An Experiment on Multi-Angle Sun Glitter Remote Sensing of Water Surface Using Multi-UAV
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Processing
2.1. UAV-Based Multi-Angle Sun Glitter Imagery
2.2. Other Data
3. Models
3.1. Water Surface Optical Radiation Transmission Model
3.2. Sun Glitter Theory Based on the Cox–Munk Model
3.3. Estimation Model for Water Surface Roughness and Refractive Index Based on Multi-Angle Sun Glitter Image
3.4. Sun Glitter Extract Model
4. Results and Discussion
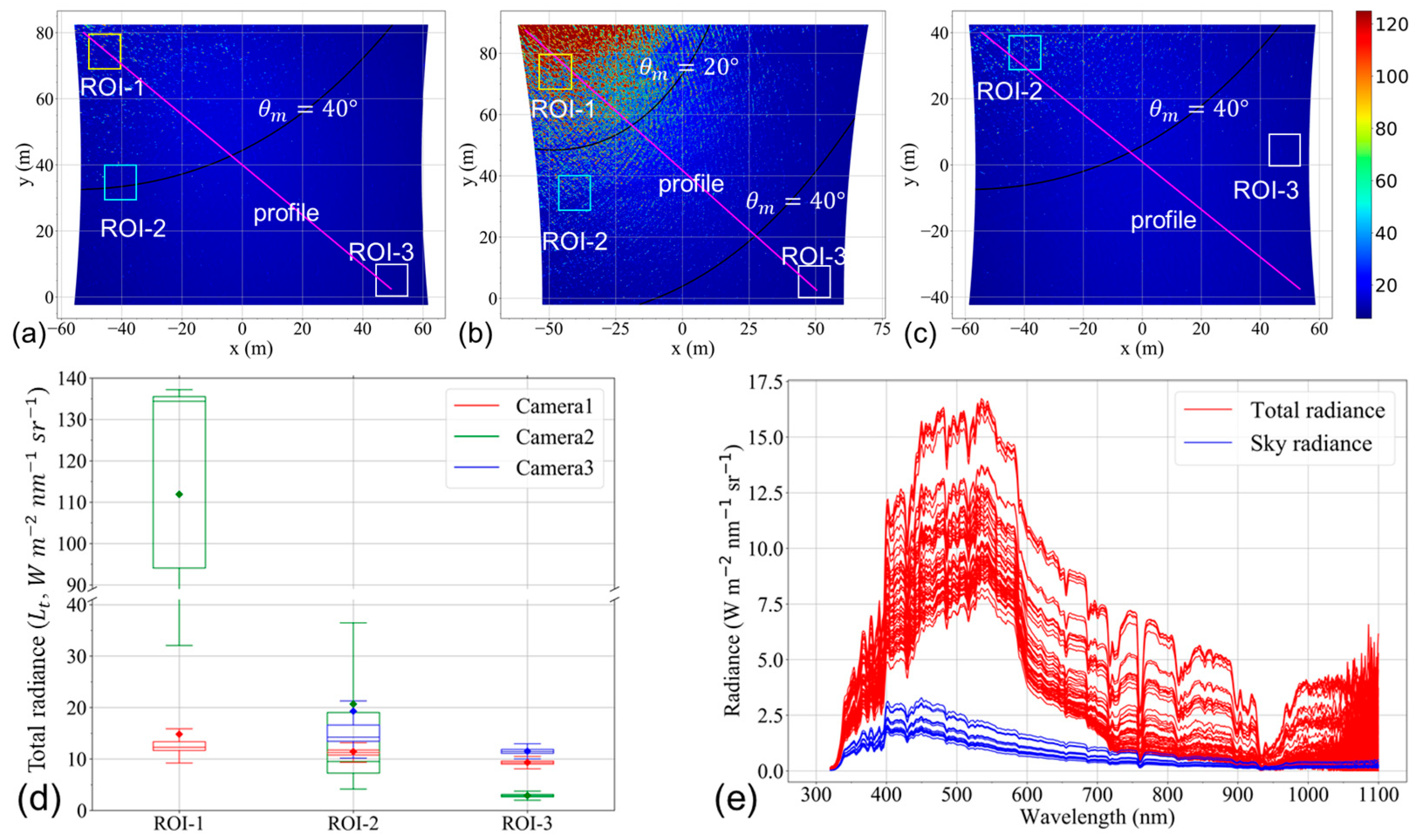
4.1. Analysis of Multi-Angle Images from UAVs
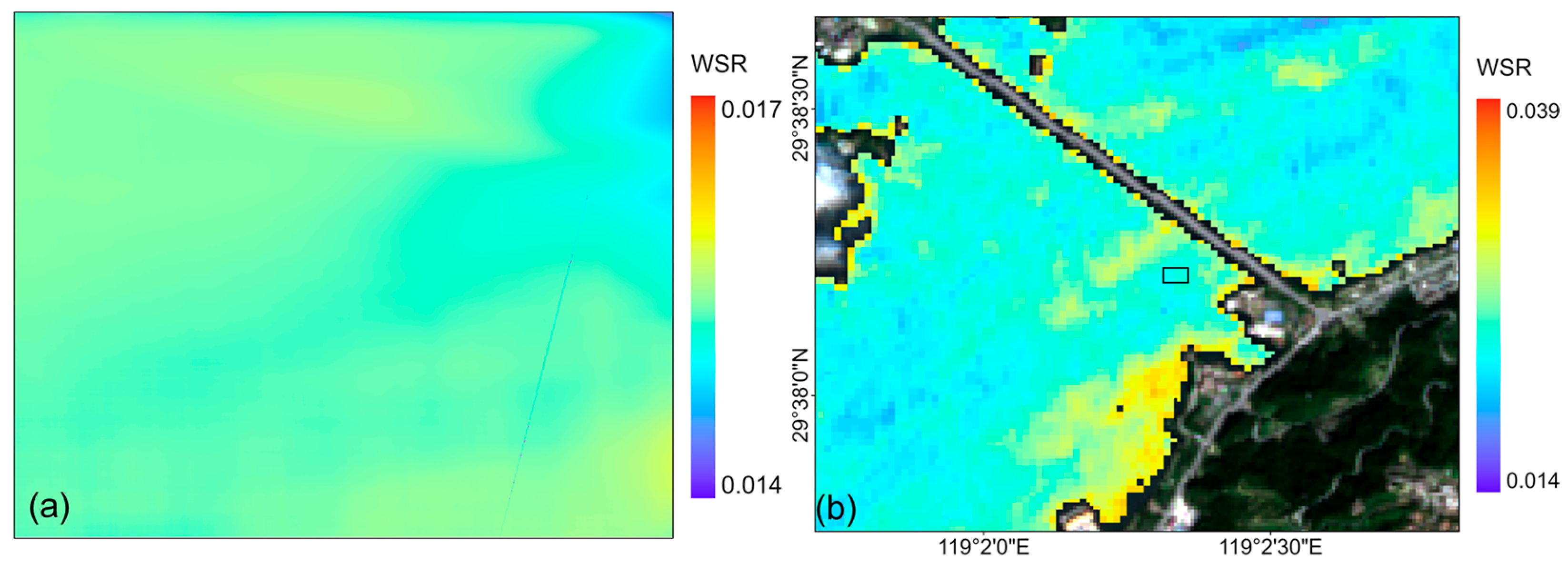
4.2. Results of Sun Glitter Extraction
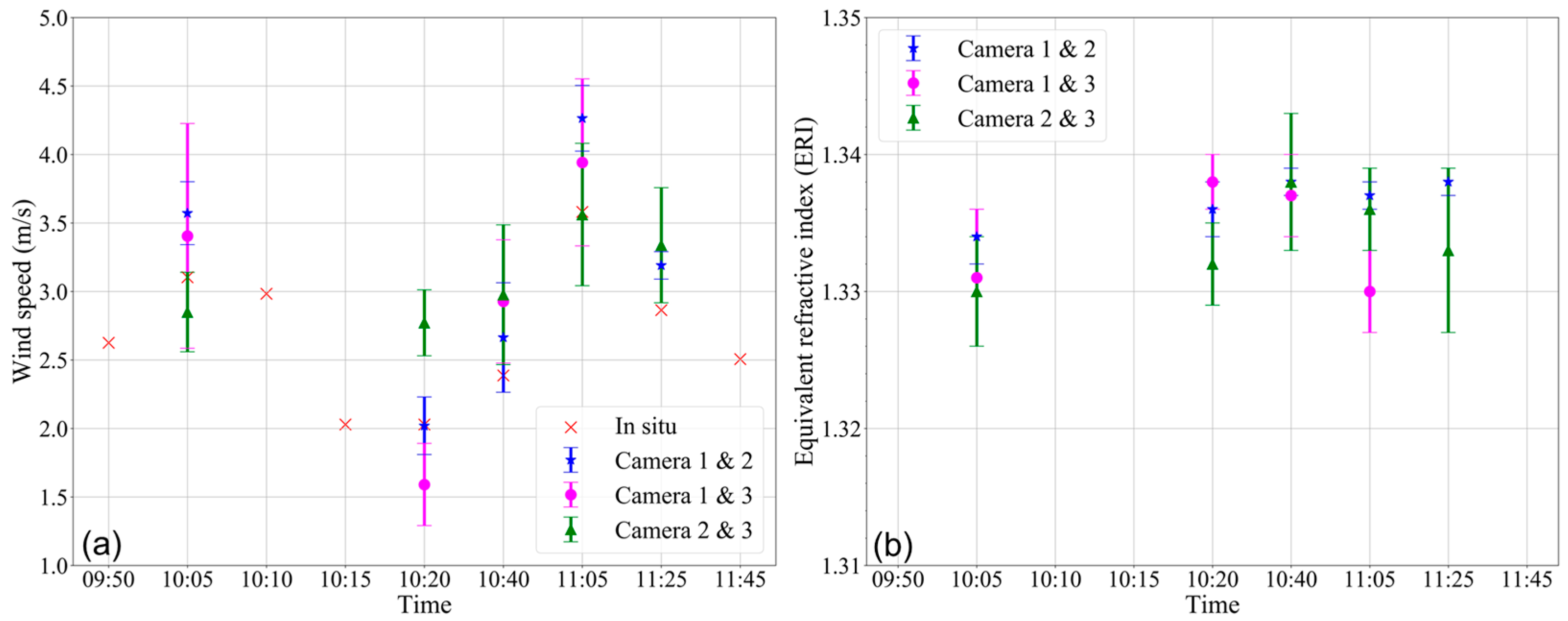
4.3. Validation of Water Surface Roughness and Refractive Index
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UAV | Unmanned aerial vehicle |
| SG | Sun glitter |
| WSR | Water surface roughness |
| ERI | Equivalent refractive index |
| CM | Cox-Munk |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| ROI | Region of interest |
References
- Bukin, O.A.; Proschenko, D.Y.; Chekhlenok, A.A.; Korovetskiy, D.A. Methods for Optical Monitoring of Oil Pollution of Sea Water Basins Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2019, 32, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Jia, G.; Cai, Y. A New Approach to Oil Spill Detection That Combines Deep Learning with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 135, 1300–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koparan, C.; Koc, A.B.; Privette, C.V.; Sawyer, C.B. In