EDGS-YOLOv8: An Improved YOLOv8 Lightweight UAV Detection Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
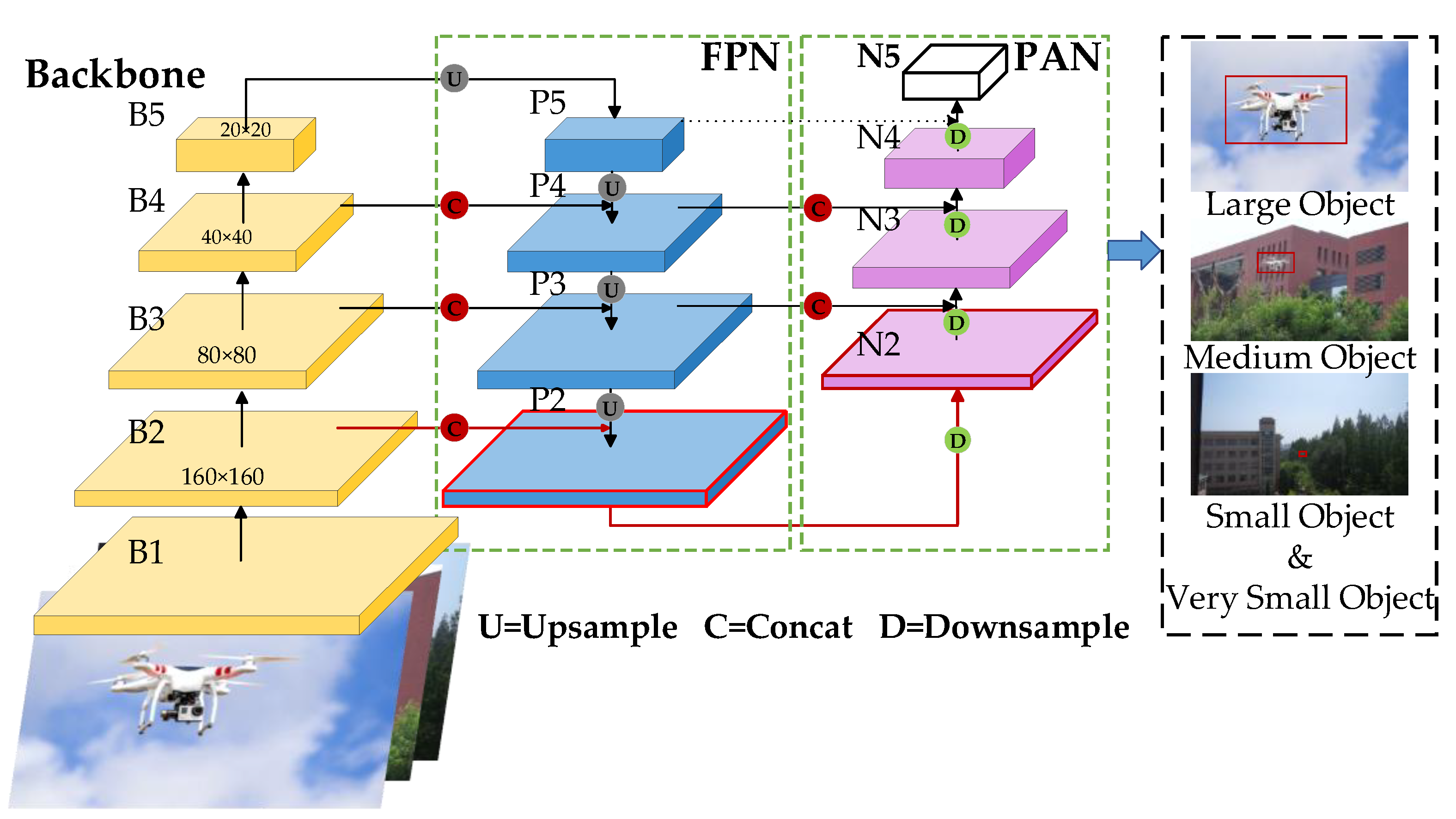
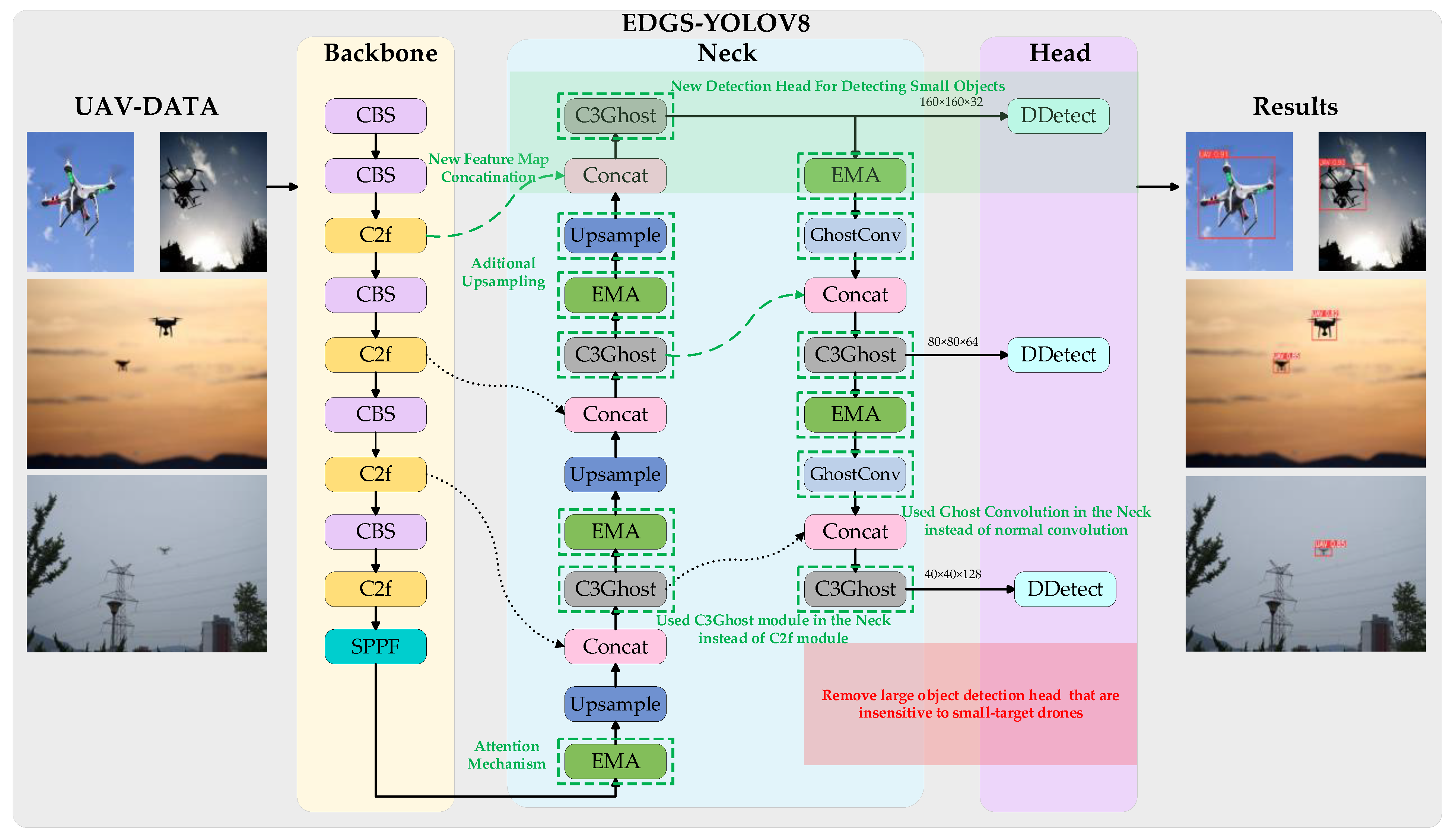
- By incorporating a dedicated small-target detection head, the algorithm enhances the recognition accuracy of UAVs by minimizing the loss of small-target feature information and emphasizing tiny targets. Additionally, eliminating the detection head in the network that is less sensitive to small-target UAVs contributes to a lighter model without compromising accuracy;
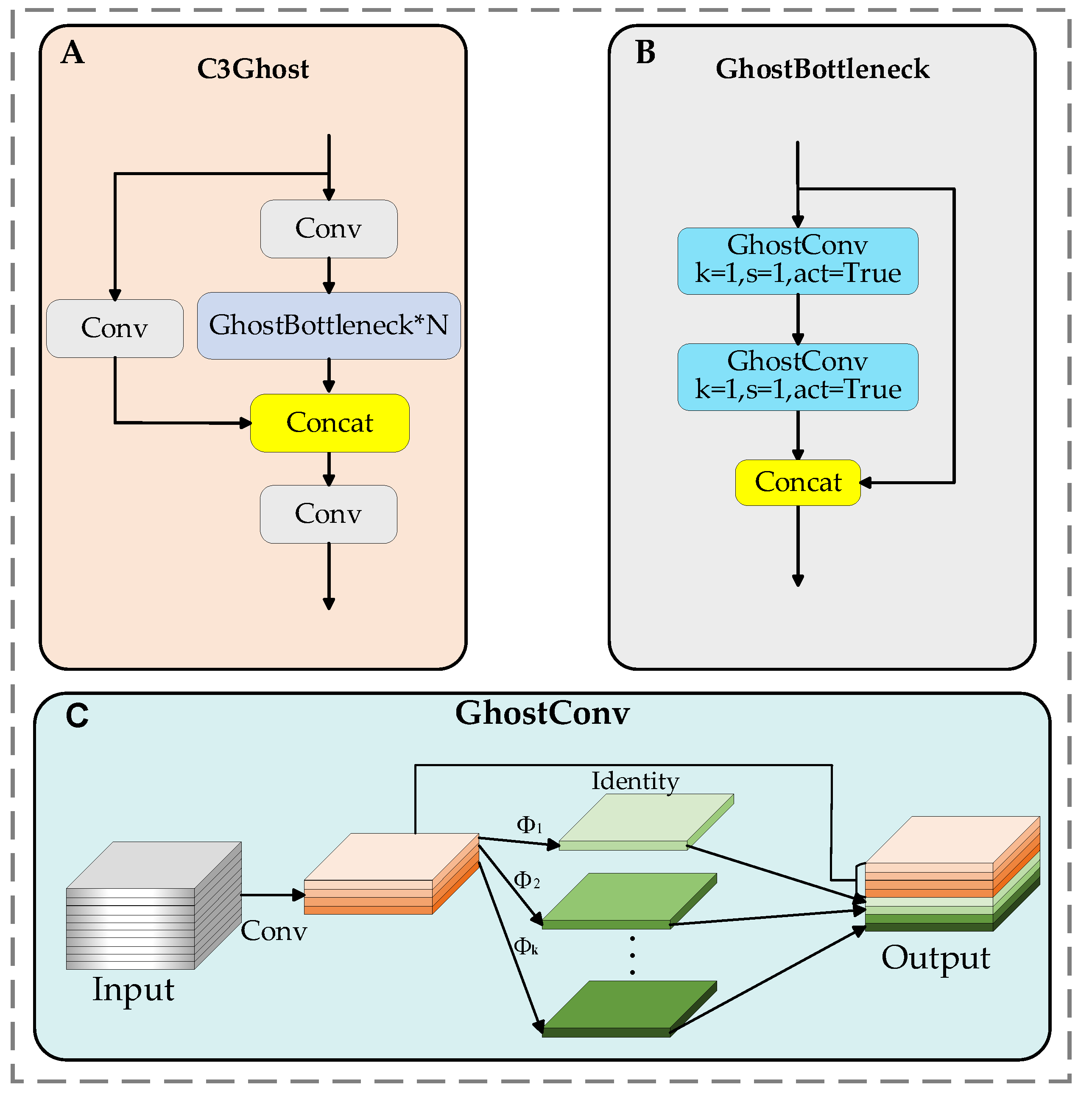
