014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.; Biswas, P. Temperature and Stress Evaluation during Friction Stir Welding of Inconel 718 Alloy Using Finite Element Numerical Simulation. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 2002–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.; Biswas, P. Thermomechanical analysis of induction assisted friction stir welding of Inconel 718 alloy: A finite element approach. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2022, 199, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Wynne, B.P.; Martin, J.P. Effect of friction stir welding speed on mechanical properties and microstructure of nickel based super alloy Inconel 718. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2013, 18, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.; Mondal, M.; Hong, S.-T.; Lee, J.-W.; Cho, H.-H. Texture and precipitation behavior of friction stir welded Inconel 825 alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Chung, Y.D.; Nakata, K. Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir lap jointed Monel 400 and Inconel 600. Met. Mater. Int. 2013, 19, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Tiwari, A.; Shukla, M.K.; Rose, A.R. Analysis of Tools used in Friction Stir Welding process. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2018, 8, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ji, S.; Xiong, L. Fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy friction stir welding joint obtained under rapid cooling condition. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 36, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Ding, Y.; Gerlich, A.P. Advances in friction stir spot welding. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2020, 45, 457–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, C.; Nelson, T. Friction stir welding of ferrous and nickel alloys. In Friction Stir Welding and Processing; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2007; pp. 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.H.; Wang, D.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Tool wear and its effect on microstructure and properties of friction stir processed Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 146, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karna, S.; Cheepu, M.; Venkateswarulu, D.; Srikanth, V. Recent Developments and Research Progress on Friction Stir Welding of Titanium Alloys: An Overview. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 330, 012068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, S.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Friction-stir welding and processing of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Su, J.; Mishra, R.S.; Xu, R.; Baumann, J.A. Tool wear mechanisms in friction stir welding of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Wear 2014, 321, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, A.; Fesharaki, M.; Khodabandeh, A.; Jahazi, M. Tool Wear Characteristics and Effect on Microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V Friction Stir Welded Joints. Metals 2016, 6, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shen, Y.; Hu, W.; Luo, L. Surface modification of Ti–6Al–4V alloy via friction-stir processing: Microstructure evolution and dry sliding wear performance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 239, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.; Ramulu, M. Effect of process conditions on superplastic forming behaviour in Ti–6Al–4V friction stir welds. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Yan, D. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Rapidly Cooled Friction Stir Welded Ti-6Al-4V Alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 4244–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Guo, S.; Duan, R.H.; Luo, Z.A.; Chen, J.; Ma, Z.Y.; Xie, G.M. Achievement of high strength and plasticity product of the nugget zone in friction stir welded high-Mn steel via controlling stacking fault energy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 862, 144427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lunetto, V.; De Maddis, M.; Lombardi, F.; Russo Spena, P. A Review of Friction Stir Welding of Industrial Alloys: Tool Design and Process Parameters. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9020036
Lunetto V, De Maddis M, Lombardi F, Russo Spena P. A Review of Friction Stir Welding of Industrial Alloys: Tool Design and Process Parameters. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2025; 9(2):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9020036
Chicago/Turabian StyleLunetto, Vincenzo, Manuela De Maddis, Franco Lombardi, and Pasquale Russo Spena. 2025. "A Review of Friction Stir Welding of Industrial Alloys: Tool Design and Process Parameters" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 9, no. 2: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9020036
APA StyleLunetto, V., De Maddis, M., Lombardi, F., & Russo Spena, P. (2025). A Review of Friction Stir Welding of Industrial Alloys: Tool Design and Process Parameters. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 9(2), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9020036









