Neuroadaptive Fixed-Time Bipartite Containment Tracking of Networked UAVs Under Switching Topologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Related Works
1.3. Motivations
1.4. Contributions
- (1)
- This paper proposes a robust fixed-time containment tracking control scheme, which ensures that all follower agents reach a bounded region determined by the leaders within a fixed-time bound, regardless of initial conditions. Compared with asymptotic and finite-time methods [41,42,46,47], the proposed scheme eliminates dependence on initial states, thus enhancing real-time performance and control reliability.
- (2)
- A neural network-based adaptive estimator is developed to approximate the unknown nonlinear dynamics of UAVs and is seamlessly integrated into a fixed-time containment control scheme. By introducing adaptive update laws and designing appropriate radial basis functions, the estimator enhances robustness to model uncertainties and enables online compensation without requiring prior knowledge of system dynamics. In contrast to [17,26,43], which assume partial model information or fixed observer gains, the proposed estimator allows accurate and flexible approximation under general nonlinear conditions.
- (3)
- To ensure fixed-time convergence under switching topologies, a topology-dependent Lyapunov-based analysis approach is developed. By explicitly accounting for dynamic topology variations, the proposed approach guarantees convergence within a fixed-time bound. Compared with existing methods designed for fixed topologies [25,30,48] or based on conservative switching conditions [49,50], the proposed framework reduces convergence time conservativeness and enhances robustness to frequent topology changes.
1.5. Organization
2. Preliminaries and Problem Formulation
2.1. Notation
2.2. Graph Theory
2.3. Problem Formulation
2.4. Neural Network-Based Approximation
2.5. Some Useful Lemmas
3. Main Results
3.1. RBFNN-Based Approximator Design
3.2. Fixed-Time Bipartite Containment Controller Design
3.3. Stability Analysis
4. Numerical Simulation
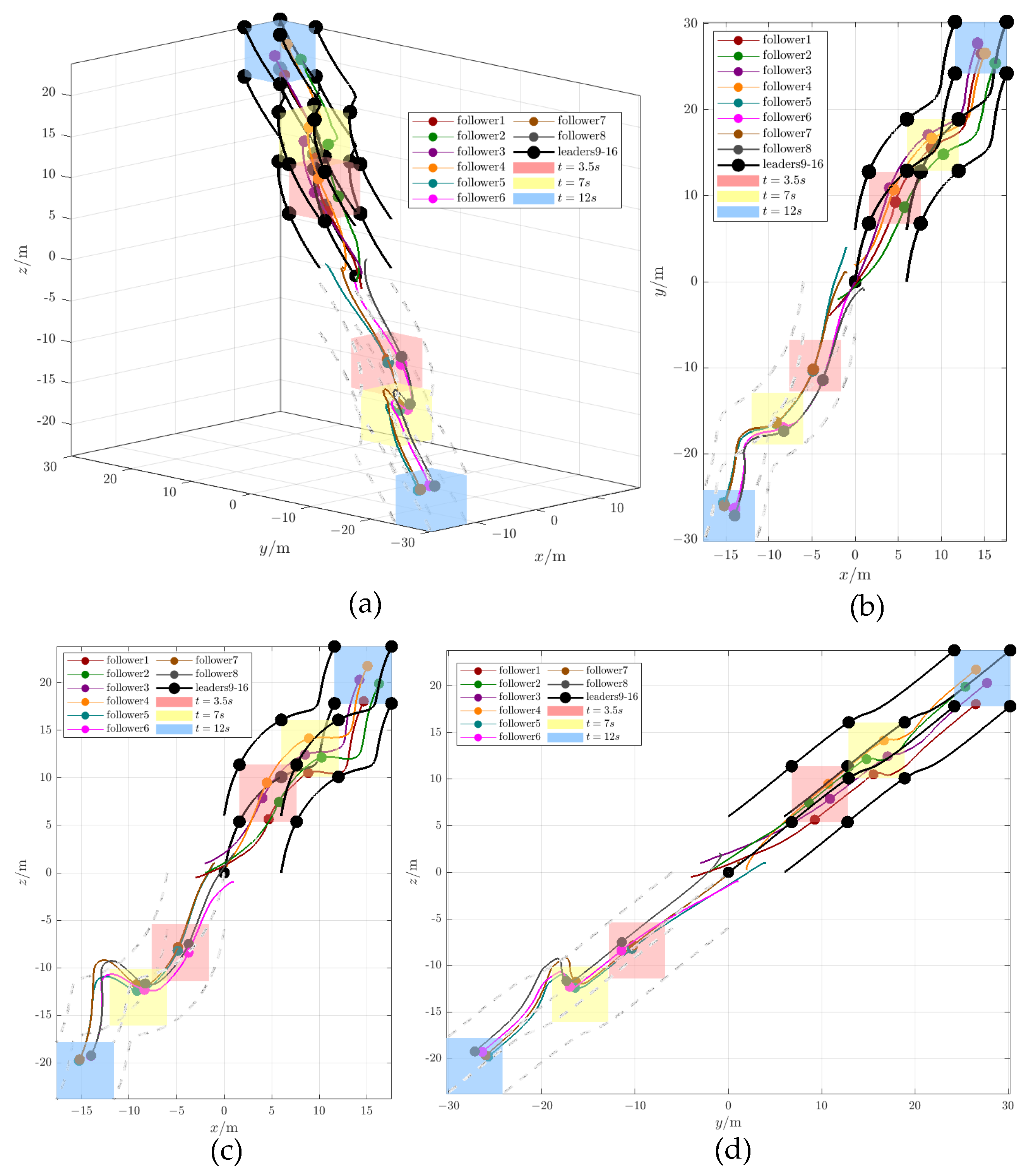
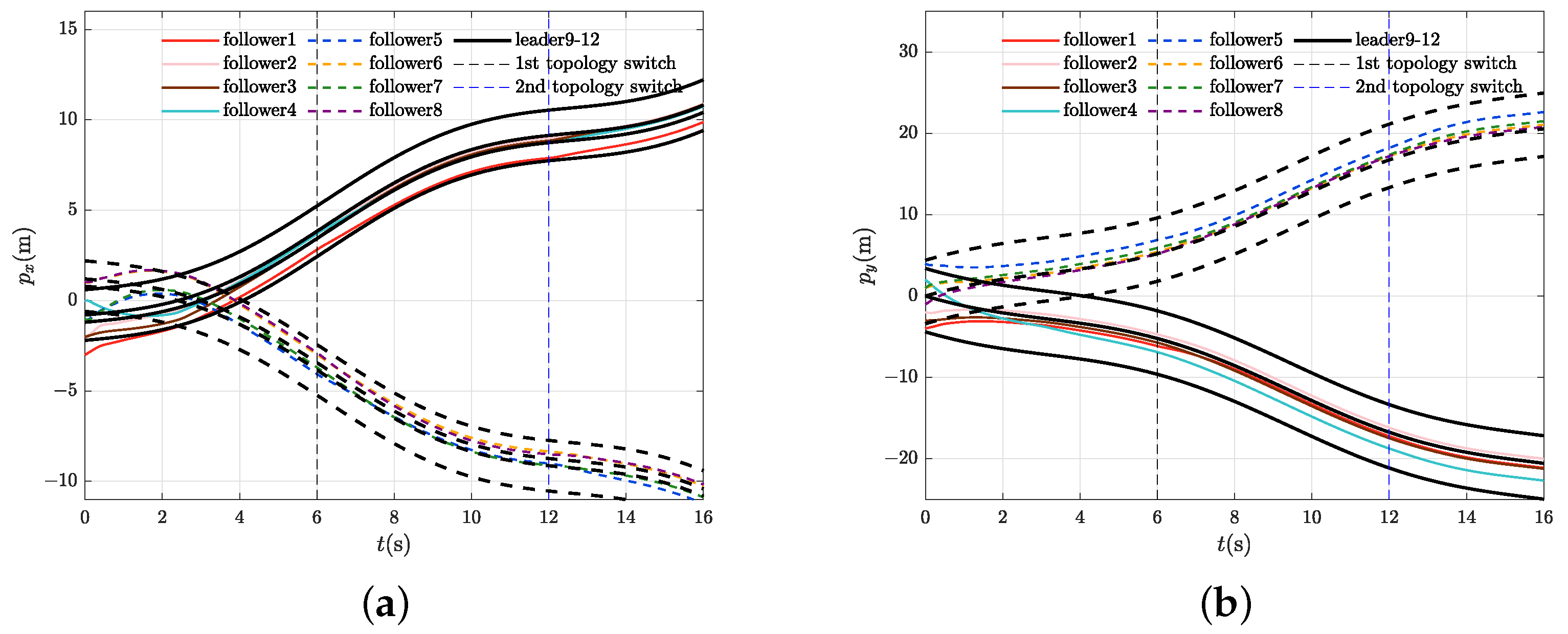
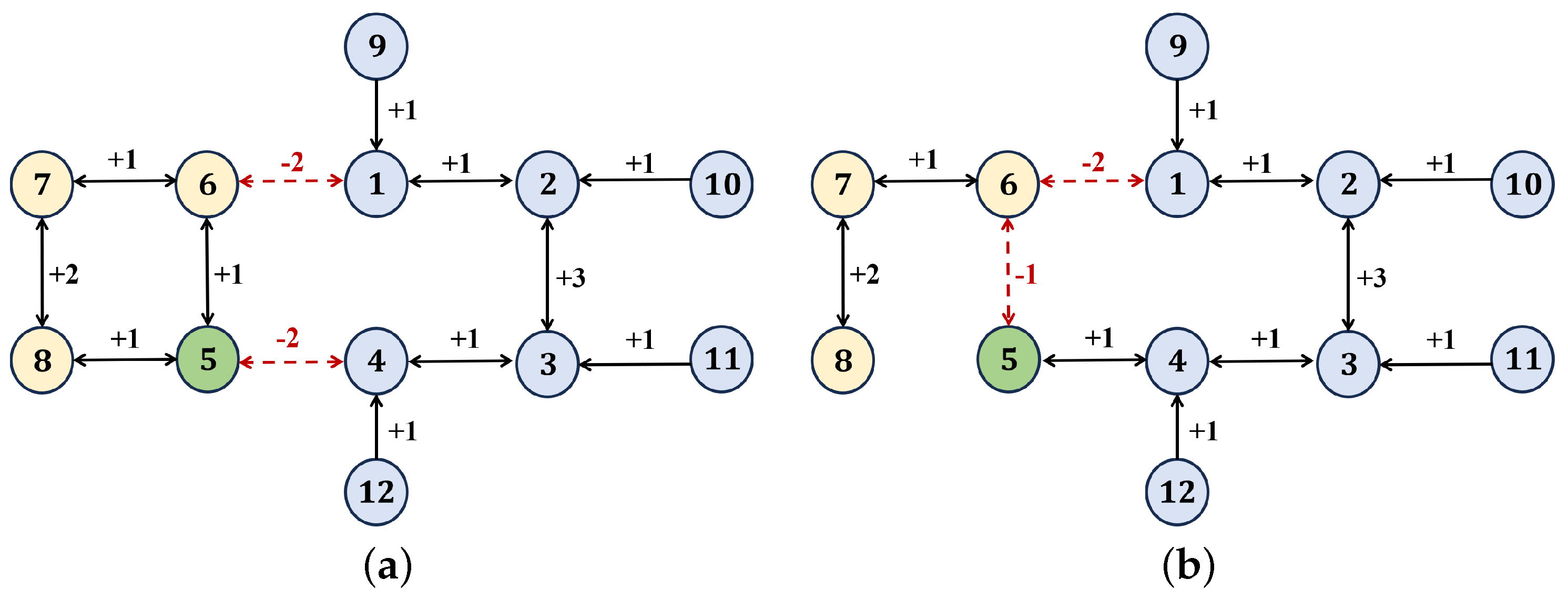
4.1. Fixed-Time Convergence Under Switching Topologies
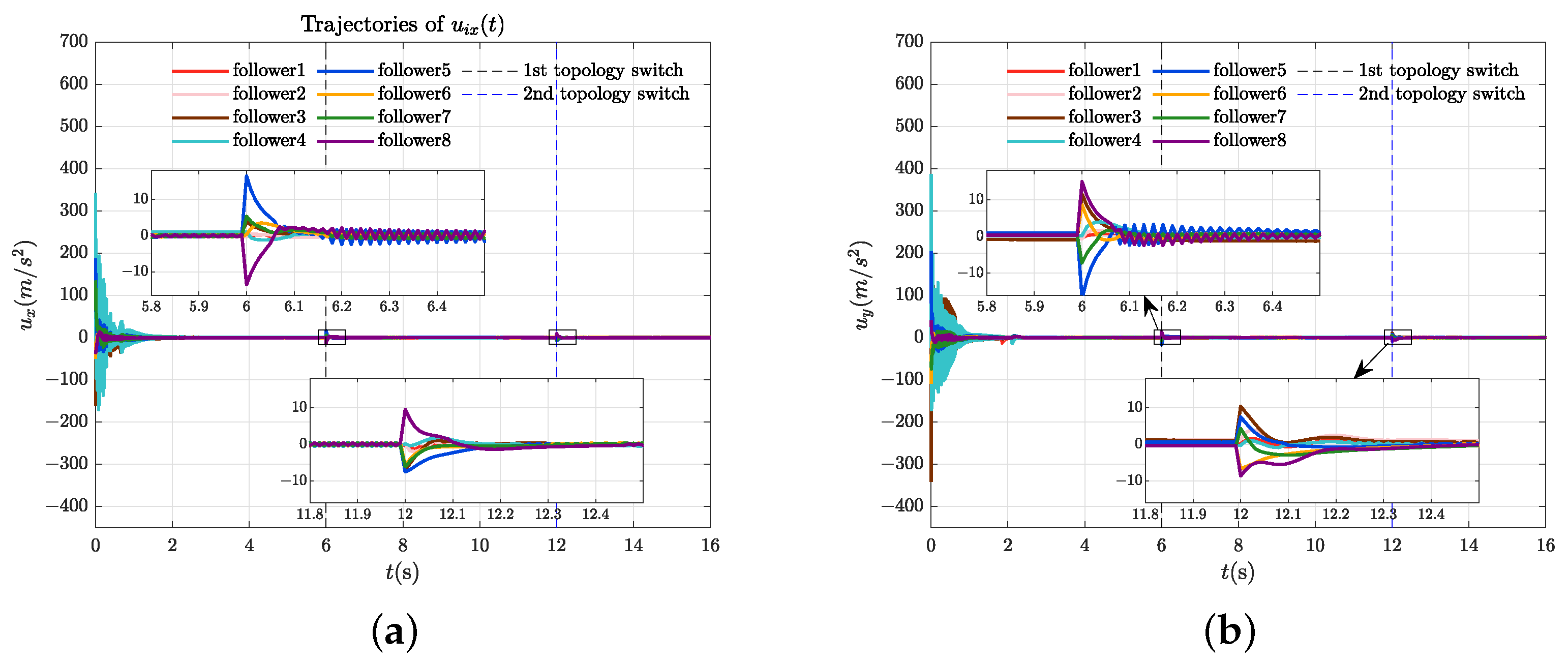
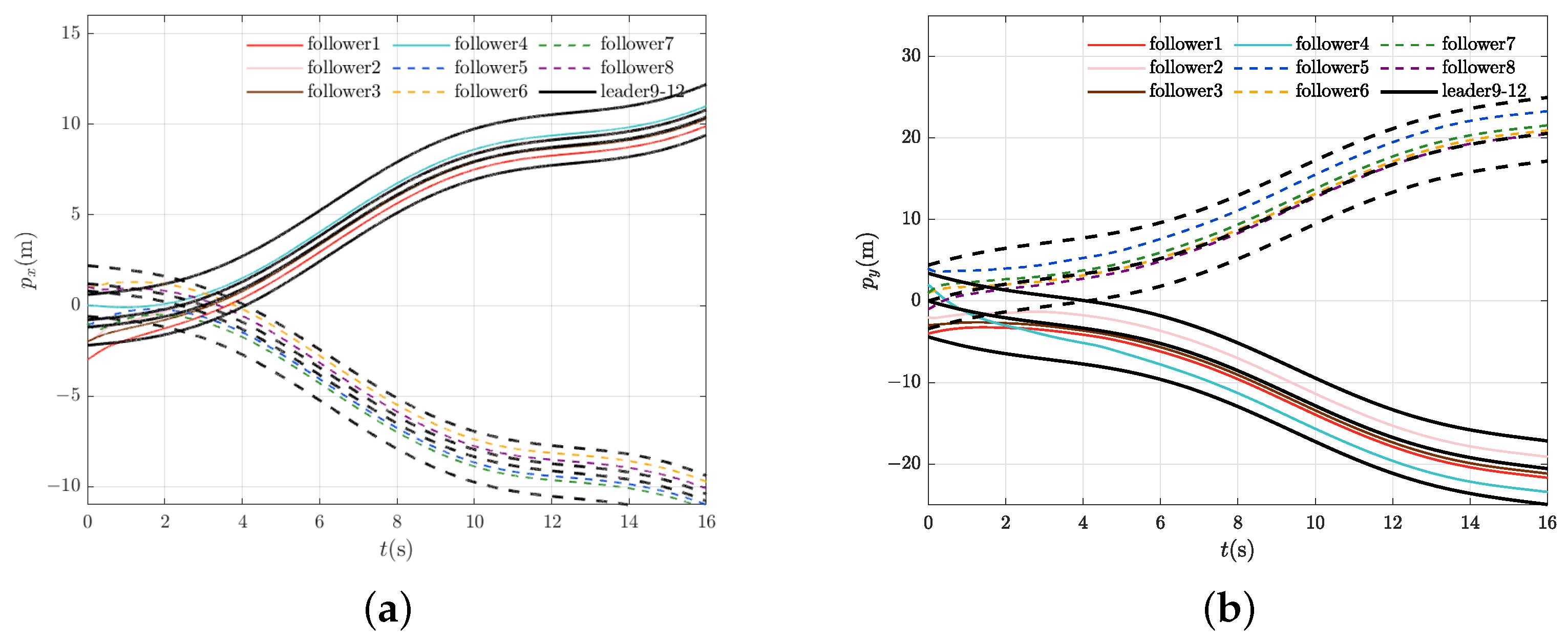
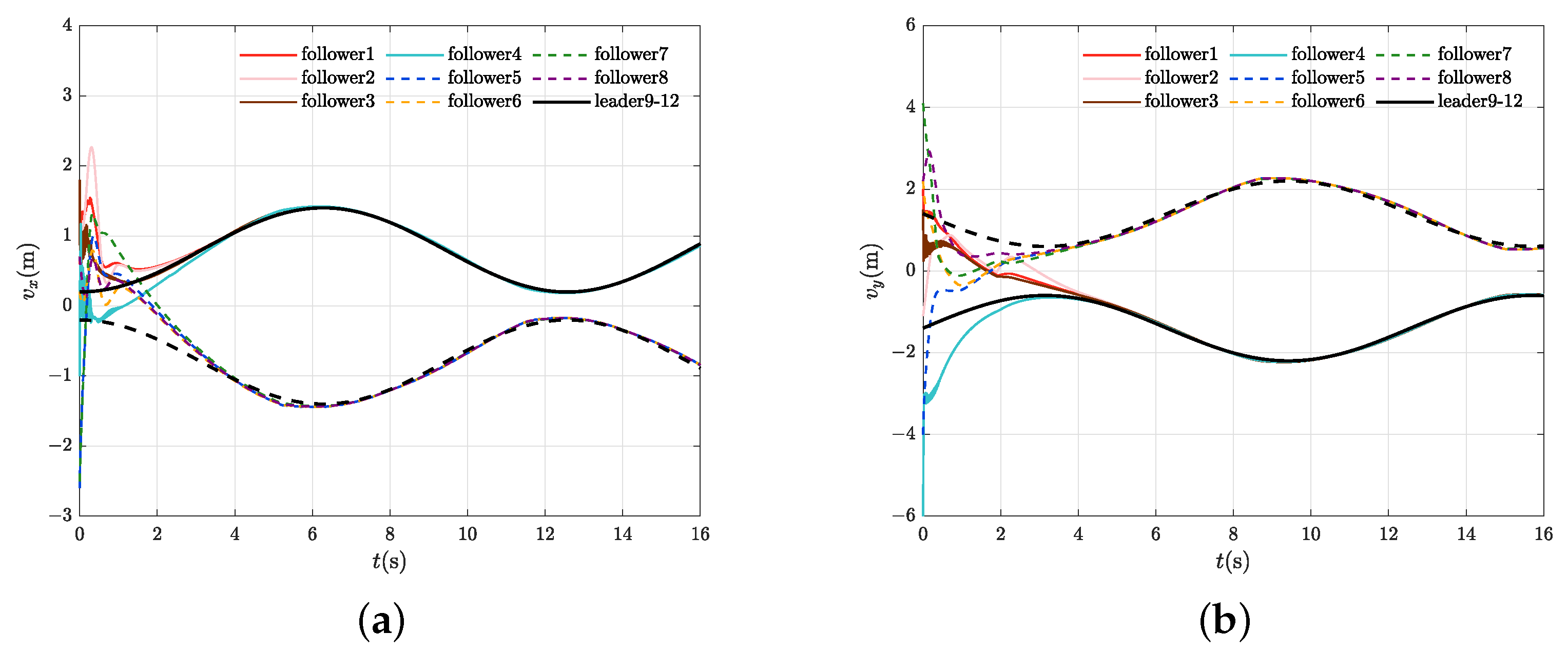
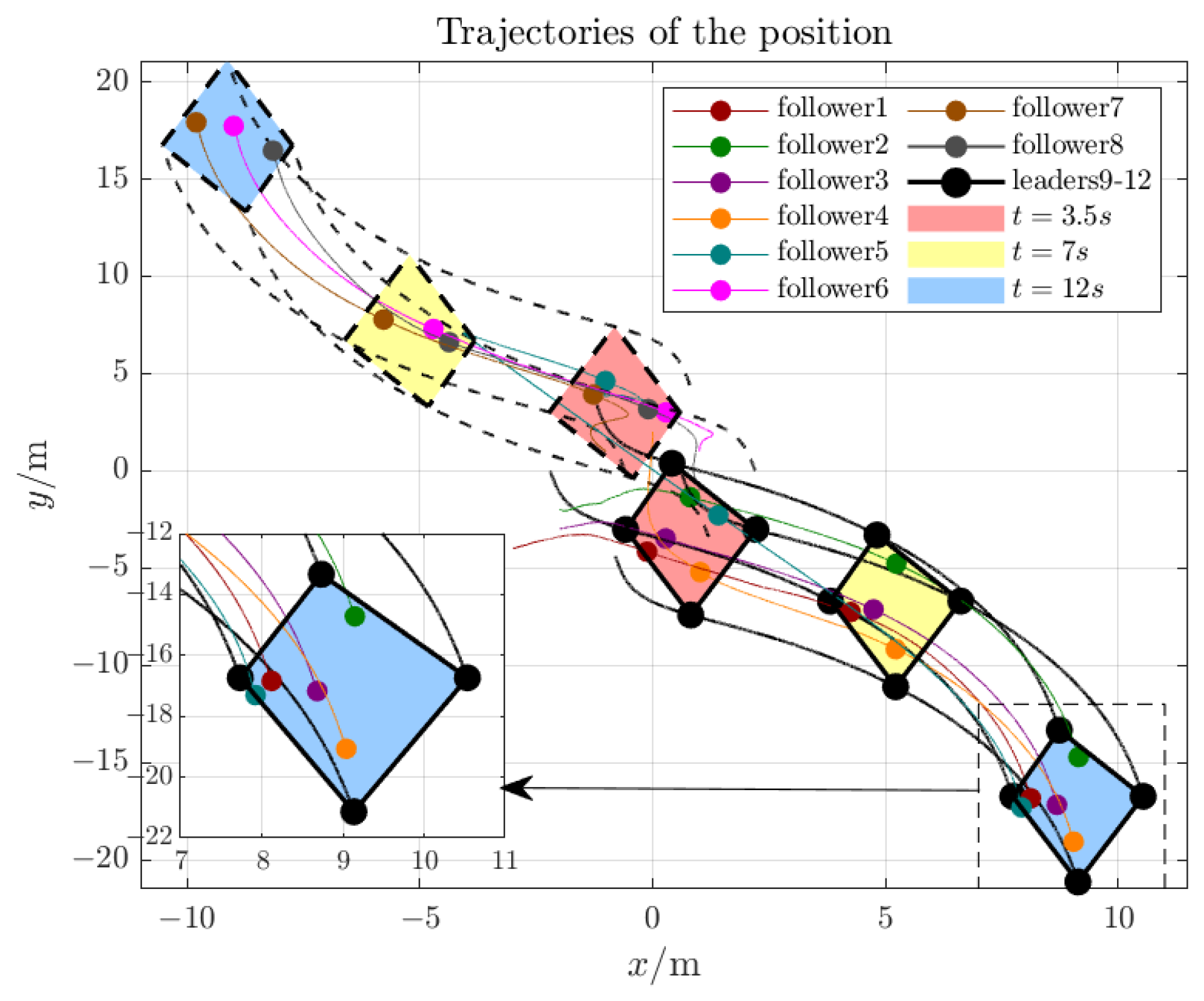
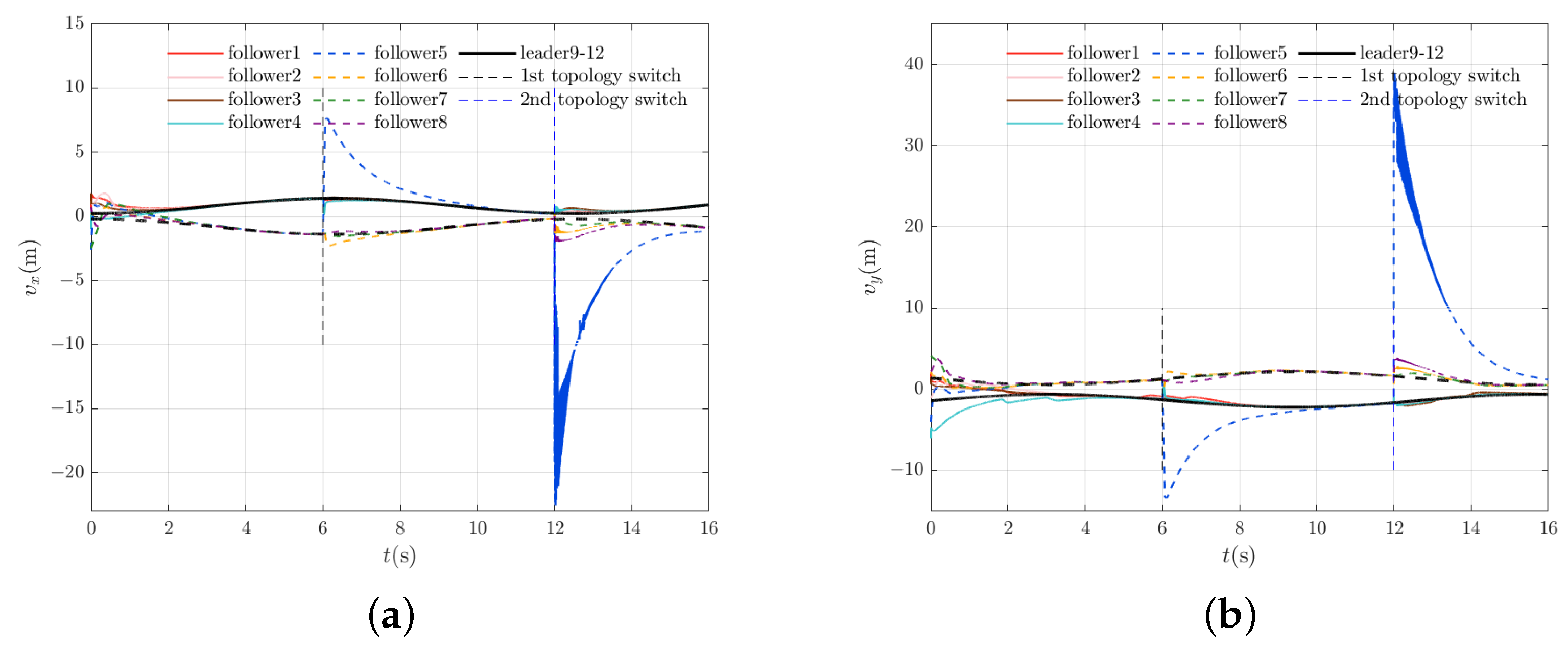
4.2. Control Performance Evaluation
4.3. Control Performance Comparison and Quantification