- The C3 module replaces the C2f module in the network’s neck, offering higher-level feature extraction capability and better multi-scale adaptability to capture richer semantic and contextual information. Additionally, the bottleneck module in the C3 module is replaced by GhostBottleneck, which reduces model parameters and mitigates information loss during long-distance feature transmission. Using ghost convolution instead of traditional convolution further lightens the UAV detection network;
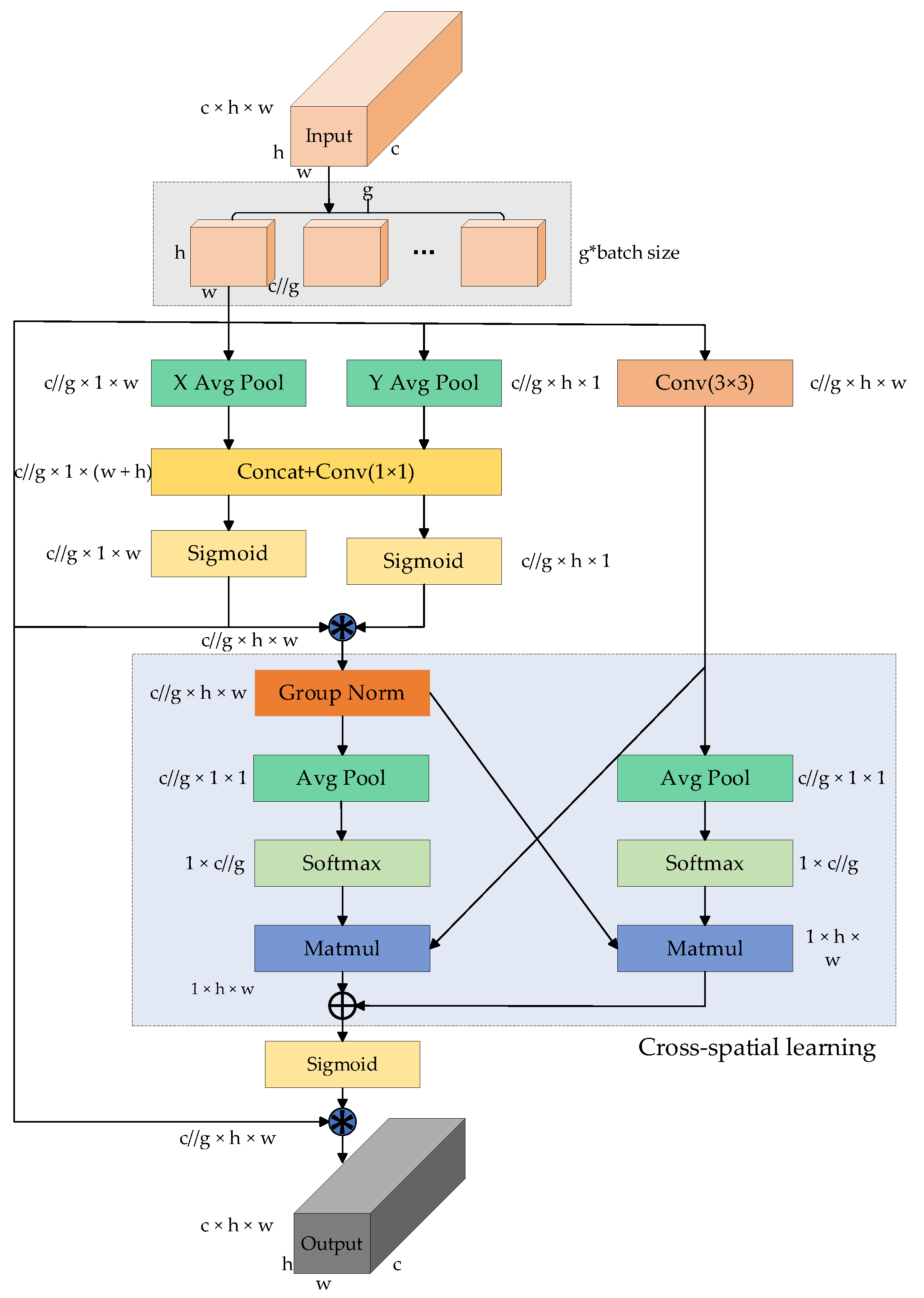
- To significantly preserve pixel-level attributes and spatial information on the feature map, we integrate the efficient multi-scale attention mechanism (EMA) into the model’s