Vibration Fatigue Assessment of UAV Wing Pylons Based on the PSD Method
Highlights
- A finite element analysis method for vibration fatigue under multi-source dynamic loads is proposed, which has been validated through physical experiments: a finite element model has been established to quantify the vibration and impact loads on the special structure of the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) wing pylon. The model has been validated through physical experiments, and the conditions of the physical experiments are completely consistent with the analysis model.
- The UAV structure fatigue life assessment method based on vibration fatigue analysis and damage accumulation theory considering model and load uncertainty is proposed: the comprehensive effects of vibration and impact loads on structural fatigue damage were taken into account to obtain the vibration fatigue characteristics of the connection area of the UAV wing pylon structure. Based on the theory of linear damage accumulation and considering model and load uncertainties, a correction coefficient was introduced to determine the converted fatigue life of the wing pylon, achieving conservative and reliable life prediction of the UAV wing pylon structure under the combined action of vibration and impact loads.
- This work provides a novel solution for finite element analysis of UAV pylon connection structures under combined vibration and impact loading conditions.
- This approach enables efficient and precise determination of the fatigue life of UAV pylons subjected to multiple loading environments.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Requirements and Methods
3. Vibration and Impact Response Analysis
3.1. Establishment of a Finite Element Model
3.2. Vibration Response Analysis
3.3. Impact Response Analysis
4. Vibration Fatigue Assessment
4.1. Fatigue Analysis Under Vibration Loads
4.2. Fatigue Analysis Under Impact Loads
4.3. Vibration Fatigue Test Validation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| PSD | Power Spectral Density |
| FCDPs | Fast Cloud Droplet Probes |
| CPI | Cloud Particle Imager |
References
- Zorman, A.; Slavič, J.; Boltežar, M. Vibration fatigue by spectral methods—A review with open-source support. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 190, 110149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Xie, R.; Li, M. Fatigue Life Estimation Method for Random Vibration Based on Power Spectral Density Segmentation. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2024, 45, 179–192. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Baktheer, A.; Pan, Y.; Aldakheel, F. Fatigue life prediction under random vibrations: An acceleration framework combining scale factor analysis and critical distance theory. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2025, 140, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dang, H.; Li, B. Prediction of Aircraft Surface Noise in Supersonic Cruise State. Aerospace 2023, 10, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; He, Y.; Xu, W. Notch fatigue behavior of a titanium alloy in the VHCF regime based on a vibration fatigue test. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 172, 107608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staffa, A.; Palmieri, M.; Morettini, G.; Zucca, G.; Crocetti, F.; Cianetti, F. Development and validation of a low-cost device for real-time detection of fatigue damage of structures subjected to vibrations. Sensors 2023, 23, 5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Hou, J.; Li, W.; Ma, C.; Wang, X. Tensile and vibration fatigue monitoring of composite laminate bolted joints with local enhancement using buckypaper sensors. Struct. Health Monit. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, S.; Shu, P.; Lv, R.; Kong, L. Identification of excitation and modal frequencies of wing rib beams using fiber bragg grating sensors: Experimental characterization and comparative simulation analysis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2025, 3126, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Gao, W.; Ankay, B.; Li, F.; Zhang, C. Aeroelastic analysis and flutter control of wings and panels: A review. Int. J. Mech. Syst. Dyn. 2021, 1, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyungi, K. Fatigue Analysis of External Fuel Tank and Pylon for Fixed Wing Aircraft. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Coop. Soc. 2020, 21, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.; Li, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Qiao, J.; Zhao, J. Structural optimization and fatigue life analysis of landing gear upper lock. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2403, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shi, Q.B.; Wang, X. Fatigue Life Prediction of Flap Safety Pins for Civil Aircraft. In Proceedings of the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers(SPIE), San Francisco, CA, USA, 31 January–2 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H.; Sun, G.; Hou, J.; Li, H. Prediction of Vibration Fatigue Life of Fiber Reinforced Composite Thin Plates with Functionally Graded Coating under Base Random Excitation. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 200, 111891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Chen, M.; Sha, Z.; Cai, D.; Jiang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, G.; Wang, X. High-cycle Random Vibration Fatigue Behavior of CFRP Composite Thin Plates. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 159, 108089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H. Experimental Study on Vibration Fatigue Behavior of Aircraft Aluminum Alloy 7050. Materials 2022, 15, 7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Lv, J.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, N.; Li, L. Experimental study on the influence of welding structure details of TC4 titanium alloy under thermo-vibration coupling environment on vibration fatigue life. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2730, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.H.; Park, H.S.; Seo, S.W.; Kwag, D.-G. Design and Experiment of a Passive Vibration Isolator for Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.R.; Balasubramanian, E.; Arunkumar, P.; Sajal, C.B. Optimization of UAV Structure and Evaluation of Vibrational and Fatigue Characteristics Through Simulation Studies. Int. J. Simul. Multidiscip. Des. Optim. 2021, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Yan, H.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Random Vibration Fatigue Analysis of Rotor UAV Folding Propeller Hub. Intern. Combust. Engine Part 2024, 07, 50–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Random Vibration Fatigue Analysis of UAV Engine Support Based on Steinberg Method. Mach. Build. Autom. 2021, 50, 216–219. [Google Scholar]
- Clothier, R.A.; Palmer, J.L.; Walker, R.A.; Fulton, N.L. Definition of an Airworthiness Certification Framework for Civil Unmanned Aircraft Systems. Saf. Sci. 2011, 49, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, G.; Kayran, A. Implementation of Dirlik’s Damage Model for the Vibration Fatigue Analysis. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2019, 21, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Defense. Environmental Engineering Considerations and Laboratory Tests, MIL-STD-810H; US Department of Defense: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 576–578.
