Distributed Offloading for Multi-UAV Swarms in MEC-Assisted 5G Heterogeneous Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We introduce a multi-agent task-offloading model in a heterogeneous network environment (which is different from the existing works that consider single-network scenarios or independent devices). Moreover, the optimization problem is formulated as a Markov decision process (MDP), which is beneficial for solving the sequential offloading decision-making for UAV swarm in dynamic environments.
- To facilitate stable offloading of UAVs in any motion state, we devised a fuzzy logic-based offloading assessment mechanism. The mechanism is executed in a decentralized manner on the UAV with low complexity and can adaptively identify available offloading nodes that are prone to disconnection or have undesirable transmission quality.
- Based on the multi-agent DRL framework, we propose a distributed offloading scheme named DOMUS. DOMUS effectively enables each UAV to learn the joint optimal policy, such as determining the computing mode and selecting the RATs and MEC servers in the offloading case.
- We performed different numerical simulations to verify the rationality and efficiency of the DOMUS scheme. The evaluation results show that the DOMUS proposed is capable of rapidly converging to a stable reward, achieving the optimal offloading performance in energy consumption and delay by comparing with four other benchmarks.
2. Related Work
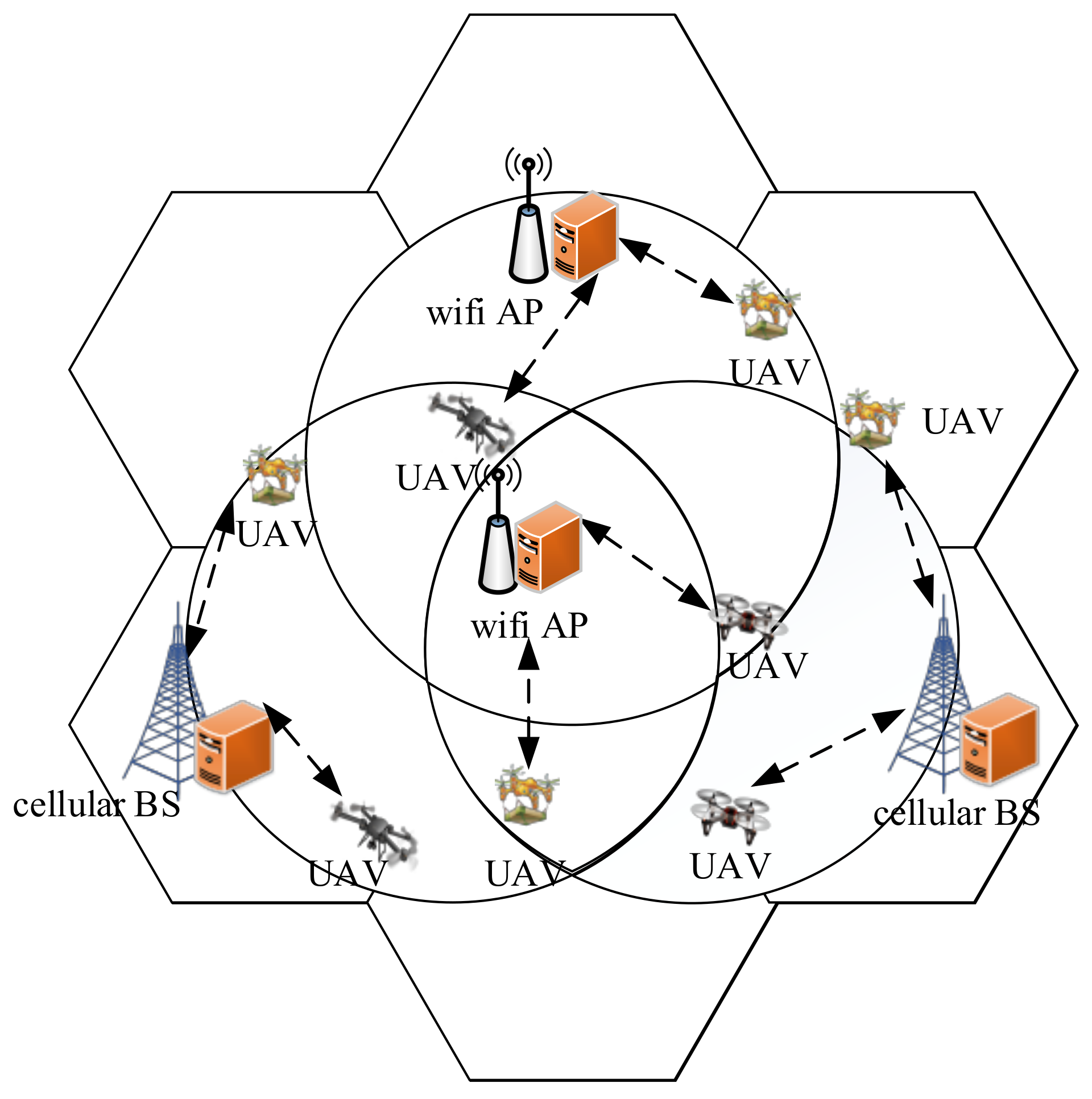
3. System Model and Problem Definition
3.1. System Model
3.2. Task Computing Models
- (1)
- Local computing model
- (2)
- MEC offloading model
3.3. Utility Model in Task Computing
3.4. Optimization Problem Formulation
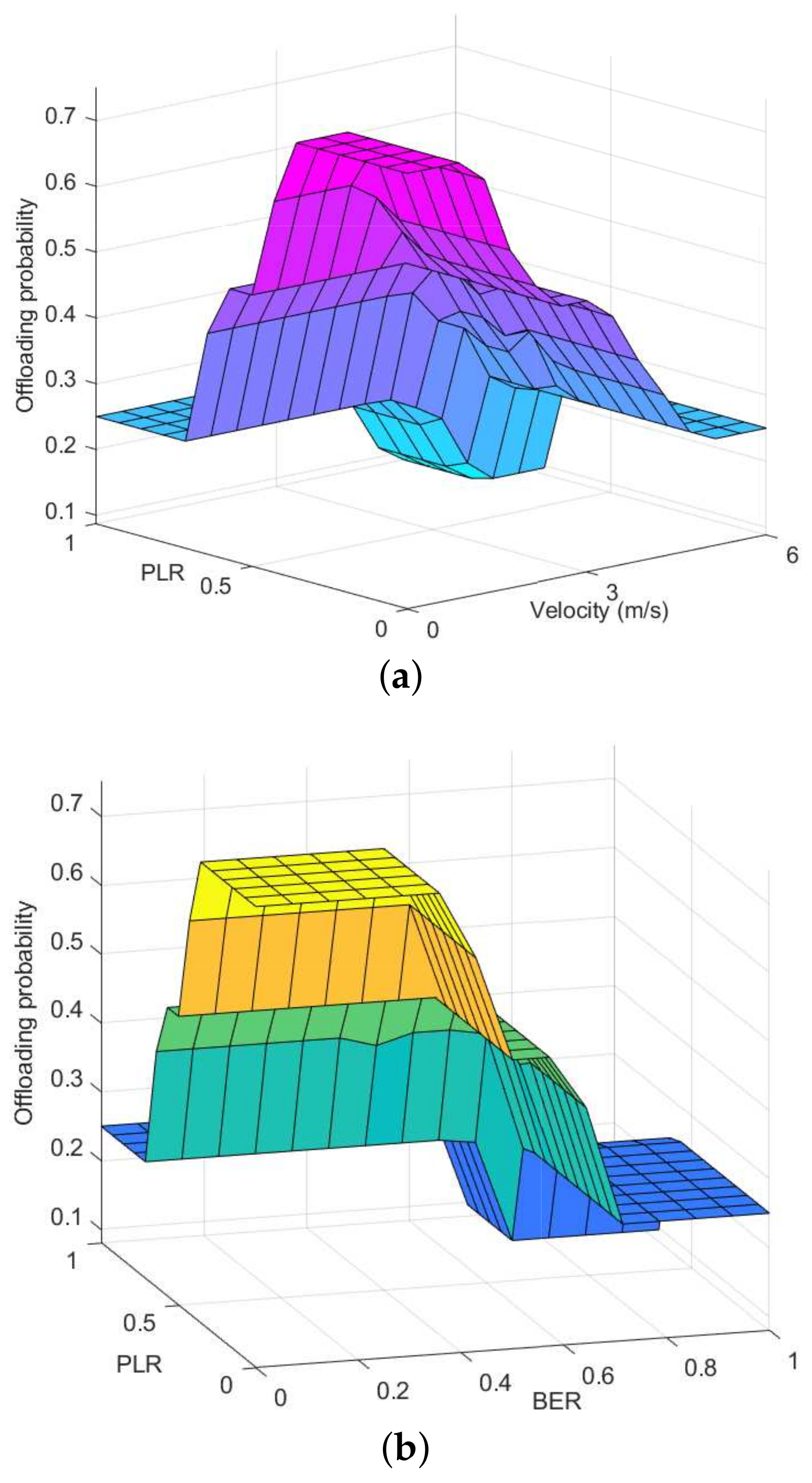
4. Offloading Assessment Based on Fuzzy Logic
| Algorithm 1 Fuzzy logic-based offloading assessment. |
| Input: Set of candidate-offloading nodes . |
| Output: Available offloading node set for the UAV u. |
