Assessment of Dataset Scalability for Classification of Black Sigatoka in Banana Crops Using UAV-Based Multispectral Images and Deep Learning Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
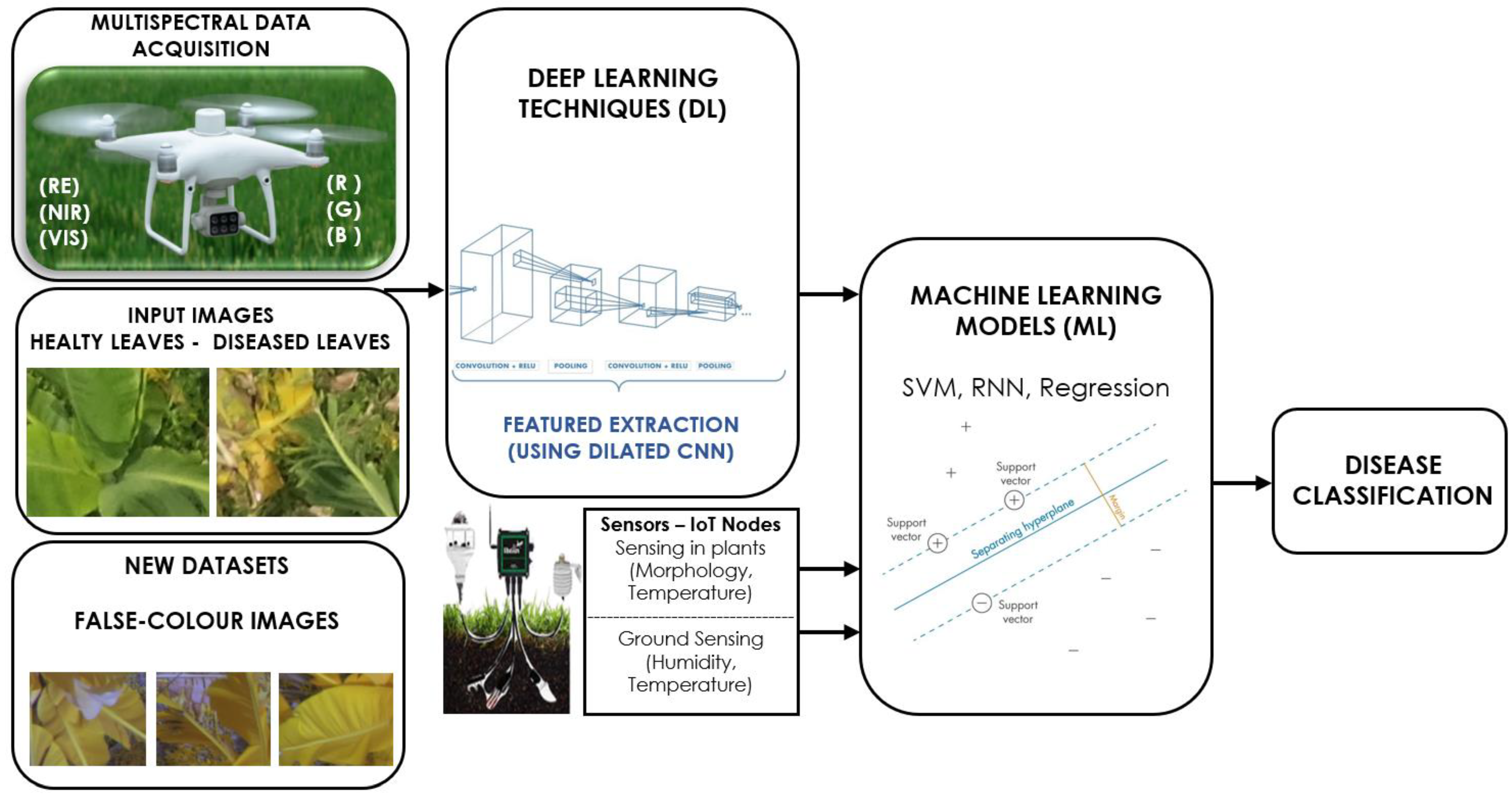
2. Materials and Methods
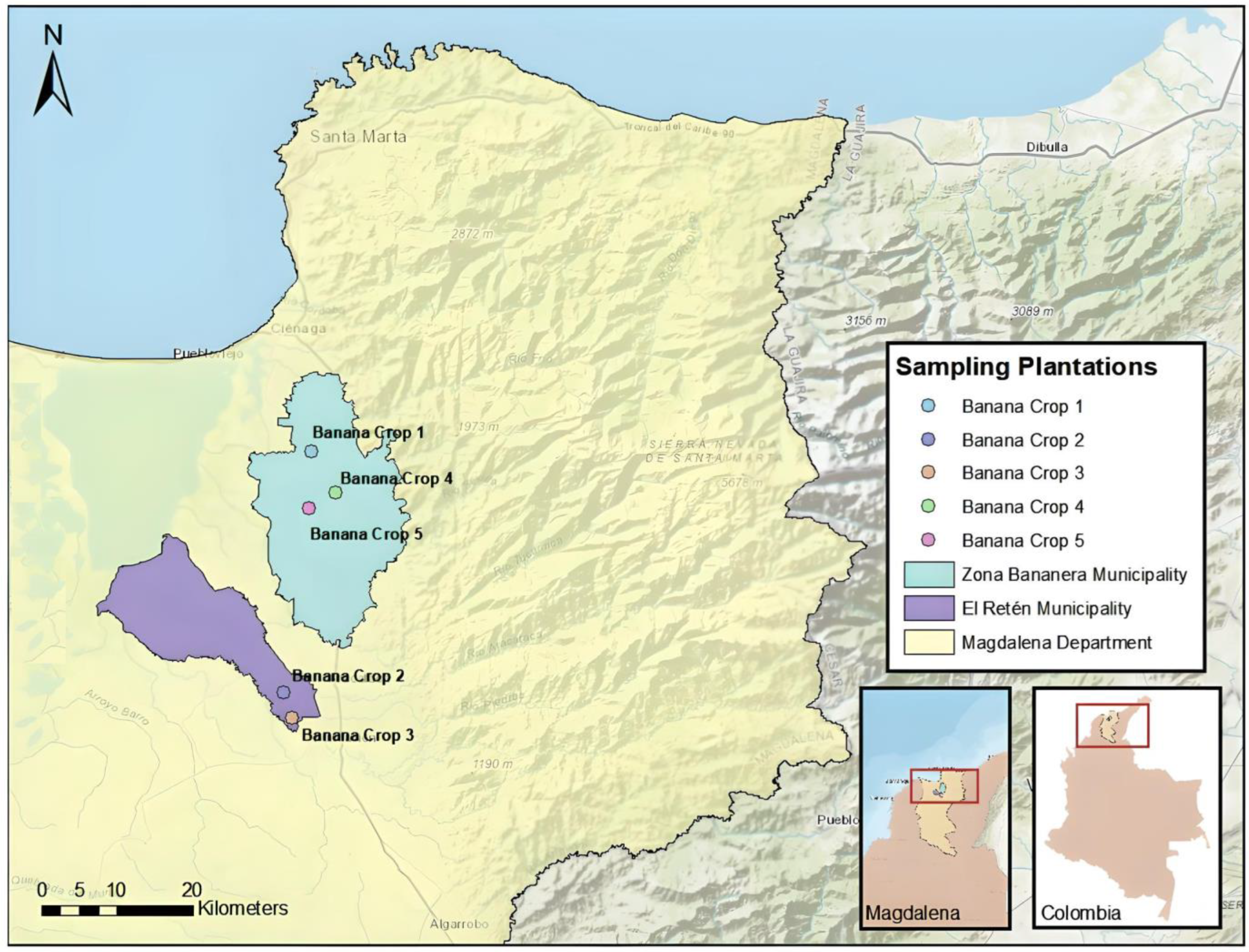
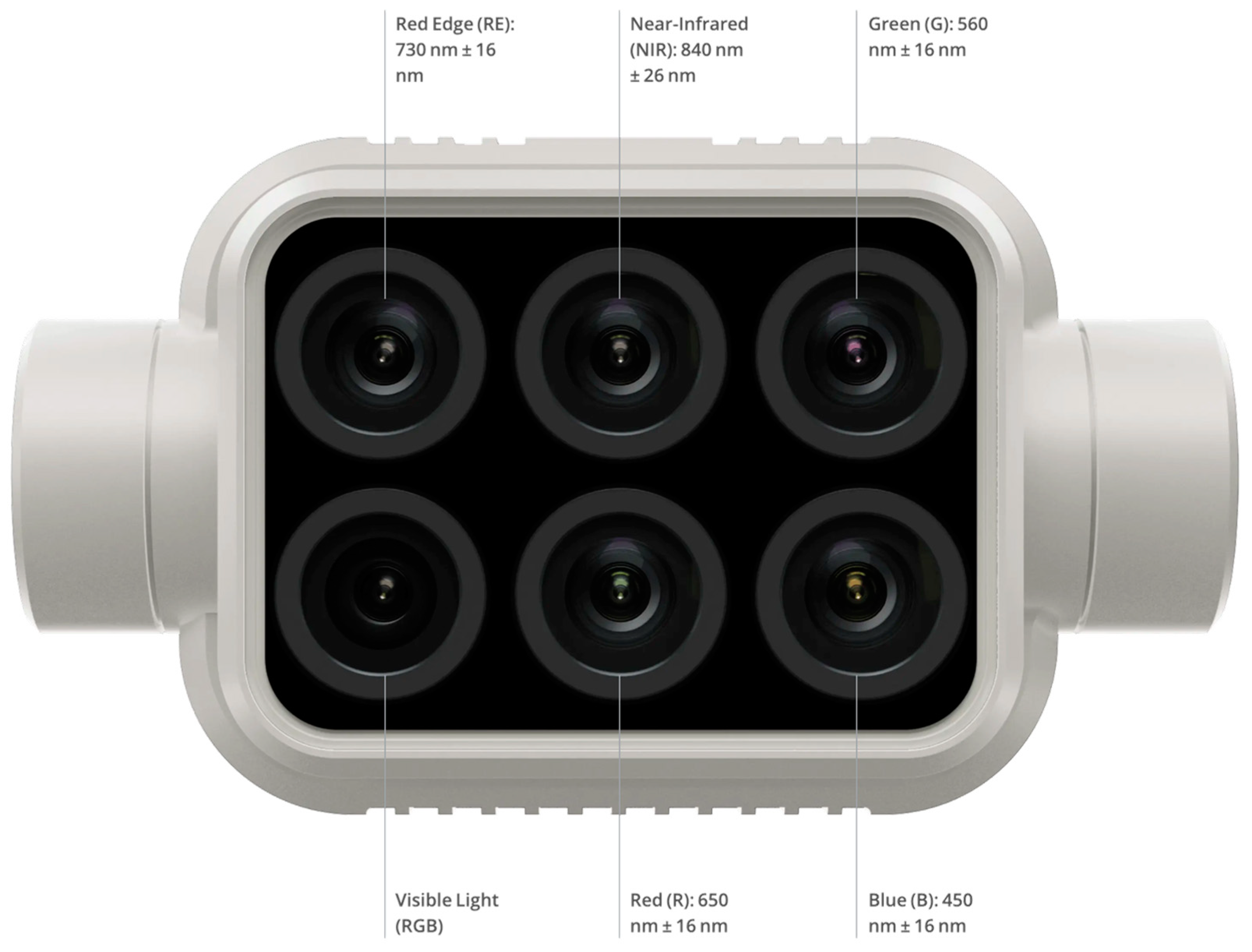
2.1. Data Acquisition with UAV
2.2. Detection Models Labels
- One row per label.
- Each row contains 4 data points: the centre of the X-axis, the centre of the Y-axis, height, and width of detection.
- All the data corresponding to coordinates must be normalised relative to the maximum width and height of the image.