neck. This mechanism, capable of parallel processing, facilitates cross-channel feature interactions. This enhancement enables EDGS-YOLOv8 to focus more accurately on crucial regions within the image, thus extracting more comprehensive, stable, and discriminative features for detection;
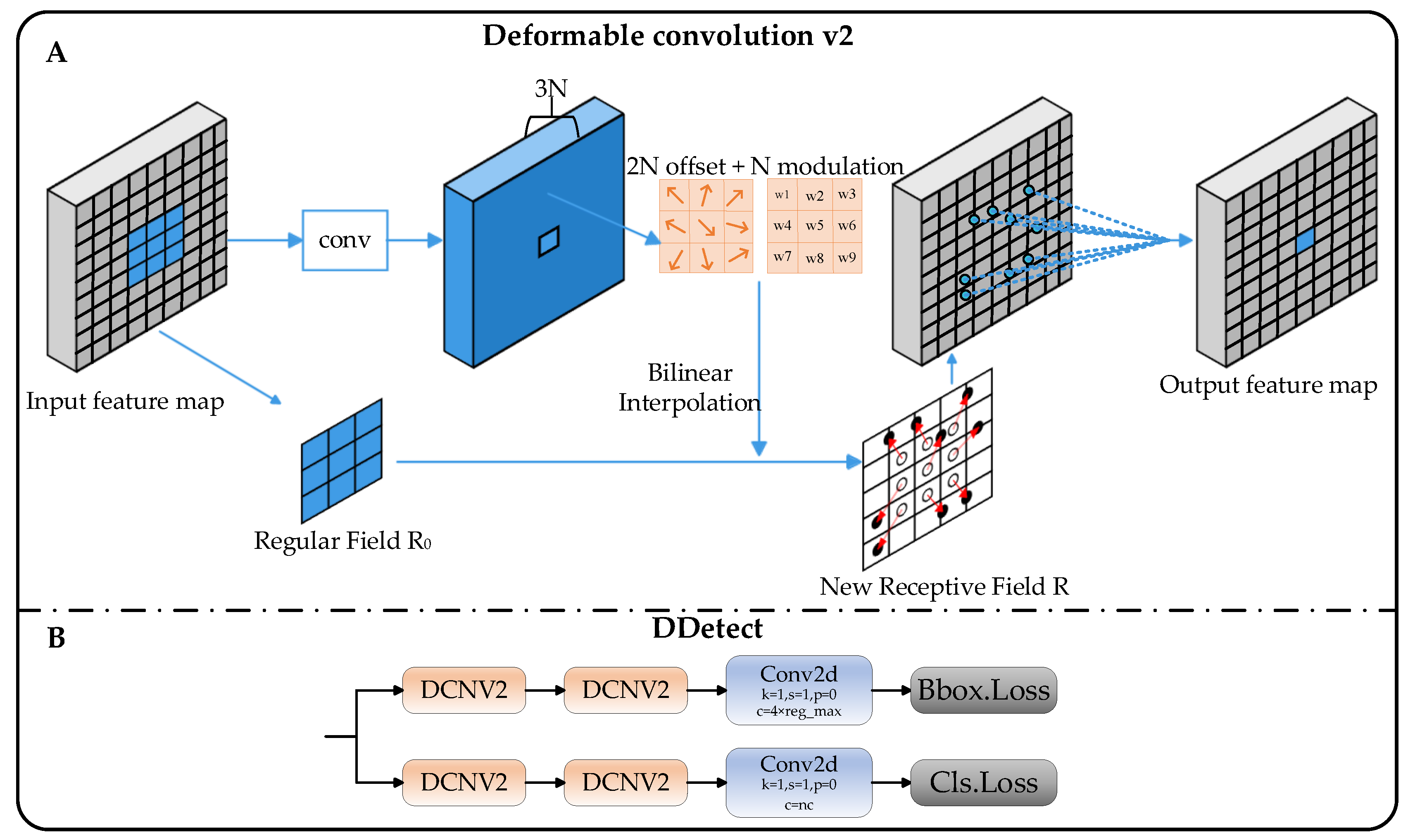
- Introducing deformable convolution net v2 to the detection head improves the model’s robustness in accurately recognizing and detecting UAV features through its local detail and geometric deformation-capturing capabilities. This initiative not only reduces the computational complexity but also results in improved detection accuracy.