Situ Water Quality Measurements Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) System. Water 2018, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Figueroa, E.G.; Wilson, A.E.; Rogers, S.R. Commercially Available Unoccupied Aerial Systems for Monitoring Harmful Algal Blooms: A Comparative Study. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2022, 20, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, X.; Dedman, S.; Rosso, M.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Xia, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J. UAV Remote Sensing Applications in Marine Monitoring: Knowledge Visualization and Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.; Munk, W. Measurement of the Roughness of the Sea Surface from Photographs of the Sun’s Glitter. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1954, 44, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, J.R.; Byrne, H.M.; Proni, J.R.; Charnell, R.L. Observations of Oceanic Internal and Surface Waves from the Earth Resources Technology Satellite. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 865–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C. Internal Wave Detection Using the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2007, 112, C11012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.P.; Awaji, T. Synoptic Mapping of Internal-Wave Motions and Surface Currents near the Lombok Strait Using the Along-Track Stereo Sun Glitter Technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennings, I.; Doerffer, R.; Germany, E.R. Comparison of Submarine Relief Features on a Radar Satellite Image and on a Skylab Satellite Photograph. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1988, 9, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Li, Y.; Li, L. Sun Glitter Imaging of Submarine Sand Waves on the Taiwan Banks: Determination of the Relaxation Rate of Short Waves. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116, C06024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, X.; Pichel, W.G.; Muller-Karger, F.E. Detection of Natural Oil Slicks in the NW Gulf of Mexico Using MODIS Imagery. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L01604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, M.; Murch, B.; Hu, C. Refinement of the Critical Angle Calculation for the Contrast Reversal of Oil Slicks under Sunglint. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Q.; Cao, W.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Lou, X. Inversion of the Refractive Index of Marine Spilled Oil Using Multi-Angle Sun Glitter Images Acquired by the ASTER Sensor. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 275, 113019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Lou, X.; Chen, P.; Fan, K.; Shi, A.; Li, D. On Optimal Imaging Angles in Multi-Angle Ocean Sun Glitter Remote-Sensing Platforms to Observe Sea Surface Roughness. Sensors 2019, 19, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, D. Multi-Camera Imaging System for UAV Photogrammetry. Sensors 2018, 18, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, M.; Przybilla, H.J.; Zurhorst, A. UAV Cameras: Overview and Geometric Calibration Benchmark. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. ISPRS Arch. 2017, 42, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q. Adaptation of the Dark Spectrum Fitting Atmospheric Correction for Aquatic Applications of the Landsat and Sentinel-2 Archives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.A.; Meindl, E.A.; Gilhousen, D.B. Determining the Power-Law Wind-Profile Exponent under near-Neutral Stability Conditions at Sea. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C. Light and Water: Radiative Transfer in Natural Waters Light and Waters; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994; 592p. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Tian, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Song, Q. The Methods of Water Spectra Measurement and Analysis I: Above-Water Method. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 8, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.C.; Gómez, J.A.D.; Martín, J.D.; Sánchez, B.A.H.; Arango, J.L.C.; Tuya, F.A.C.; Díaz-Varela, R. An UAV and Satellite Multispectral Data Approach to Monitor Water Quality in Small Reservoirs. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Y.; Jiao, J.; Zhou, J.; Ju, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, Y.; et al. Correction of Multi-Scale Sunglint Reflections from the Water Surface in Airborne High-Spatial Resolution Optical Images. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 45910–45917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, H.R. Atmospheric Correction of Ocean Color Imagery in the Earth Observing System Era. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 17081–17106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.R.; Alpers, W. The Role of the Critical Angle in Brightness Reversals on Sunglint Images of the Sea Surface. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115, C09019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, M. Evaluation of Sun Glint Models Using MODIS Measurements. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010, 111, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, K.; Lou, X.; Li, Y.; Zheng, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Ren, L.; Li, D.; Shi, A. Observation of Sea Surface Roughness at a Pixel Scale Using Multi-Angle Sun Glitter Images Acquired by the ASTER Sensor. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 208, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhang, M.; Mao, Z. Polarized Remote Inversion of the Refractive Index of Marine Spilled Oil from PARASOL Images under Sunglint. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 2710–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W. An Inconvenient Sea Truth: Spread, Steepness, and Skewness of Surface Slopes. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 377–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Jiao, J.; Ding, J.; Fu, W.; Qian, W. Using Sea Wave Simulations to Interpret the Sunglint Reflection Variation with Different Spatial Resolutions. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurovskaya, M.; Rascle, N.; Kudryavtsev, V.; Chapron, B.; Marié, L.; Molemaker, J. Wave Spectrum Retrieval from Airborne Sunglitter Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, R.; Schmechtig, C. Adjacency Effects on Water Surfaces: Primary Scattering Approximation and Sensitivity Study. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muslim, A.M.; Chong, W.S.; Safuan, C.D.M.; Khalil, I.; Hossain, M.S. Coral Reef Mapping of UAV: A Comparison of Sun Glint Correction Methods. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Richardson, M.; King, D.J. The Impacts of Environmental Variables on Water Reflectance Measured Using a Lightweight Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-Based Spectrometer System. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnesecchi, F.; Byfield, V.; Cipollini, P.; Corsini, G.; Diani, M. An Optical Model for the Interpretation of Remotely Sensed Multispectral Images of Oil Spill. Remote Sens. Ocean Sea Ice Large Water Reg. 2008 2008, 7105, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, W.; Xia, M.; Li, W.; Yang, K. In Situ Measurement of Seawater Salinity with an Optical Refractometer Based on Total Internal Reflection Method. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 25510–25523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huibers, P.D.T. Models for the Wavelength Dependence of the Index of Refraction of Water. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 3785–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
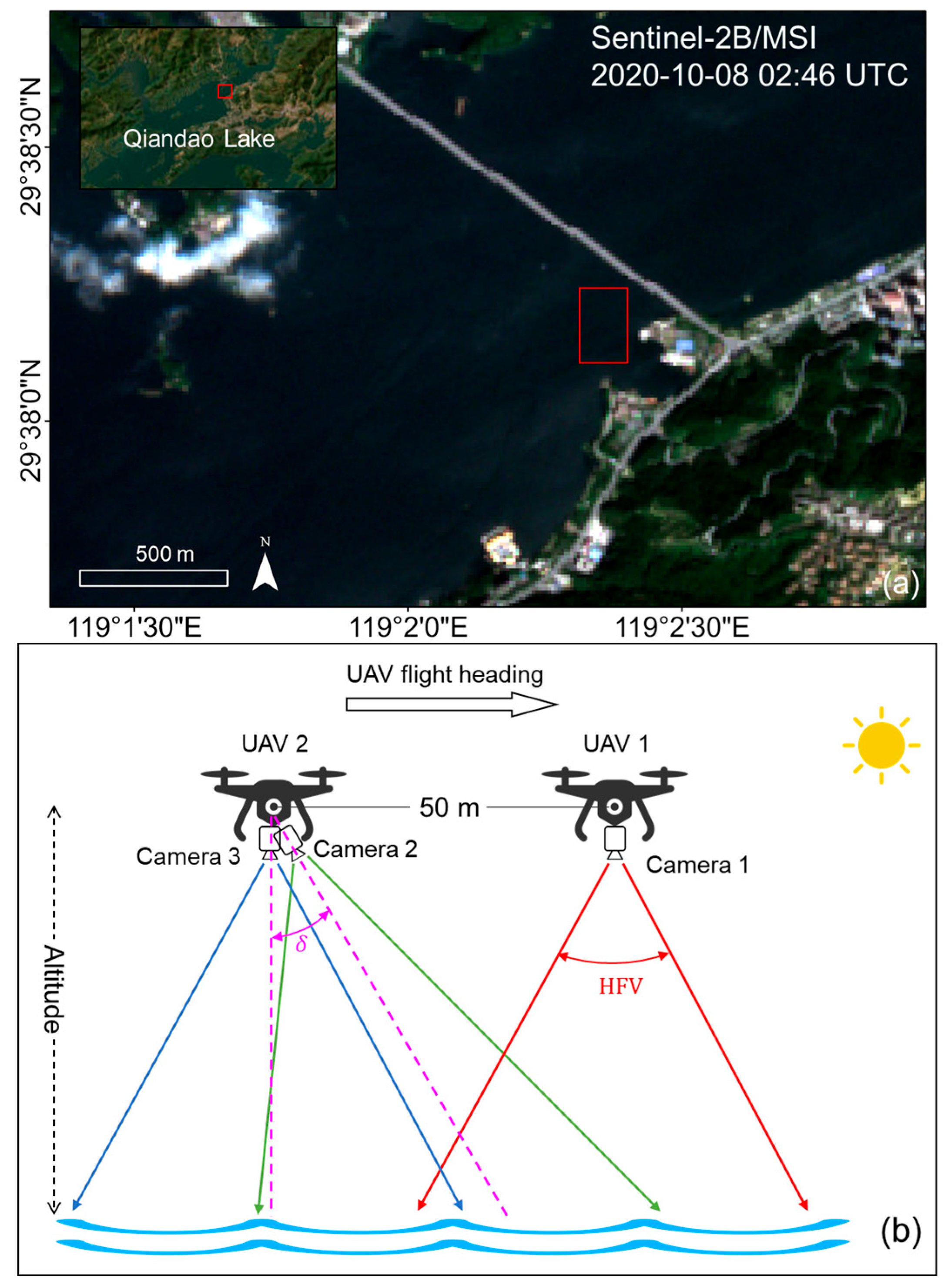

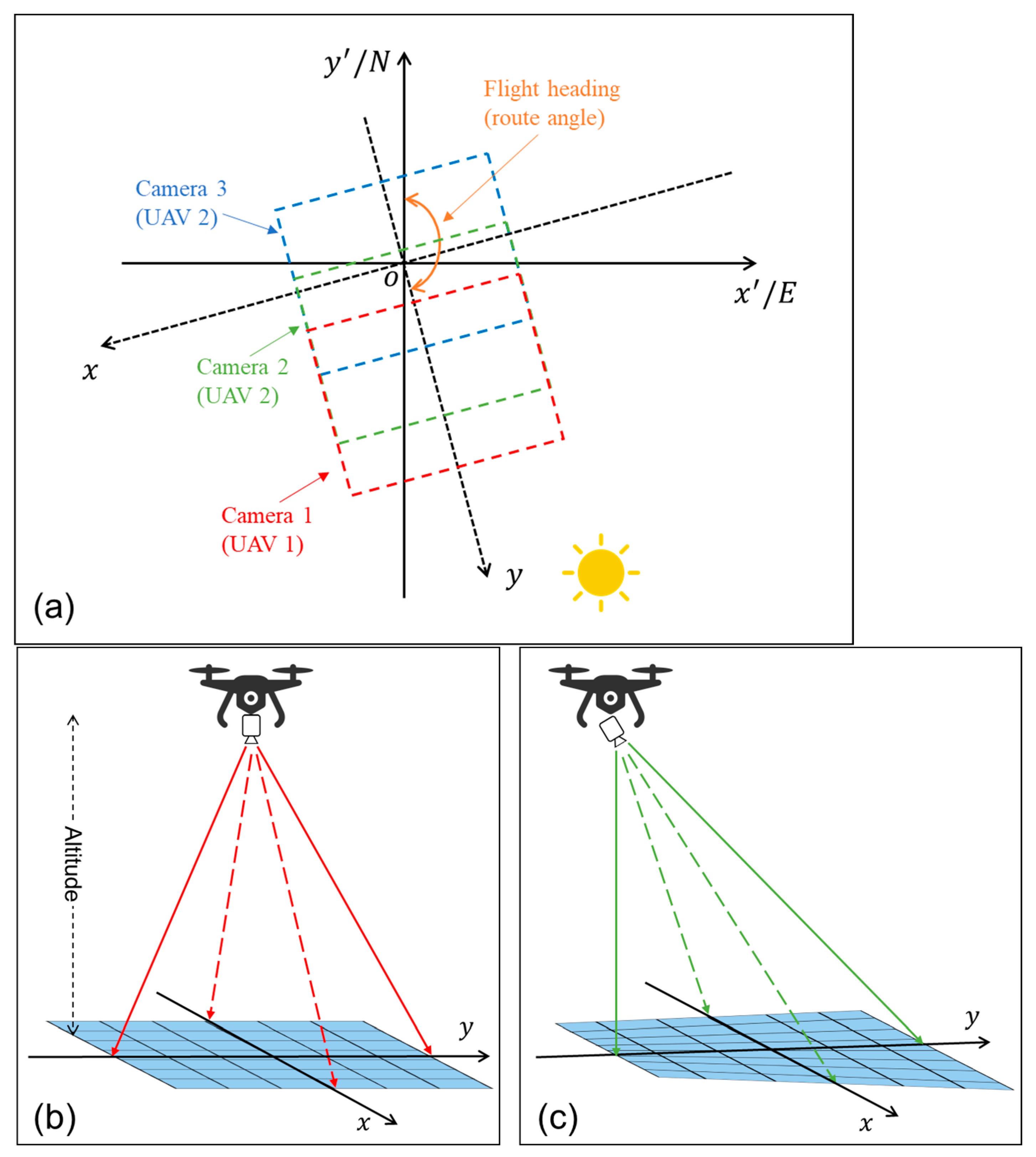
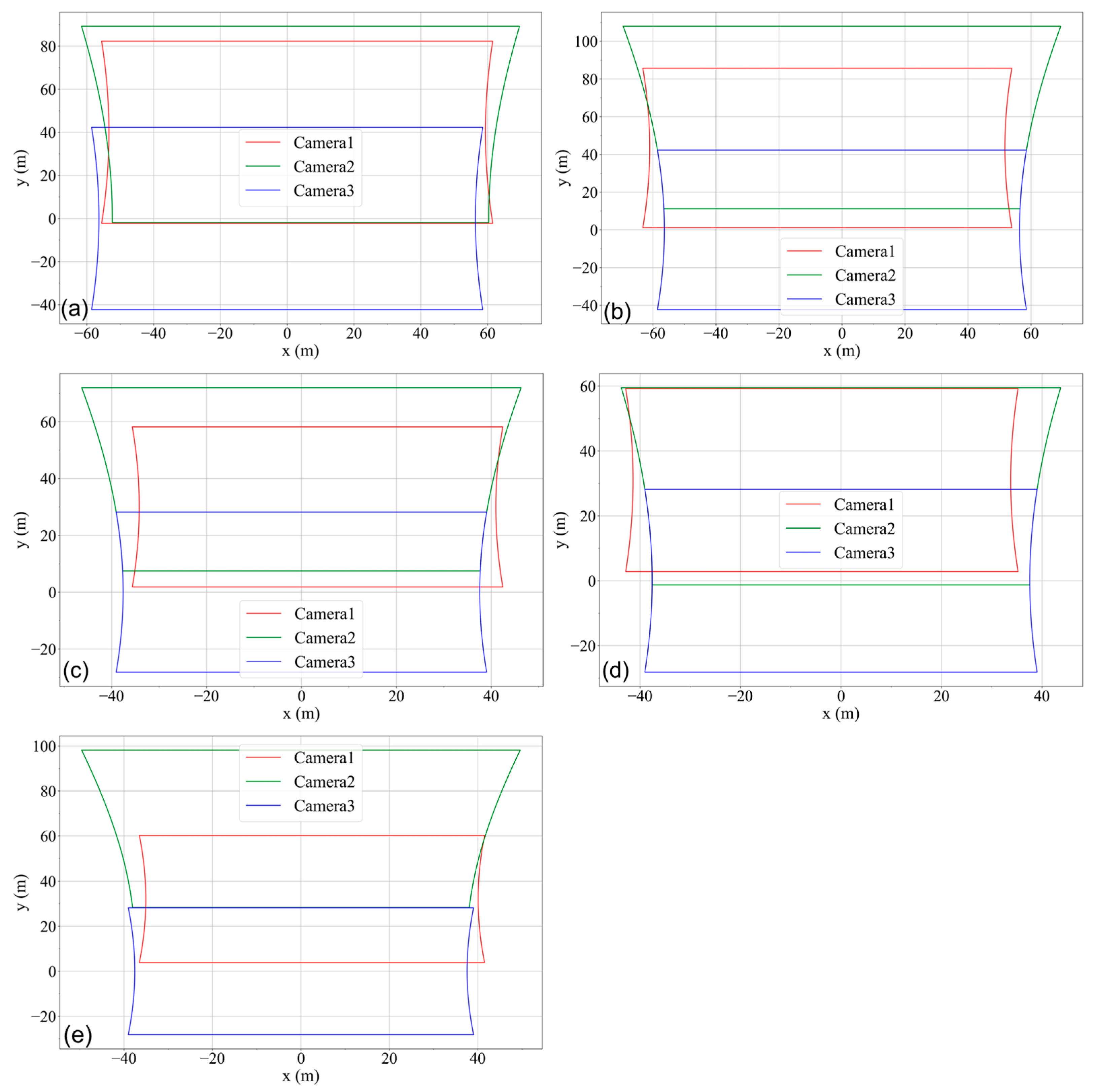

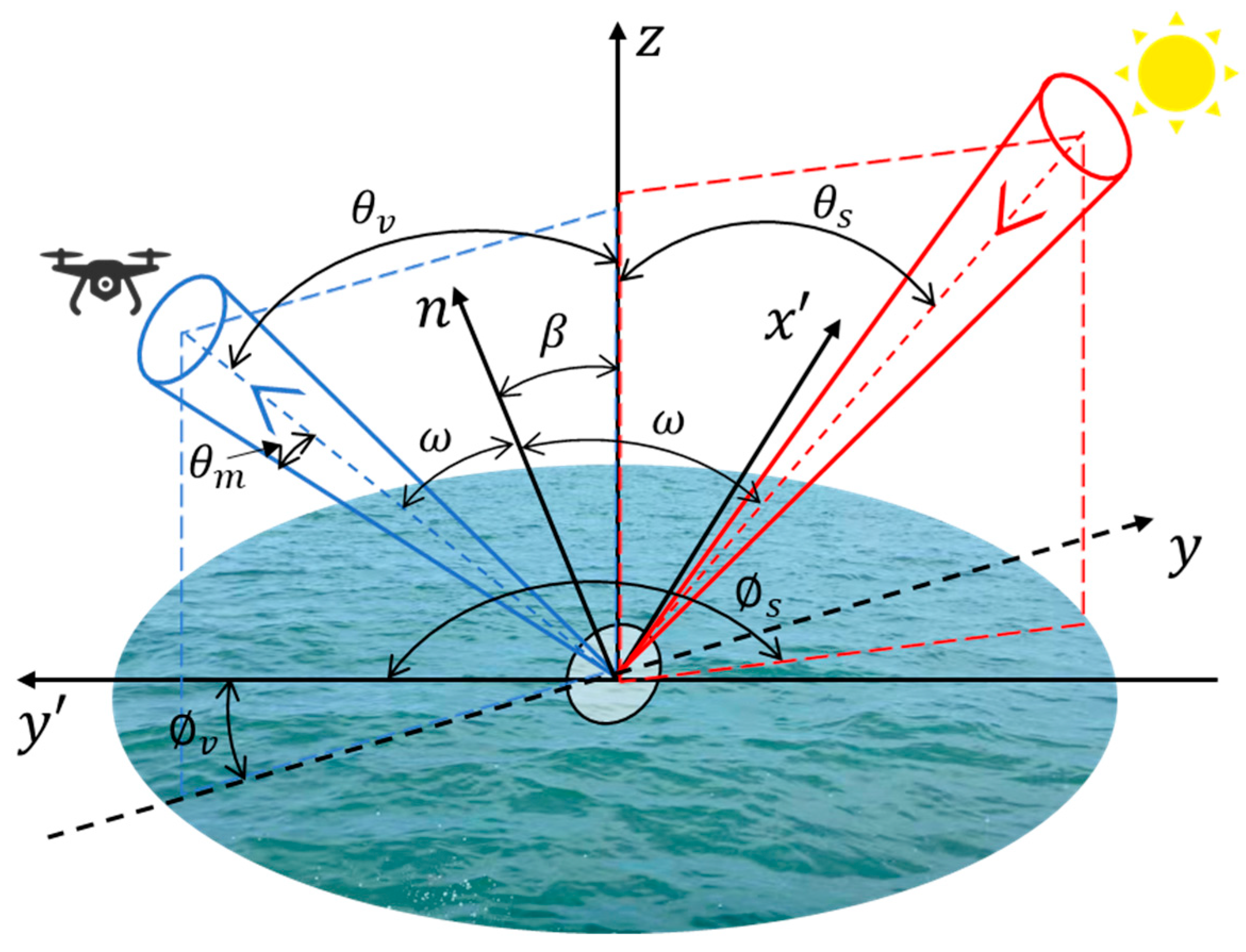



| Equipment | Parameter | Index |
|---|---|---|
| MAPIR Survey3N | Horizontal field of view (HFV) | 41° (47 mm) |
| Image size | 4000 × 3000 pixels | |
| Spatial resolution | 2.3 cm/pixel (120 m altitude) | |
| Focal length | 8.25 mm | |
| Band | NIR 850 nm, Red 660 nm, Green 550 nm | |
| DJI-M600PRO | Maximum load | 6 kg |
| Flight duration | 16 min | |
| Maximum wind resistance level | 8 m/s | |
| Maximum flight altitude | 4500 m | |
| Maximum horizontal speed | 65 km/h |
| Parameter | Flight 1 | Flight 2 | Flight 3 | Flight 4 | Flight 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (UTC+8) | 10:05 | 10:20 | 10:40 | 11:05 | 11:25 |
| Flight altitude (m) | 150 | 150 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Ground sampling distance (cm/px) | 2.82 | 2.82 | 1.88 | 1.88 | 1.88 |
| Image count | 32 | 34 | 35 | 32 | 33 |
| Camera-2 tilt angle (°) | 15 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 25 |
| Flight heading (°) | 165 | 165 | 165 | 165 | 165 |
| Sun zenith (°) | 42 | 40 | 37 | 30 | 20 |
| Sun azimuth (°) | 140 | 150 | 155 | 160 | 165 |