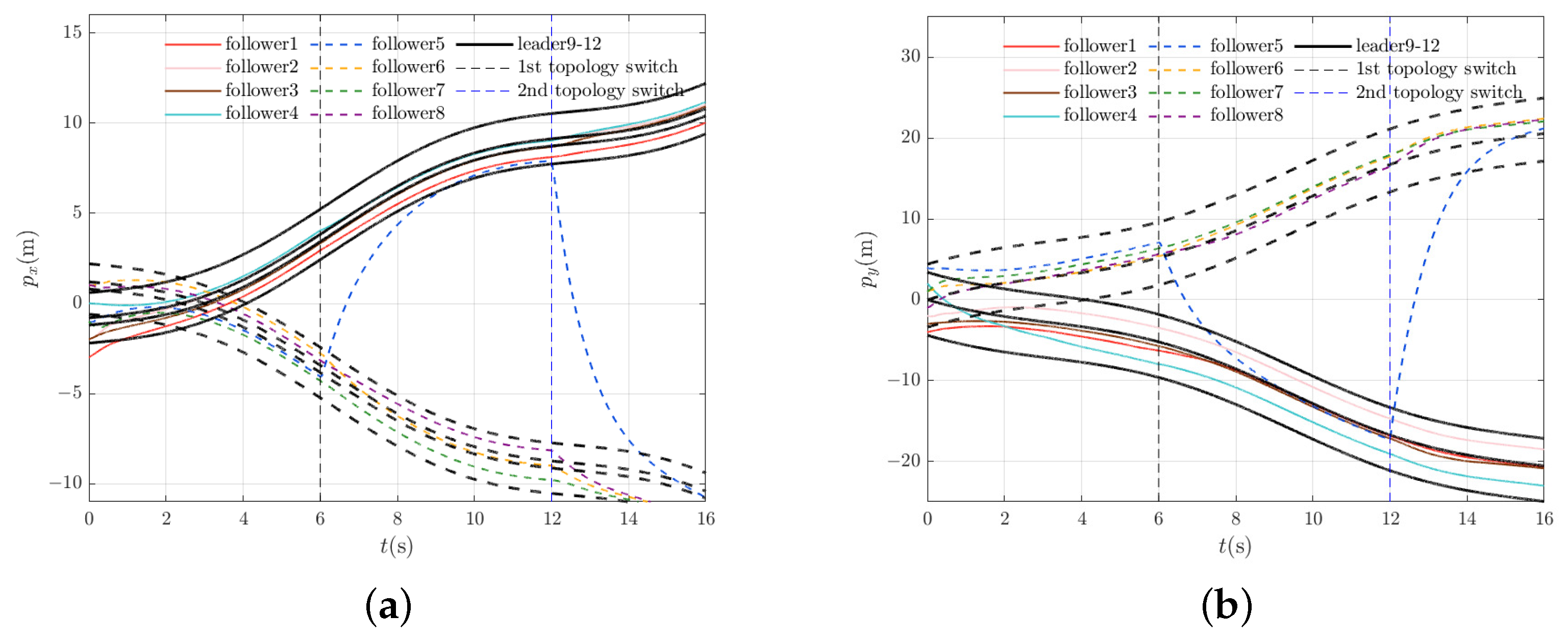
4.4. Considerations for Special Circumstances
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, H. Reliability-Constrained Uncertain Spacecraft Sliding Mode Attitude Tracking Control with Interval Parameters. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2025, 61, 6589–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, S.; Shi, M.; Yue, J.; Lin, B.; Qin, K. Collision Avoidance Time-Varying Group Formation Tracking Control for Multi-Agent Systems. Appl. Intell. 2025, 55, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Pan, Y.; Cao, L.; Chen, L. Predefined-Time Fault-Tolerant Consensus Tracking Control for Multi-UAV Systems With Prescribed Performance and Attitude Constraints. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 4058–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Liu, W.; Song, K.; Shi, L.; Xiong, Z. Containment Control of Multirobot Systems With Nonuniform Time-Varying Delays. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2025, 41, 1657–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, B. Fully Distributed Event-Triggered Security Control for DC Microgrids Subject to DoS Attacks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2025, 16, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yan, S.; Shi, L.; Yue, J.; Shi, M.; Lin, B.; Qin, K. Multiagent Consensus Tracking Control over Asynchronous Cooperation–Competition Networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2025, 55, 4347–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yan, S.; Li, W. Consensus and Products of Substochastic Matrices: Convergence Rate with Communication Delays. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Syst. 2025, 55, 4752–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, L.; Shi, M.; Lin, B.; Qin, K. Cooperative Formation Tracking of Multi-Agent Systems over Switching Signed Networks. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.S.; Che, W.W.; Deng, C.; Wu, Z.G. Observer-Based Event-Triggered Containment Control for MASs Under DoS Attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 13156–13167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, L.; Shi, M.; Yue, J.; Lin, B.; Qin, K. Leader-Following Containment Control of Hybrid Fractional-Order Networked Agents with Nonuniform Time Delays. