Influence of the Production Process on the Binding Mechanism of Clinched Aluminum Steel Mixed Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
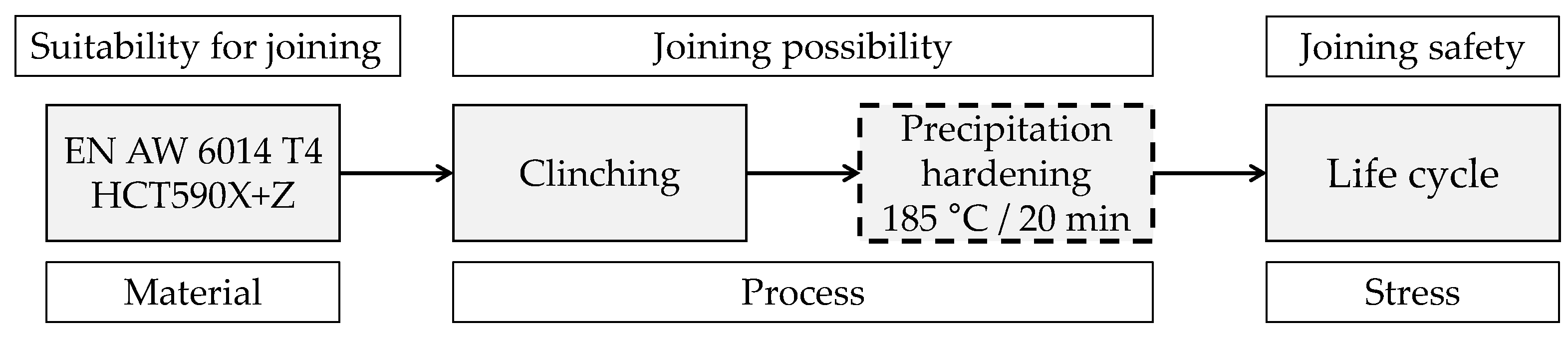
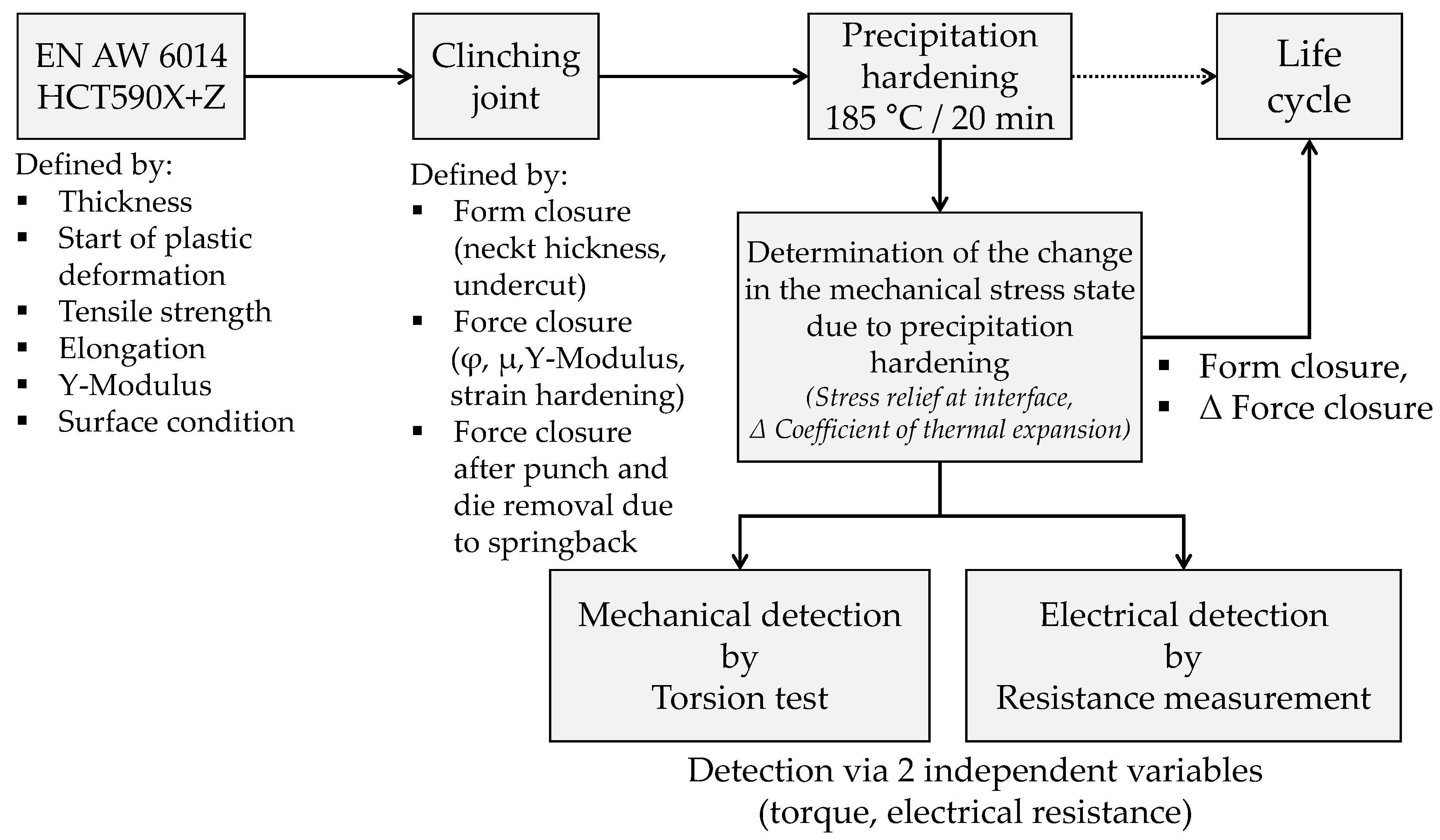
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Design of Joints
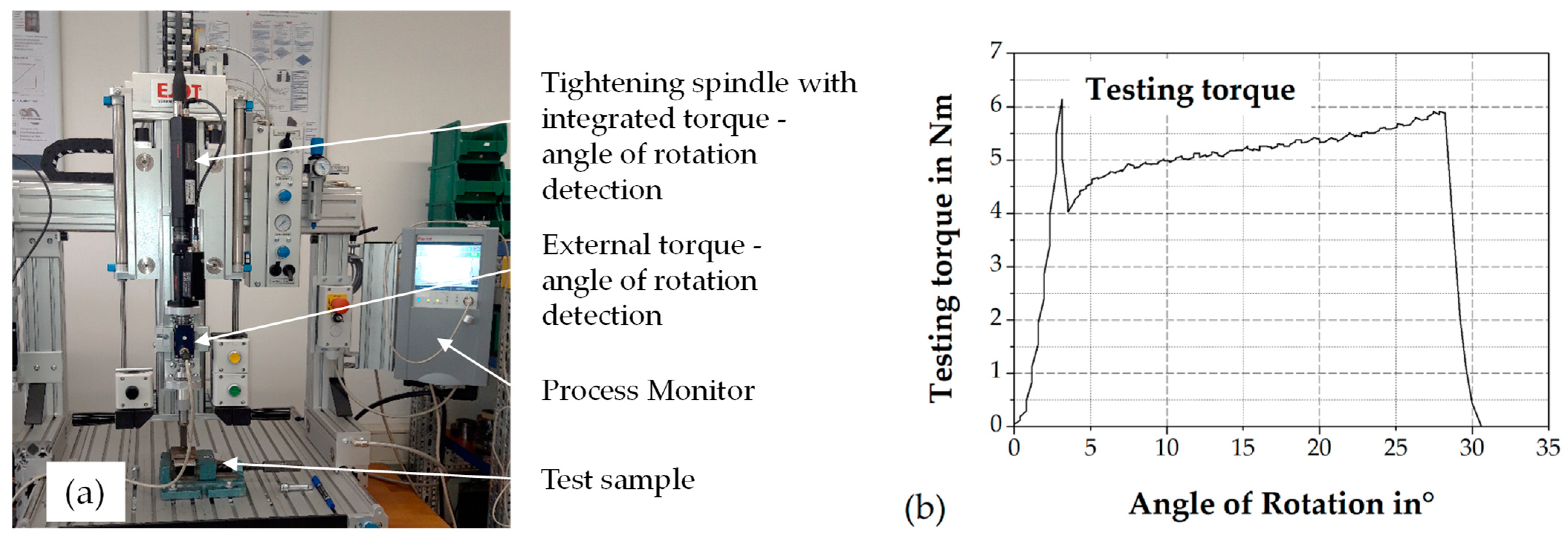
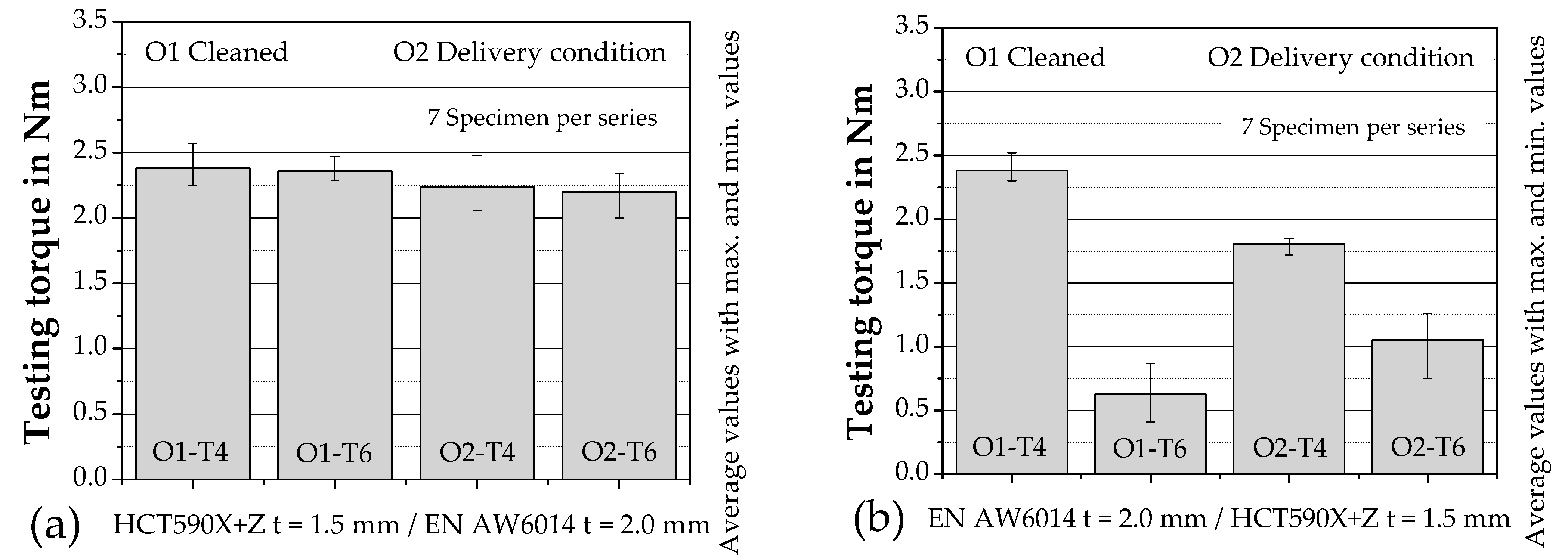
2.3. Mechanical Test
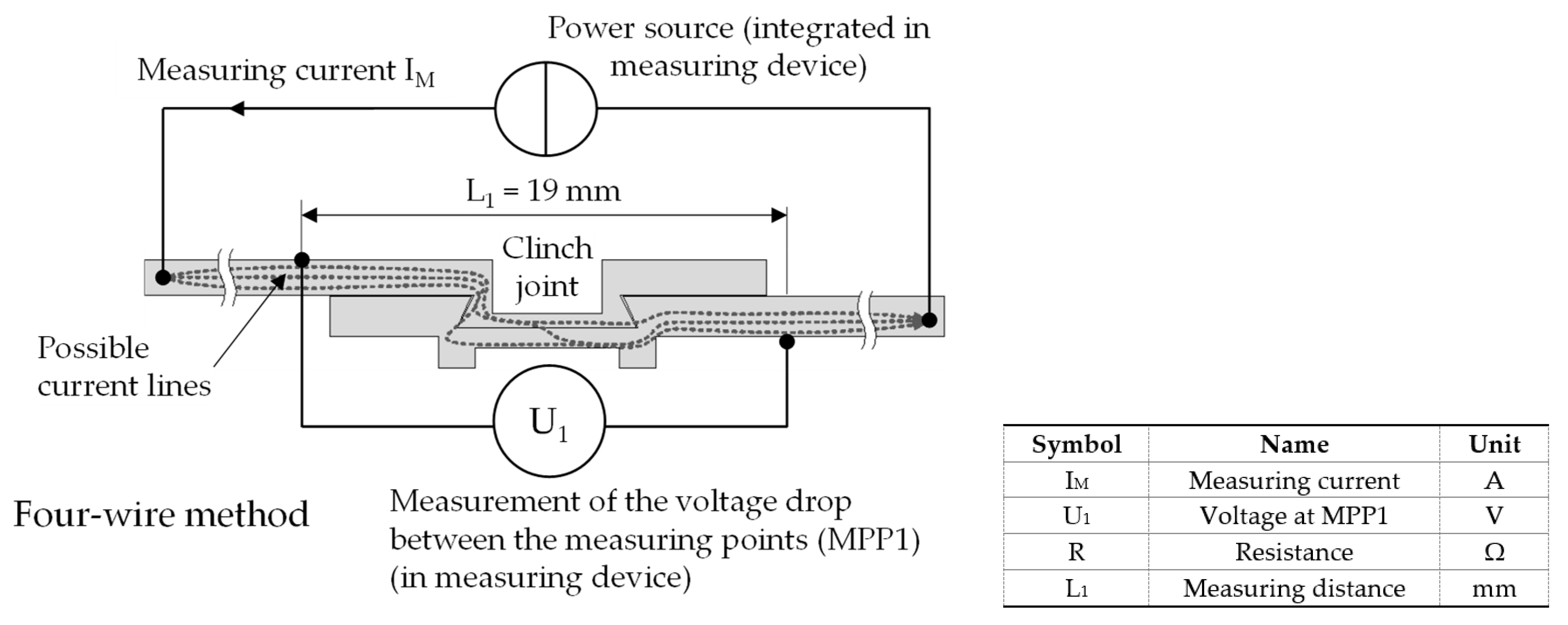
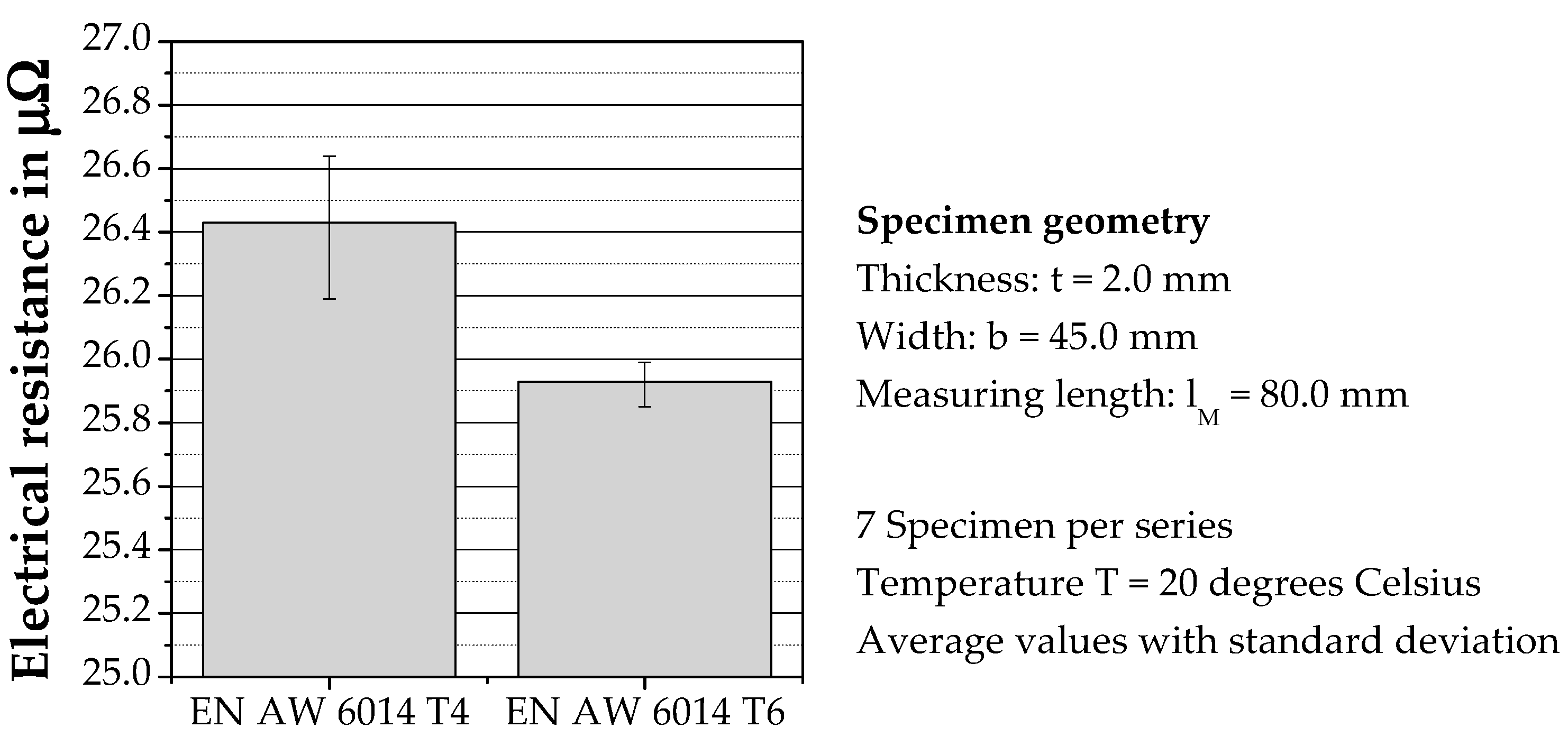
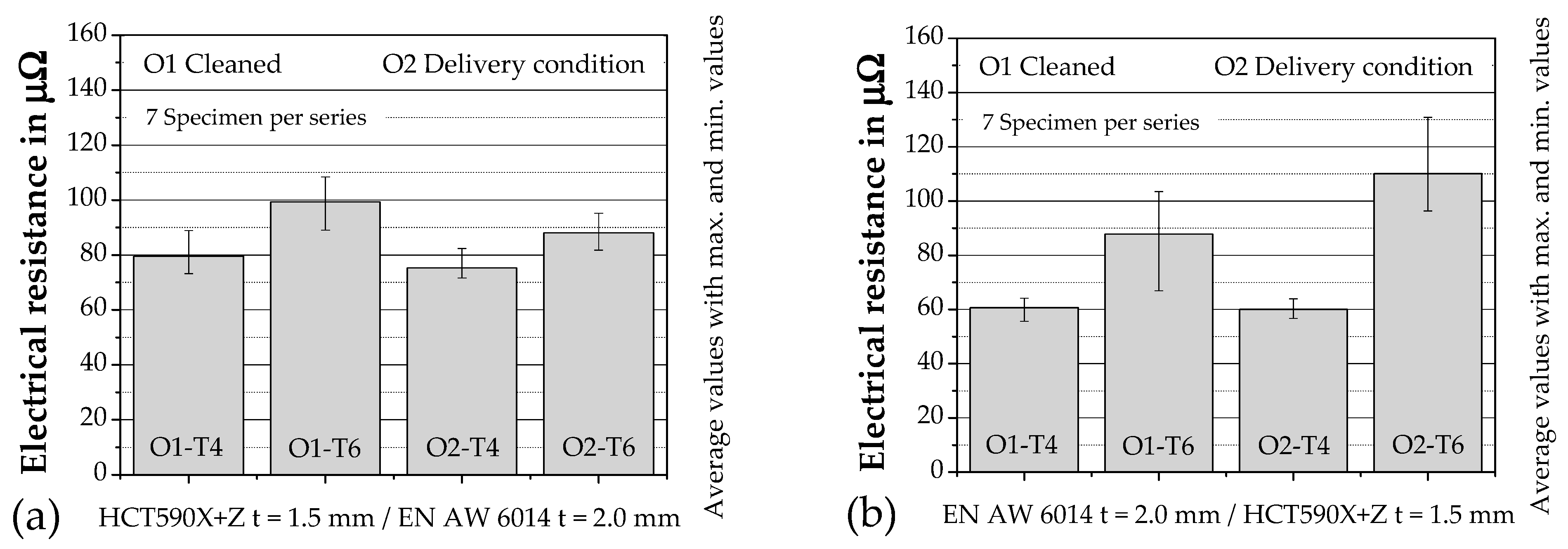
2.4. Electrical Test
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X. Clinching for sheet materials. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2017, 18, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groche, P.; Wohletz, S.; Brenneis, M.; Pabst, C.; Resch, F. Joining