Research on Lightweight Tracking of Small-Sized UAVs Based on the Improved YOLOv8N-Drone Architecture
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
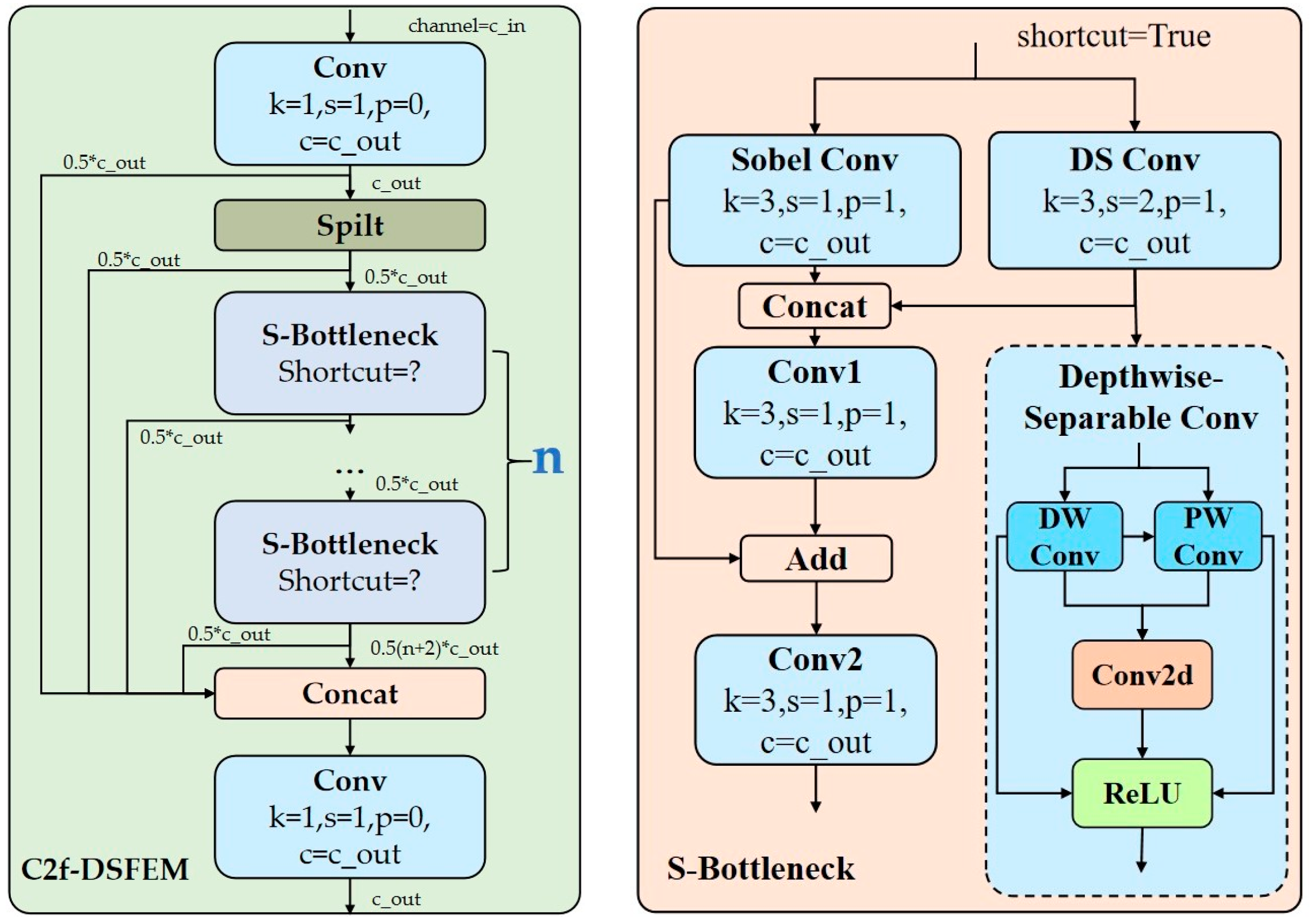
- The C2f-DSFEM module has been developed to handle the complexities introduced by the indistinctness of edge features and the inadequacy of multi-scale feature integration for diminutive UAV targets. This module has been designed to achieve bidirectional enhancement of edge details and efficient semantic features by integrating Sobel convolution and depth-separable convolution across multiple layers. This approach overcomes the limitations of the conventional single convolution module, which exhibits insufficient capability in capturing features of diminutive targets in complex backgrounds.