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Netw. 2023, 9, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Li, H.; Ma, H.; Zhou, Q. Distributed Containment Control for Human-in-the-Loop MASs With Unknown Time-Varying Parameters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2022, 69, 5300–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jabbari, F.; Sun, X.M. Containment control of multi-agent systems with input saturation and unknown leader inputs. Automatica 2021, 130, 109677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, H.; Tao, J.; Cai, Q.; Shi, P. Containment control for fractional-order networked system with intermittent sampled position communication. Neural Netw. 2024, 178, 106425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Shi, L.; Shi, M.; Yue, J.; Lin, B.; Qin, K. Analyzing Containment Control Performance for Fractional-Order Multi-Agent Systems via a Delay Margin Perspective. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 2810–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Ferrari-Trecate, G.; Egerstedt, M.; Buffa, A. Containment Control in Mobile Networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2008, 53, 1972–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S.; Han, F.-J. Containment control for first-order multi-agent systems with time-varying delays and uncertain topologies. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2016, 66, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Stuart, D.; Ren, W.; Meng, Z. Distributed Containment Control for Multiple Autonomous Vehicles With Double-Integrator Dynamics: Algorithms and Experiments. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2011, 19, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, X. Fuzzy control of singular fractional order multi-agent systems with actuator saturation. Inf. Sci. 2024, 665, 120397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hua, C.; Wu, S.; Guan, X. Output Feedback Distributed Containment Control for High-Order Nonlinear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 47, 2032–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Wu, Y.; Ren, H.; Li, H.; Shi, Y. Event-based adaptive sliding-mode containment control for multiple networked mechanical systems with parameter uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Jiang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Du, C. Fully distributed finite-time adaptive robust time-varying formation-containment control for satellite formation. Int. J. Control 2023, 97, 1223–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Ren, W.; Li, B.; Ma, G. Distributed Containment Control for Multiple Unknown Second-Order Nonlinear Systems With Application to Networked