G-YOLO: A Lightweight Infrared Aerial Remote Sensing Target Detection Model for UAVs Based on YOLOv8
Abstract
1. Introduction
- An innovative lightweight UAV-based target detection model named G-YOLO is proposed for infrared small targets detection in complex environments. The model can effectively improve the detection performances of UAV while significantly reducing model complexity and parameters.
- The backbone network of YOLOv8 is improved and designed based on the GhostBottleneckV2 lightweight network, while the original Conv convolution in the remaining part of the network is replaced by the DWConv module. The backbone network employs a more efficient channel separation strategy and incorporates additional feature reuse techniques to optimize model performance while preserving its lightweight nature. The proposed structure significantly reduces the number of parameters and computational requirements, thereby enhancing detection efficiency while preserving its ability to detect, thus leading to improved overall performance.
- The neck structure is enhanced by the ODConv module, which dynamically adjusts the size and position of the convolution kernel based on input data features. This enhancement increases the model’s adaptability to changes in target position and size, thereby improving its detection capabilities. The SEAttention attention mechanism is employed to dynamically allocate distinct weights to each channel, thereby facilitating the network in prioritizing salient feature information, enhancing the model’s ability to capture crucial information, and improving its detection capability.
- The loss function, SlideLoss, is introduced by comparing the predicted results of target detection with the actual labels during the training process to obtain an error value, which in turn is used to update the model parameters through error back-propagation to enhance the model’s suitability for the given task.
