Fixed-Time Formation Control for MAV/UAVs with Switching Threshold Event-Triggered Strategy
Abstract
Highlights
- Develops a fixed-time back-stepping formation control strategy for MAV/UAV systems.
- Introduces a novel switching threshold event-triggered mechanism.
- Designs a fixed-time filter to deal with the ‘explosion of complexity’ problem and improves the system’s stability.
- Switches the trigger conditions for controller updates according to the system state, which reduces conservatism while ensuring safety.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Different to prior works [3,14,15], which neglect convergence performance in MAV/UAV formation control, this paper proposes a fixed-time backstepping formation controller for MAV/UAV systems under external disturbances and modeling uncertainties. The stability of the closed-loop system is rigorously proven using Lyapunov-based analysis.
- By proposing a novel fixed-time command filtered backstepping approach, this paper effectively addresses the “explosion of complexity” problem while enhancing system stability.
2. Preliminaries and Problem Formulation
2.1. Notations
2.2. MAV/UAVs Dynamic Model
2.3. Problem Statement
2.4. Control Objective
3. Event-Triggered Fixed-Time Formation Tracking Control Design
- Remark 3.The novel fixed-time command filter helps avoid the issue of complexity explosion. Meanwhile, according to (24), is related to the formation tracking error . When is large, undergoes significant oscillations, which affects the stability of the system. By using the fixed-time filter, the impact of on the system can be avoided, making the system more stable.
- Remark 4.Note that can be made arbitrarily small by increasing , , and decreasing . Therefore, the formation tracking error can be made arbitrarily small by appropriate choice of the design parameters. During the simulation, it is also important to choose suitable ϕ, , , , to balance triggering times and control perfermance.
4. Performance Evaluation
4.1. Simulation Setup
4.1.1. Simulation Metrics
4.1.2. Simulation Scenarios
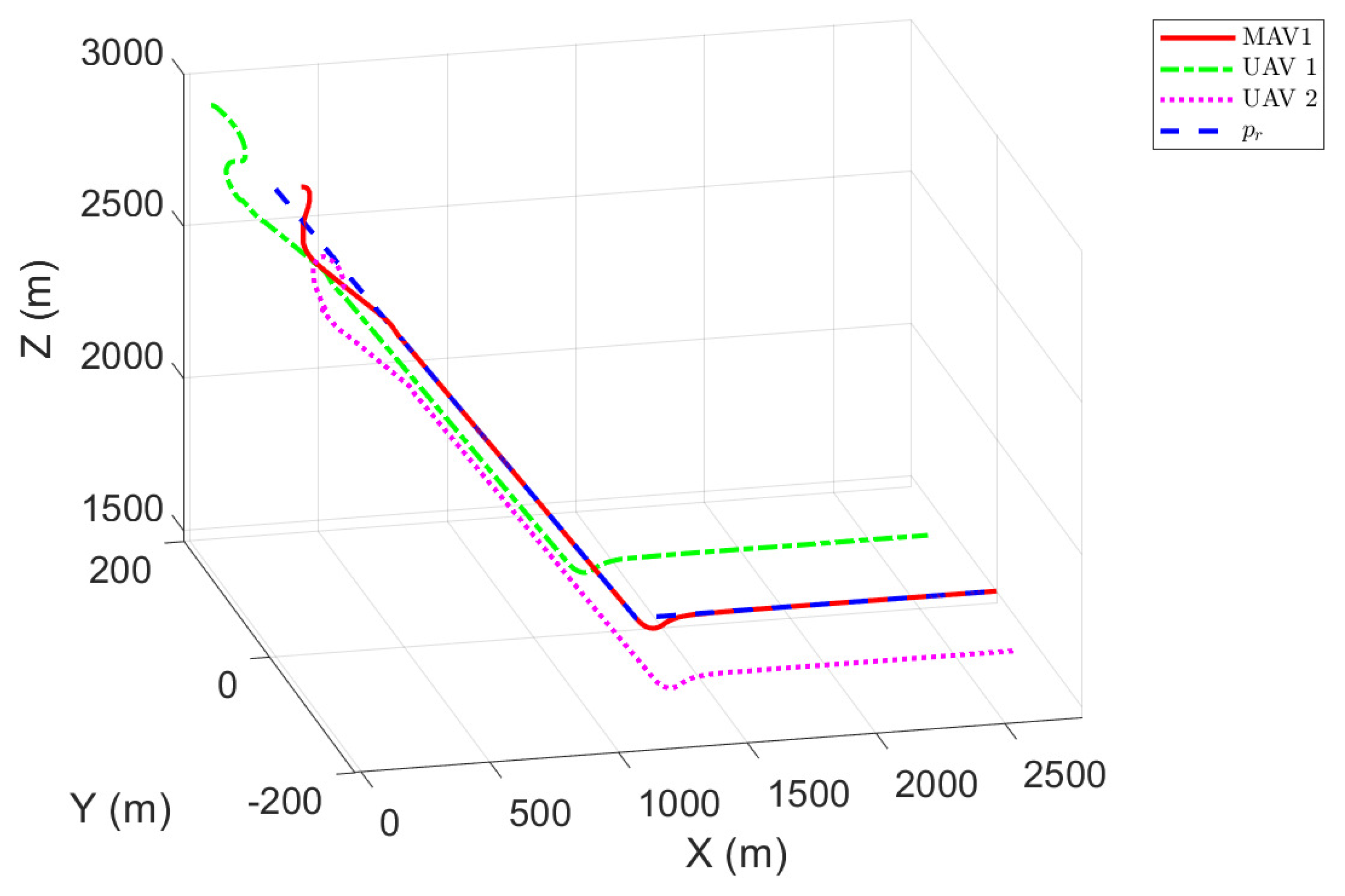
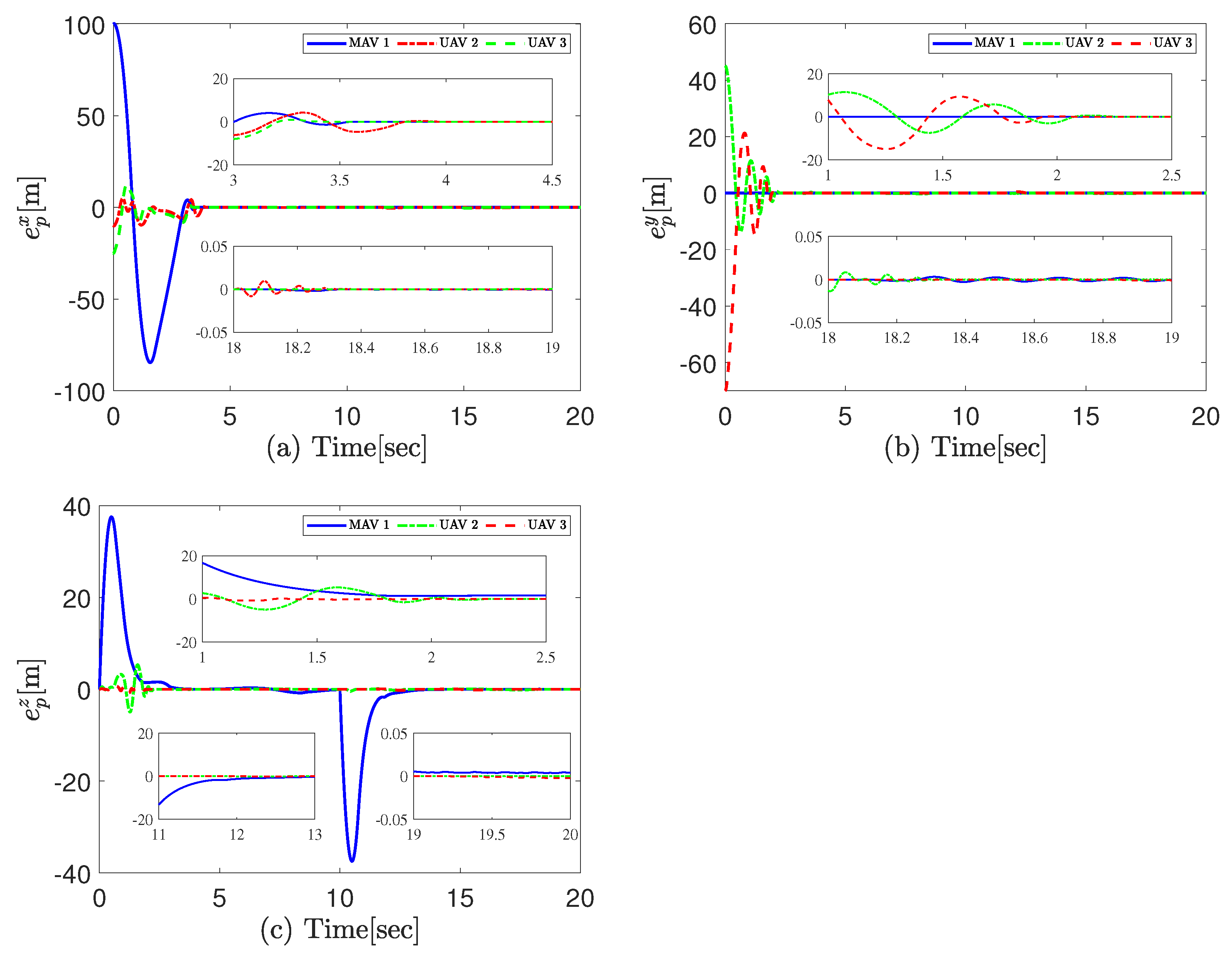
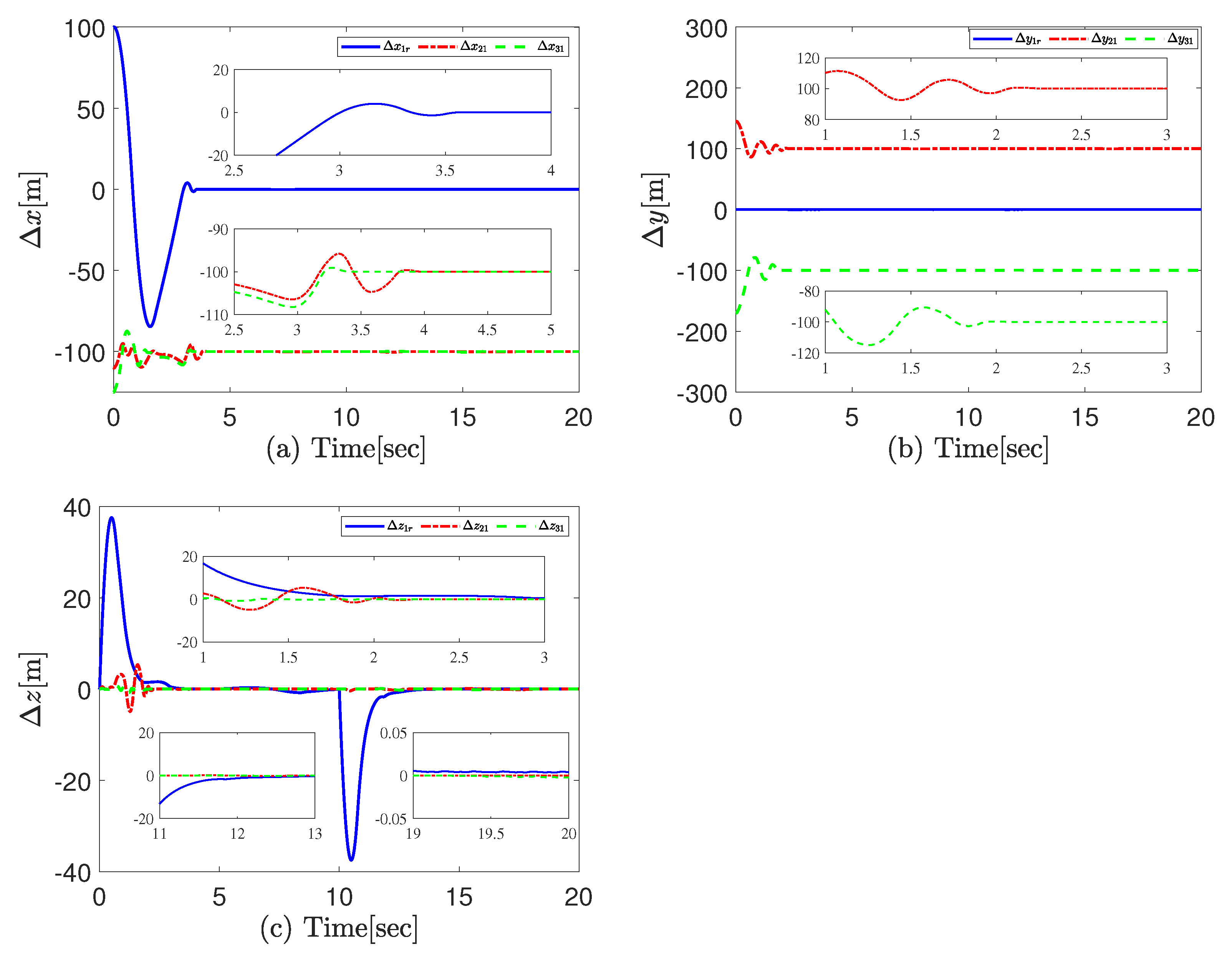
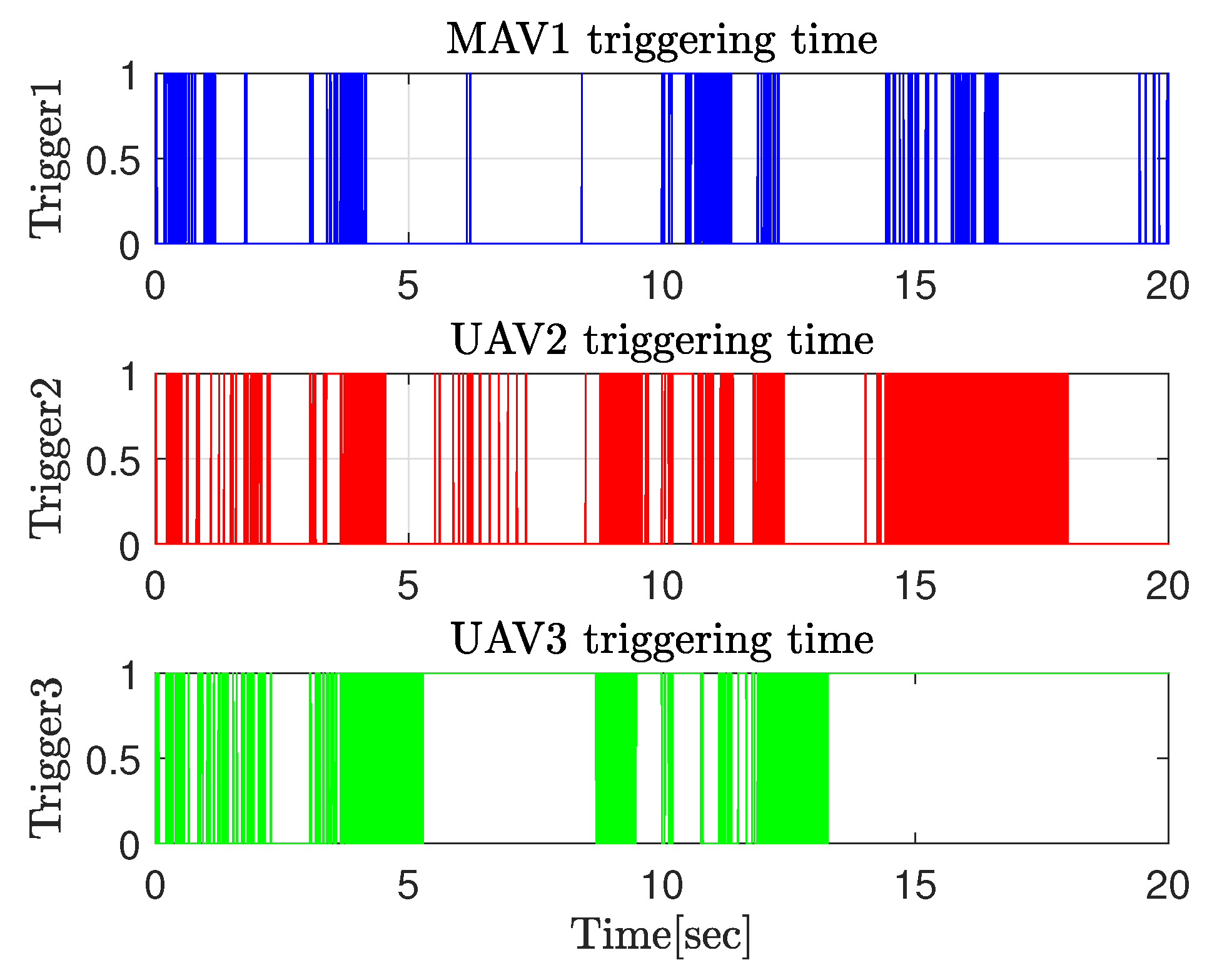
4.2. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