- YS/T 1629.1-2023; Wrought Aluminium Alloy Plates and Sheets for Aviation Products-Part 1:7050T7451 Plates. Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2024.



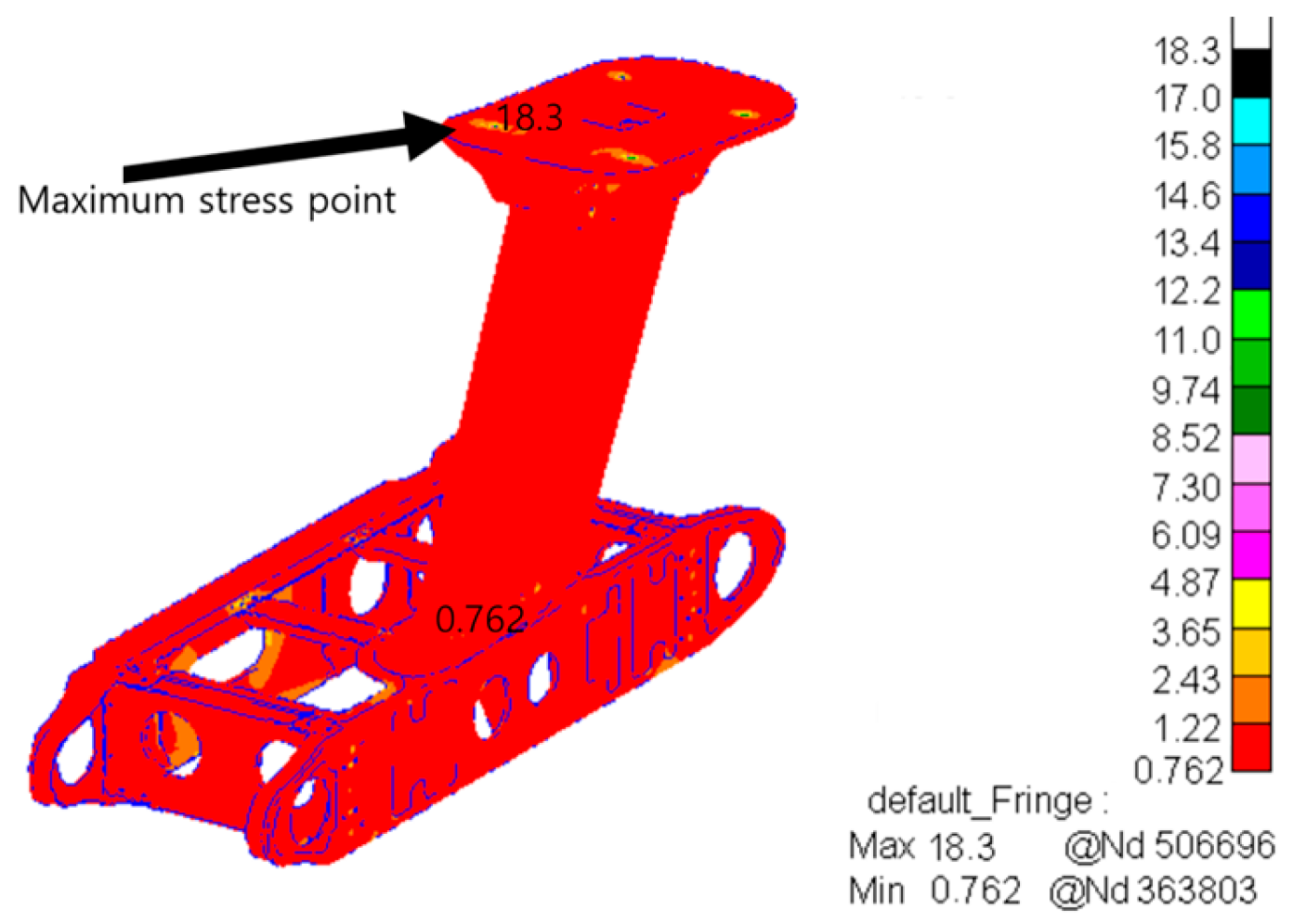
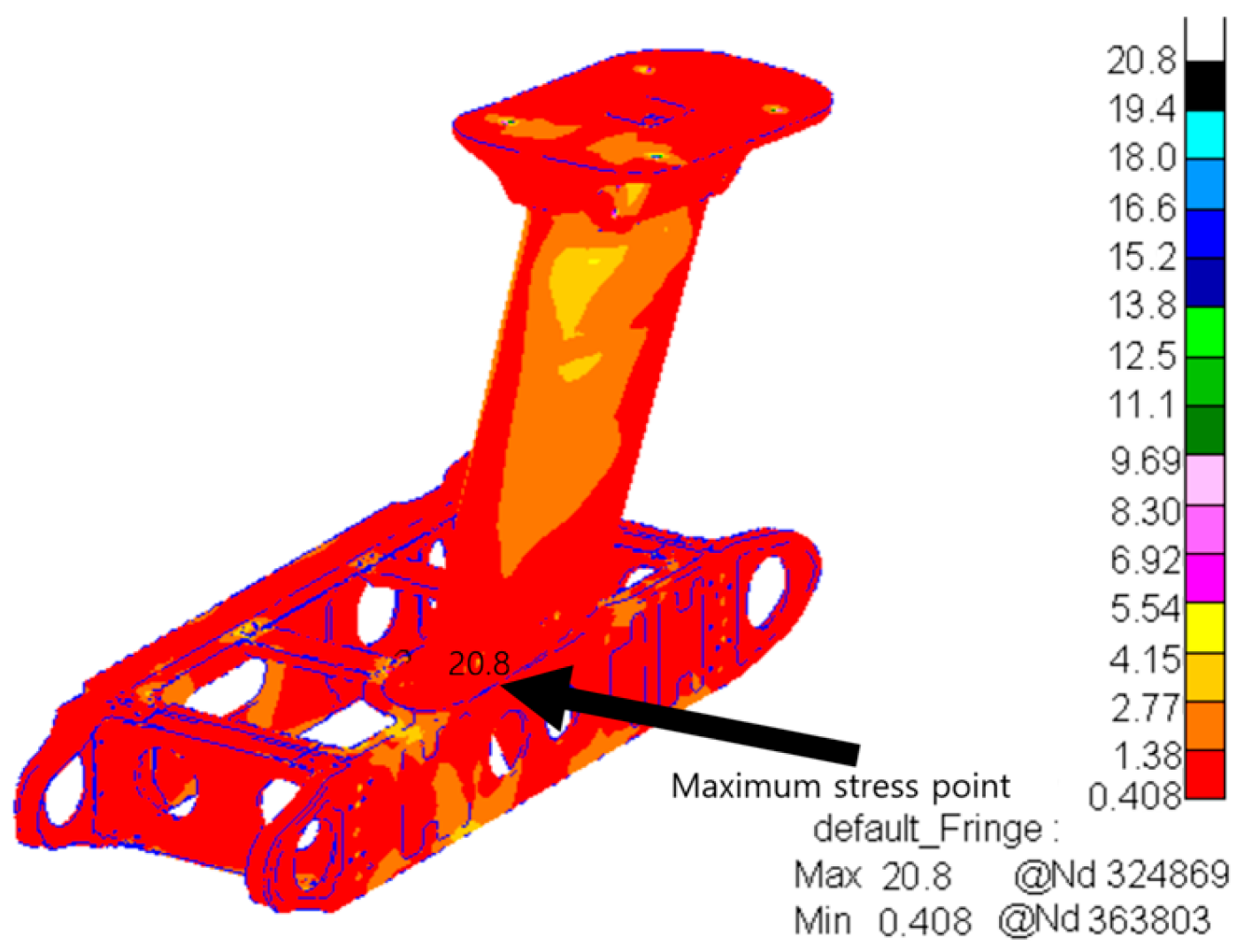
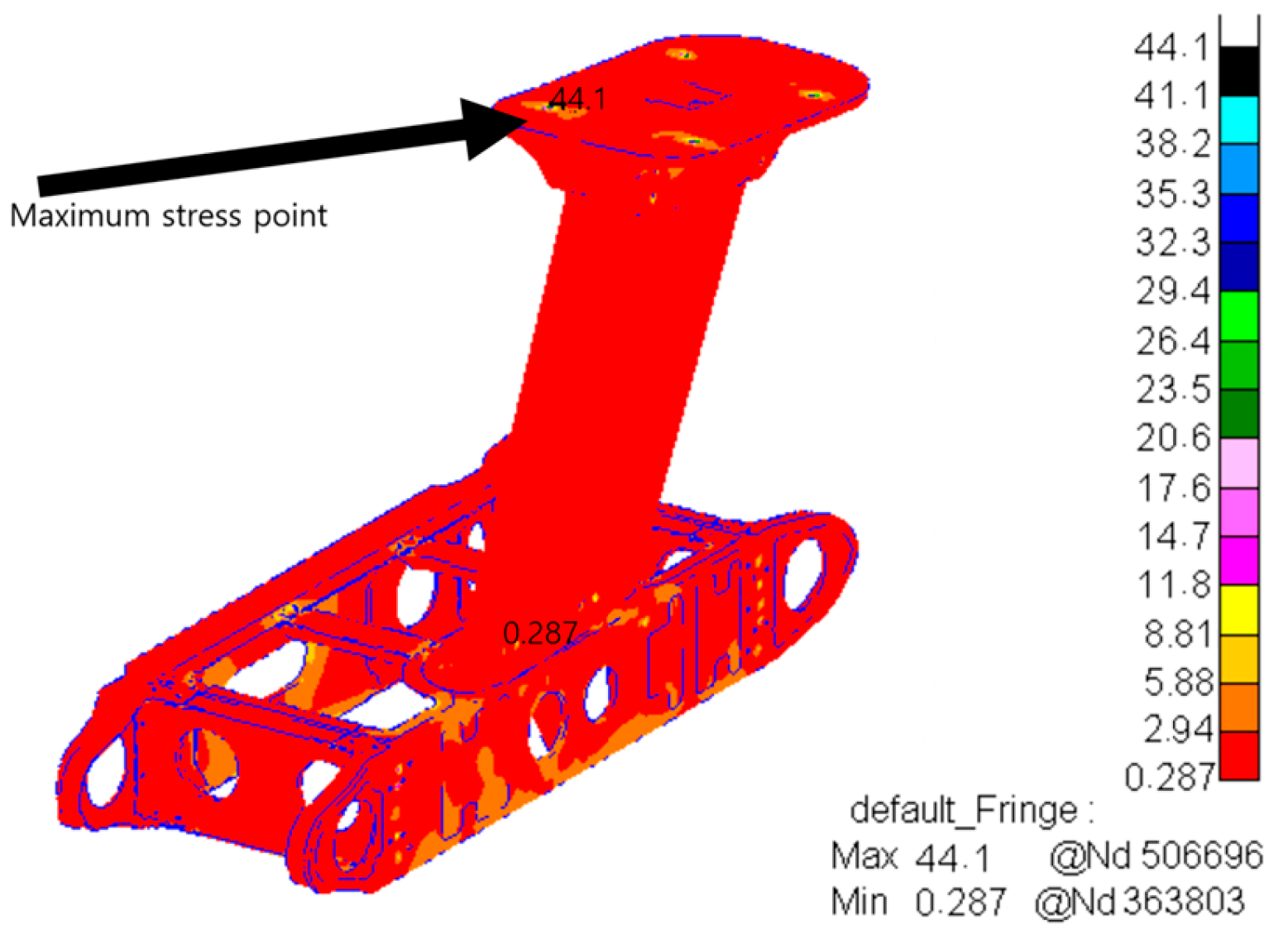
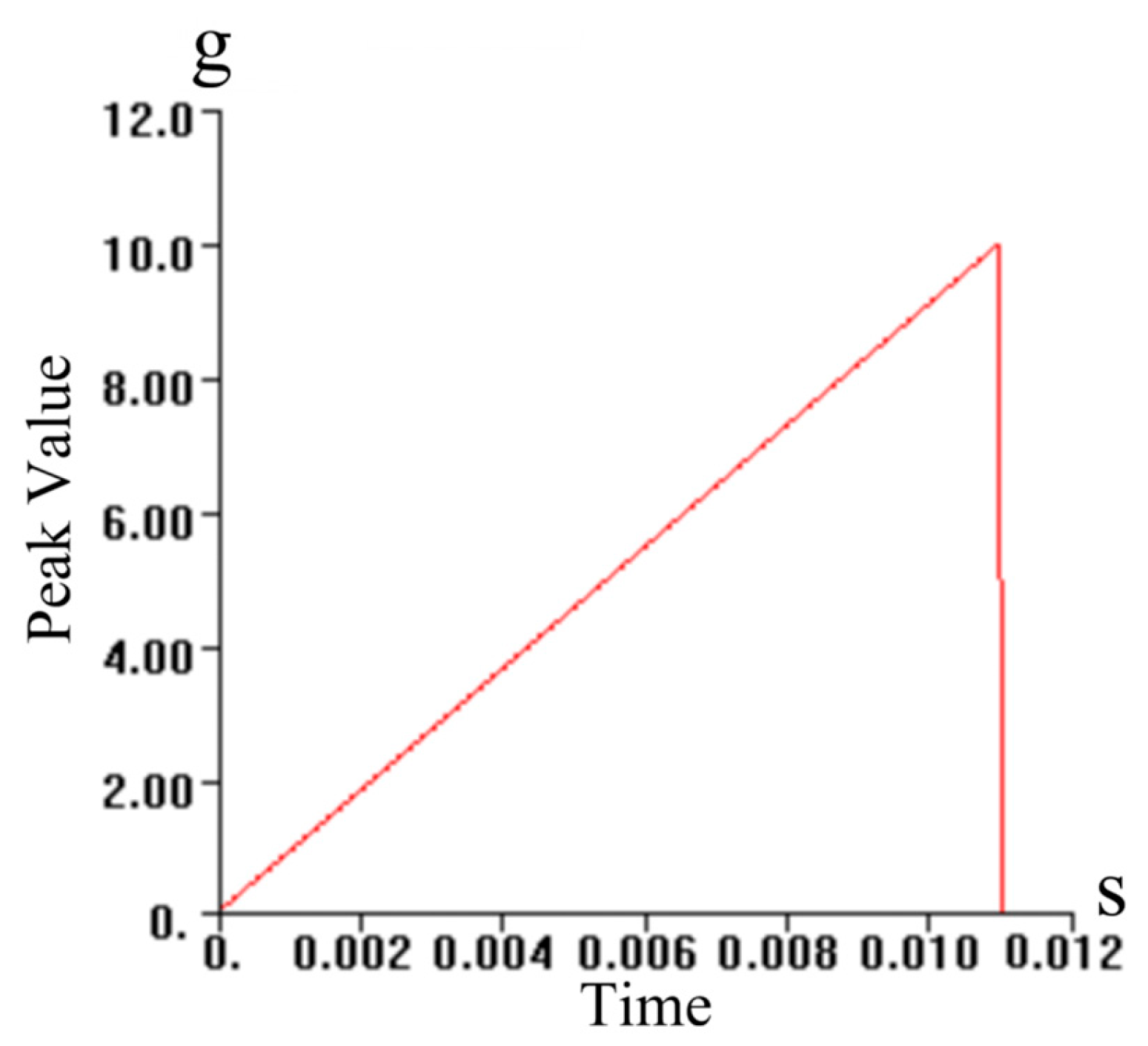

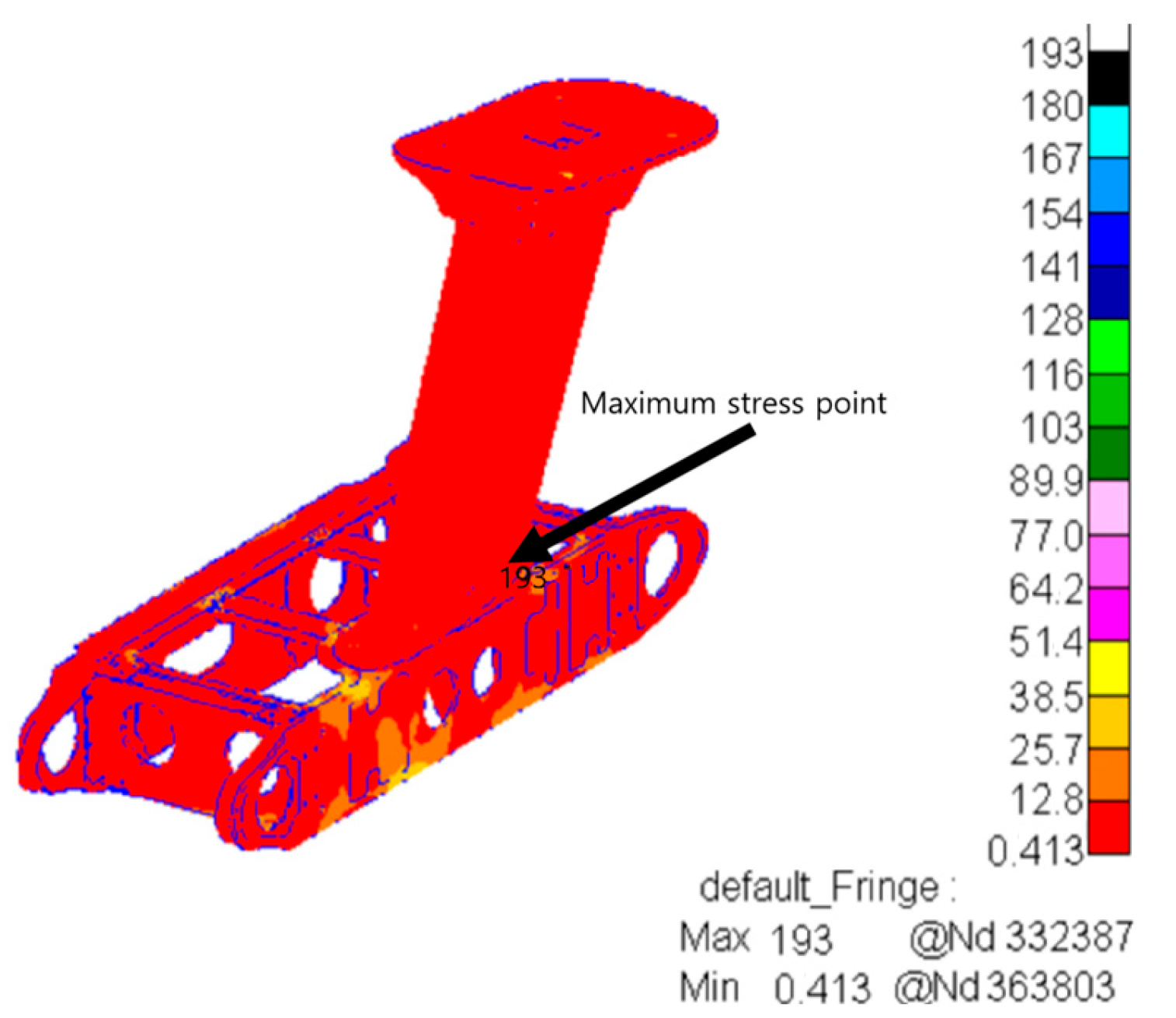
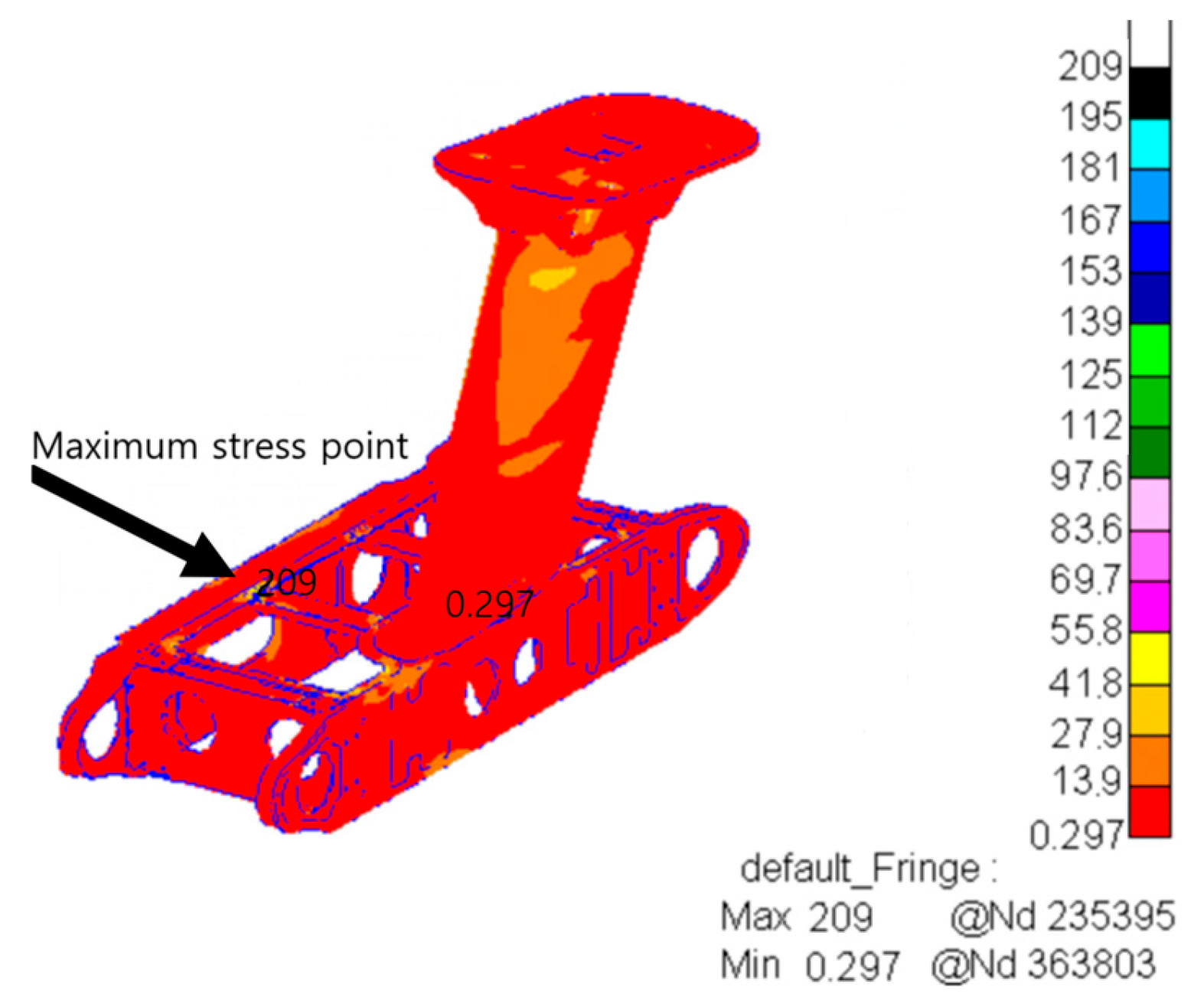




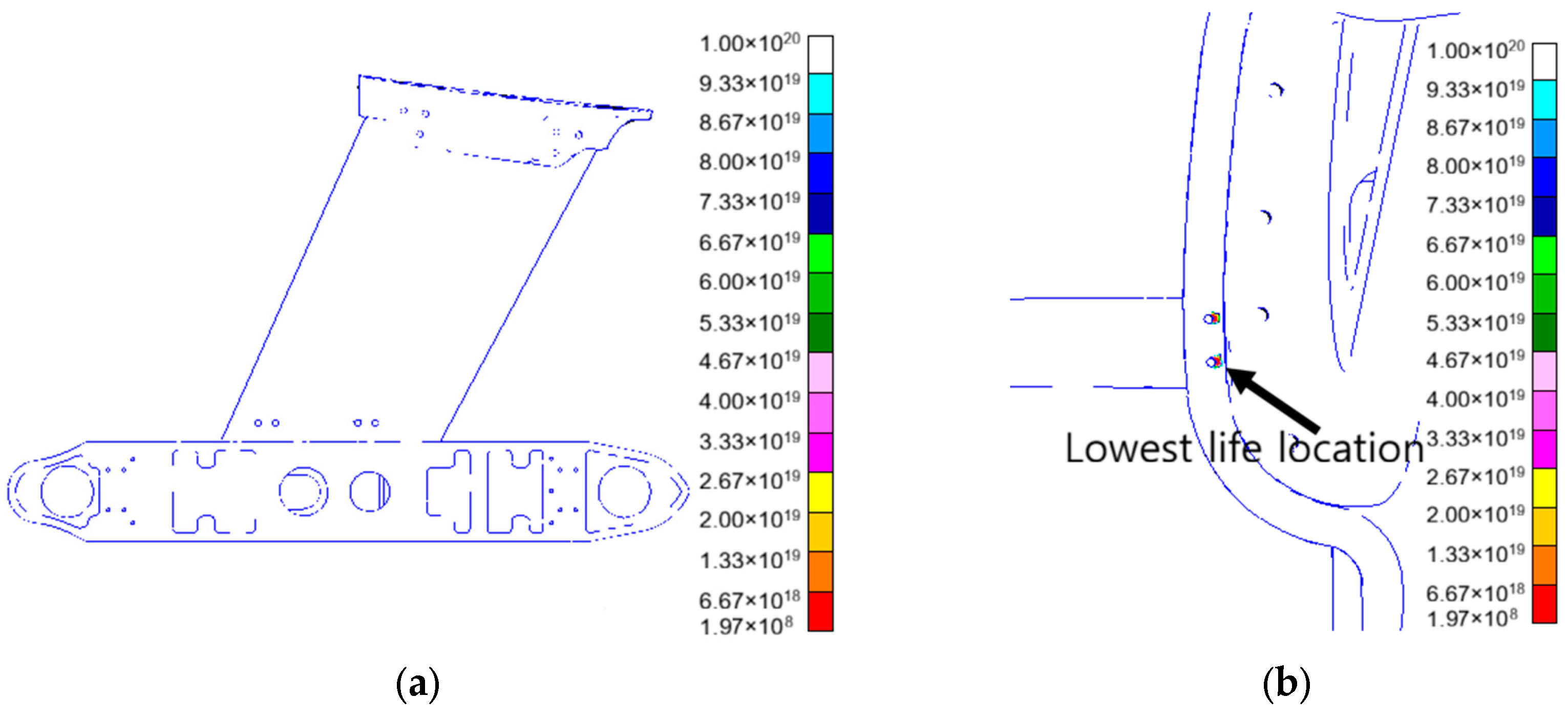