2. Related Work
3. Proposed Method
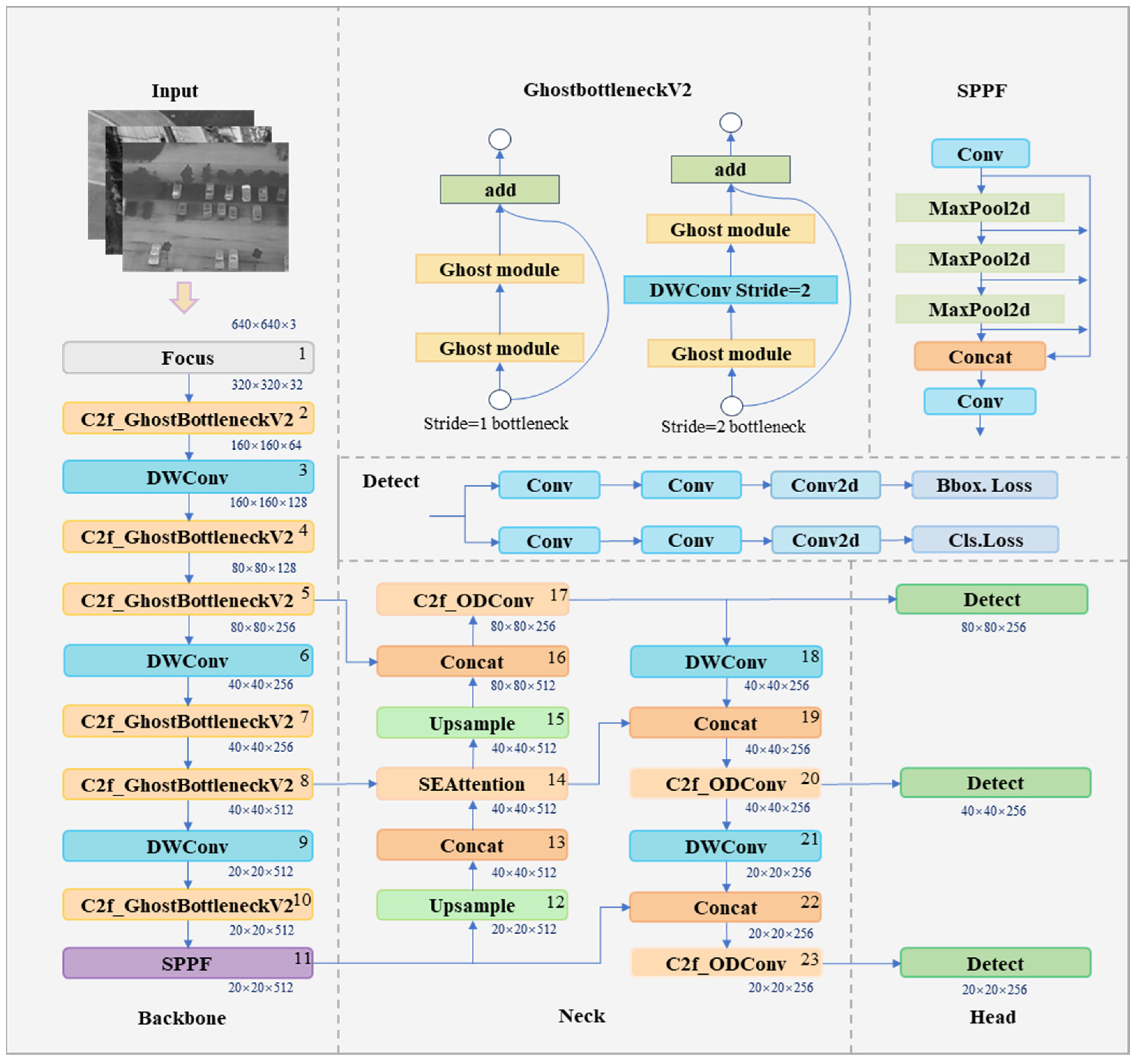
3.1. Lightweight Network Architecture G-YOLO
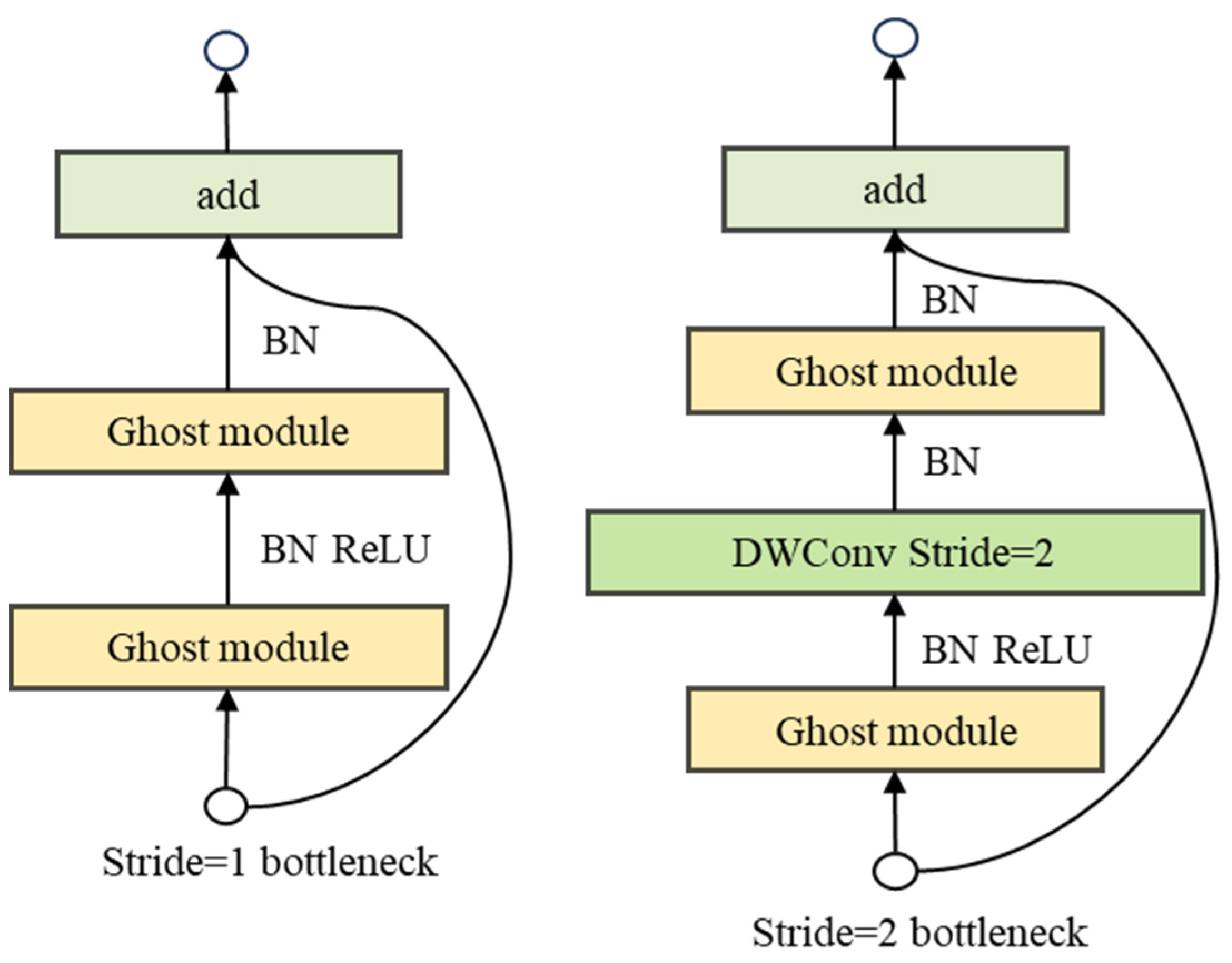
3.1.1. Improved Backbone Network Based on GhostBottleneck-V2
3.1.2. ODConv Feature Extraction Model
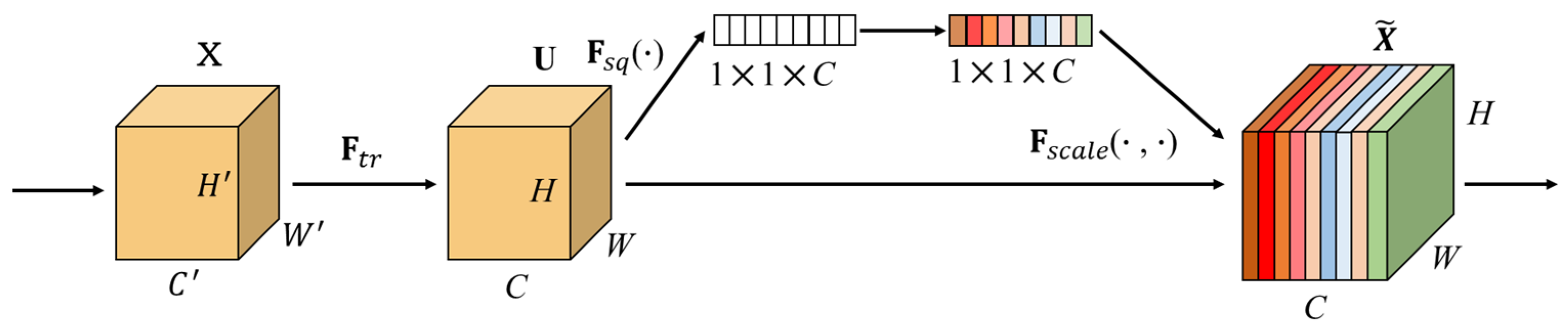
3.1.3. Channel Attention Mechanism SEAttention
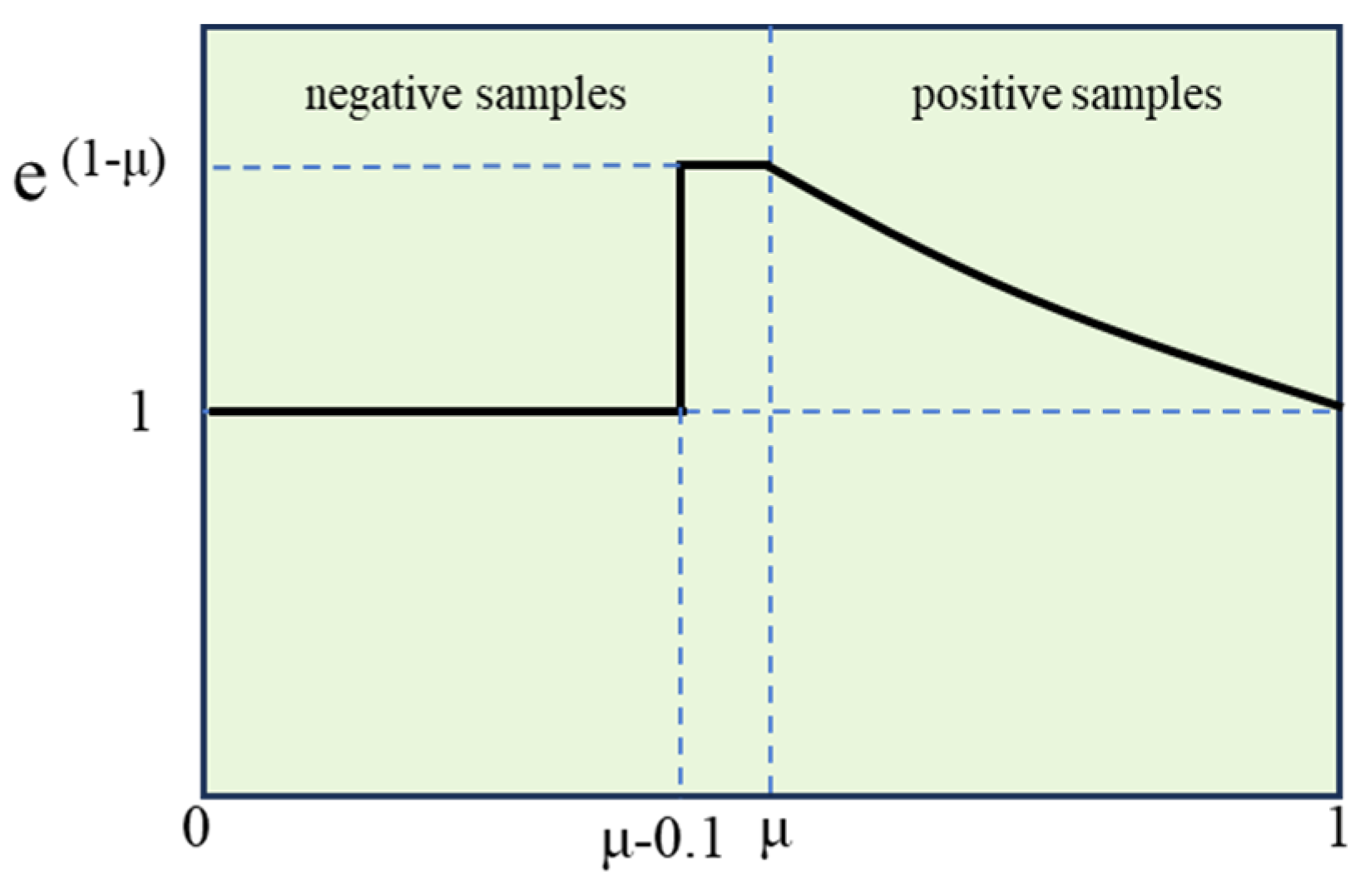
3.1.4. SlideLoss Loss Function
3.2. Datasets
3.3. The Evaluation Criteria
4. Results of the Experiments
4.1. Experimental Platform and Parameter Settings
4.2. Ablation Experiments
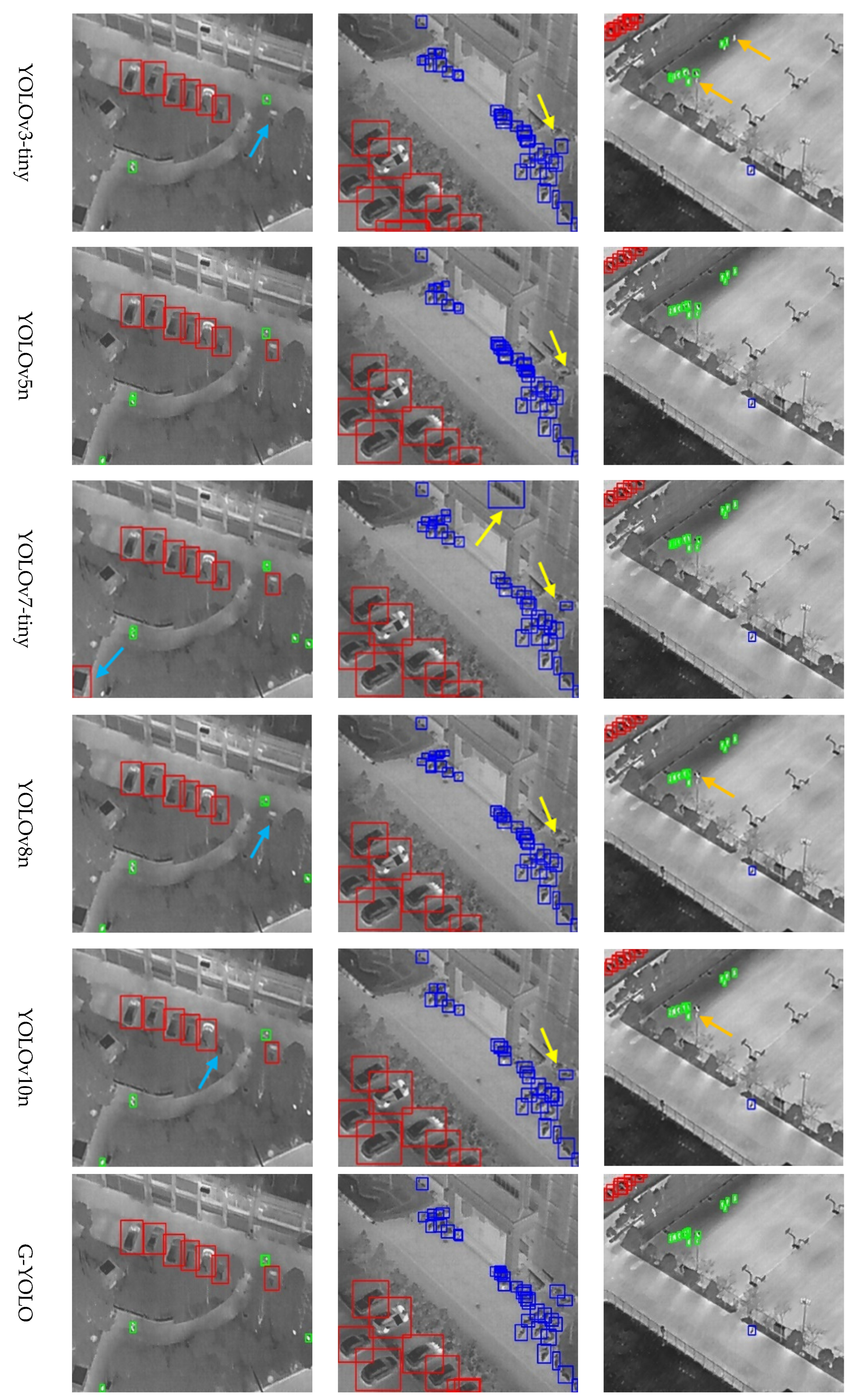
4.3. Comparative Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Li, D.; Qi, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Infrared Small Target Detection Method with Trajectory Correction Fuze Based on Infrared Image Sensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Deng, J.; Luo, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, J.; Peng, Z. Local Convergence Index-Based Infrared Small Target Detection against Complex Scenes. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, S.; Yanmaz, E.; Brown, T.X.; Bettstetter, C. Multi-objective UAV path planning for search and rescue. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 5569–5574. [Google Scholar]
- Shokouhifar, M.; Hasanvand, M.; Moharamkhani, E.; Werner, F. Ensemble Heuristic—Metaheuristic Feature Fusion Learning for Heart Disease Diagnosis Using Tabular Data. Algorithms 2024, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choutri, K.; Mohand, L.; Dala, L. Design of search and rescue system using autonomous Multi-UAVs. Intell. Decis. Technol. 