by forming—A review on joint mechanisms, applications and future trends. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2014, 214, 1972–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Ko, D.C.; Kim, B.M. Design of mechanical clinching tools for joining of aluminium alloy sheets. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewenz, L.; Kalich, J.; Zimmermann, M.; Füssel, U. Effect of different tool geometries on the mechanical properties of Al-Al clinch joints. Key Eng. Mater. 2021, 883, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshtayeh, M.M.; Hrairi, M.; Mohiuddin, A.K.M. Clinching process for joining dissimilar materials: State of the art. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 82, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Kato, T.; Mori, K. Joining of aluminium alloy and mild steel sheets using mechanical clinching. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications, Ltd: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2007; Volume 561-565, pp. 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Ko, D.C.; Kim, B.M. Parametric study on mechanical clinching process for joining aluminum alloy and high-strength steel sheets. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Matsuda, A.; Kato, T.; Mori, K.I. Plastic joining of aluminium alloy and high strength steel sheets by mechanical clinching. Steel. Res. Int. 2008, 79, 649–656. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, Y.; Mori, K.; Kato, T. Joining of high strength steel and aluminium alloy sheets by mechanical clinching with dies for control of metal flow. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Kishimoto, M.; Kato, T. Joining of hot-dip coated steel sheets by mechanical clinching. Int. J. Mater. 2009, 2, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füssel, U.; Kalich, J.; Großmann, S.; Schlegel, S.; Ramonat, A. Optimierung Umformtechnischer Fügeverfahren zur Kontaktierung Elektrischer Leiter. EFB Forschungsbericht Nr. 506; European Research Association for Sheet Metal Working: Hannover, Germany, 2019; ISBN 978-3867765596. [Google Scholar]
- Schweißbarkeit—Metallische Werkstoffe—Allgemeine Grundlagen; DIN-Fachbericht ISO/TR 581: 2007-04 (Deutsche Fassung); Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2007.