2.3. Classification Models Labels
2.4. Evaluation of the Classification and Detection Models
2.5. Training Protocol
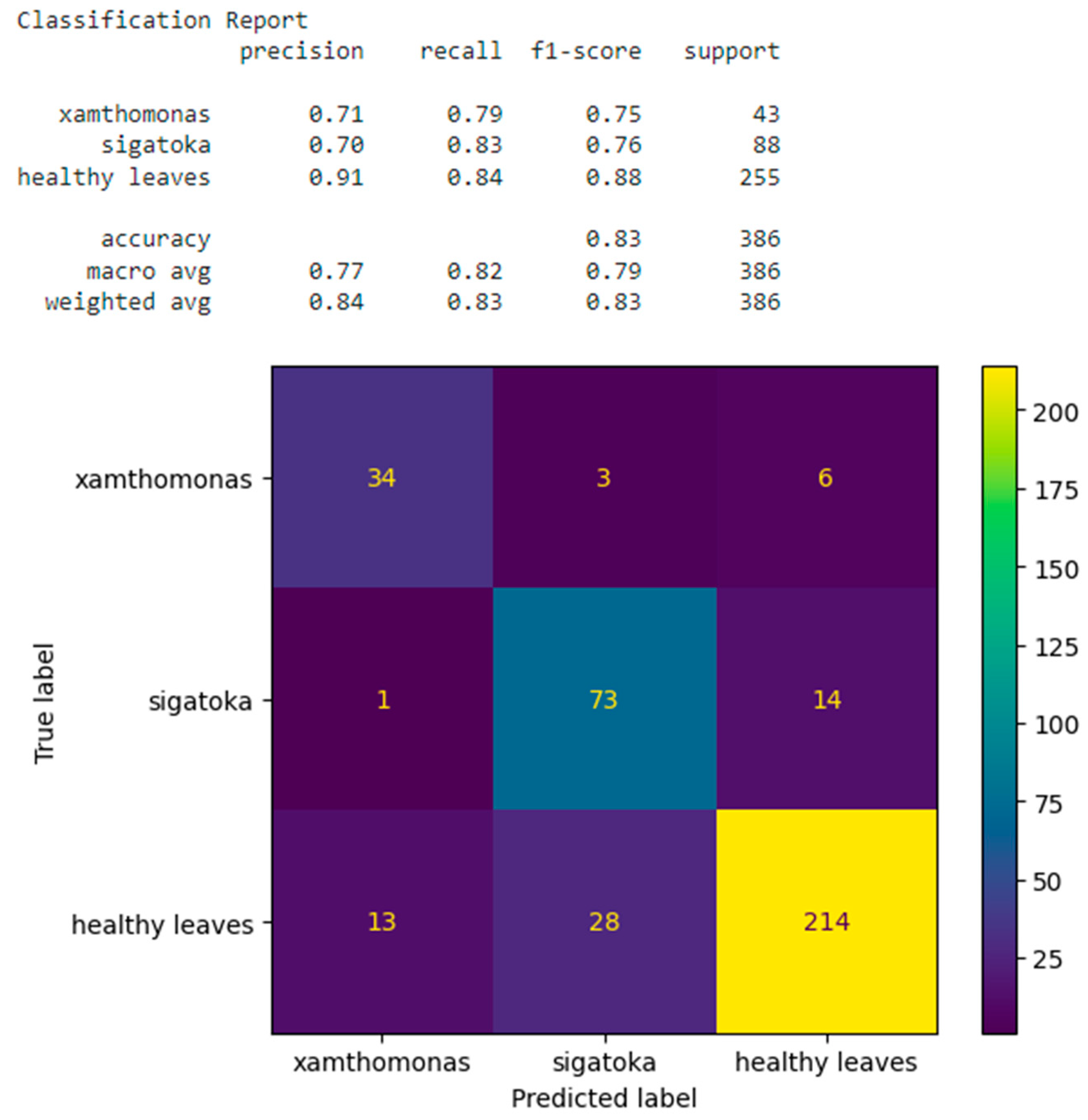
3. Results
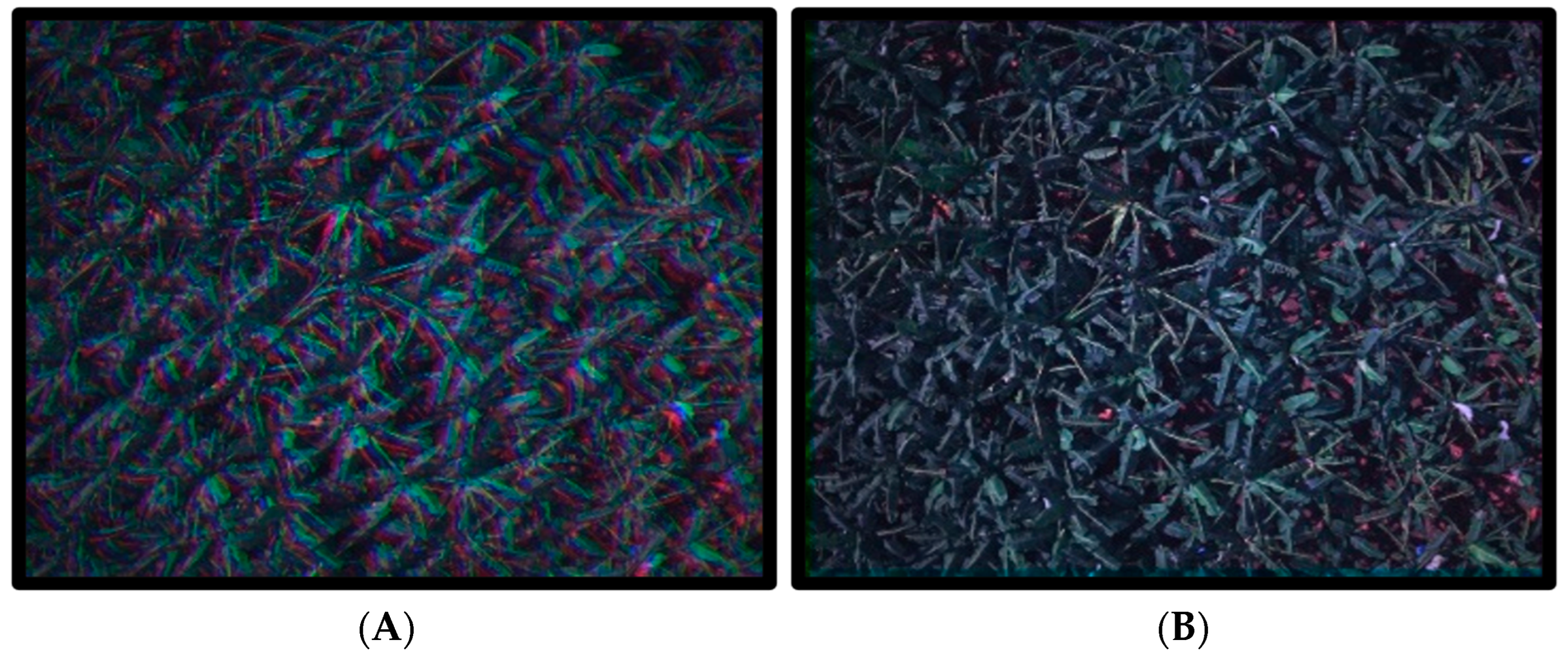
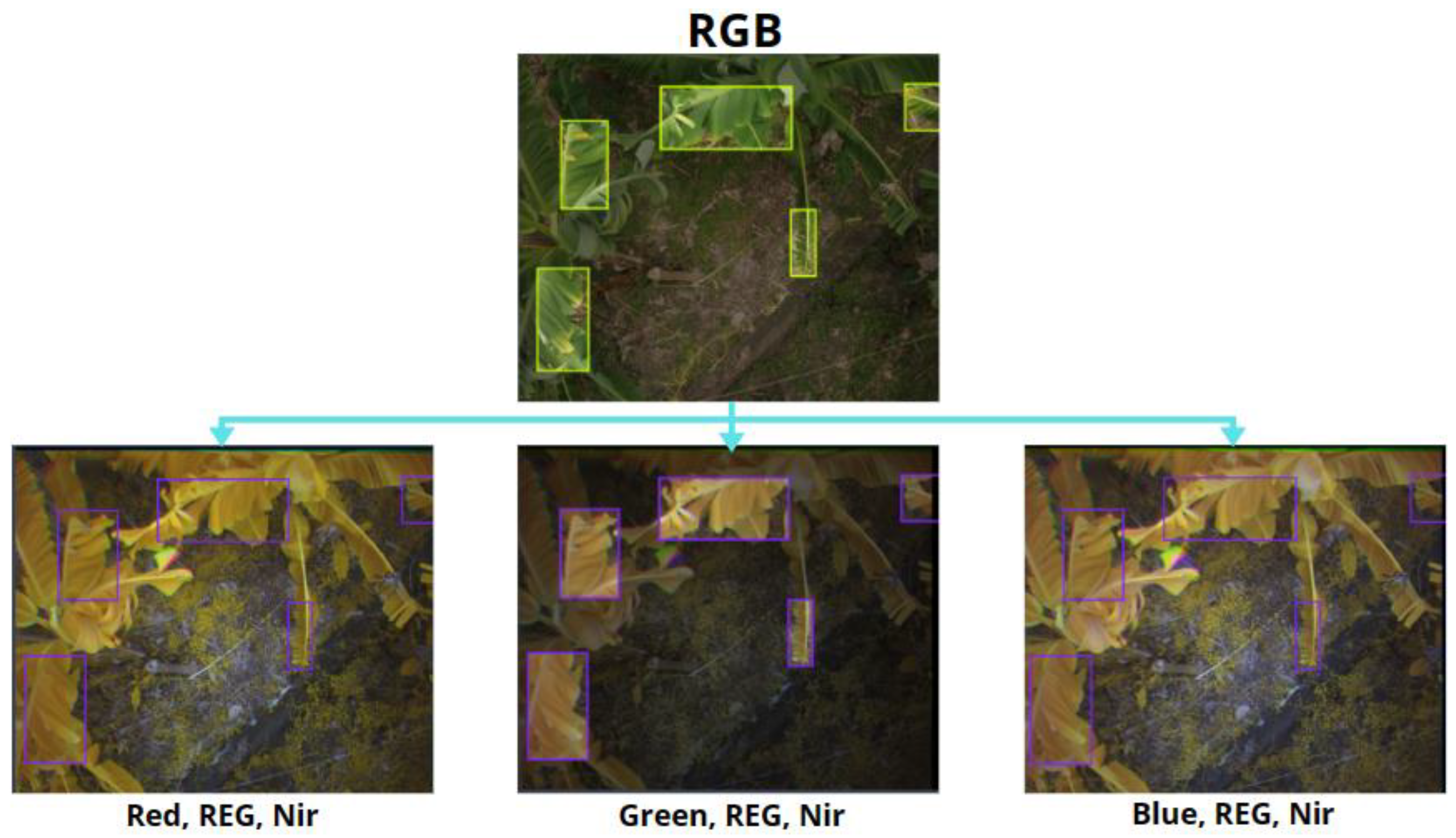
3.1. Dataset Creation
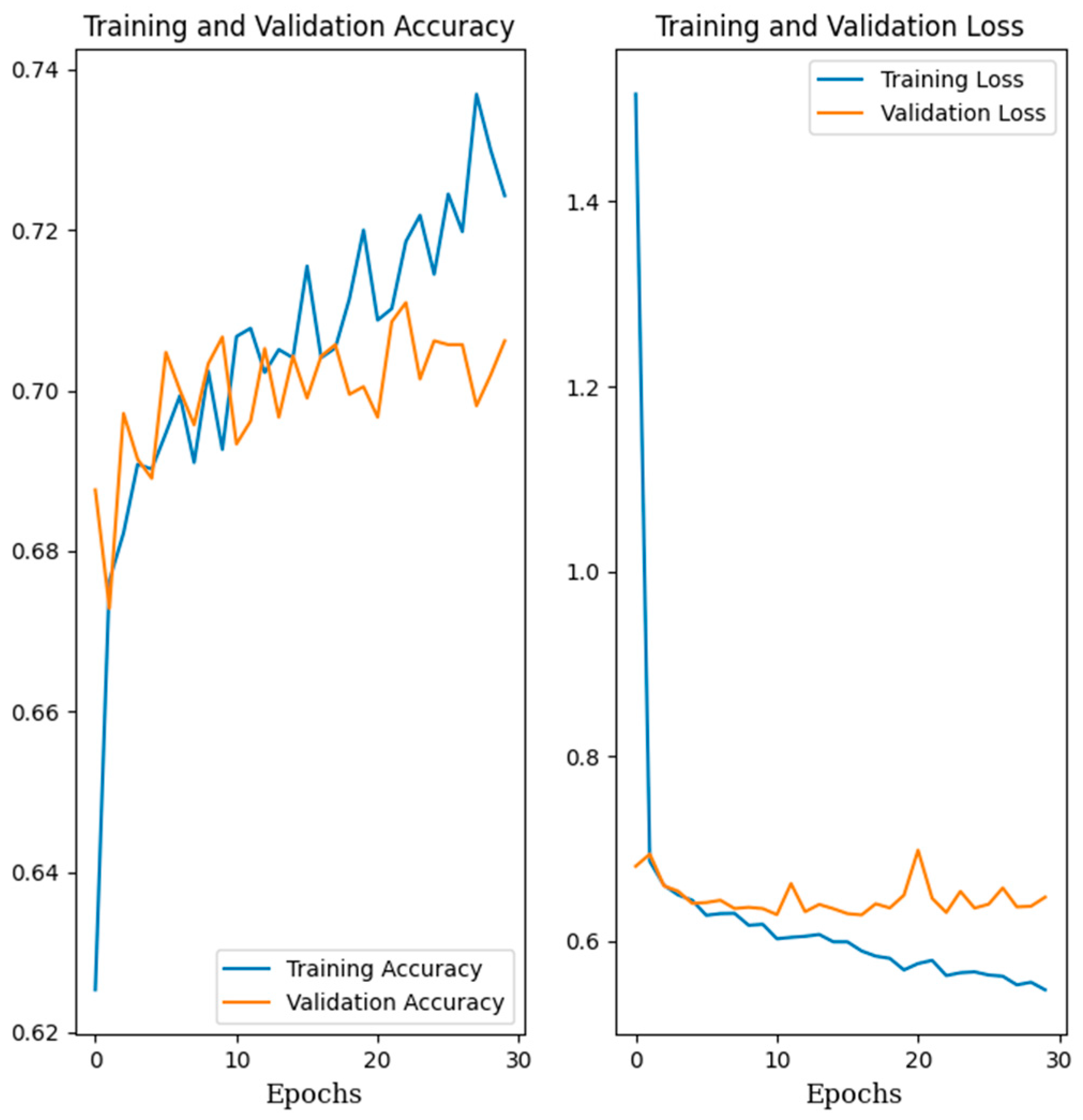
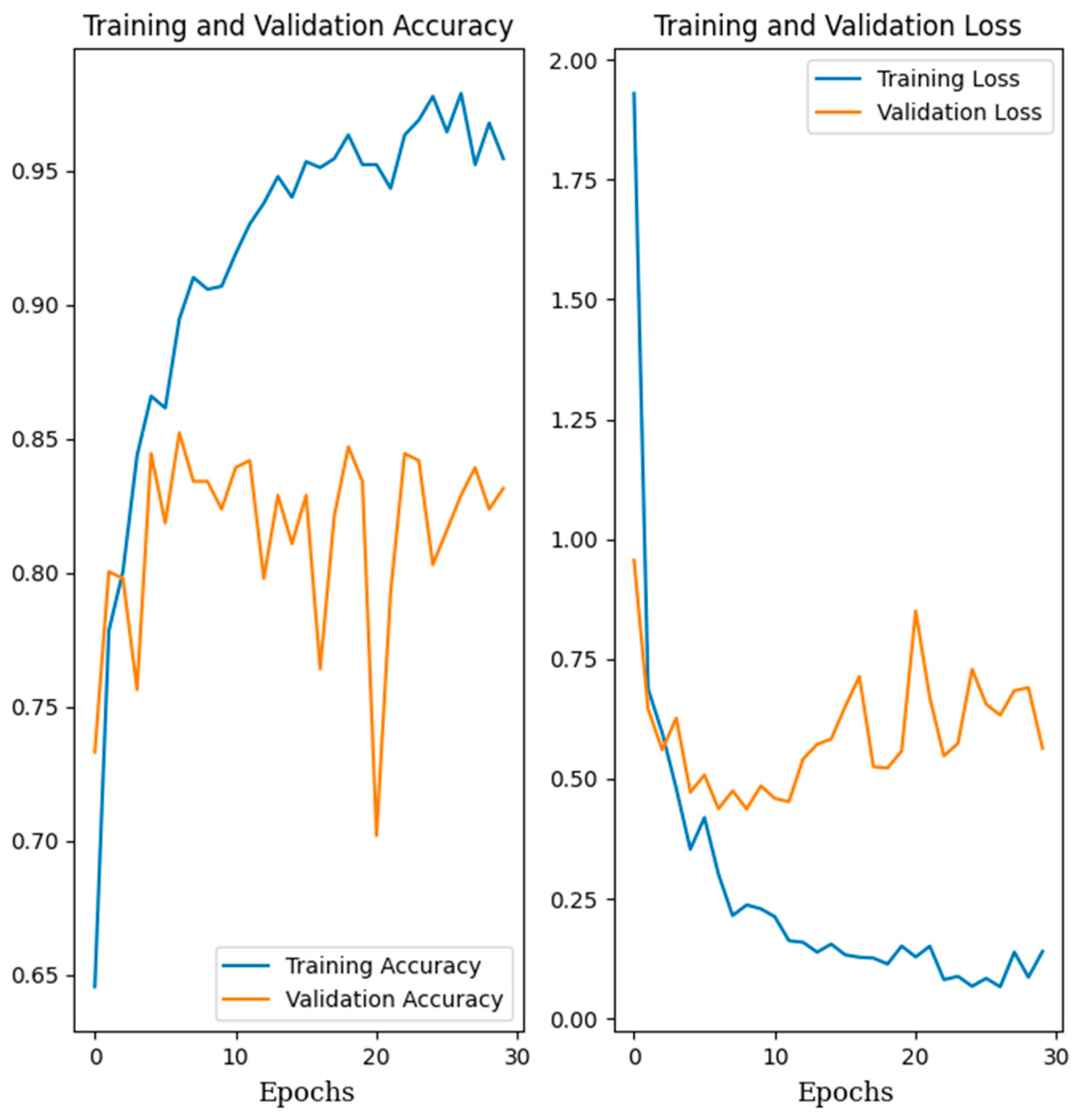
3.2. Training Classification Algorithms with Our Own Datasets
3.3. Training Classification Algorithms with Open Datasets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Banana Market Review—Preliminary Results 2023. Rome. Available online: https://www.fao.org/markets-and-trade/commodities/bananas/en (accessed on 30 March 2024).
- FAO. FAO Publications Catalogue 2023. Rome. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/cc7285en (accessed on 30 March 2024).
- OECD; FAO. Environmental Sustainability in Agriculture 2023. Rome. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/items/f3c4d1dd-6092-4627-9001-1e1d76f82470 (accessed on 30 March 2024).