Lagrangian Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 26, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wen, C.; Hu, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. Distributed Adaptive Containment Control for a Class of Nonlinear Multiagent Systems With Input Quantization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 2419–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Huang, T.; Kurths, J. Event-Triggered Adaptive Containment Control for Heterogeneous Stochastic Nonlinear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 8524–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yan, H.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, M. Fixed-Time Bipartite Containment Control for Heterogeneous Multiagent Systems Under DoS Attacks: An Event-Triggered Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Syst. 2025, 55, 2782–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Ren, W.; You, Z. Distributed finite-time attitude containment control for multiple rigid bodies. Automatica 2010, 46, 2092–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, Q.; Yu, W. Finite-Time Containment Control for Second-Order Multiagent Systems Under Directed Topology. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2014, 61, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Xie, G. Finite-time containment control of multi-agent systems with static or dynamic leaders. Neurocomputing 2017, 226, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahamatkhah, E.; Tabatabaei, M. Containment control of linear discrete-time fractional-order multi-agent systems with time-delays. Neurocomputing 2020, 385, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Hu, X. Fixed-Time Containment Control for Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with External Disturbances. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Han, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zeng, Z. Neural Network-Based Fixed-Time Tracking and Containment Control of Second-Order Heterogeneous Nonlinear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 11565–11579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altafini, C. Dynamics of Opinion Forming in Structurally Balanced Social Networks. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchibe, E.; Asada, M. Incremental Coevolution with Competitive and Cooperative Tasks in a Multirobot Environment. Proc. IEEE 2006, 94, 1412–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Wu, J.; Zhan, X.; Yan, H. Finite-Time Bipartite Consensus for Second-Order Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems Under Random Switching Topologies. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 4474–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Duan, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Z. Bipartite Fixed-Time Output Consensus of Heterogeneous Linear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ren, R.; Shi, M.; Lin, B.; Qin, K. Seeking Secure Adaptive Distributed Discrete-Time Observer for Networked Agent Systems under External Cyber Attacks. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2025, 71, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qin, K.; Li, G.; Shi, M.; Zhang, X. Robust Bipartite Tracking Consensus of Multi-Agent Systems via Neural Network Combined with Extended High-Gain Observer. ISA Trans. 2023, 136, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Ding, D.; Feng, J. Bipartite formation control of second-order multi-agent systems with antagonistic interactions under dynamic event-triggered adaptive schemes. Inf. Sci. 2025, 690, 121606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yue, J.; Shi, M.; Lin, B.; Qin, K. Neural network-based dynamic target enclosing control for uncertain nonlinear multi-agent systems over signed networks. Neural Netw. 2025, 184, 107057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Peng, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Qiu, J. Bipartite Containment Control of Multi-Agent Systems Subject to Adversarial Inputs Based on Zero-Sum Game. Inf. Sci. 2024, 681, 121234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Bipartite containment control of multi-agent systems under DoS attacks: An event-triggered scheme. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. 2025, 35, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D. Bipartite containment tracking of signed networks. Automatica 2017, 79, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Hu, B.; Guan, Z.H.; Zhang, D.X.; Li, T. Observer-Based Bipartite Containment Control for Singular Multi-Agent Systems Over Signed Digraphs. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Huang, T. Fixed-Time Optimal Bipartite Containment Control for Stochastic Nonlinear Multiagent Systems With Unknown Hysteresis. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 5516–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ding, S.; Xu, N.; Niu, B.; Zhao, X. Periodic event-triggered bipartite containment control for nonlinear multi-agent systems with input delay. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2024, 55, 2008–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Z.; Gao, Z. Neural-Network-Based Finite-Time Bipartite Containment Control for Fractional-Order Multi-Agent Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 7418–7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhan, X.; Han, T.; Yan, H. Distributed adaptive finite-time bipartite containment control of linear multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 4354–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, G.; Jia, L.; Zhang, H. Event-Triggered Practical Fixed-Time Containment Control for Stochastic Multiagent Systems With Input Delay. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 2762–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Hua, C. Dynamic Event/Self-Triggered Full-State Bipartite Containment Control for Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems Under Switching Topologies. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 1852–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Xiao, J. Bipartite containment control of fractional multi-agent systems with input delay on switching signed directed networks. ISA Trans. 2023, 135, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Qi, J.; Wang, M.; Wu, C.; Yang, G. Collision-Free Distributed Control for Multiple Quadrotors in Cluttered Environments With Static and Dynamic Obstacles. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tong, S. Fuzzy Adaptive Resilient Formation Control for Nonlinear Multiagent Systems Subject to DoS Attacks. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentelman, H.; Stoorvogel, A.; Hautus, M.; Dewell, L. Control Theory for Linear Systems. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2002, 55, B87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, G.; Littlewood, J.; Polya, G. Inequalities; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, A.; de Ruiter, A.; Kumar, K. Distributed finite-time velocity-free attitude coordination control for spacecraft formations. Automatica 2016, 67, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lu, W.; Chen, J.; Cao, J.; Xu, S. Adaptive neural network-based practical fixed-time consensus tracking for second-order nonlinear multi-agent systems with switching topologies. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2024, 34, 8442–8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Song, Y.; Wen, C. Prescribed Time Consensus Control of Multiagent Systems With Minimized Time-Varying Cost Function. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2024, 69, 3381–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababa, M.P.; Aghababa, H. A general nonlinear adaptive control scheme for finite-time synchronization of chaotic systems with uncertain parameters and nonlinear inputs. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 69, 1903–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; El Ghaoui, L.; Feron, E.; Balakrishnan, V. Linear Matrix Inequalities in System and Control Theory; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, R.; Tang, W.; Sheng, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, T. Dynamic Event-Triggered Bipartite Consensus for Multiagent Systems Under Switching Topologies on Time Scales. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Syst. 2025, 55, 6359–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, M.; Wang, N.; Zhang, B. Distributed Consensus Control for 6-DOF Fixed-Wing Multi-UAVs in Asynchronously Switching Topologies. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 74, 5649–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, D.; Li, Y.X.; Tong, S. Fixed-time adaptive neural tracking control for a class of uncertain nonstrict nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing 2019, 363, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Song, F.; Li, T. Prescribed-Time Consensus of Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems by Dynamic Event-Triggered and Self-Triggered Protocol. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 16768–16779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ma, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H. Neural-based prescribed-time consensus control for multiagent systems via dynamic memory event-triggered mechanism. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2025, 68, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
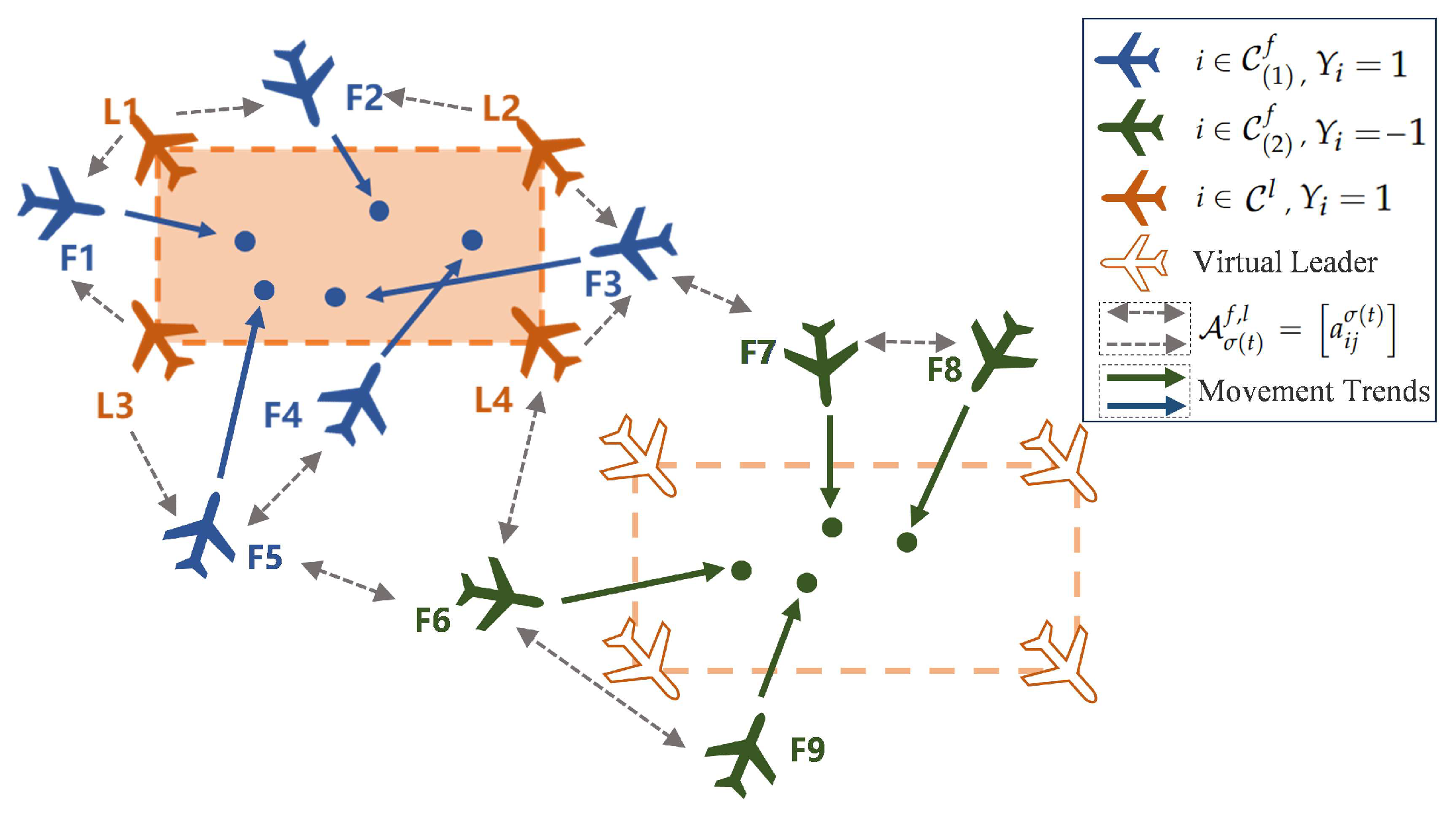
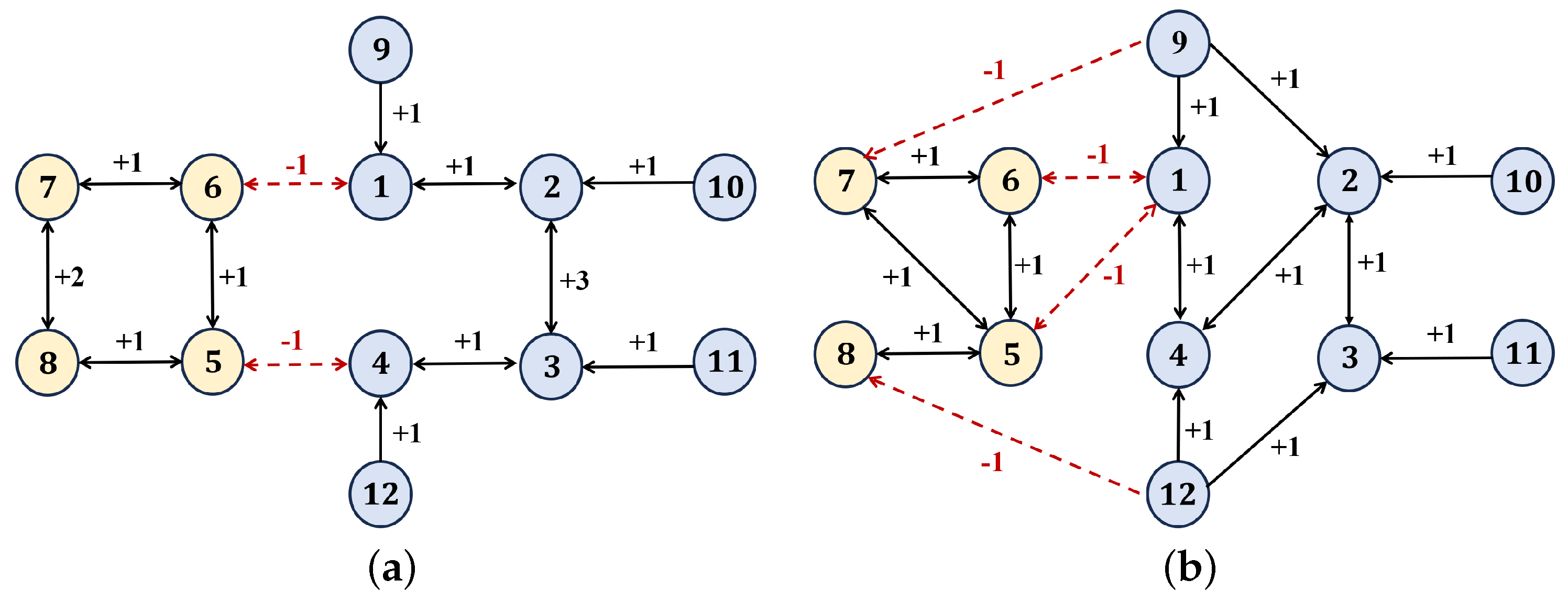
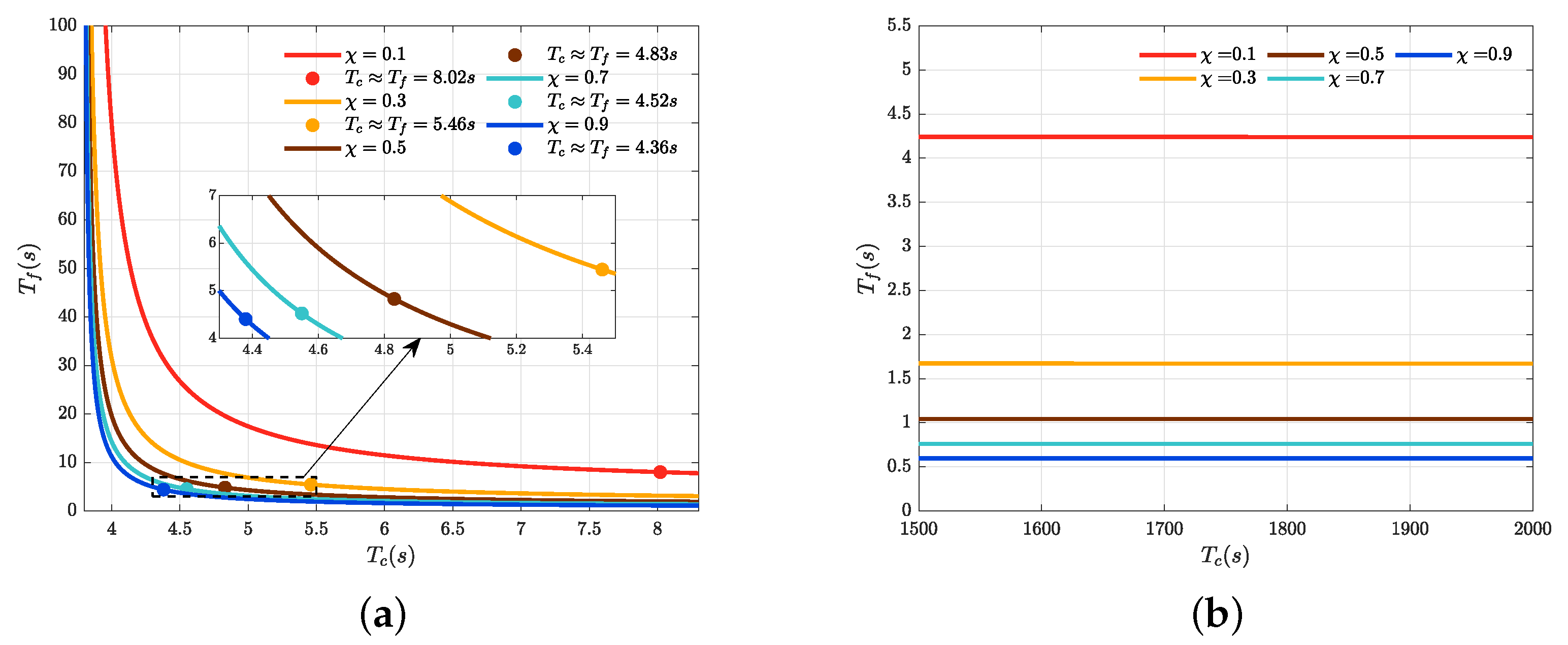


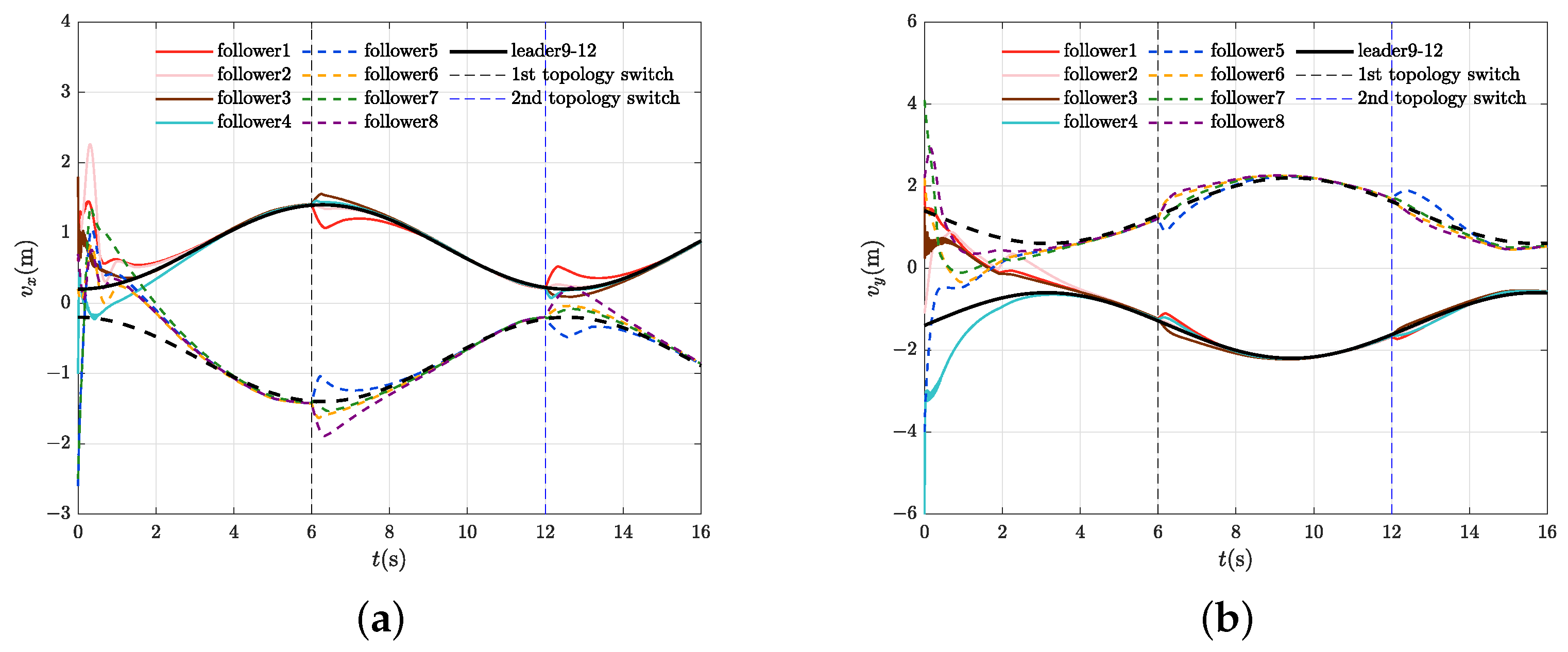




| Parameter | Name | Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| composite error-gain parameters | ||
| adaptation gain parameters | ||
| a | fractional power index (small order) | |
| b | fractional power index (large order) | |
| sign-function gain | ||
| controller gain | ||
| fixed time-related parameters | ||
| fixed time-related parameters | positive constants (related to switch topology complexity and system dynamics) |