DURC Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.; Song, Y.; Park, D.; Jung, M.; Kim, B. Workload reduction effect of PVI(pilot-vehicle interface) operation based on the high level command for the pilot in manned-unmanned teaming mission. J. Korean Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2023, 51, 735–741. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zhao, L. A dual aircraft maneuver formation controller for MAV/UAV based on the hybrid intelligent agent. Drones 2023, 8, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Lv, M.; Zhang, B. Two-level hierarchical-interaction-based group formation control for MAV/UAVs. Aerospace 2022, 9, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ai, J. Adaptive factor fuzzy controller for keeping multi-UAV formation while avoiding dynamic obstacles. Drones 2024, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, B. Game-based fault-tolerant formation containment control for fixed-wing UAVs under the fully actuated system framework. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2025, 160, 110052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, S. Leader-follower formation reconfiguration control for fixed-wing UAVs using multiplayer stackelberg–nash game. Drones 2025, 9, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Yu, W.; Cao, J.; Baldi, S. Consensus in High-Power Multiagent Systems With Mixed Unknown Control Directions via Hybrid Nussbaum-Based Control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 5184–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Mcisaac, K.; Patel, R. Modified Newton’s method applied to potential field-based navigation for mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2006, 22, 384–391. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Duan, H.; Fan, Y. Multiple unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous formation based on the behavior mechanism in pigeon flocks. Control Theory Appl. 2015, 32, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, Z.; Schwager, M. Agile coordination and assistive collision avoidance for quadrotor swarms using virtual structures. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Pan, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, X. A formation maintenance and reconstruction method of UAV swarm based on distributed control. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 104, 105981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, M.; Yang, H.; Zhao, N.; Wang, G. Air-ground cooperative UAV formation control algorithm design and simulation for communications. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2023, 45, 2839–2846. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Lv, M.; Cui, S.; Bu, X.; Park, J. Learning-based optimal cooperative formation tracking control for multiple UAVs: A feedforward-feedback design framework. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y. Control method of manned/unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative formation based on mission effectiveness. In Proceedings of the IEEE Chinese Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference (CGNCC), Nanjing, China, 12–14 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, M.; Duan, H. Three-dimension cluster space formation control of manned/unmanned aerial team subject to input constraint. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 8596–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.; Song, H.; Jan, M.; Khan, M.; He, X.; Farouk, A.; Jin, Z. UAV-assisted IoT applications, QoS requirements and challenges with future research directions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmardi, S.; Nascita, A.; Pescape, A.; Merlino, G.; Scarpa, M. An integration perspective of security, privacy, and resource efficiency in IoT-Fog networks: A comprehensive survey. Comput. Netw. 2025, 270, 111470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Lv, M.; Pei, B.; Fu, A. Event-triggered adaptive fuzzy fault-tolerant attitude control for tailless flying-wing UAV with fixed-time convergence. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 4858–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Li, S. Event-triggered bipartite formation control for switched nonlinear multi-agent systems with function constraints on states. Actuators 2025, 14, 14010023. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, T.; Gu, Z.; Xie, X. Observer-based event-triggered sliding mode control for secure formation tracking of multi-UAV systems. Actuators 2023, 10, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Sun, C. Event-triggered reinforcement learning control for the quadrotor UAV with actuator saturation. Neurocomputing 2020, 415, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Wen, C.; Liu, Z.; Su, H.; Cai, J. Event-triggered adaptive control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2017, 62, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Dong, J. Distributed event-triggered fixed-time DSC of multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 2484–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhou, Q.; Dong, G.; Li, H. Observer-based adaptive event-triggered control for nonstrict-feedback nonlinear systems with output constraint and actuator failures. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, M.; Wang, N.; Yuan, Y.; Chang, J. Synergistic Constrained Control of 6-DOF Fixed-Wing Multi-UAVs with Dynamic Self-Triggered Communication. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 14818–14832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Lu, Q.; Tao, X.; Peng, D.; Zhang, B. Dynamic event-triggered fixed-time consensus control and its applications to magnetic map construction. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 10, 2000–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Huang, P.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, F.; Xia, Y. Distributed adaptive dynamic event-triggered secondary control for islanded microgrids with disturbances. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 4268–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Yu, W.; Cao, J.; Baldi, S. A Separation-Based Methodology to Consensus Tracking of Switched High-Order Nonlinear Multiagent Systems, IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 5467–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Jiang, B.; Shi, P.; Zhao, J. Cooperative adaptive fuzzy tracking control for networked unknown nonlinear multiagent systems with time-varying actuator faults. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 22, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunberg, J.; Hu, X.; Goncalves, J. Consensus and formation control on SE(3) for switching topologies. Automatica 2016, 66, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, L.; Lu, H.; Zuo, Z.; Zong, Q.; Zhang, Y. Multivariable finite time attitude control for quadrotor UAV: Theory and experimentation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 2567–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cui, G.; Li, Z.; Tao, C. Fuzzy approximation-based adaptive finite-time tracking control for a quadrotor UAV with actuator faults. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 24, 3756–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Lu, K. Order-supplementary finite-time trajectory tracking control of quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicles. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 8229–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, N.; Li, W.; Liang, M. Event-triggered finite-time fuzzy tracking control for a time-varying state constrained quadrotor system based on disturbance observer. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 151, 109325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Ahn, C.; Zhang, B.; Fu, A. Fixed-Time antisaturation cooperative control for networked fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicles considering actuator failures. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 8812–8825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, D.; Yang, H. Fixed-time disturbance observer-based fixed-time path following control for small fixed-wing UAVs under wind disturbances. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2024, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, R.; Zheng, S.; Dong, S.; Sun, G. Fixed-time disturbance observer-based robust fault-tolerant tracking control for uncertain quadrotor UAV subject to input delay. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 107, 2363–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gong, W.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, B.; Ran, D. Appointed fixed time observer-based sliding mode control for a quadrotor UAV under external disturbances. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Liu, C.; Su, H.; Zhang, Q. On decentralized adaptive full-order sliding mode control of multiple UAVs. ISA Trans. 2017, 71, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba, D.; Li, Y.; Tong, S. Fixed-time adaptive neural tracking control for a class of uncertain nonstrict nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing 2019, 363, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lin, Y. Decentralized adaptive tracking control for a class of interconnected nonlinear time-varying systems. Automatica 2015, 54, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Q. Adaptive output feedback control of stochastic nonholonomic systems with nonlinear parameterization. Automatica 2018, 98, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tie, L. A new class of finite-time nonlinear consensus protocols for multi-agent systems. Int. J. Control 2014, 87, 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, N.; Kawano, Y.; Cao, M. Neural network-based adaptive control for spacecraft under actuator failures and input saturations. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 3696–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| 160 m/s | 100 m | 0 m | 3000 m | |
| 140 m/s | −10 m | 145 m | 3000 m | |
| 150 m/s | −25 m | −170 m | 3000 m |
| Control Schemes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compared controller 1 | 20,000 | 20,000 | 20,000 |
| Compared controller 2 | 3375 | 4410 | 4287 |
| Compared controller 3 | 4542 | 4523 | 4953 |
| Proposed controller | 2150 | 4014 | 1807 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, X.; Lv, M.; Shen, D.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yu, P. Fixed-Time Formation Control for MAV/UAVs with Switching Threshold Event-Triggered Strategy. Drones 2025, 9, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100710
Han X, Lv M, Shen D, Shi Y, Zhang B, Yu P. Fixed-Time Formation Control for MAV/UAVs with Switching Threshold Event-Triggered Strategy. Drones. 2025; 9(10):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100710
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Xueyan, Maolong Lv, Di Shen, Yuyuan Shi, Boyang Zhang, and Peng Yu. 2025. "Fixed-Time Formation Control for MAV/UAVs with Switching Threshold Event-Triggered Strategy" Drones 9, no. 10: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100710
APA StyleHan, X., Lv, M., Shen, D., Shi, Y., Zhang, B., & Yu, P. (2025). Fixed-Time Formation Control for MAV/UAVs with Switching Threshold Event-Triggered Strategy. Drones, 9(10), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9100710