| 1: while Obtaining sensor data in a time period do |
| 2: for do |
| 3: Velocity, PLR, BER, ⟵ .velocity,.PLR,.BER according to Equations (14) and (15); |
| 4: BER, PLR ⟵ (BER), (PLR); |
| 5: ⟵ Fuzzy Logic (velocity, PLR, BER); |
| 6: if then |
| 7: ⟵m; |
| 8: end if |
| 9: end for |
| 10: end while |
5. Multi-Agent A2C-Based Decentralized Task Offloading
5.1. Multi-Agent MDP Model in the A2C Framework
5.2. Multi-Agent A2C Framework
5.3. A2C-Based Decentralized Offloading Algorithm
| Algorithm 2 A2C-based decentralized offloading algorithm. |
| Input: UAV swarm , MEC server , the learning rates , of the actor and critic network, the maximum episodes , the step size of one episode , the update interval , and the discount factor ; |
| Output: for all UAVs. |
| 1: for UAV do |
| 2: Initialize the parameters and with respect to the actor and critic network; |
| 3: end for |
| 4: for Episode do |
| 5: Reset the state: , , , and ; |
| 6: for UAV do |
| 7: Execute Algorithm 1 to obtain ; |
| 8: Obtain the state ; |
| 9: end for |
| 10: for Step do |
| 11: for UAV do |
| 12: Takes action by actor ; |
| 13: end for |
| 14: Perform computation offloading according to the joint actions ; |
| 15: Obtain the current reward and calculate the new state ; |
| 16: if then |
| 17: Update for the critic networks based on Equation (26); |
| 18: Compute for the actor networks using Equation (27); |
| 19: end if |
| 20: end for |
| 21: end for |