| Frequency (Hz) | Vibration Spectral Value (g2/Hz) |
|---|---|
| 15 | 0.01 |
| 73.125 | 0.01 |
| 73.125 | 0.3 |
| 76.875 | 0.3 |
| 76.875 | 0.01 |
| 146.25 | 0.01 |
| 146.25 | 0.075 |
| 153.75 | 0.075 |
| 153.75 | 0.01 |
| 219.375 | 0.01 |
| 219.375 | 0.034 |
| 230.625 | 0.034 |
| 230.625 | 0.01 |
| 292.5 | 0.01 |
| 292.5 | 0.0168 |
| 307.5 | 0.0168 |
| 307.5 | 0.01 |
| 2000 | 0.01 |
| Time (s) | Peak Value(g) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 0.011 | 10 |
| 0.01101 | 0 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 510.0 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | 441.0 |
| Elastic Modulus (GPa) | 73.0 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.34 |
| Fatigue Limit (MPa) (Longitudinal smooth circular specimen, when the stress ratio is 0.1) | 241.0 |
| Load Direction | Test Product Number | Duration Before Fatigue Fracture | Location of Fatigue Fracture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heading | #1 | 18 h 36 min | Bolt of the test product and upper fixture |
| #2 | 16 h 06 min | ||
| #3 | 12 h 52 min | ||
| Vertical | #1 | 12 h 24 min | Bolt of the horizontal box |
| #2 | 10 h 48 min | ||
| #3 | 13 h 44 min | ||
| Lateral | #1 | 10 h 28 min | Bolt of the test product and upper fixture |
| #2 | 8 h 37 min | ||
| #3 | 9 h 39 min |