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
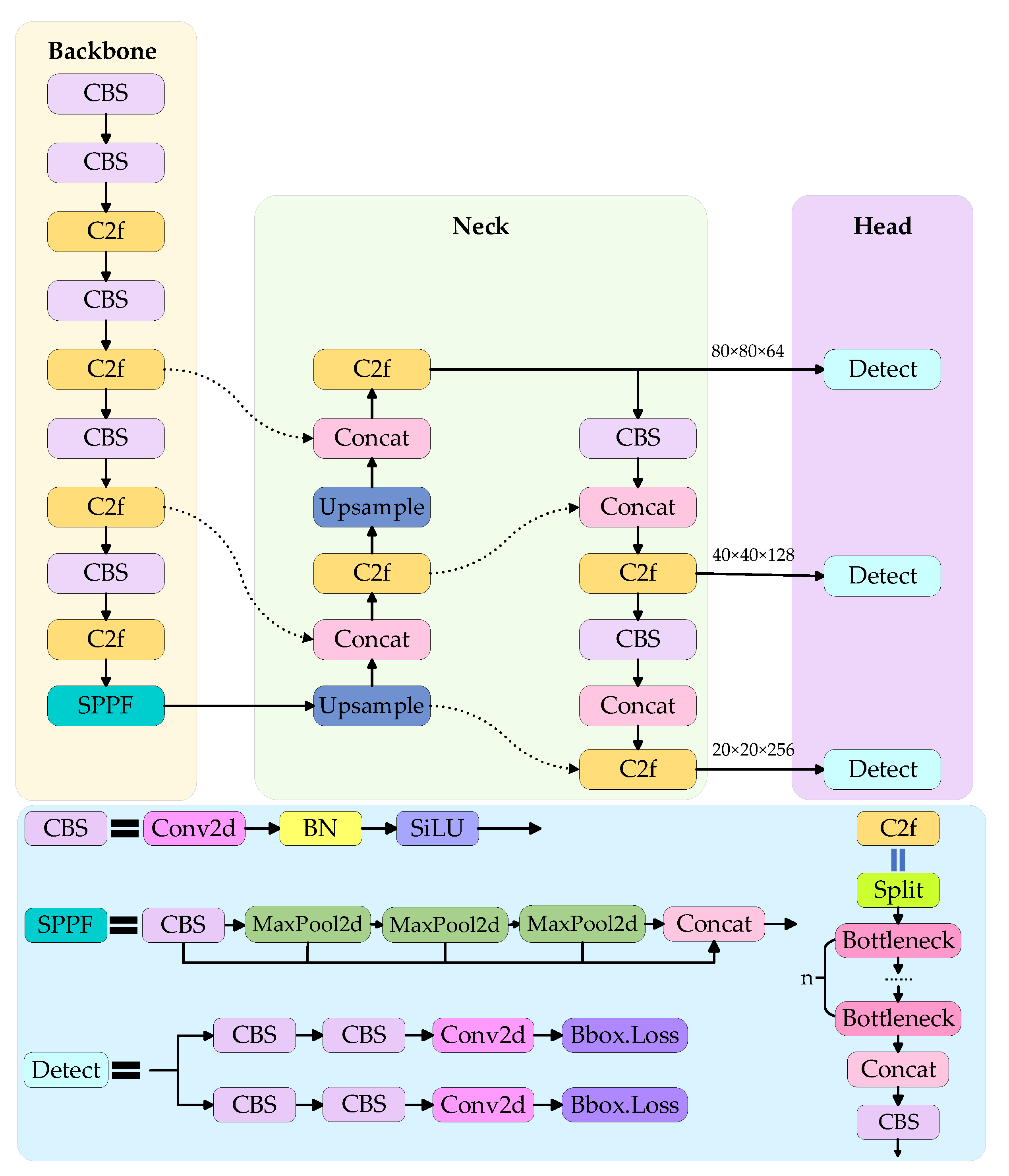
3.1. YOLOv8
3.2. Improvement of the Neck
3.3. C3Ghost
3.4. Efficient Multi-Scale Attention Module
3.5. DDetect
3.6. EDGS-YOLOv8
4. Results
4.1. Dataset and Its Preprocessing
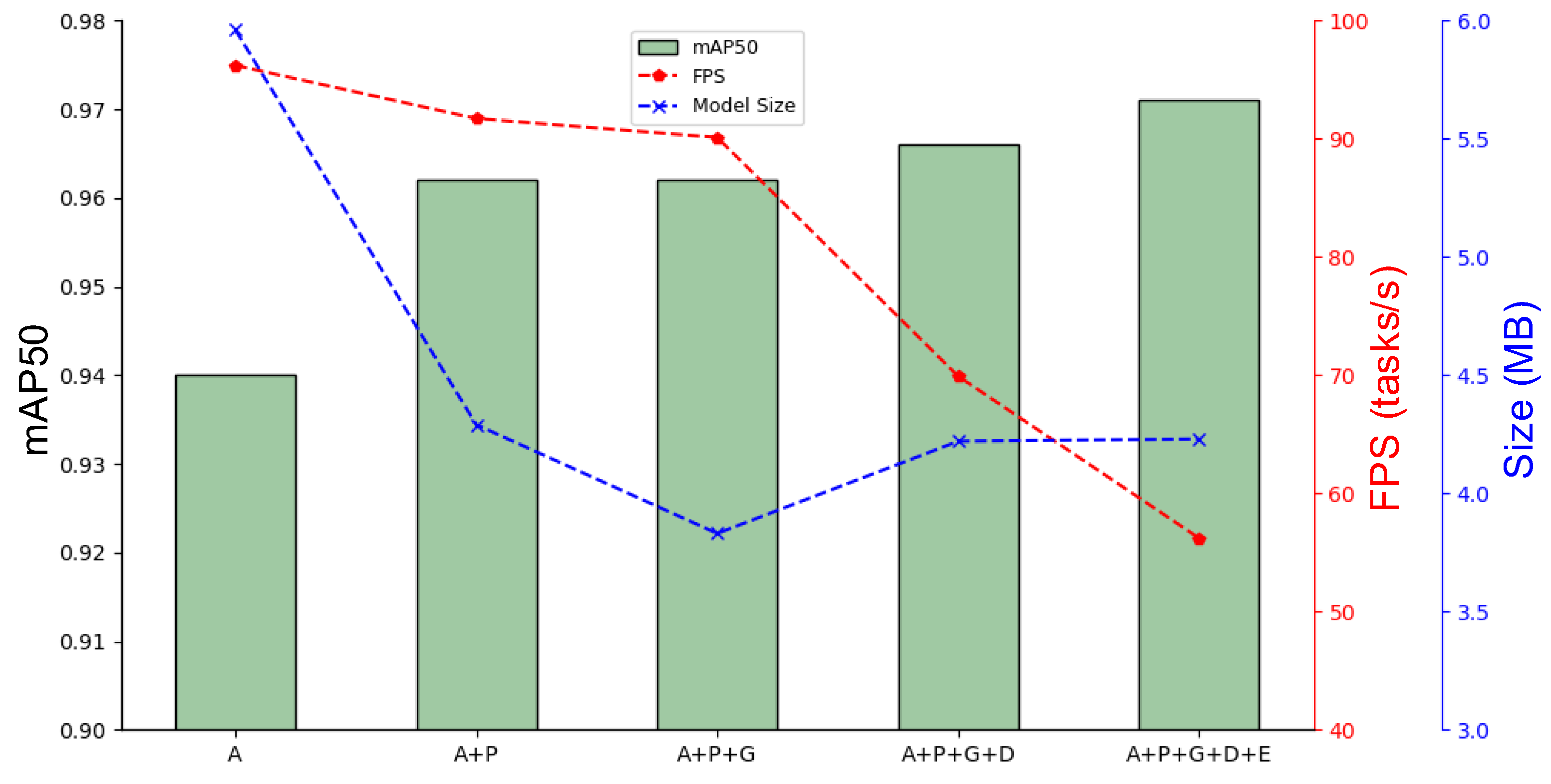
4.2. Ablation Experiment
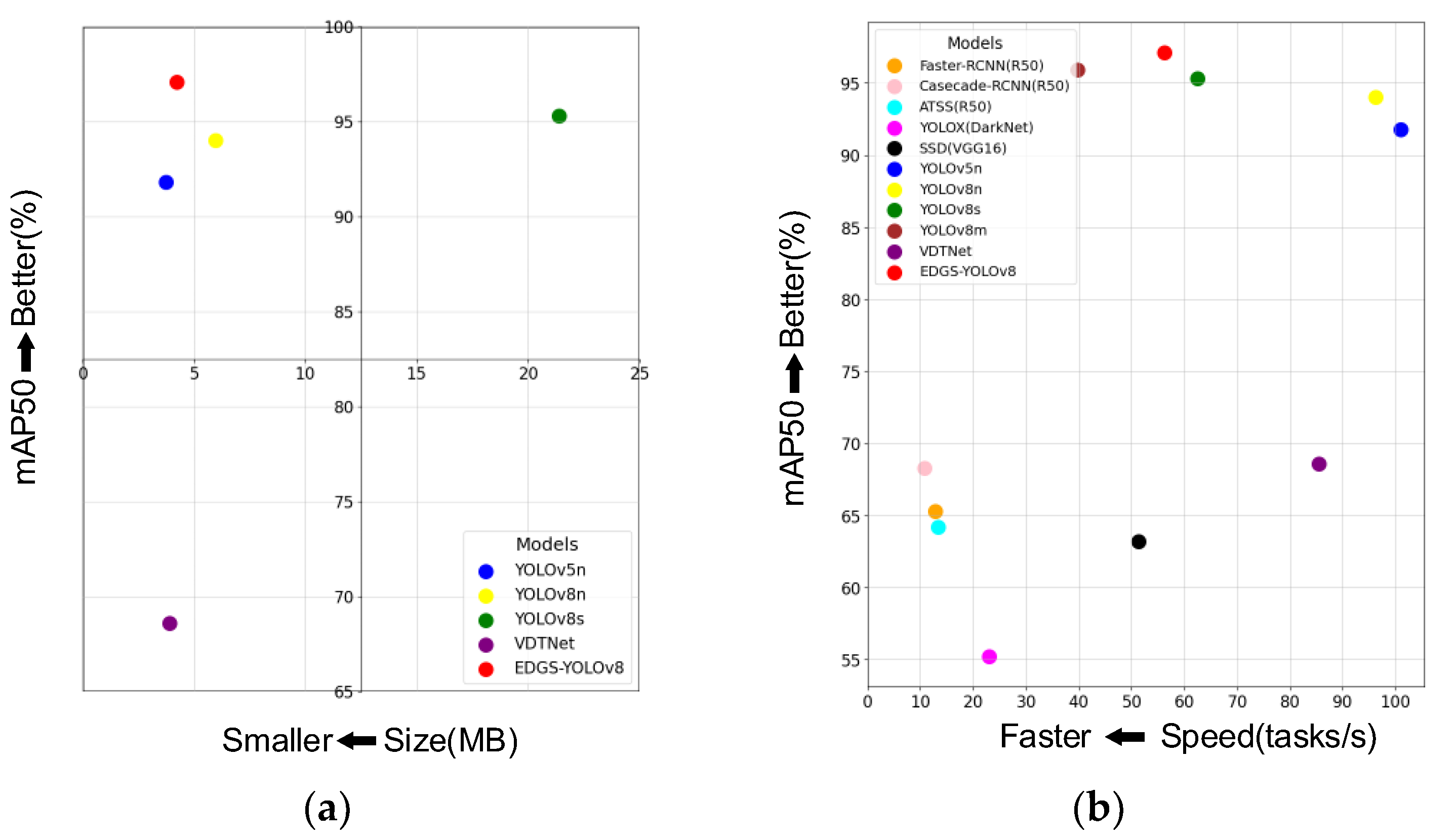
4.3. Performance Comparison Experiment with the Deep Learning Model
4.4. Experimental Results from the Public Dataset Det-Fly
4.5. Comparison of Small Object Detection Algorithms
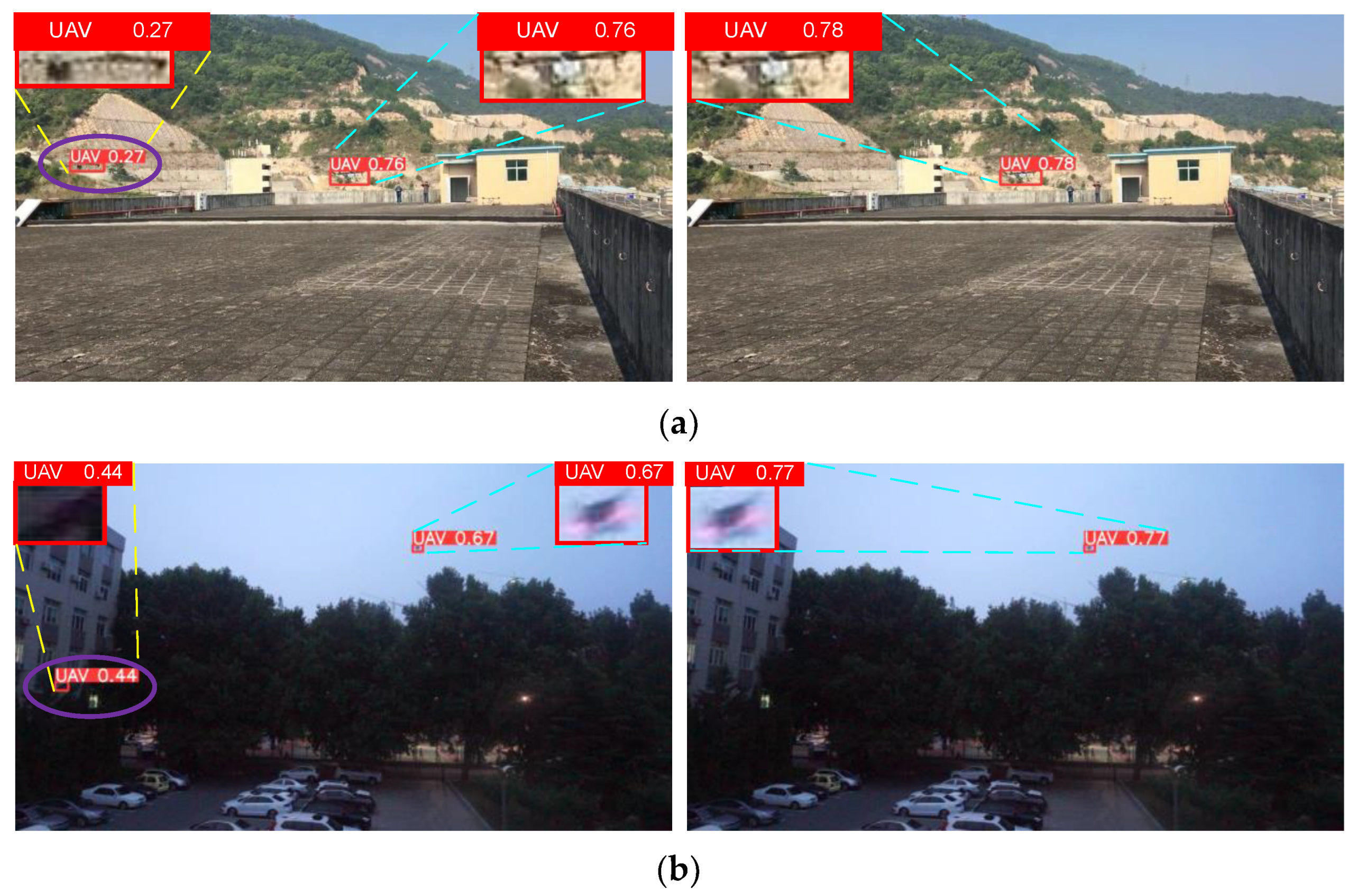
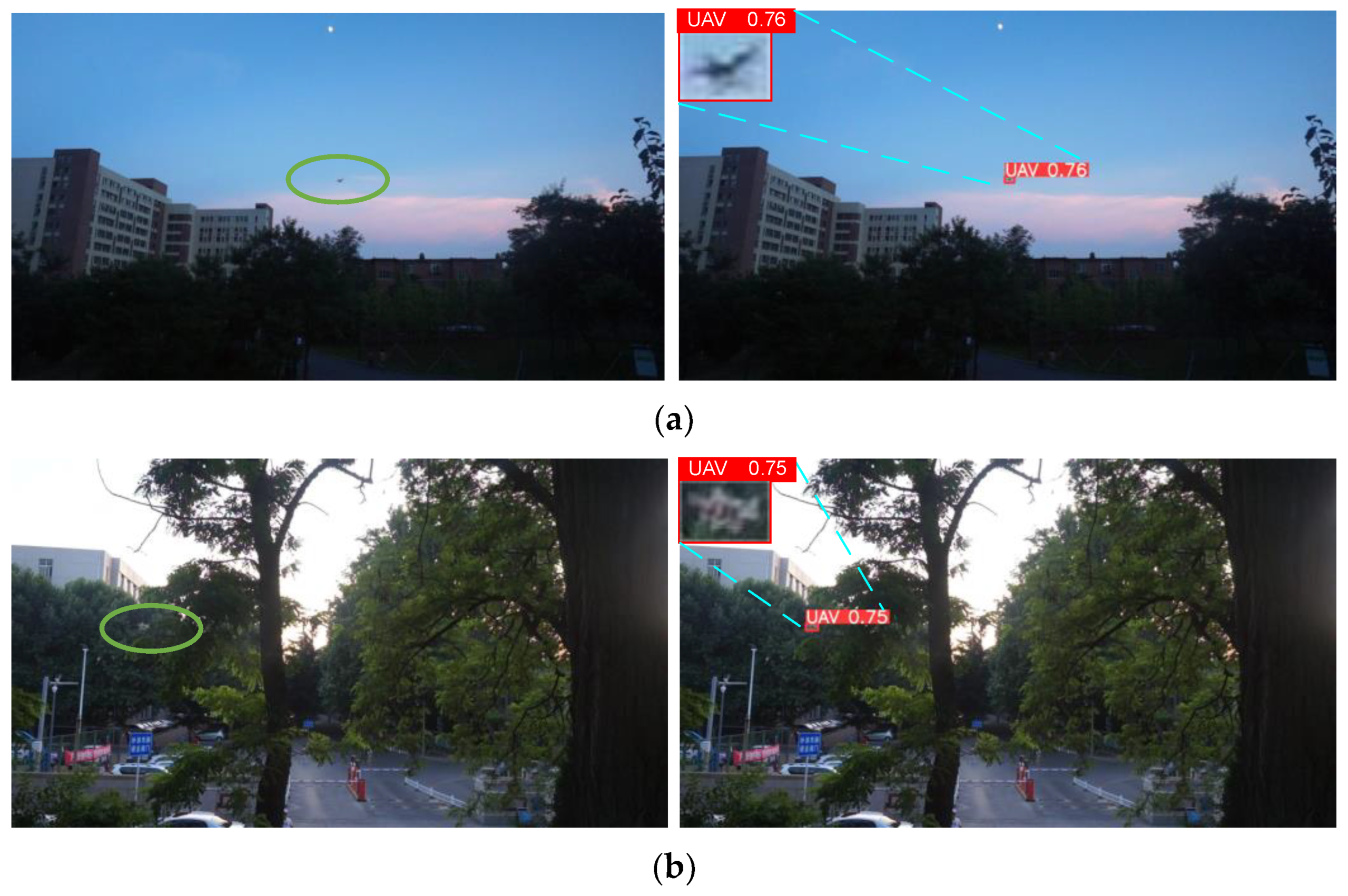
4.6. Visualization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wan, D.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, H.; Qi, F.; Chen, X.; Liang, G. Analysis of UAV patrol inspection technology suitable for distribution lines. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2237, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, C. Research on UAV aided earthquake emergency system. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 610, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeybek, M. Accuracy assessment of direct georeferencing UAV images with onboard global navigation satellite system and comparison of CORS/RTK surveying methods. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 065402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.Z.; Kaleem, Z.; Jamalipour, A. Machine learning inspired sound-based amateur drone detection for public safety applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 2526–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vattapparamban, E.; Güvenç, I.; Yurekli, A.I.; Akkaya, K.; Uluağaç, S. Drones for smart cities: Issues in cybersecurity, privacy, and public safety. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Paphos, Cyprus, 5–9 September 2016; pp. 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Mekdad, Y.; Aris, A.; Babun, L.; El Fergougui, A.; Conti, M.; Lazzeretti, R.; Uluagac, A.S. A survey on security and privacy issues of UAVs. Comput. Netw. 2023, 224, 109626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Abd Ghani, M.K.; Arunkumar, N.; Hamed, R.I.; Abdullah, M.K.; Burhanuddin, M. A real time computer aided object detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma using genetic algorithm and artificial neural network based on Haar feature fear. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 89, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Shen, C. A real-time detection approach for bridge cracks based on YOLOv4-FPM. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Huang, S.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Z. Multisensor Dynamic Alliance Control Problem Based on Fuzzy Set Theory in the Mission of Target Detecting and Tracking. J. Sens. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, X.; Zheng, G.; Liu, X. Object detection of UAV for anti-UAV based on improved YOLO v3. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Guangzhou, China, 27–30 July 2019; pp. 8386–8390. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, H.; Zhang, Y. Target detection of low-altitude uav based on improved yolov3 network. J. Robot. 2022, 2022, 4065734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadrass Javan, F.; Samadzadegan, F.; Gholamshahi, M.; Ashatari Mahini, F. A modified YOLOv4 Deep Learning Network for vision-based UAV recognition. Drones 2022, 6, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delleji, T.; Slimeni, F.; Fekih, H.; Jarray, A.; Boughanmi, W.; Kallel, A.; Chtourou, Z. An upgraded-YOLO with object augmentation: Mini-UAV detection under low-visibility conditions by improving deep neural networks. Oper. Res. Forum 2022, 3, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Lyu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q. TPH-YOLOv5: Improved YOLOv5 based on transformer prediction head for object detection on drone-captured scenarios. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2778–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Ju, Z.; Sun, T.; Dong, F.; Li, J.; Yang, R.; Fu, Q.; Lian, C.; Shan, P. Tgc-yolov5: An enhanced yolov5 drone detection model based on transformer, gam & ca attention mechanism. Drones 2023, 7, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Huang, S.; Jin, D.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Guo, Y. LA-YOLO: An effective detection model for multi-UAV under low altitude background. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 055401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, K.; Hou, H.; Liu, C. Real-time detection of drones using channel and layer pruning, based on the yolov3-spp3 deep learning algorithm. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.-C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Yang, J.; Shen, J.; Liang, D.; Ning-Zhong, L.; Zhou, H. TIB-Net: Drone detection network with tiny iterative backbone. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 130697–130707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Hu, L.; Fan, J.; Yan, S.; Li, R. A deep learning-based object detection scheme by improving YOLOv5 for sprouted potatoes datasets. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 85416–85428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.; Song, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Niu, J. Investigation into recognition algorithm of helmet violation based on YOLOv5-CBAM-DCN. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 60622–60632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Meng, L.; Gao, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, X.; Du, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, E. A lightweight UAV swarm detection method integrated attention mechanism. Drones 2022, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Yu, L.; Wen, J.; Han, Y. T-YOLO: A lightweight and efficient detection model for nutrient buds in complex tea-plantation environments. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 5698–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, B.M. VDTNet: A High-Performance Visual Network for Detecting and Tracking of Intruding Drones. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ma, A.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, T. Efficient and lightweight grape and picking point synchronous detection model based on key point detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, Q.; Huang, H.; Han, Z.; Gu, Q. A modified YOLOv8 detection network for UAV aerial image recognition. Drones 2023, 7, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. YOLO by Ultralytics. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/CITATION.cff (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Jocher, G.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; Chaurasia, A.; Changyu, L.; Hogan, A.; Hajek, J.; Diaconu, L.; Kwon, Y.; Defretin, Y. ultralytics/yolov5: v5. 0-YOLOv5-P6 1280 models, AWS, Supervise. ly and YouTube integrations. Zenodo. Zenodo. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1580–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Kim, J. Object detection with location-aware deformable convolution and backward attention filtering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9452–9461. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Yang, M.; Li, H.; Li, T.; Hu, B.; Wang, C. Restricted deformable convolution-based road scene semantic segmentation using surround view cameras. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 4350–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, B.; Duan, G.; Tan, J. Visual defect inspection of metal part surface via deformable convolution and concatenate feature pyramid neural networks. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 9681–9694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, W.; He, Z.; Wang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, P.; Van Gool, L.; Han, J. VisDrone-MOT2021: The vision meets drone multiple object tracking challenge results. Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2839–2846. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Shivanna, R.; Cheng, D.; Jain, S.; Lin, D.; Hong, L.; Chi, E. Dcn v2: Improved deep & cross network and practical lessons for web-scale learning to rank systems. In Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 19–23 April 2021; pp. 1785–1797. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, D. Vision-based anti-uav detection and tracking. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 25323–25334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ramos, A.; Rodriguez-Vazquez, J.; Sampedro, C.; Campoy, P. Adaptive inattentional framework for video object detection with reward-conditional training. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 124451–124466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, D.H.; Chung, T.; Kolsch, M.; Wachs, J.; Bouman, C. Multi-target detection and tracking from a single camera in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 4992–4997. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Wang, K.; Peng, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, Q.; Xing, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, J.; Guo, G.; Han, Z. Anti-UAV: A large multi-modal benchmark for UAV tracking. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.08466. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade r-cnn: Delving into high quality object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Chi, C.; Yao, Y.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9759–9768. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings Part I 14. pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lv, D.; Li, Z.; Lan, Z.; Zhao, S. Air-to-air visual detection of micro-uavs: An experimental evaluation of deep learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Zhu, P.; Wen, L.; Bian, X.; Lin, H.; Hu, Q.; Peng, T.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. VisDrone-DET2019: The vision meets drone object detection in image challenge results. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]



| Parameters | Setup |
|---|---|
| Epochs | 800 |
| entry 2 Batch Size | 4 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| NMS IoU | 0.7 |
| Initial Learning Rate | 1 × 10−2 |
| Final Learning Rate | 1 × 10−4 |
| Momentum | 0.937 |
| Weight-Decay | 5 × 10−4 |
| Image Translation | 0.1 |
| Image Scale | 0.5 |