- (2)
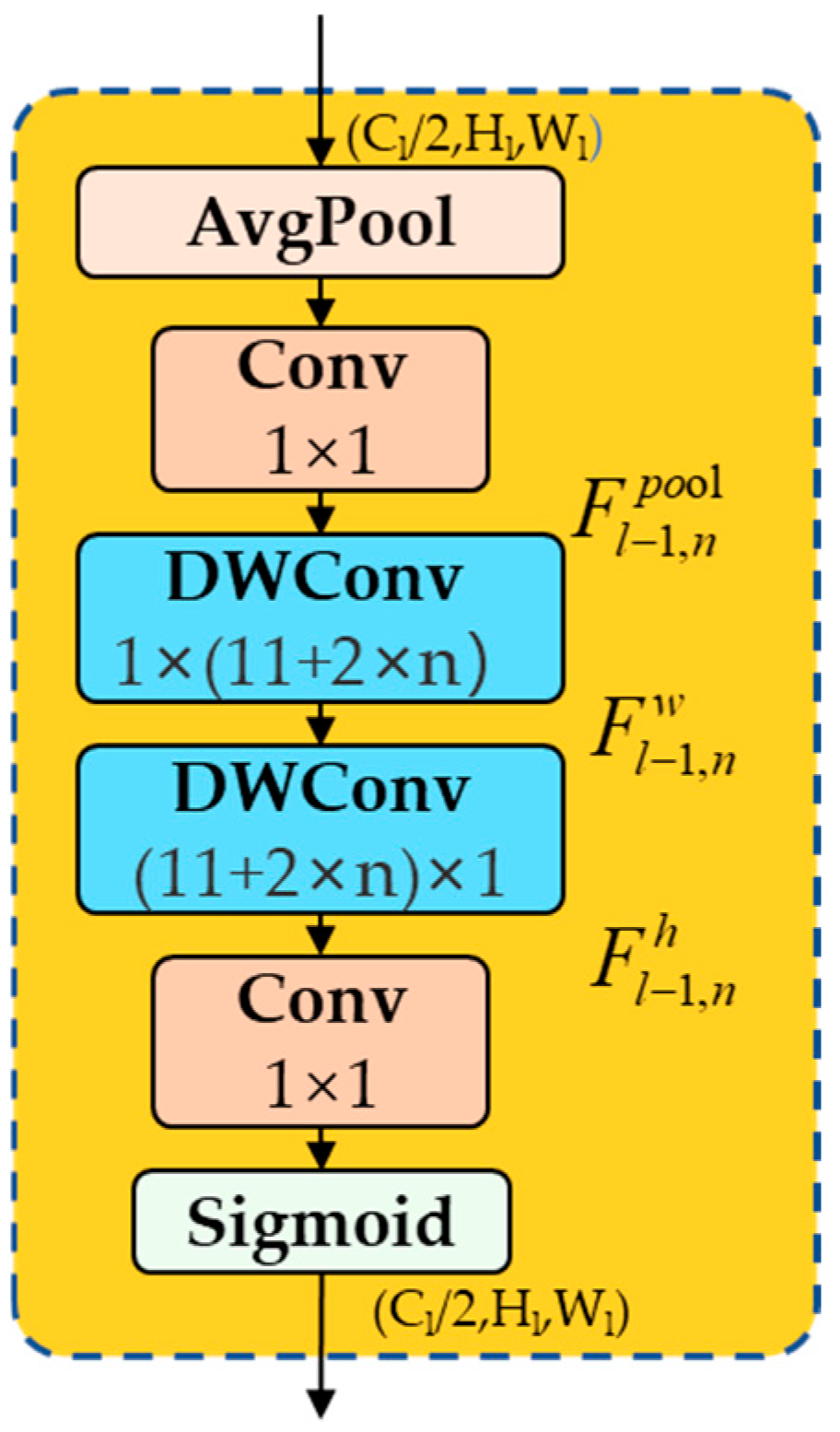
- The existing attention mechanisms (e.g., SE, CBAM) have been criticized for their inability to focus sufficiently on the target area in lightweight scenarios. In response to this criticism, an improved CAA mechanism has been proposed. This mechanism achieves adaptive suppression of background interference while maintaining a low computational cost through a position-aware weight allocation strategy. Furthermore, it addresses the problem of balancing the accuracy and efficiency of small target localization in traditional attention mechanisms.
- (3)
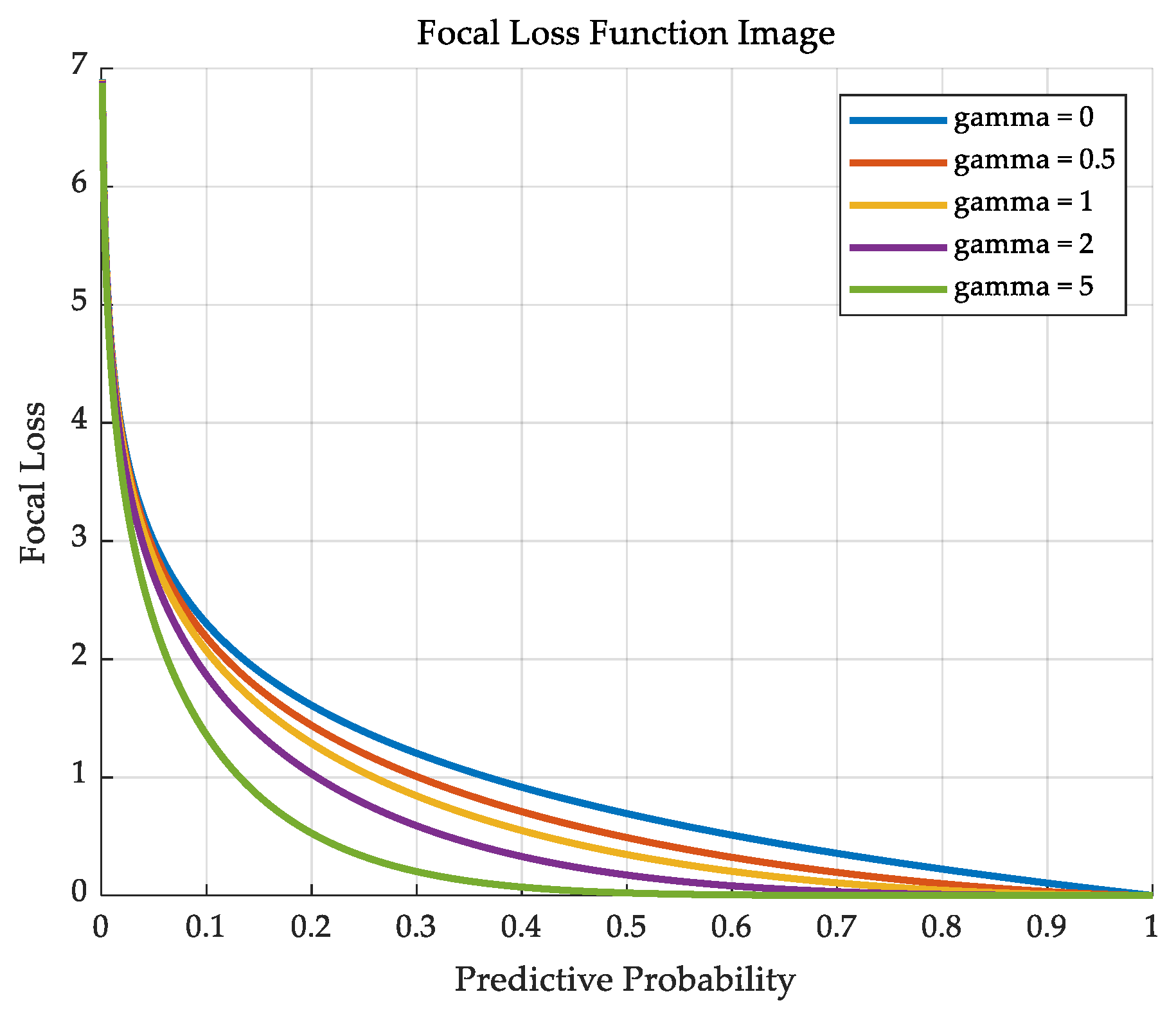
- The synergistic framework of ‘Feature Enhancement—Attention Focus—Loss Optimisation’ combines Focal Loss with an enhanced detector and a DeepSORT tracking algorithm. This combination is intended to solve the problem of tracking drift and frequent ID switching, which is caused by sample imbalance in highly dynamic scenes. It is asserted that this will result in a significant improvement in tracking stability when compared with the existing YOLO Series + DeepSORT solution.
2. Models and Methods
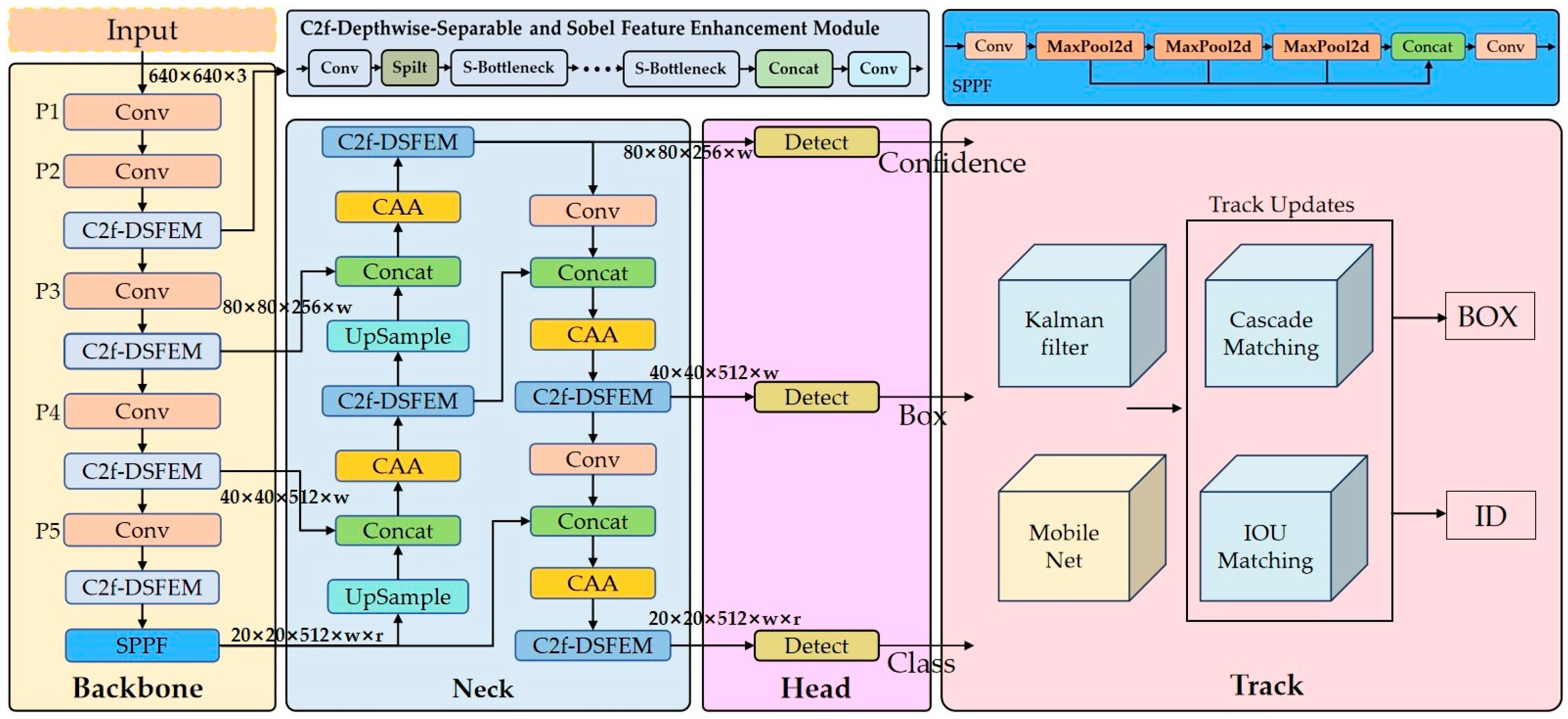
2.1. Modeling Framework
2.2. Depth Separable and Edge-Sensitive Feature Enhancement Module
2.3. Context Anchor Attention Mechanism Module
2.4. Loss Function Improvement Study
2.5. Target Tracking Algorithm
3. Experiment and Result Analysis
3.1. Experimental Basis
3.1.1. Experimental Condition
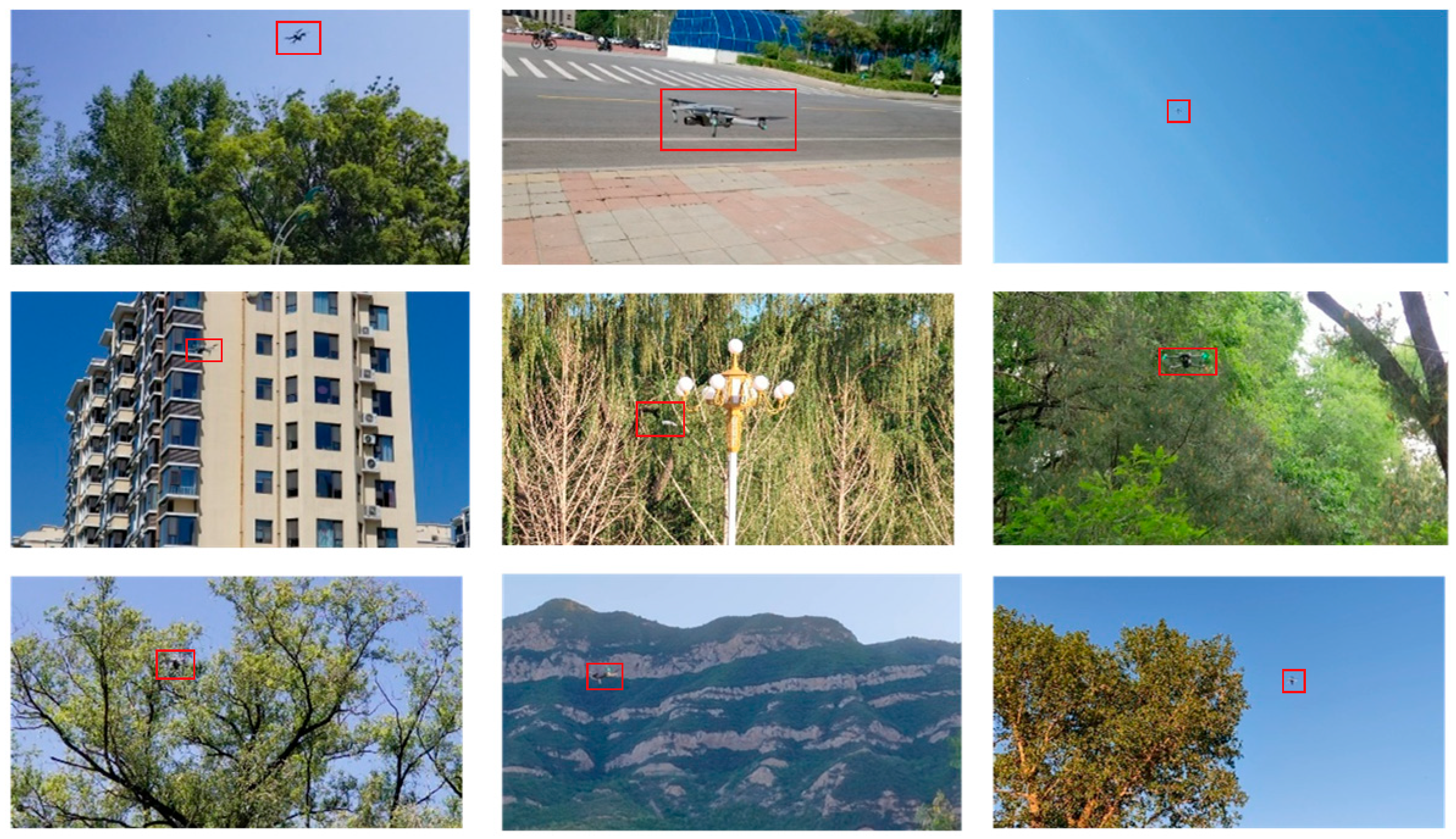
3.1.2. Dataset Construction
3.2. Algorithm Detection Performance Validation
3.2.1. Evaluation Metrics
3.2.2. Detection of Performance Ablation Experiments
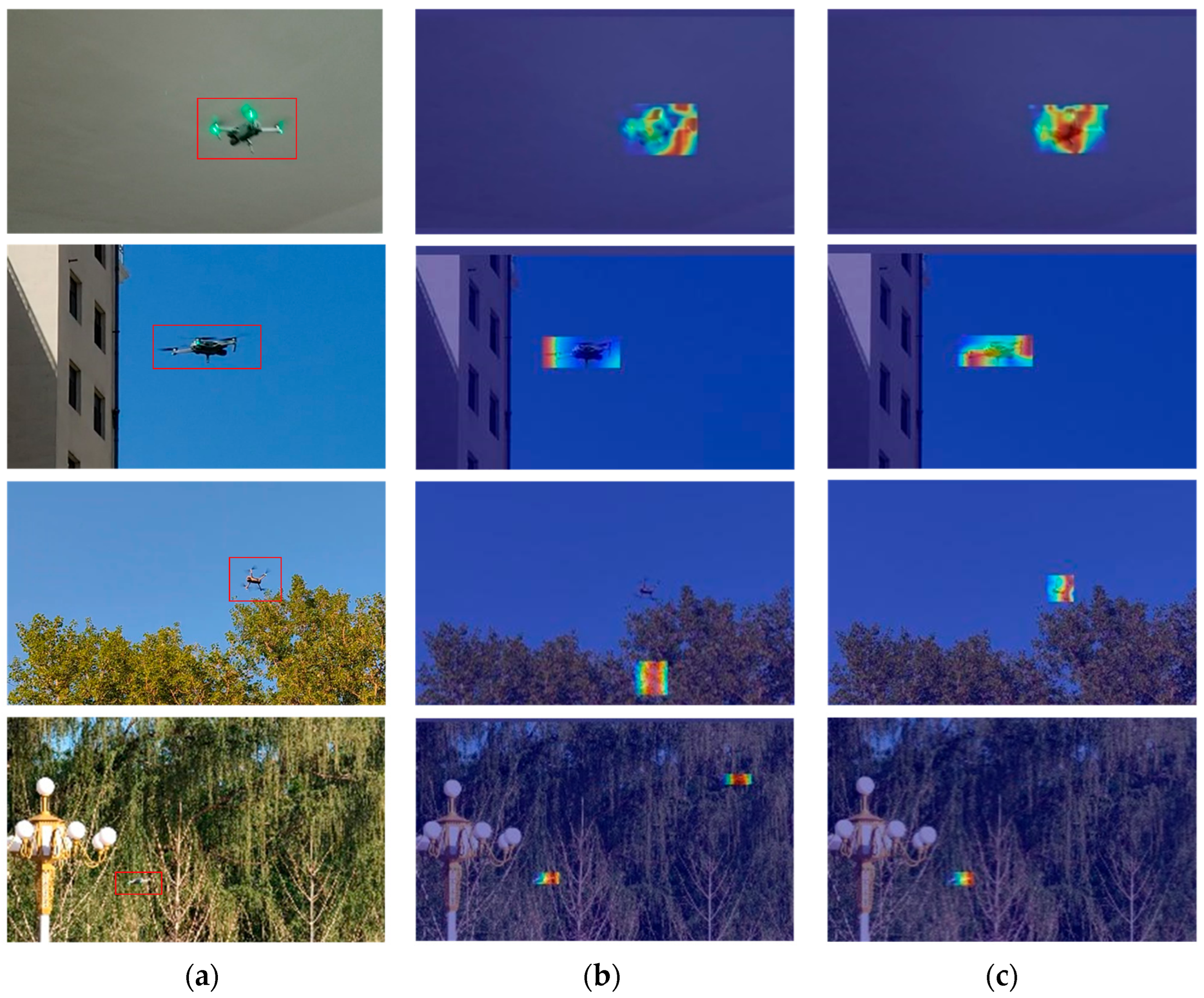
3.2.3. Visualization Experiment
3.3. Algorithm Tracking Performance Validation
3.3.1. Tracking Performance Comparison Experiment