- Riedel, F. Eigenschaftsverbesserung von Durchsetzfügeverbindungen durch die Kombination mit Stoffschluss; Shaker Verlag GmbH: Düren, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Füssel, U.; Kalich, J.; Großmann, K.; Schlegel, S.; Schmid, J. Elektrisches Eigenschaftsprofil umformtechnischer Fügeverbindungen; EFB-Forschungsbericht Nr. 389; European Research Association for Sheet Metal Working: Hannover, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-86776-432-2. [Google Scholar]
- Salamati, M.; Soltanpour, M.; Fazli, A.; Zajkani, A. Processing and tooling considerations in joining by forming technologies; part A—Mechanical joining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 101, 261–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibmeier, J.; Lin, R.; Odén, M.; Scholtes, B. Residual stress distribution around clinched joints. Mater. Sci. Forum 2002, 404–407, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottstein, G. Physikalische Grundlagen der Materialkunde; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; ISBN 978-3-540-71104-9. [Google Scholar]
- Datasheet Automotive. Novelis Advanz™ 6F—e170; Novelis Global Automotive; Novelis AG: Kuesnacht, Switzerland, 2019.
- Product Information. CR330Y590T-DP (HCT590X + Z, HCT600XD, HC340XD); Salzgitter Flachstahl GmbH: Salzgitter, Germany, 2020.
- DVS-Merkblätter und Richtlinien Mechanisches Fügen; DVS-Fachbücher Band 153; DVS Media GmbH: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-87155-230-4.
