Correction: Xia et al. A Quantum-Resistant Identity Authentication and Key Agreement Scheme for UAV Networks Based on Kyber Algorithm. Drones 2024, 8, 359
Authorship Correction
Text Correction
- The UAV and ground control station need to share elliptic curve parameters, such as , and relevant functions of the Kyber algorithm, specifically to select suitable secure elliptic curves and internal functions such as Kyber.Encaps().
- The ground station creates multiple private keys {,} and s {,}, and it shares the private key , unique ID , and its own public key with the UAV. Then, calculates according to Formula (1),generates according to Formula (2), calculates according to Formula (2),generates according to Formula (3),and calculates according to Formula (4).
- After obtaining the parameters {,,,} distributed by the ground station, the UAV needs to acquire the parameters {,,} through preprocessing and store them. The UAV calculates according to Formula (5),generates according to Formula (6), and calculates according to Formula (6),
Error in Figure
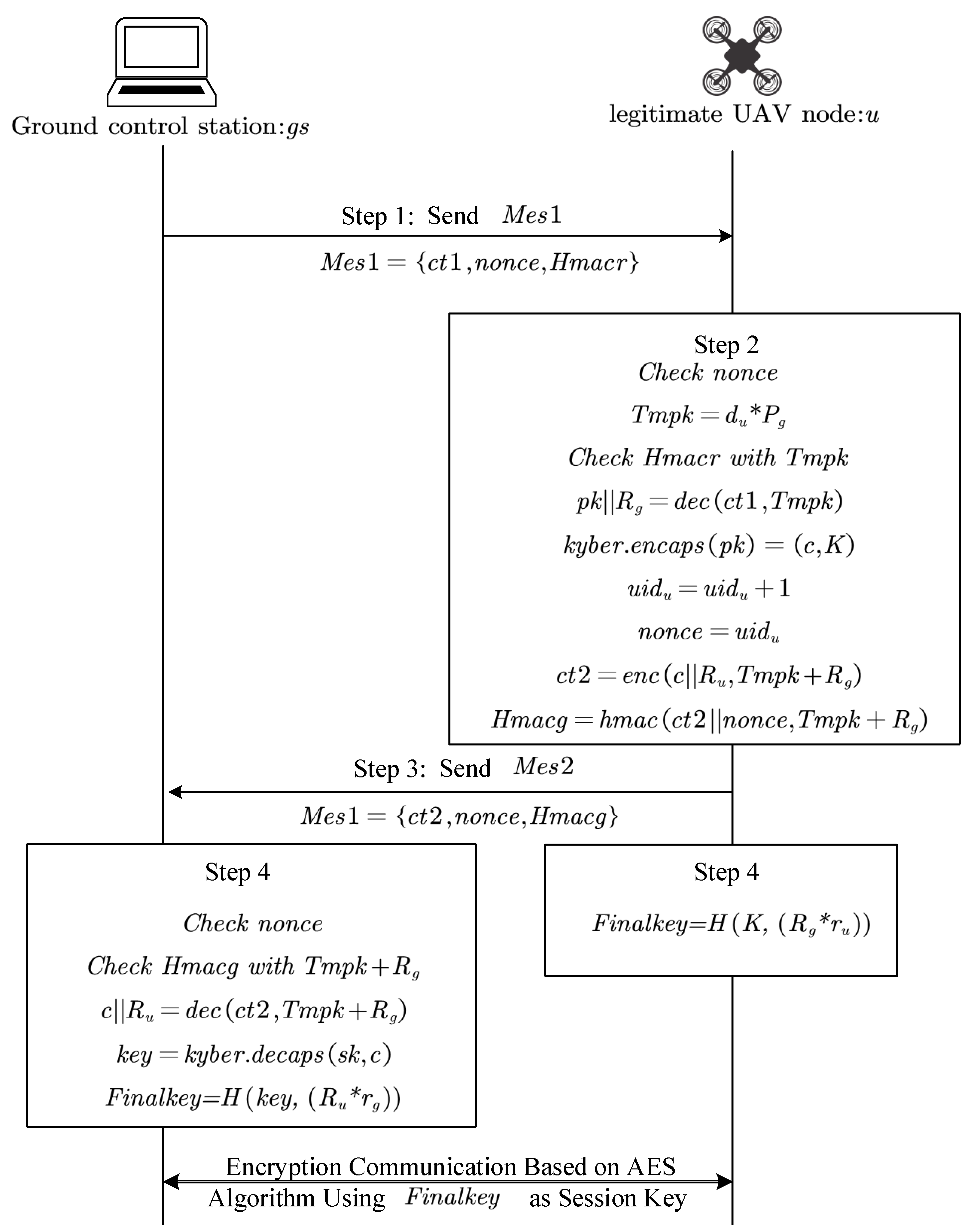
Reference
- Xia, T.; Wang, M.; He, J.; Yang, G.; Fan, L.; Wei, G. A Quantum-Resistant Identity Authentication and Key Agreement Scheme for UAV Networks Based on Kyber Algorithm. Drones 2024, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, T.; Wang, M.; He, J.; Yang, G.; Fan, L.; Wei, G. Correction: Xia et al. A Quantum-Resistant Identity Authentication and Key Agreement Scheme for UAV Networks Based on Kyber Algorithm. Drones 2024, 8, 359. Drones 2025, 9, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9010041
Xia T, Wang M, He J, Yang G, Fan L, Wei G. Correction: Xia et al. A Quantum-Resistant Identity Authentication and Key Agreement Scheme for UAV Networks Based on Kyber Algorithm. Drones 2024, 8, 359. Drones. 2025; 9(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9010041
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Tao, Menglin Wang, Jun He, Gang Yang, Linna Fan, and Guoheng Wei. 2025. "Correction: Xia et al. A Quantum-Resistant Identity Authentication and Key Agreement Scheme for UAV Networks Based on Kyber Algorithm. Drones 2024, 8, 359" Drones 9, no. 1: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9010041
APA StyleXia, T., Wang, M., He, J., Yang, G., Fan, L., & Wei, G. (2025). Correction: Xia et al. A Quantum-Resistant Identity Authentication and Key Agreement Scheme for UAV Networks Based on Kyber Algorithm. Drones 2024, 8, 359. Drones, 9(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9010041