- Rubhara, T.; Gaffey, J.; Hunt, G.; Murphy, F.; O’Connor, K.; Buckley, E.; Vergara, L.A. A Business Case for Climate Neutrality in Pasture-Based Dairy Production Systems in Ireland: Evidence from Farm Zero C. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.B.; Abdullah, H.M.; Arman, S.E.; Rahman, S.S.; Al Mahmud, K. BananaSqueezeNet: A very fast, lightweight convolutional neural network for the diagnosis of three prominent banana leaf diseases. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 4, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, D.; Mishra, S.; Sutar, N. Banana and its by-product utilisation: An overview. J. Scient. Indust. Res. 2010, 69, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Asociación de Bananeros de Colombia|Augura (Corporate Authorship). “Coyuntura Bananera 2022”. 2022. Available online: https://augura.com.co/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Coyuntura-Bananera-2022-2.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Datta, S.; Jankowicz-Cieslak, J.; Nielen, S.; Ingelbrecht, I.; Till, B.J. Induction and recovery of copy number variation in banana through gamma irradiation and low-coverage whole-genome sequencing. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1644–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte Fajardo, J.; Bayona Andrade, O.; Criollo Bonilla, R.; Cevallos-Cevallos, J.; Mariduena-Zavala, M.; Ochoa Donoso, D.; Vicente Villardon, J.L. Early detection of black Sigatoka in banana leaves using hyperspectral images. Appl. Plant Sci. 2020, 8, e11383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebimieowei, E.; Wabiye, Y.-H. Control of black Sigatoka disease: Challenges and prospects. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 508–514. [Google Scholar]
- Escudero, C.A.; Calvo, A.F.; Bejarano, A. Black Sigatoka Classification Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2022, 11, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, J.; Barraza, F.; Campo, R. Efecto del sombrío sobre la sigatoka negra (Mycosphaerella fijiensis Morelet) en cultivo de plátano cv hartón (Musa AAB Simmonds). Rev. UDCA Actual. Divulg. Científica 2016, 19, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossin, M.; Sulaiman, M.N. A Review on Evaluation Metrics for Data Classification Evaluations. Int. J. Data Min. Knowl. Manag. Process 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wu, J.; Gu, W. Modeling and Control for Triadic Compound Controlled Flying Saucer. In Proceedings of the 2006 6th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Dalian, China, 21–23 June 2006; pp. 6293–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J. Automatic Image-Based Plant Disease Severity Estimation Using Deep Learning. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2017, 2017, 2917536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calou, V.B.C.; dos Santos Teixeira, A.; Moreira, L.C.J.; Lima, C.S.; de Oliveira, J.B.; de Oliveira, M.R.R. The use of UAVs in monitoring yellow sigatoka in banana. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 193, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Lakho, G.M.; Keerio, H.A.; Sattar, M.N.; Hussain, G.; Mehdi, M.; Vistro, R.B.; Mahmoud, E.A.; Elansary, H.O. Application of Drone Surveillance for Advance Agriculture Monitoring by Android Application Using Convolution Neural Network. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, W.H.; Steppe, K. Perspectives for Remote Sensing with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Precision Agriculture. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neupane, B.; Horanont, T.; Hung, N.D. Deep learning based banana plant detection and counting using high-resolution red-green-blue (RGB) images collected from unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, N.B.; Rajendran, P.S. Comparative Analysis of Banana Leaf Disease Detection and Classification Methods. In Proceedings of the 2022 6th International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC), Erode, India, 29–31 March 2022; pp. 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, K.; Doshi, A.; Patel, P.; Shah, M. A comprehensive review on automation in agriculture using artificial intelligence. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2019, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Mao, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Duan, F.; Yan, Y. UAV-based multispectral remote sensing for precision agriculture: A comparison between different cameras. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 146, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendini, H.N.; Jacon, A.D.; Moreira Pessôa, A.C.; Pompeu Pavenelli, J.A.; Moraes, W.S.; Ponzoni, F.J.; Fonseca, L.M. Caracterização Espectral de Folhas de Bananeira (Musa spp.) para detecção e diferenciação da Sigatoka Negra e Sigatoka Amarela. In Proceedings of the Anais XVII Simpósio Brasileiro de Sensoriamento Remoto, João Pessoa, PB, Brasil, 25–29 April 2015; pp. 2536–2543. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279189023 (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Yeom, J.; Jung, J.; Chang, A.; Ashapure, A.; Maeda, M.; Maeda, A.; Landivar, J. Comparison of Vegetation Indices Derived from UAV Data for Differentiation of Tillage Effects in Agriculture. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DJI. P4 Multispectral User Manual 6 July 2020. Available online: https://www.dji.com/uk/p4-multispectral/downloads (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Tsagaris, V.; Anastassopoulos, V. Multispectral image fusion for improved RGB representation based on perceptual attributes. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 3241–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, A.E.; Polo, M.A.P.; Gomez-Rojas, J.; Ramos, R.L. Canopy Extraction in a Banana Crop From UAV Captured Multispectral Images. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 40th Central America and Panama Convention (CONCAPAN), Panama City, Panama, 9–12 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Qi, S.; Shen, Y.; Ni, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T. Multispectral Image Alignment With Nonlinear Scale-Invariant Keypoint and Enhanced Local Feature Matrix. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roboflow Inc. «Roboflow», 7 May 2019. Available online: https://roboflow.com/ (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Hang, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B. Classification of Plant Leaf Diseases Based on Improved Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2019, 19, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Universidad Nacional de Quilmes. Introducción a la Teledetección/3. La Herramienta de la Teledetección: El Análisis Visual y el Procesamiento de Imágenes. Available online: https://static.uvq.edu.ar/mdm/teledeteccion/unidad-3.html (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- Yordanos, H. Banana Leaf Disease Images. Mendeley Data 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arman, E.; Bhuiyan, B.; Abdullahil, M.; Muhammad, H.; Shariful; Chowdhury; Tanha, T.; Arban, M. Banana Leaf Spot Diseases (BananaLSD) Dataset for Classification of Banana Leaf Diseases Using Machine Learning. Mendeley Data 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radócz, L.; Szabó, A.; Tamás, A.; Illés, Á.; Bojtor, C.; Ragán, P.; Vad, A.; Széles, A.; Harsányi, E.; Radócz, L. Investigation of the Detectability of Corn Smut Fungus (Ustilago maydis DC. Corda) Infection Based on UAV Multispectral Technology. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choosumrong, S.; Hataitara, R.; Sujipuli, K.; Weerawatanakorn, M.; Preechaharn, A.; Premjet, D.; Laywisadkul, S.; Raghavan, V.; Panumonwatee, G. Bananas diseases and insect infestations monitoring using multi-spectral camera RTK UAV images. Spat. Inf. Res. 2023, 31, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulridha, J.; Batuman, O.; Ampatzidis, Y. UAV-Based Remote Sensing Technique to Detect Citrus Canker Disease Utilizing Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, T.B.; Xu, C.-Y.; Neupane, A.; Guo, W. Recent Advances in Crop Disease Detection Using UAV and Deep Learning Techniques. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkonyi, L.; Rubanga, D.; Richard, M.; Zekeya, N.; Sawahiko, S.; Maiseli, B.; Machuve, D. Early identification of Tuta absoluta in tomato plants using deep learning. Sci. Afr. 2020, 10, e00590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, M.D.; Jadhav, P.P.; Pawar, S. Pomegranate leaf disease detection using supervised and unsupervised algorithm techniques. Cybern. Syst. 2023, 54, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanga, S.; Mero, V.; Machuve, D.; Mwanganda, D. Mobile-based deep learning models for banana diseases detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.03718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