2021, 14, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Bai, H.; Chen, T. Special Vehicle Detection from UAV Perspective via YOLO-GNS Based Deep Learning Network. Drones 2023, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Tan, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X. DB-YOLOv5: A UAV Object Detection Model Based on Dual Backbone Network for Security Surveillance. Electronics 2023, 12, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Xia, M.; Zhou, G.; Chang, Y.; Yan, L. Infrared Small UAV Target Detection Based on Residual Image Prediction via Global and Local Dilated Residual Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 7002305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Chen, Y.; Cai, W.; Niu, M.; Li, J. LD-YOLOv10: A Lightweight Target Detection Algorithm for Drone Scenarios Based on YOLOv10. Electronics 2024, 13, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Ni, J.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, Y.; Cao, W. A Survey of Object Detection for UAVs Based on Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, P. Overview of UAV Target Detection Algorithms Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Information Technology, Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (ICIBA), Chongqing, China, 17–19 December 2021; pp. 736–745. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. European Conference on Computer Vision. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2014; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y. Multi-Stage Multi-Scale Local Feature Fusion for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yu, M.; Chen, F.; Wu, H.; Luo, F. Surgical Tool Detection in Open Surgery Based on Faster R-CNN, YOLO v5 and YOLOv8. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 7th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 15–17 March 2024; pp. 1830–1834. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 7, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Zhou, A.; Fu, X.; Ma, Y.; Piao, C. UAV-YOLO: Small Object Detection on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Perspective. Sensors 2020, 20, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2014; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.02696. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, D.; Kupec, J.; Hong, J.; Daoudi, A. Real-Time Flying Object Detection with YOLOv8. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.09972. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yeh, I.-H.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv9: Learning What You Want to Learn Using Programmable Gradient Information. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13616. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOLOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.; Liu, B.; Zhao, B.; Liu, E. Small Object Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv8 for Remote Sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 1734–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z. ITD-YOLOv8: An Infrared Target Detection Model Based on YOLOv8 for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Drones 2024, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. GhostNet: More Features From Cheap Operations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1577–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Dong, M. Channel-Spatial Dynamic Convolution: An Exquisite Omni-dimensional Dynamic Convolution. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing (ICSP), Xi’an, China, 21–23 April 2023; pp. 1707–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Mao, F.; Song, M.; He, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Xue, H. Class Regularization: Improve Few-shot Image Classification by Reducing Meta Shift. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.08395. [Google Scholar]
- Rouhi, A.; Arezoomandan, S.; Kapoor, R.; Klohoker, J.; Patal, S.; Shah, P.; Umare, H.; Han, D. An Overview of Deep Learning in UAV Perception. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 5–8 January 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, U.; Joshi, K.; Shukla, S.K.; Rajawat, A.S. An Overview of Moving Object Detection Using YOLO Deep Learning Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Disruptive Technologies (ICDT), Greater Noida, India, 15–16 March 2024; pp. 1014–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, H.; Wu, H.; Yuan, G. RN-YOLO: A Small Target Detection Model for Aerial Remote-Sensing Images. Electronics 2024, 13, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Research on Detection and Recognition Technology of a Visible and Infrared Dim and Small Target Based on Deep Learning. Electronics 2023, 12, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Huang, L.; Tang, B.H. ASFF-YOLOv5: Multielement Detection Method for Road Traffic in UAV Images Based on Multiscale Feature Fusion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, O.; Ozer, S. YOLODrone: Improved YOLO Architecture for Object Detection in Drone Images. In Proceedings of the 2021 44th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Brno, Czech Republic, 26–28 July 2021; pp. 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Xinxin, L.; Zuojun, L.; Chaofang, H.; Changshou, X. Light-Weight Multi-Target Detection and Tracking Algorithm Based on M3-YOLOv5. In Proceedings of the 2023 42nd Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Tianjin, China, 24–26 June 2023; pp. 8159–8164. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Yang, Z.; Liu, B.; Sun, S. A Lightweight Infrared Small Target Detection Network Based on Target Multiscale Context. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 7000305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Qu, Y.; Gong, M.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X. VE-YOLOv6: A Lightweight Small Target Detection Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Neural Networks, Information and Communication Engineering (NNICE), Guangzhou, China, 10–12 January 2024; pp. 873–876. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Q.; Wu, Y.; Tian, L.; Lin, C. A Lightweight Traffic Sign Detection Algorithm based on Improved YOLOv7. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Human-Computer Interaction (ICHCI), Guangzhou, China, 4–6 August 2023; pp. 428–431. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla Carrasco, D.; Rashwan, H.A.; García, M.Á.; Puig, D. T-YOLO: Tiny Vehicle Detection Based on YOLO and Multi-Scale Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 22430–22440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Ma, X.; Chen, J.; Tang, X. PHSI-RTDETR: A Lightweight Infrared Small Target Detection Algorithm Based on UAV Aerial Photography. Drones 2024, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Improved YOLOv5 for Aerial Images Object Detection with the Introduction of Attention Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2023 2nd International Conference on Data Analytics, Computing and Artificial Intelligence (ICDACAI), Zakopane, Poland, 17–19 October 2023; pp. 817–824. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhan, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. LMSD-YOLO: A Lightweight YOLO Algorithm for Multi-Scale SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xu, G.; Cheng, S. Object Detection in UAV Aerial Images Based on Improved YOLOv7-tiny. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning (CVIDL), Zhuhai, China, 12–14 May 2023; pp. 370–374. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Zhou, W.; Shi, W. HIT-UAV: A High-altitude Infrared Thermal Dataset for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.0324. [Google Scholar]