| Flight ID | Difference of Angle (°) | Maximum (m/s) | Average (m/s) | Minimum (m/s) | In-Situ 1 (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flight 1 (150 m) | 15 | 3.92 | 3.57 | 3.10 | 3.10 |
| Flight 2 (150 m) | 20 | 2.62 | 2.02 | 1.70 | 2.03 |
| Flight 3 (100 m) | 20 | 4.05 | 2.67 | 2.14 | 2.39 |
| Flight 4 (100 m) | 15 | 4.71 | 4.26 | 3.78 | 3.58 |
| Flight 5 (100 m) | 25 | 3.61 | 3.19 | 3.09 | 2.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Liao, G.; Cao, W.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Lou, X. An Experiment on Multi-Angle Sun Glitter Remote Sensing of Water Surface Using Multi-UAV. Drones 2025, 9, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9060400
Wang C, Zhang H, Liao G, Cao W, Wang J, Li D, Lou X. An Experiment on Multi-Angle Sun Glitter Remote Sensing of Water Surface Using Multi-UAV. Drones. 2025; 9(6):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9060400
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chen, Huaguo Zhang, Guanghong Liao, Wenting Cao, Juan Wang, Dongling Li, and Xiulin Lou. 2025. "An Experiment on Multi-Angle Sun Glitter Remote Sensing of Water Surface Using Multi-UAV" Drones 9, no. 6: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9060400
APA StyleWang, C., Zhang, H., Liao, G., Cao, W., Wang, J., Li, D., & Lou, X. (2025). An Experiment on Multi-Angle Sun Glitter Remote Sensing of Water Surface Using Multi-UAV. Drones, 9(6), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9060400