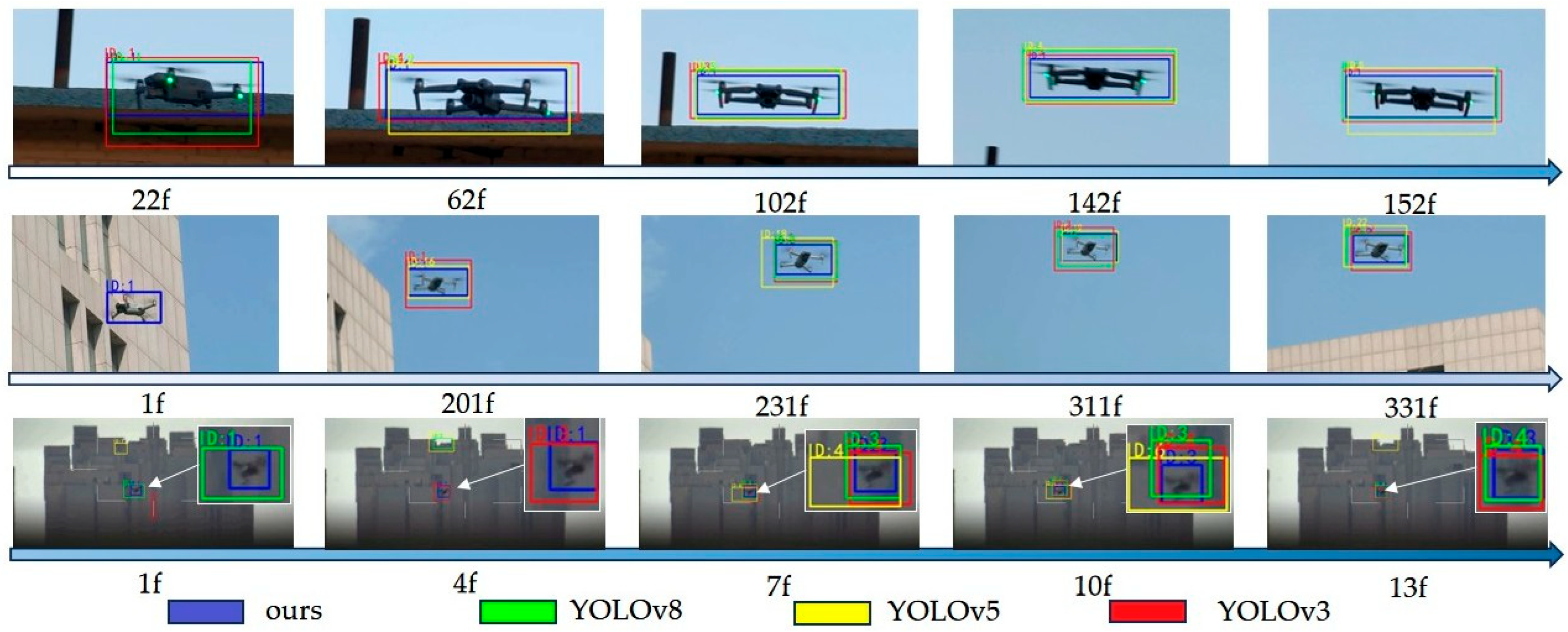
3.3.2. Continuous Frame Visualization Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DSFEM | Depthwise-Separable and Sobel Feature Enhancement Module |
| CAA | Context Anchor Attention |
| UAVs | unmanned aerial vehicles |
| mAP | mean average precision |
References
- Hu, P.; Zhang, R.; Yang, J.; Chen, L. Development status and key technologies of plant protection UAVs in China: A review. Drones 2022, 6, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, W.H.; Khamis, M.F. Drone use in military and civilian application: Risk to national security. J. Media Inf. Warf. (JMIW) 2022, 15, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Jorge, H.; Aldao, E.; Fontenla-Carrera, G.; Veiga-López, F.; Balvís, E.; Ríos-Otero, E. Counter drone technology: A review. Preprints 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Dosari, K.; Hunaiti, Z.; Balachandran, W. Systematic review on civilian drones in safety and security applications. Drones 2023, 7, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshref-Javadi, M.; Winkenbach, M. Applications and research avenues for drone-based models in logistics: A classification and review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 177, 114854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.D. Radar challenges, current solutions, and future advancements for the counter unmanned aerial systems mission. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2023, 38, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; De Maio, A.; Zheng, J.; Su, T.; Carotenuto, V.; Aubry, A. An adaptive radar signal processor for UAVs detection with super-resolution capabilities. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 20778–20787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olorunshola, O.; Jemitola, P.; Ademuwagun, A. Comparative study of some deep learning object detection algorithms: R-CNN, fast R-CNN, faster R-CNN, SSD, and YOLO. Nile J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2023, 1, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Qi, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, N.; Zhou, H. Human detection under UAV: An improved faster R-CNN approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 5th International Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI), Nanjing, China, 10–12 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Maske, S.R. Micro-UAV detection using Mask R-CNN. Ph.D. Dissertation, National College of Ireland, Dublin, Ireland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, M.; Hebel, M.; Borgmann, B.; Laurenzis, M.; Arens, M. Potential of lidar sensors for the detection of UAVs. In Laser Radar Technology and Applications XXIII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10636, pp. 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.; Chen, K.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Ye, J. Object detection in 20 years: A survey. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, C.; Budavari, B. Enhancing small moving target detection performance in Low-Quality and Long-Range infrared videos using optical fow techniques. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsanad, H.R.; Sadik, A.Z.; Ucan, O.N.; Ilyas, M.; Bayat, O. YOLO-V3 based real-time drone detection algorithm. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 26185–26198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. YOLO-Drone: An optimized YOLOv8 network for tiny UAV object detection. Elec-Tronics 2023, 12, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fan, K.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, N. Real-time small drones detection based on pruned yolov4. Sensors 2021, 21, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamri FN, M.; Gunawan, T.S.; Yusoff, S.H.; Alzahrani, A.A.; Bramantoro, A.; Kartiwi, M. Enhanced small drone detection using optimized YOLOv8 with attention mechanisms. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 90629–90643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ju, Z.; Sun, T.; Dong, F.; Li, J.; Yang, R.; Fu, Q.; Lian, C.; Shan, P. Tgc-yolov5: An enhanced yolov5 drone detection model based on transformer, gam & ca attention mechanism. Drones 2023, 7, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Liang, H.; Yang, Q.; Fang, L.; Kadoch, M.; Cheriet, M. A real-time tracking algorithm for multi-target UAV based on deep learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, R. UAV Object detection and tracking in video using YOLOv3 and DeepSORT. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Computer Science for Interdisciplinary Applications (ICETCS), Bengaluru, India, 22–23 April 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazlane, Y.; Hilali Alaoui, A.E.; Medomi, H.; Bnouachir, H. Real-Time airborne target tracking using DeepSort algorithm and Yolov7 Model. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delleji, T.; Fkih, H.; Kallel, A.; Chtourou, Z. Visual tracking of mini-UAVs using modified YOLOv5 and improved DeepSORT algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2022 6th International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing (ATSIP), Sfax, Tunisia, 24–27 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yuding, X.; Zhuang, S.; Wang, P.; Ling, Y.; Lv, Z.; Lu, W. Research on Real-time detection and tracking algorithm for low slow small targets based on the DeepSort. In Proceedings of the 2024 3rd Asia Conference on Algorithms, Computing and Machine Learning, Shanghai, China, 22–24 March 2024; pp. 