- Zähr, J. Einfluss des Oberflächenzustandes auf das Thermische Fügen von Aluminium; TUDpress Verlag der Wissenschaften Dresden: Dresden, Germany, 2011; ISBN 978-3-942710-28-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kogut, L.; Komvopoulos, K. Electrical contact resistance theory for conductive rough surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 3153–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, L. Electrical performance of contaminated rough surfaces in contact. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 103723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, H. Mittelspannungstechnik—Schaltanlagen Berechnen und Entwerfen, 2nd ed.; Huss Medien GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2005; ISBN 978-3-341-01495-0. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, S.; Großmann, S.; Löbl, H.; Hoidis, M.; Kaltenborn, U.; Magier, T. Joint resistance of bolted copper-copper busbar joints depending on joint force at temperatures beyond 105 °C. In Proceedings of the 56th IEEE Holm Conference on Electrical Contacts, Charleston, SC, USA, 4–7 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, S.; Großmann, S.; Kalich, J.; Füssel, U. Kontakt—und Langzeitverhalten umformtechnischer stromführender Verbindungen für den Einsatz in der E-Mobilität. In Proceedings of the Kontaktverhalten und Schalten-25, Fachtagung Albert-Keil-Kontaktseminar, Karlsruhe, Germany, 9–11 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rieder, W. Elektrische Kontakte: Eine Einführung in ihre Physik und Technik; VDE-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2000; ISBN 9783800725427. [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann, F. Anwendungstechnologie Aluminium; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; ISBN 978-3-540-71196-4. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, Z.X.; Wang, P.C. Quality inspection of clinched joints of steel and aluminum. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.J.; Melo, M.L.N.; Silva, R.S.M.; Caixeta, D.O. Relationship between Electrical Conductivity and the Stage of the Heat Treatments of Aging and Overaging of the Aluminum Alloy AA2024. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications, Ltd: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 930, pp. 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikzad, K.S.; Javidani, M.; Maltais, A.; Chen, X. Investigation on electrical conductivity and hardness of 6xxx aluminum conductor alloys with different Si levels. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys 2020 (ICAA17), Grenoble, France, 26–29 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, M.; Shen, F.; Yi, D.; Wang, B. Influence of deformation and annealing on electrical conductivity, mechanical properties and texture of Al-Mg-Si alloy cables. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 710, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Hanaor, D.; Proust, G.; Brassart, L.; Gan, Y. Interfacial electro-mechanical behaviour at rough surfaces. In Extreme Mechanics Letters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 9, pp. 422–429. [Google Scholar]

| EN AW 6014 | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Zn | Ti | V | Other Each | Other Total |
| 0.3–0.6 | max. 0.35 | max. 0.25 | 0.05–0.2 | 0.4–0.8 | max. 0.20 | max. 0.10 | max. 0.10 | max. 0.10 | max. 0.05 | max. 0.15 | |
| HCT 590X+Z | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Al Total | Cr + Mo | Nb + Ti | |||
| 0.15 | 0.75 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.015–1.500 | 1.400 | 0.150 | ||||
| Sheet Thickness in mm | Surface Condition | Micrograph | Tools A—Punch B—Die | Neck Thickness tn in mm | Undercut tu in mm | Bottom Thickness tb in mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Series 1 t1 = 2.0 t2 = 1.5 | Cleaned |  | A56100/BD8016 | 0.42 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.87 ± 0.01 |
|
Series 2 t1 = 2.0 t2 = 1.5 | Delivery Condition |  | A56100/BD8016 | 0.44 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 0.79 ± 0.01 |
|
Series 3 t1 = 1.5 t2 = 2.0 | Cleaned |  | ABY461850100/BB8008 | 0.39 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 1.00 ± 0.01 |
|
Series 4 t1 = 1.5 t2 = 2.0 | Delivery Condition |  | ABY461850100/BB8008 | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.99 ± 0.01 |
| Rp0.2 in MPa | Rm in MPa | AG in % | A80 in % | Rp0.2/Rm | n5 | r10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T4 | ≤130 | ≥175 | ≥20 | ≥23 | ≤0.55 | ≥0.26 | ≥0.6 |
| T6 | ≥200 | ≥260 | ≥14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalich, J.; Füssel, U. Influence of the Production Process on the Binding Mechanism of Clinched Aluminum Steel Mixed Compounds. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5040105
Kalich J, Füssel U. Influence of the Production Process on the Binding Mechanism of Clinched Aluminum Steel Mixed Compounds. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2021; 5(4):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5040105
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalich, Jan, and Uwe Füssel. 2021. "Influence of the Production Process on the Binding Mechanism of Clinched Aluminum Steel Mixed Compounds" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 5, no. 4: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5040105
APA StyleKalich, J., & Füssel, U. (2021). Influence of the Production Process on the Binding Mechanism of Clinched Aluminum Steel Mixed Compounds. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 5(4), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp5040105