| Image Flip Left-Right | 0.5 |
| Mosaic | 1.0 |
| Close Mosaic | Last 10 epochs |
| Model | Precision | Recall | mAP50 | mAP95 | GFLOPS | Model Size | FPS (Tasks/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.959 | 0.896 | 0.94 | 0.668 | 8.1 | 5.96 MB | 96.2 |
| A+P | 0.977 | 0.923 | 0.962 | 0.696 | 11.9 | 4.29 MB | 91.7 |
| A+P+G | 0.972 | 0.923 | 0.962 | 0.697 | 10.1 | 3.83 MB | 90.1 |
| A+P+G+D | 0.976 | 0.93 | 0.966 | 0.699 | 7.7 | 4.22 MB | 69.9 |
| A+P+G+E+D | 0.97 | 0.935 | 0.971 | 0.702 | 7.9 | 4.23 MB | 56.2 |
| Model | Backbone | mAP50 | Model Size | FPS(Tasks/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster-RCNN [27] | ResNet50 | 0.653 | - | 12.8 |
| ResNet18 | 0.605 | - | 19.4 | |
| VGG16 | 0.633 | - | 9.3 | |
| Casecade-RCNN [46] | ResNet50 | 0.683 | - | 10.7 |
| ResNet18 | 0.652 | - | 14.7 | |
| VGG16 | 0.667 | - | 8.0 | |
| ATSS [47] | ResNet50 | 0.642 | - | 13.3 |
| ResNet18 | 0.61 | - | 20.5 | |
| VGG16 | 0.641 | - | 9.5 | |
| YOLOX [48] | ResNet50 | 0.427 | - | 21.7 |
| ResNet18 | 0.400 | - | 53.7 | |
| DarkNet | 0.552 | - | 23.0 | |
| SSD [49] | VGG16 | 0.632 | - | 51.3 |
| YOLOv5n [30] | 0.918 | 3.73 MB | 101 | |
| YOLOv8n [29] | 0.94 | 5.96 MB | 96.2 | |
| YOLOv8s [29] | 0.953 | 21.4 MB | 62.5 | |
| YOLOv8m [29] | 0.959 | 197 MB | 39.8 | |
| LA-YOLO [18] | 0.929 | - | - | |
| VDTNet [26] | 0.686 | 3.9 M | 85.5 | |
| EDGS-YOLOv8 (Ours) | 0.971 | 4.23 MB | 56.2 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1 | mAP50 | mAP95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 0.921 | 0.872 | 0.90 | 0.911 | 0.6 |
| Ours | 0.914 | 0.919 | 0.92 | 0.934 | 0.621 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1 | mAP50 | mAP95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 0.415 | 0.31 | 0.34 | 0.292 | 0.166 |
| Ours | 0.421 | 0.332 | 0.36 | 0.313 | 0.176 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Mi, W.; Wang, Y. EDGS-YOLOv8: An Improved YOLOv8 Lightweight UAV Detection Model. Drones 2024, 8, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8070337
Huang M, Mi W, Wang Y. EDGS-YOLOv8: An Improved YOLOv8 Lightweight UAV Detection Model. Drones. 2024; 8(7):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8070337
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Min, Wenkai Mi, and Yuming Wang. 2024. "EDGS-YOLOv8: An Improved YOLOv8 Lightweight UAV Detection Model" Drones 8, no. 7: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8070337
APA StyleHuang, M., Mi, W., & Wang, Y. (2024). EDGS-YOLOv8: An Improved YOLOv8 Lightweight UAV Detection Model. Drones, 8(7), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8070337