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhu, M.; Tao, R.; Ren, H. Fine-grained feature perception for unmanned aerial vehicle target detection algorithm. Drones 2024, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Miyazaki, J. Multi-directional sobel operator kernel on GPUs. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2023, 177, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Li, C.; Su, X.; Liu, H.; Li, J. Multi-Scale depthwise separable convolution for semantic segmentation in Street–Road scenes. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, L. SL-YOLO: A stronger and lighter drone target detection model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.11477. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Lai, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, Z.; Yao, Y. Poly kernel inception network for remote sensing detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 27706–27716. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, B. Enhanced heterogeneous graph attention network with a novel multilabel focal loss for Document-Level relation extraction. Entropy 2024, 26, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Chuang, C.-T. Real-Time object localization using a fuzzy controller for a Vision-Based drone. Inventions 2024, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, D. Vision-based anti-uav detection and tracking. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 25323–25334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, V.; Vrba, M.; Saska, M. On training datasets for machine learning-based visual relative localization of micro-scale UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–4 June 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 10674–10680. [Google Scholar]
- Pawełczyk, M.; Wojtyra, M. Real world object detection dataset for quadcopter unmanned aerial vehicle detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 174394–174409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lv, D.; Li, Z.; Lan, Z.; Zhao, S. Air-to-air visual detection of micro-uavs: An experimental evaluation of deep learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Aggarwal, P.; Choi, J.; Kuo CC, J. A deep learning approach to drone monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2017 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–15 December 2017; pp. 686–691. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.M.; Su, W.H. APHS-YOLO: A lightweight model for Real-Time detection and classification of stropharia Rugoso-Annulata. Foods 2024, 13, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Wang, K.; Peng, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, Q.; Xing, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, J.; Guo, G.; Han, Z. Anti-UAV: A large multi-modal benchmark for UAV tracking. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.08466. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, P.; Mei, K.; Xue, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, W.; Mao, L. Research on enhanced dynamic pig counting based on YOLOv8n and Deep SORT. Sensors 2025, 25, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

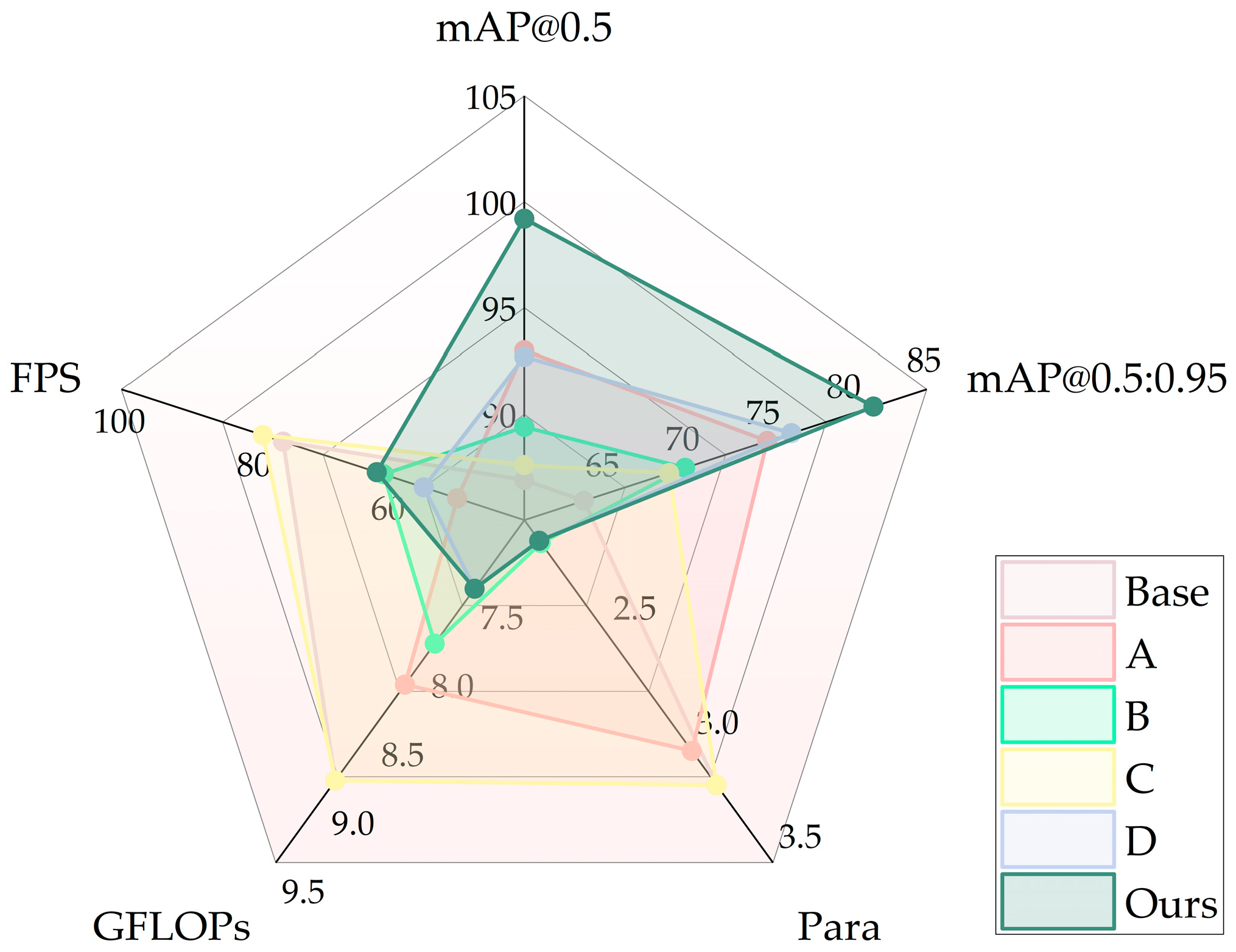
| Model | Backbone | Neck | Loss Function | mAP@0.5/% | mAP@0.5:0.95 | Params (M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| base | 86.9 | 63.7 | 3.2 | 8.9 | 76.0 | |||
| A | √ | 93.0 | 75.1 | 3.0 | 8.2 | 50.0 | ||
| B | √ | 89.4 | 70.0 | 2.1 | 7.9 | 61.0 | ||
| C | √ | 87.6 | 69.0 | 3.2 | 8.9 | 79.0 | ||
| D | √ | √ | 92.7 | 76.6 | 2.1 | 7.5 | 55.0 | |
| Ours | √ | √ | √ | 99.2 | 81.7 | 2.1 | 7.5 | 62.0 |