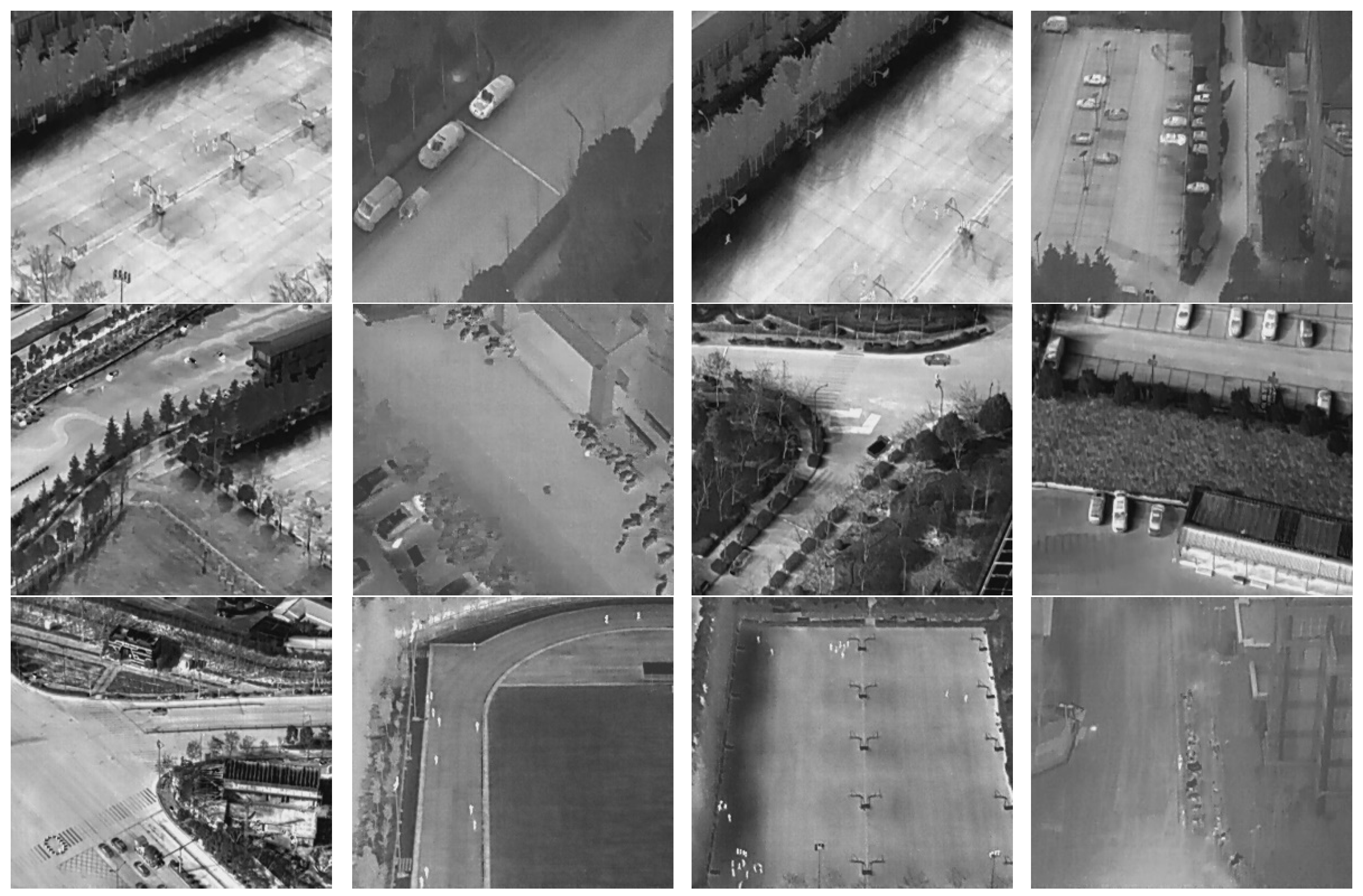



| Small (0, 32 × 32) | Medium (32 × 32, 96 × 96) | Large (96 × 96, 640 × 512) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIT-UAV | 17,118 | 7249 | 384 |
| Train set | 12,045 | 5205 | 268 |
| Test set | 3331 | 1379 | 70 |
| Validation set | 1742 | 665 | 46 |
| Names | Related Configurations |
|---|---|
| GPU | NVIDIA Quadro P6000 |
| CPU | Intel(R) Core (TM) i9-9900k |
| Size of GPU memory | 32 G |
| System for operating | Win 10 |
| The computational platform. | CUDA10.2 |
| Deep learning framework | Pytorch |
| YOLOv8n | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ghostbottleneckv2 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| ODConv | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| SEA | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| DWConv | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Slideloss | √ | ||||||||
| Parameters | 3.1 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| FLOPs/G | 8.1 | 5.6 | 6.7 | 7.9 | 7.8 | 4.3 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 3.7 |
| F1 (%) | 91.4 | 90.1 | 90.6 | 91.2 | 91.1 | 88.6 | 87.2 | 87.0 | 87.1 |
| APVehicle (%) | 98.4 | 98.2 | 98.8 | 98.7 | 98.6 | 97.7 | 97.1 | 97.2 | 97.2 |
| mAP50 (%) | 94.9 | 92.5 | 94.2 | 94.1 | 93.9 | 92.1 | 91.1 | 91.2 | 91.4 |
| FPS (bt = 16) | 485 | 540 | 492 | 476 | 483 | 552 | 539 | 552 | 556 |
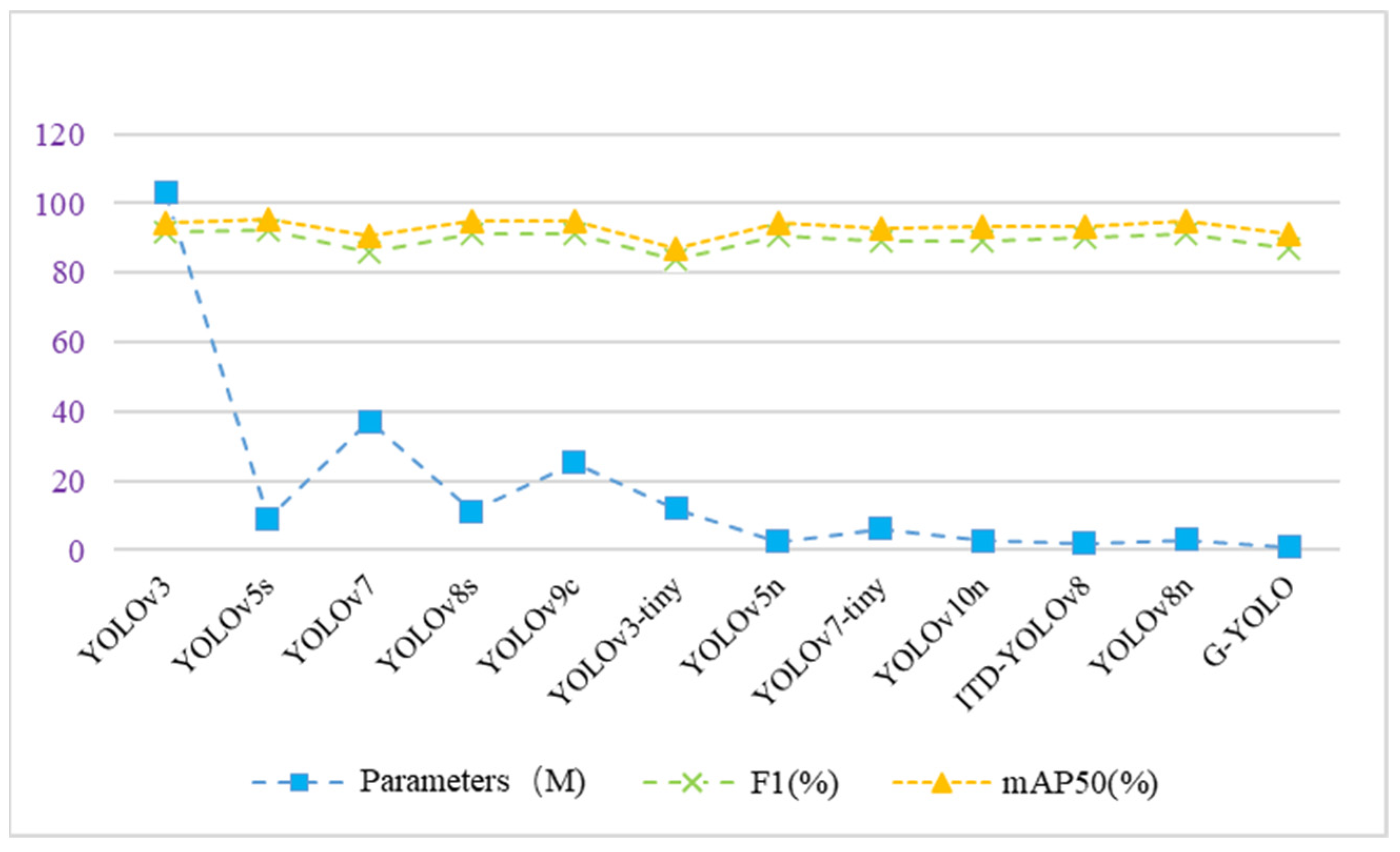
| Model | Size | Parameters | F1 (%) | (%) | (%) | mAP50 (%) | FLOPs/G | FPS (bt = 16) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv3 | 640 | 103 M | 91.8 | 92.3 | 98.7 | 92.6 | 94.5 | 282.2 | 45 |
| YOLOv5s | 640 | 9.1 M | 92.1 | 93.9 | 98.7 | 93.7 | 95.4 | 23.8 | 251 |