| Cooperative Followers | Antagonistic Followers | Leaders | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| follower 1 | follower 5 | leader 9 | |||
| follower 2 | follower 6 | leader 10 | |||
| follower 3 | follower 7 | leader 11 | |||
| follower 4 | follower 8 | leader 12 | |||
| Cooperative Followers | Antagonistic Followers | Leaders | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| follower 1 | follower 5 | leader 9 | |||
| follower 2 | follower 6 | leader 10 | |||
| follower 3 | follower 7 | leader 11 | |||
| follower 4 | follower 8 | leader 12 | |||
| Cooperative Followers | Antagonistic Followers | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Name | ||||||||
| follower 1 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.15 | follower 5 | −0.80 | −0.20 | −0.50 | 0.50 |
| follower 2 | −0.25 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.60 | follower 6 | 0.10 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 0.70 |
| follower 3 | −0.60 | 0.30 | 0.50 | 0.40 | follower 7 | 0.20 | 0.50 | −0.20 | 0.30 |
| follower 4 | −0.75 | −0.4 | 0.55 | −0.40 | follower 8 | −0.30 | 0.80 | 0.10 | −0.60 |
| Time Period | MAE | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed controller | [0.312, 1.135] | [0.442, 4.466] | 4.95 | |
| [0.056, 0.100] | [0.118, 0.076] | 2.45 | ||
| [0.065, 0.123] | [0.135, 0.068] | 2.46 | ||
| Controller in [31] | [0.234, 1.545] | [0.453, 3.489] | 5.00 | |
| [0.214, 0.373] | [0.667, 1.189] | 5.88 | ||
| [0.108, 0.180] | [0.336, 0.542] | 3.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, Y.; Shi, M.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, R.; Qin, K. Neuroadaptive Fixed-Time Bipartite Containment Tracking of Networked UAVs Under Switching Topologies. Drones 2025, 9, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100725
Kang Y, Shi M, Yao Y, Zhou R, Qin K. Neuroadaptive Fixed-Time Bipartite Containment Tracking of Networked UAVs Under Switching Topologies. Drones. 2025; 9(10):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100725
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Yulin, Mengji Shi, Yuan Yao, Rui Zhou, and Kaiyu Qin. 2025. "Neuroadaptive Fixed-Time Bipartite Containment Tracking of Networked UAVs Under Switching Topologies" Drones 9, no. 10: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100725
APA StyleKang, Y., Shi, M., Yao, Y., Zhou, R., & Qin, K. (2025). Neuroadaptive Fixed-Time Bipartite Containment Tracking of Networked UAVs Under Switching Topologies. Drones, 9(10), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100725