| Test Vedio | Detectors | MOTA | IDF1 | FNt | FPt | IDSWt | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| video 1 | YOLOv3 | 59.6 | 81.6 | 11.0 | 73.0 | 5.0 | 27.9 |
| YOLOv5 | 60.5 | 81.6 | 16.0 | 66.0 | 5.0 | 37.2 | |
| YOLOv8 | 59.1 | 64.8 | 47.0 | 123.0 | 6.0 | 41.8 | |
| Ours | 85.0 | 92.4 | 9.0 | 20.0 | 1.0 | 38.6 | |
| vedio 2 | YOLOv3 | 39.1 | 71.3 | 692.0 | 1102.0 | 24.0 | 29.6 |
| YOLOv5 | 25.3 | 65.6 | 847.0 | 1370.0 | 12.0 | 37.6 | |
| YOLOv8 | 17.7 | 60.2 | 1112.0 | 1330.0 | 15.0 | 52.8 | |
| Ours | 58.3 | 78.2 | 652.0 | 532.0 | 2.0 | 38.6 | |
| video 3 | YOLOv3 | 35.3 | 55.2 | 492.0 | 660.0 | 15.0 | 28.6 |
| YOLOv5 | 24.6 | 51.8 | 493.0 | 509.0 | 15.0 | 38.6 | |
| YOLOv8 | 16.1 | 52.2 | 490.0 | 513.0 | 13.0 | 49.8 | |
| Ours | 45.3 | 60.3 | 280.0 | 375.0 | 5.0 | 38.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Lei, G.; Wang, L.; Guo, C. Research on Lightweight Tracking of Small-Sized UAVs Based on the Improved YOLOv8N-Drone Architecture. Drones 2025, 9, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9080551
Zhao Y, Ma Q, Lei G, Wang L, Guo C. Research on Lightweight Tracking of Small-Sized UAVs Based on the Improved YOLOv8N-Drone Architecture. Drones. 2025; 9(8):551. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9080551
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yongjuan, Qiang Ma, Guannan Lei, Lijin Wang, and Chaozhe Guo. 2025. "Research on Lightweight Tracking of Small-Sized UAVs Based on the Improved YOLOv8N-Drone Architecture" Drones 9, no. 8: 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9080551
APA StyleZhao, Y., Ma, Q., Lei, G., Wang, L., & Guo, C. (2025). Research on Lightweight Tracking of Small-Sized UAVs Based on the Improved YOLOv8N-Drone Architecture. Drones, 9(8), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9080551