| YOLOv7 | 640 | 37.2 M | 86.1 | 87.6 | 96.3 | 87.7 | 90.5 | 105.1 | 76 |
| YOLOv8s | 640 | 11.1 M | 91.1 | 92.6 | 98.7 | 92.8 | 94.7 | 28.4 | 222 |
| YOLOv9c | 640 | 25.3 M | 91.4 | 92.3 | 98.7 | 93.5 | 94.9 | 238.9 | 43 |
| YOLOv3-tiny | 640 | 12.1 M | 84.0 | 82.3 | 97.8 | 81.5 | 87.2 | 18.9 | 400 |
| YOLOv5n | 640 | 2.5 M | 90.7 | 91.9 | 98.6 | 92.1 | 94.2 | 7.1 | 540 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 640 | 6.1 M | 89.2 | 91.3 | 97.2 | 89.9 | 92.8 | 13.2 | 250 |
| YOLOv10n | 640 | 2.7 M | 89.1 | 91.0 | 98.1 | 91.2 | 93.4 | 8.2 | 476 |
| ITD-YOLOv8 | 640 | 1.8 M | 90.3 | 91.7 | 98.2 | 90.7 | 93.5 | 6.0 | 328 |
| YOLOv8n | 640 | 3.1 M | 91.4 | 93.2 | 98.4 | 92.9 | 94.9 | 8.1 | 485 |
| G-YOLO | 640 | 0.8 M | 87.1 | 89.7 | 97.2 | 87.4 | 91.4 | 3.7 | 556 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z. G-YOLO: A Lightweight Infrared Aerial Remote Sensing Target Detection Model for UAVs Based on YOLOv8. Drones 2024, 8, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8090495
Zhao X, Zhang W, Xia Y, Zhang H, Zheng C, Ma J, Zhang Z. G-YOLO: A Lightweight Infrared Aerial Remote Sensing Target Detection Model for UAVs Based on YOLOv8. Drones. 2024; 8(9):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8090495
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiaofeng, Wenwen Zhang, Yuting Xia, Hui Zhang, Chao Zheng, Junyi Ma, and Zhili Zhang. 2024. "G-YOLO: A Lightweight Infrared Aerial Remote Sensing Target Detection Model for UAVs Based on YOLOv8" Drones 8, no. 9: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8090495
APA StyleZhao, X., Zhang, W., Xia, Y., Zhang, H., Zheng, C., Ma, J., & Zhang, Z. (2024). G-YOLO: A Lightweight Infrared Aerial Remote Sensing Target Detection Model for UAVs Based on YOLOv8. Drones, 8(9), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8090495