| Load Direction | Test Product Number | Root Mean Square Strain/με | Root Mean Square Stress/MPa | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heading | #1 | 243 | 17.74 | Bolt hole edge of the test product and upper fixture |
| #2 | 245 | 17.89 | ||
| #3 | 229 | 16.72 | ||
| Vertical | #1 | 275 | 20.08 | Bolt hole edge of the horizontal box |
| #2 | 266 | 19.42 | ||
| #3 | 268 | 19.56 | ||
| Lateral | #1 | 579 | 42.27 | Bolt hole edge of the test product and upper fixture |
| #2 | 593 | 43.29 | ||
| #3 | 581 | 42.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sui, L.; Sun, Y.; Sun, H. Vibration Fatigue Assessment of UAV Wing Pylons Based on the PSD Method. Drones 2025, 9, 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9120838
Sui L, Sun Y, Sun H. Vibration Fatigue Assessment of UAV Wing Pylons Based on the PSD Method. Drones. 2025; 9(12):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9120838
Chicago/Turabian StyleSui, Lijun, Youchao Sun, and Haonan Sun. 2025. "Vibration Fatigue Assessment of UAV Wing Pylons Based on the PSD Method" Drones 9, no. 12: 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9120838
APA StyleSui, L., Sun, Y., & Sun, H. (2025). Vibration Fatigue Assessment of UAV Wing Pylons Based on the PSD Method. Drones, 9(12), 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9120838