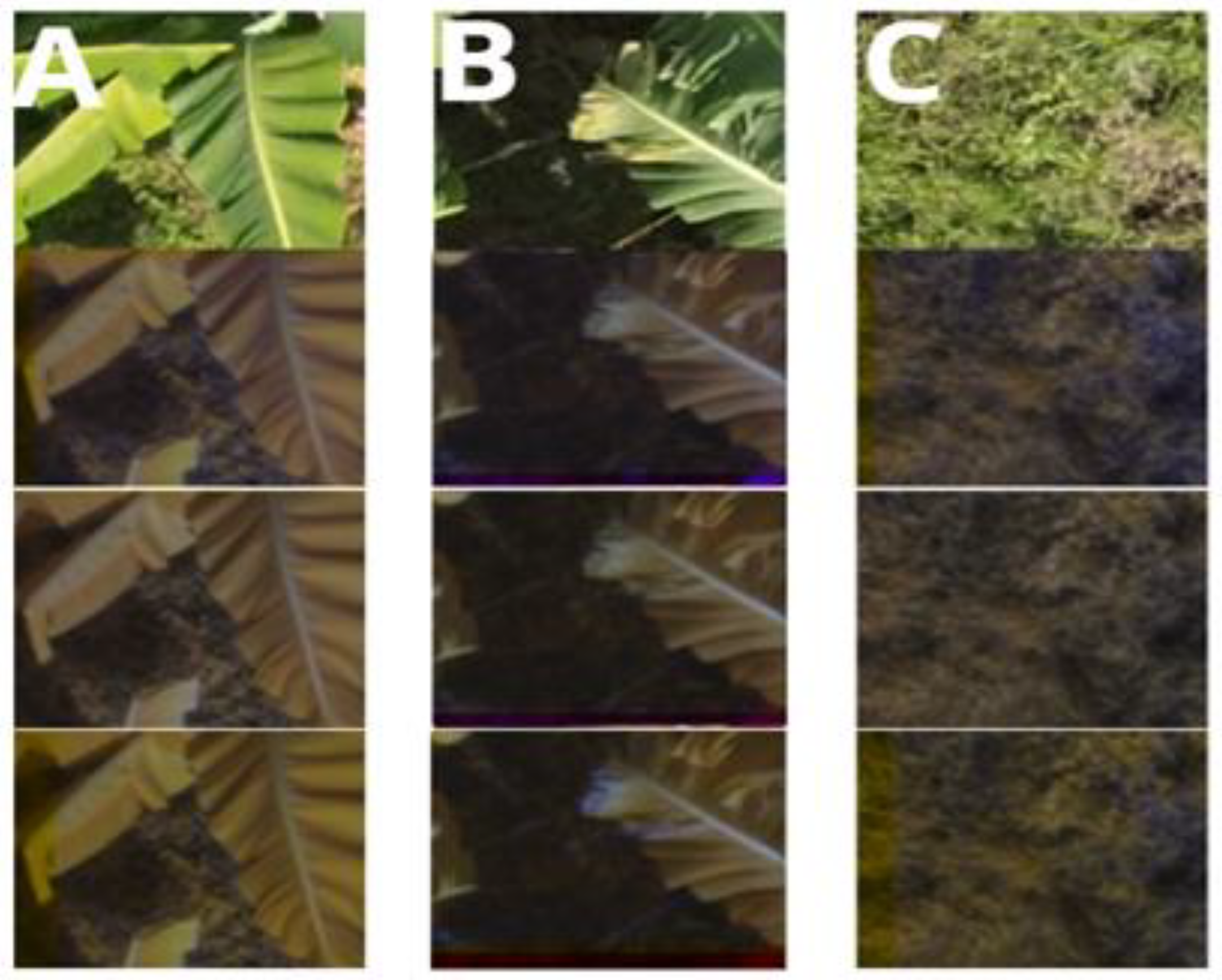
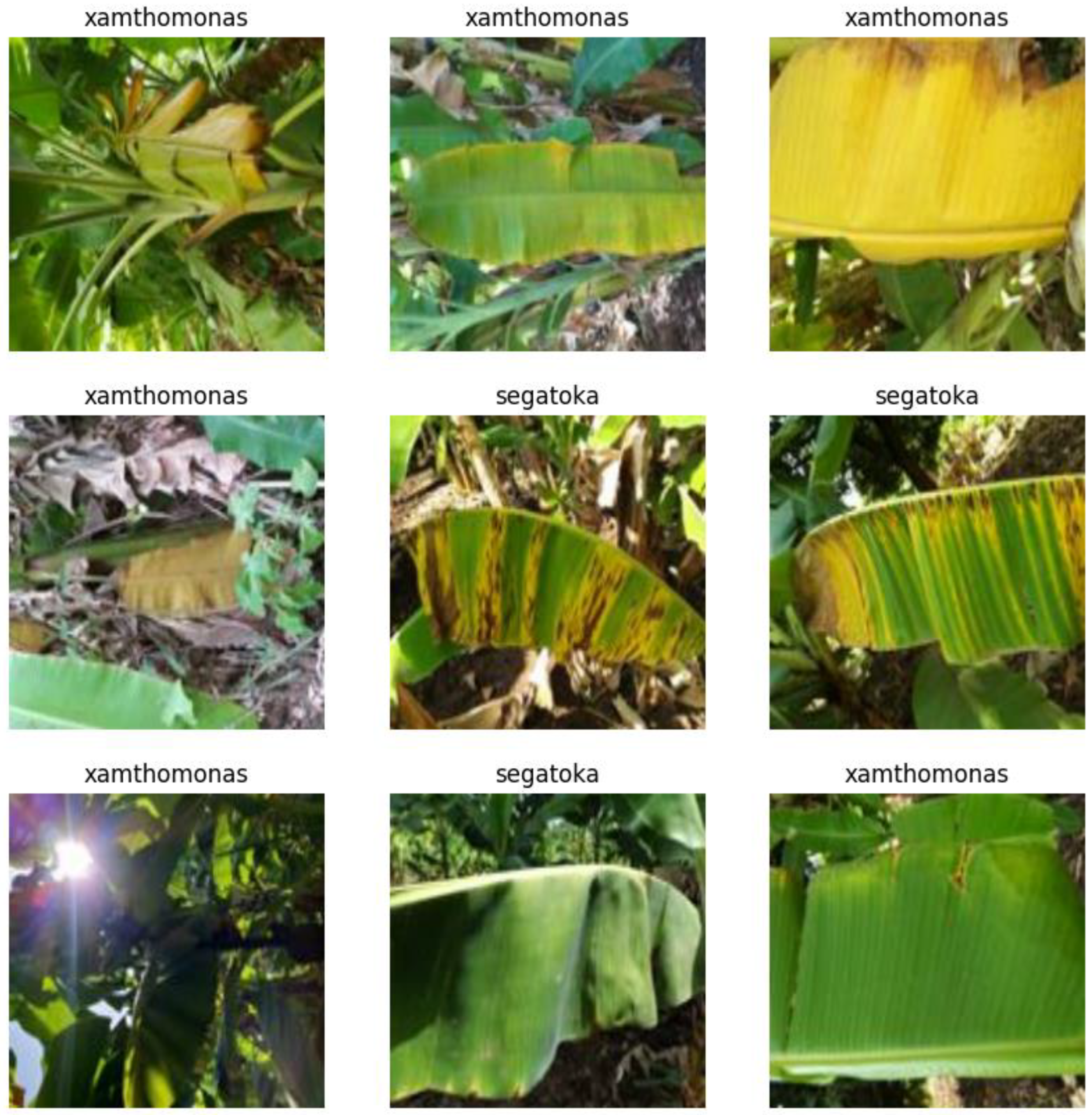








| Confusion Matrix | Predicted Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive Prediction | Negative Prediction | ||
| Actual Values | Positive label | True positive (TP) | False negative (FN) |
| Negative label | False positive (FP) | True negative (TN) | |
| Metric | Equation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (acc) | Calculates how often predictions equal labels. | |
| Precision (p) | Quantifies the number of positive class predictions that actually belong to the positive class. | |
| Recall (r) | Quantifies the number of true positives and the number of false negatives. | |
| F1-Score (F1) | This is the harmonic mean of precision and recall. Its output range is [0, 1]. It works for both multi-class and multi-label classification. |
| Colour Space | Spectrum Combination | Wavelengths |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Blue, Red Edge, Near-Infrared | 450 nm, 730 nm, 840 nm |
| 2 | Green, Red Edge, Near-Infrared | 560 nm, 730 nm, 840 nm |
| 3 | Red, Red Edge, Near-Infrared | 650 nm, 730 nm, 840 nm |
| Architecture | Spectrum Combination | Training Accuracy | Validation Accuracy | Precision of Sigatoka Class | Recall of Sigatoka Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EfficientNetV2B3 | RGB | 0.8090 | 0.7833 | 0.75 | 0.64 |
| EfficientNetV2B3 | R, REG, NIR | 0.8306 | 0.7648 | 0.71 | 0.67 |
| EfficientNetV2B3 | G, REG, NIR | 0.8304 | 0.7562 | 0.68 | 0.58 |
| EfficientNetV2B3 | B, REG, NIR | 0.8337 | 0.7633 | 0.70 | 0.61 |
| VGG19 | RGB | 0.8018 | 0.7714 | 0.68 | 0.77 |
| VGG19 | R, REG, NIR | 0.8043 | 0.7581 | 0.69 | 0.70 |
| VGG19 | G, REG, NIR | 0.8020 | 0.7495 | 0.74 | 0.59 |
| VGG19 | B, REG, NIR | 0.8276 | 0.7476 | 0.67 | 0.70 |
| MobileNetV2 | RGB | 0.8247 | 0.7852 | 0.63 | 0.39 |
| MobileNetV2 | R, REG, NIR | 0.8653 | 0.7890 | 0.75 | 0.72 |
| MobileNetV2 | G, REG, NIR | 0.8259 | 0.7638 | 0.68 | 0.72 |
| MobileNetV2 | B, REG, NIR | 0.8265 | 0.7610 | 0.70 | 0.65 |
| Architecture | Spectrum Combination | Training Accuracy | Validation Accuracy | Precision Of Sigatoka Class | Recall of Sigatoka Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EfficientNetV2B3 | RGB | 0.9579 | 0.8733 | 0.85 | 0.86 |
| VGG19 | RGB | 0.9546 | 0.8394 | 0.70 | 0.83 |
| MobileNetV2 | RGB | 0.9092 | 0.7720 | 0.79 | 0.61 |
| Architecture | Spectrum Combination | Training Accuracy | Validation Accuracy | Precision of Sigatoka Class | Recall of Sigatoka Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EfficientNetV2B3 | RGB | 0.9964 | 0.9677 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
| VGG19 | RGB | 0.9886 | 0.9677 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
| MobileNetV2 | RGB | 0.9725 | 0.8387 | 0.90 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Linero-Ramos, R.; Parra-Rodríguez, C.; Espinosa-Valdez, A.; Gómez-Rojas, J.; Gongora, M. Assessment of Dataset Scalability for Classification of Black Sigatoka in Banana Crops Using UAV-Based Multispectral Images and Deep Learning Techniques. Drones 2024, 8, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8090503
Linero-Ramos R, Parra-Rodríguez C, Espinosa-Valdez A, Gómez-Rojas J, Gongora M. Assessment of Dataset Scalability for Classification of Black Sigatoka in Banana Crops Using UAV-Based Multispectral Images and Deep Learning Techniques. Drones. 2024; 8(9):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8090503
Chicago/Turabian StyleLinero-Ramos, Rafael, Carlos Parra-Rodríguez, Alexander Espinosa-Valdez, Jorge Gómez-Rojas, and Mario Gongora. 2024. "Assessment of Dataset Scalability for Classification of Black Sigatoka in Banana Crops Using UAV-Based Multispectral Images and Deep Learning Techniques" Drones 8, no. 9: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8090503
APA StyleLinero-Ramos, R., Parra-Rodríguez, C., Espinosa-Valdez, A., Gómez-Rojas, J., & Gongora, M. (2024). Assessment of Dataset Scalability for Classification of Black Sigatoka in Banana Crops Using UAV-Based Multispectral Images and Deep Learning Techniques. Drones, 8(9), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8090503