6. Performance Evaluation
6.1. Parameter Settings
6.2. Fitness Demonstration of Offloading Targets
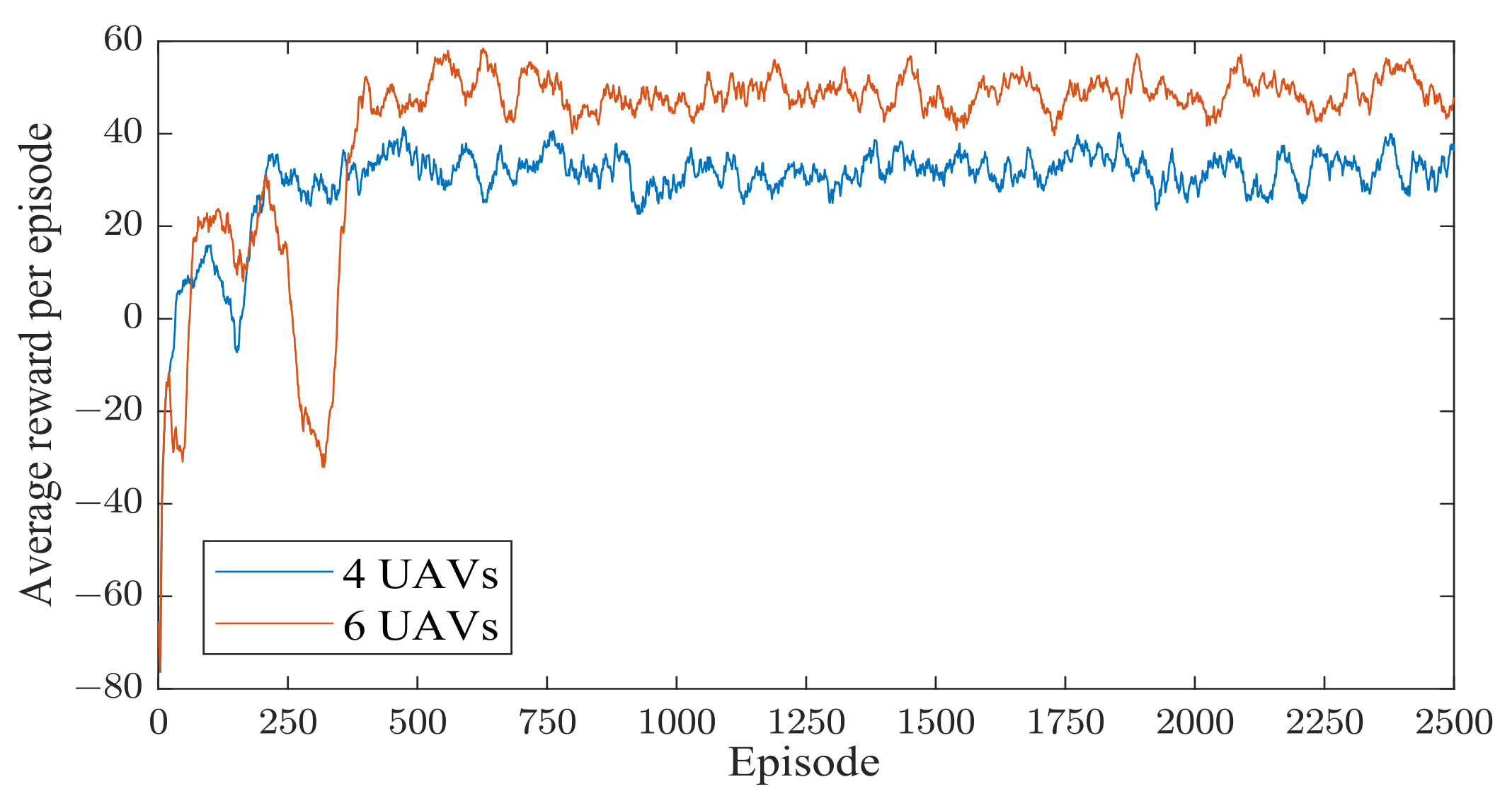
6.3. Convergence Performance
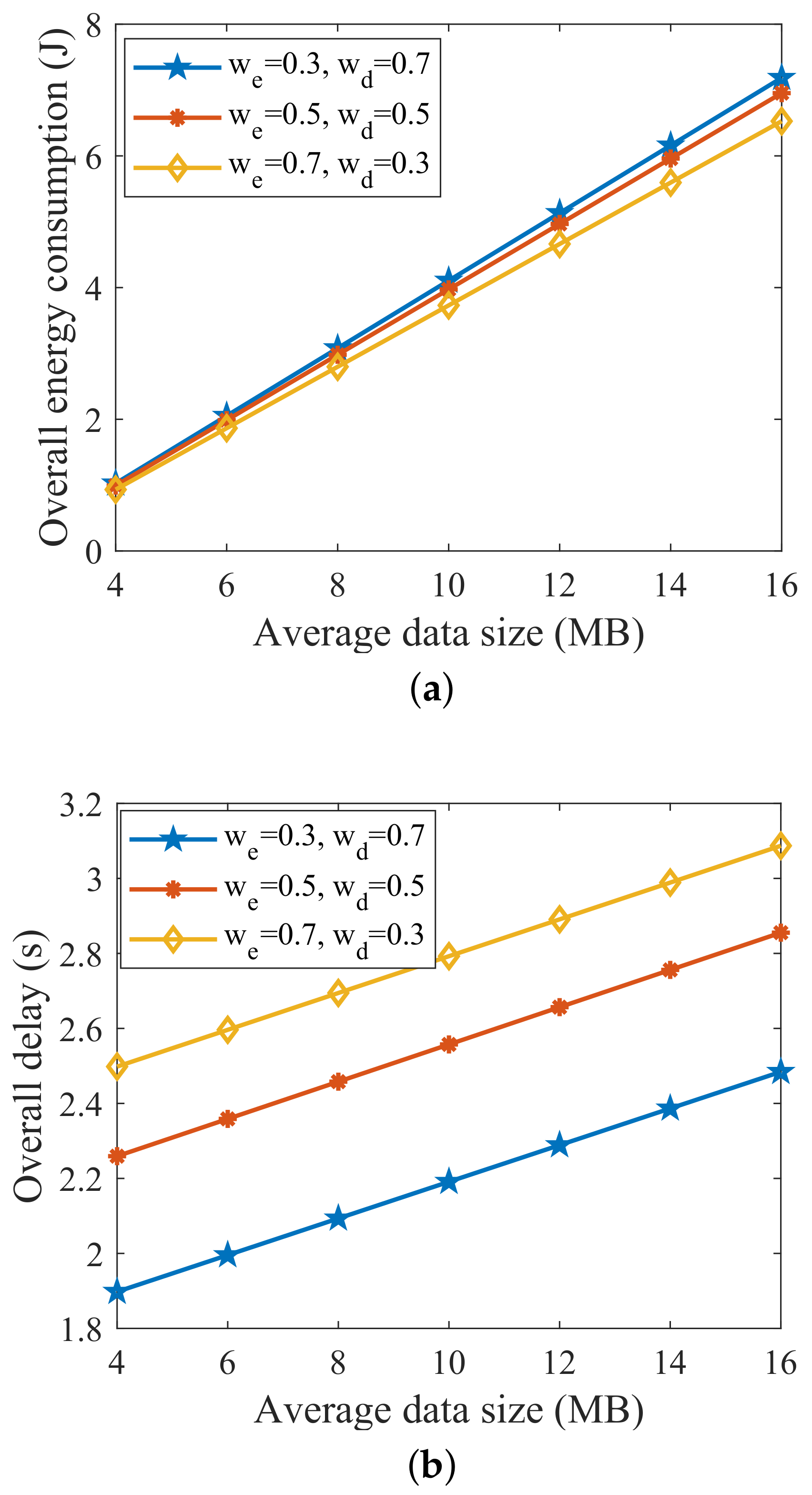
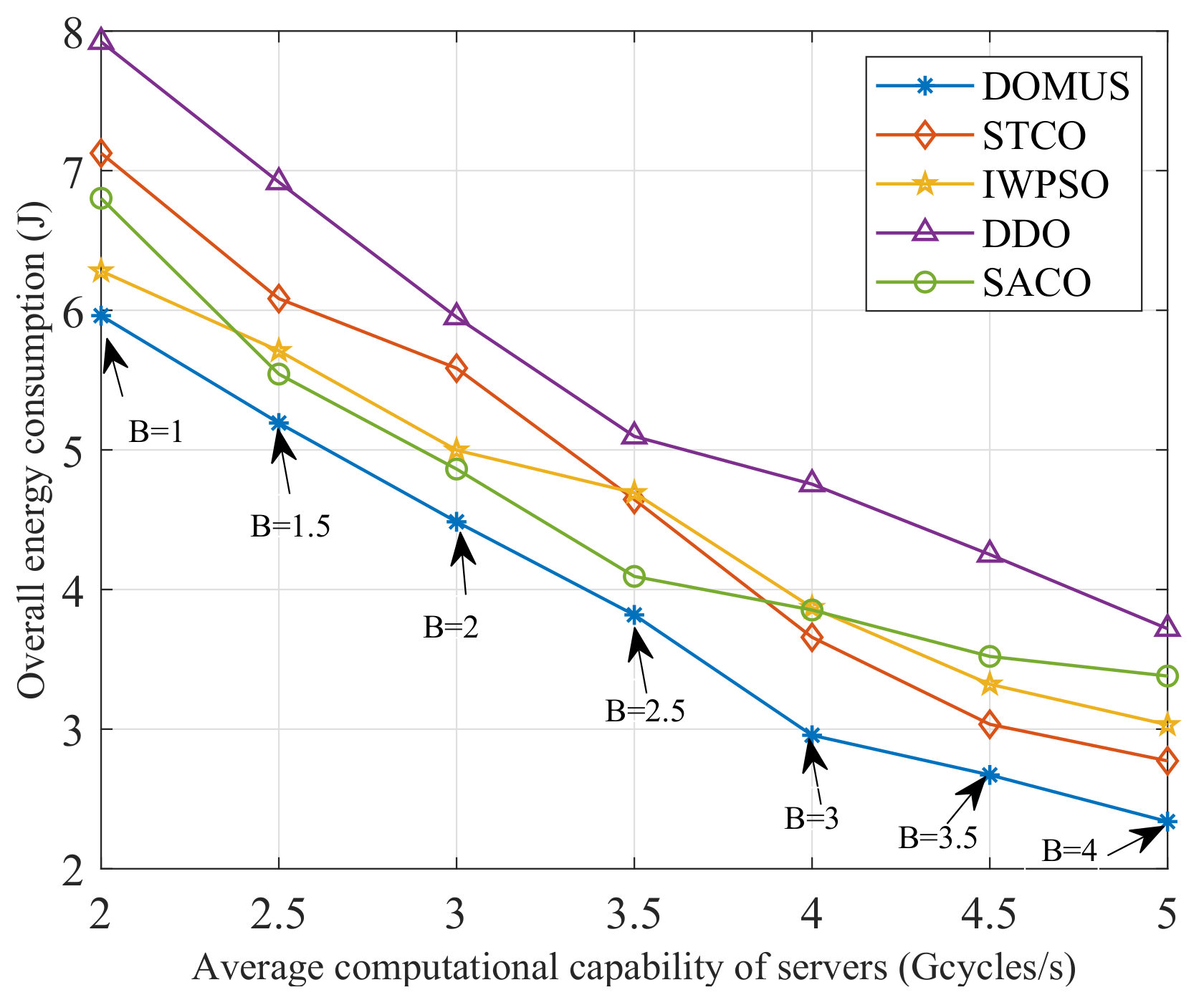
6.4. Impact of Weighting Factors
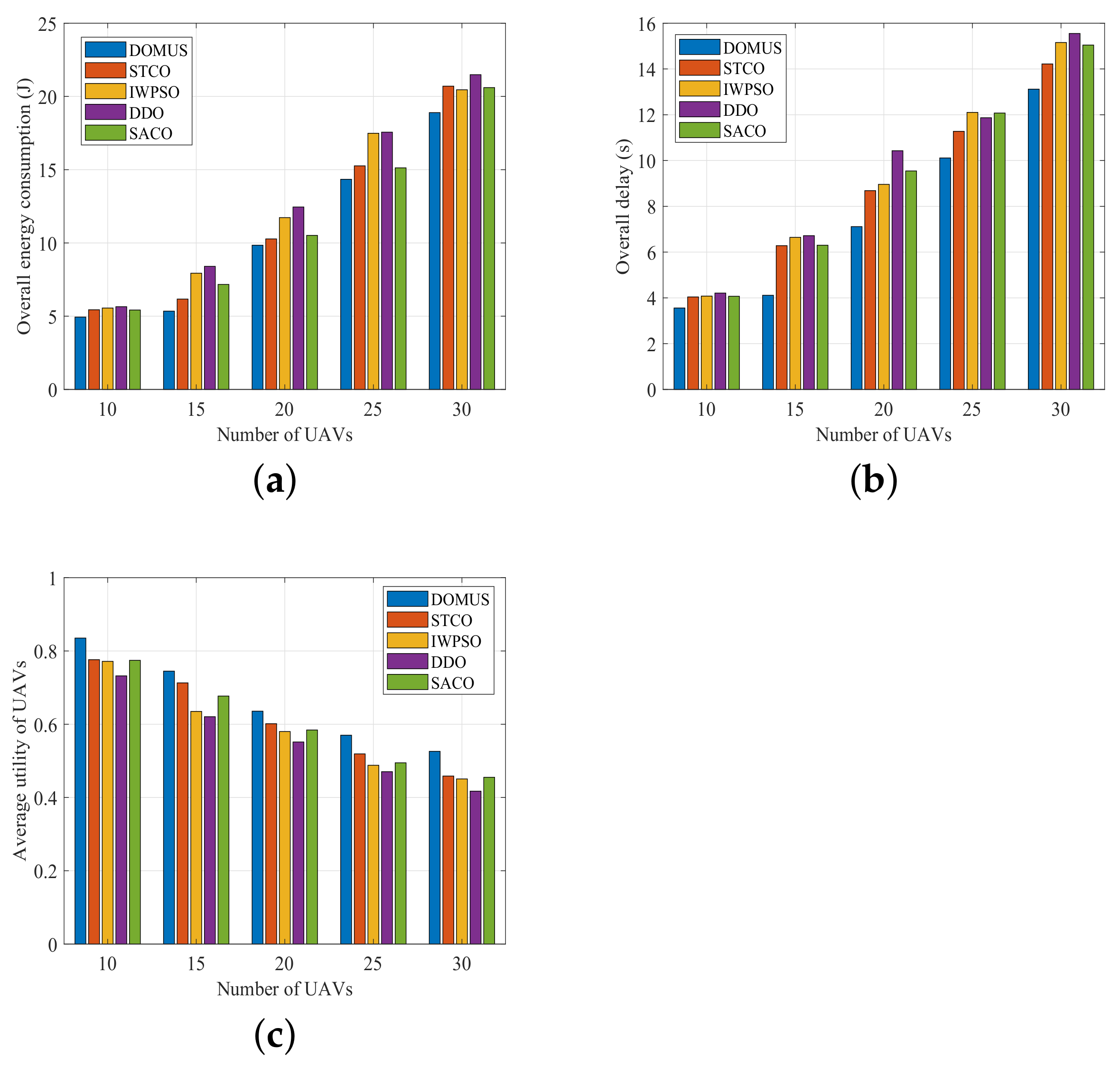
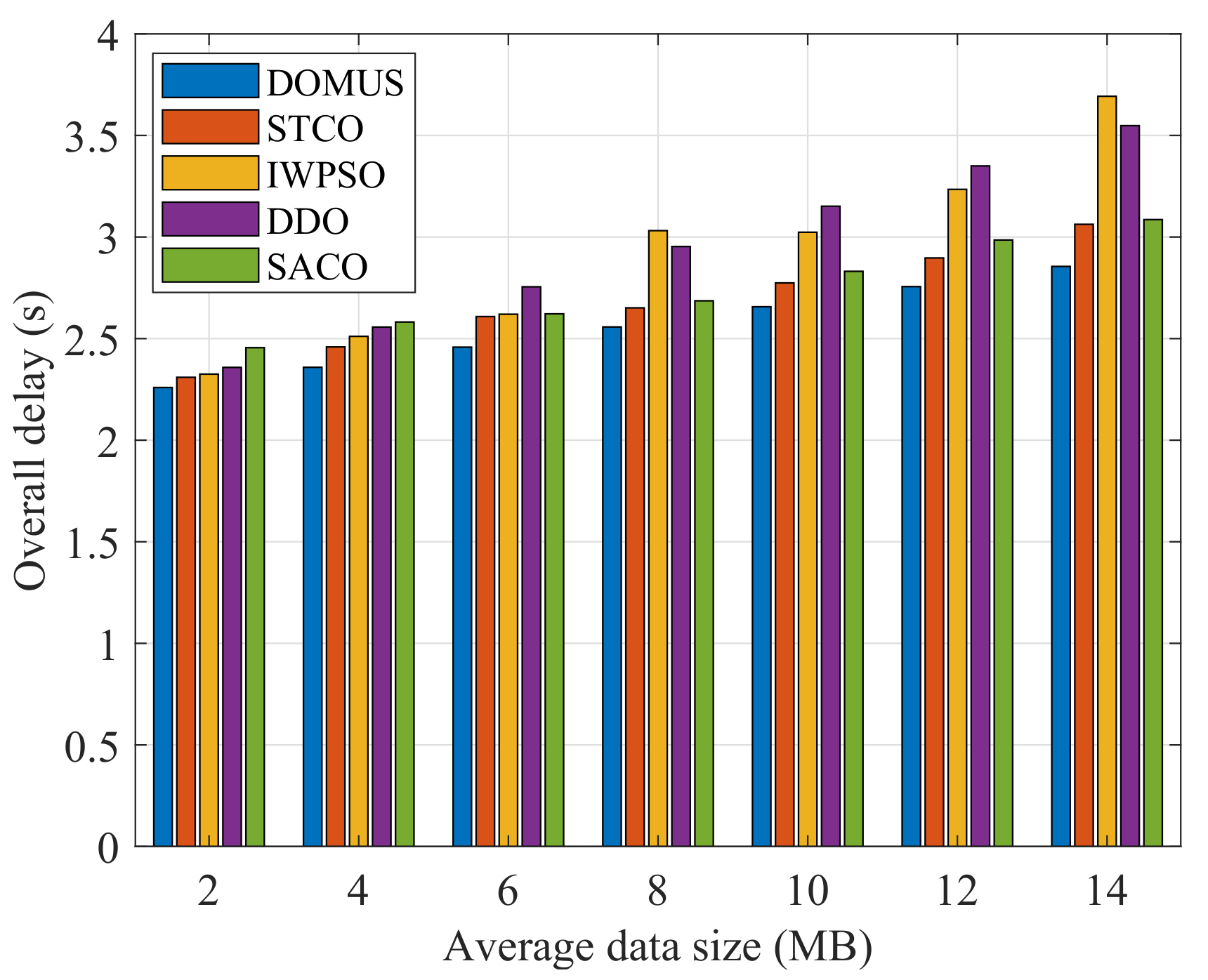
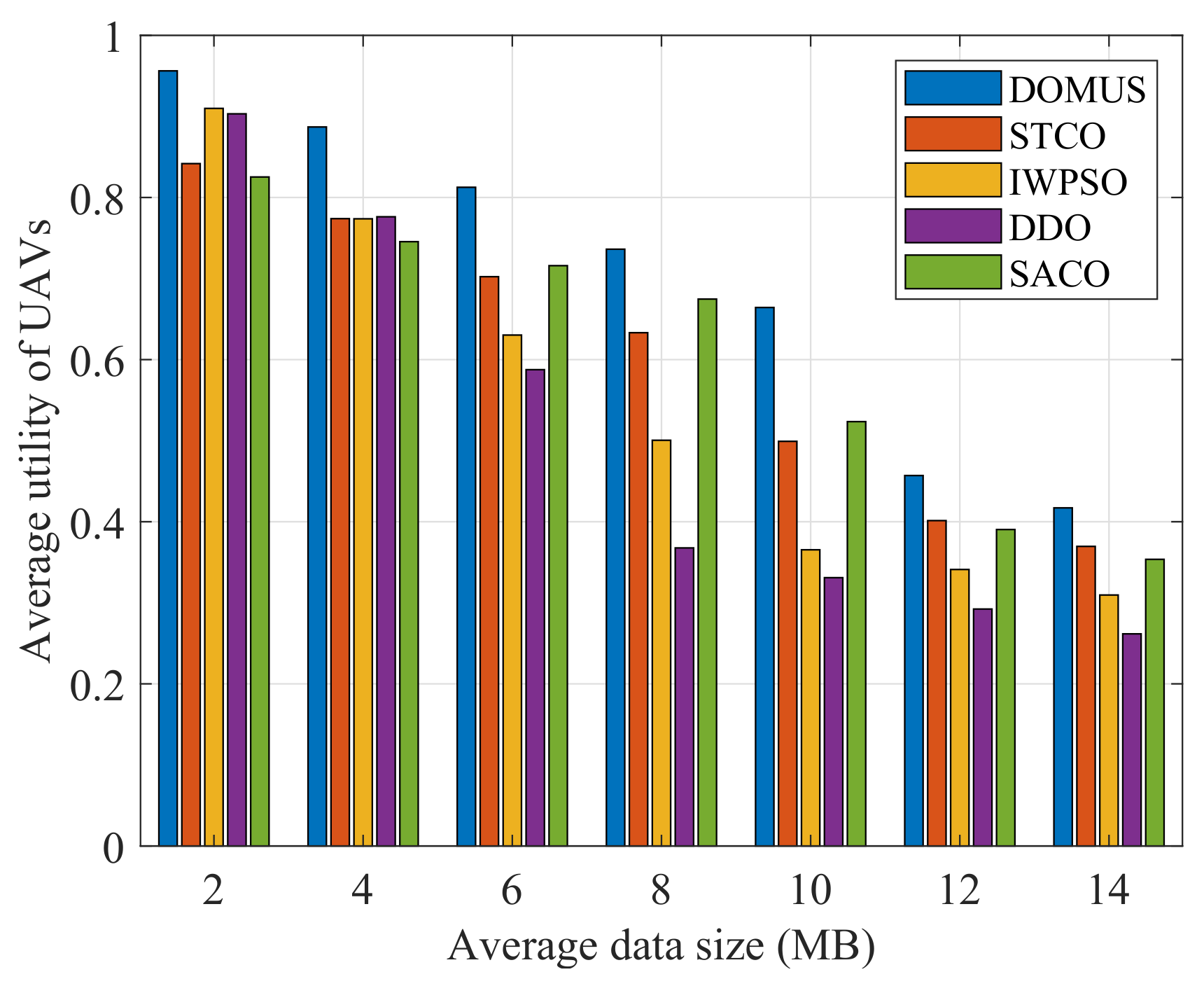
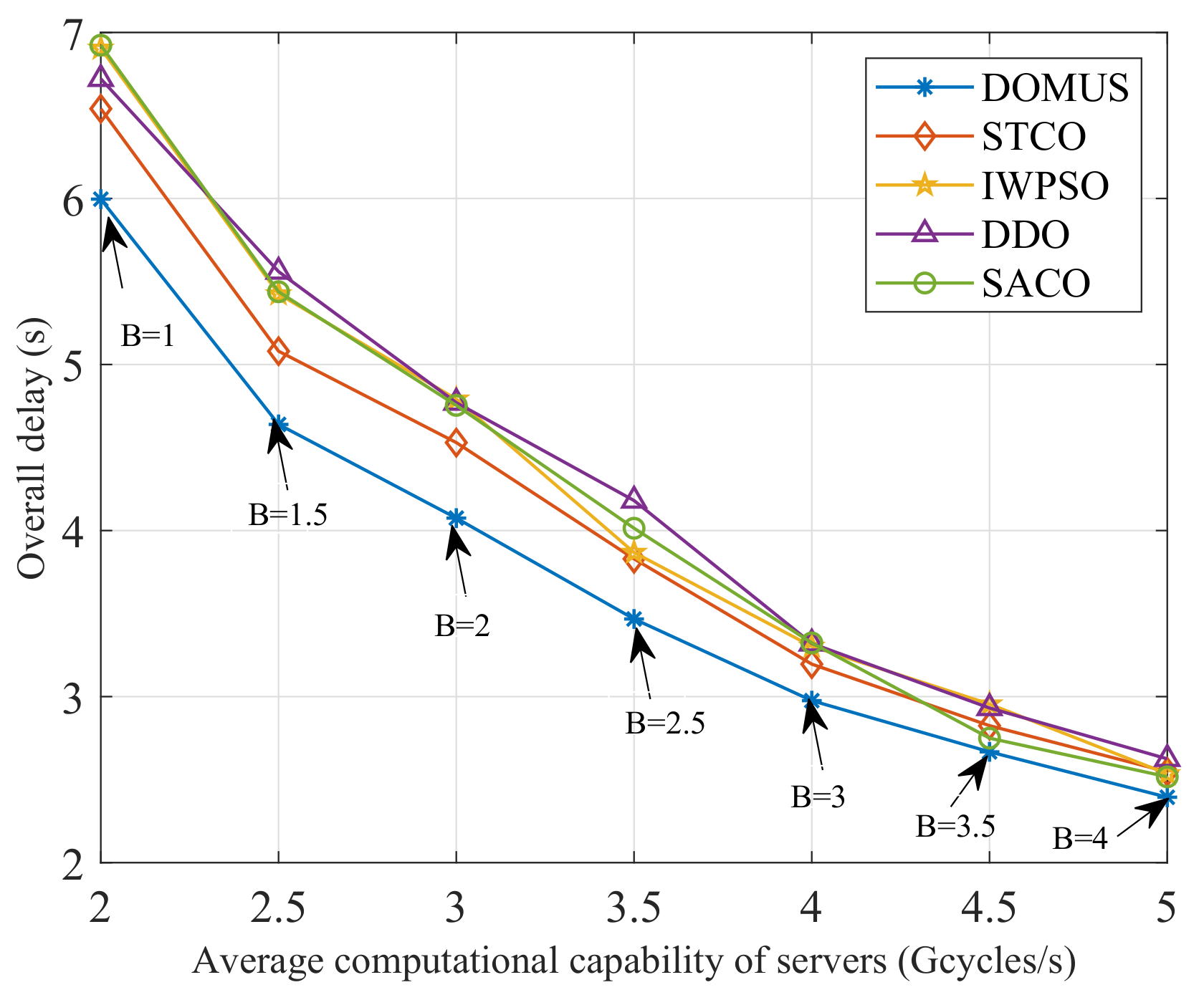
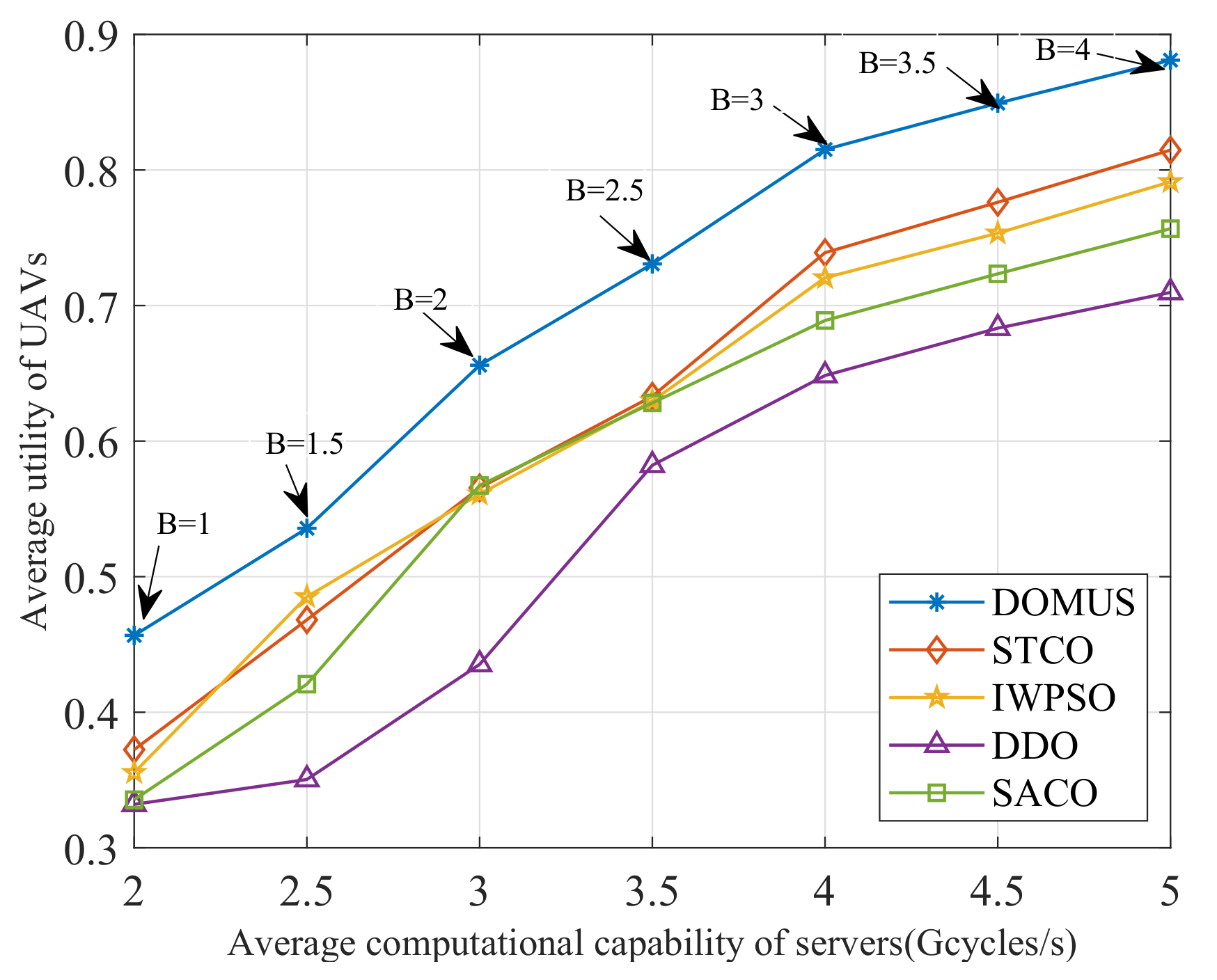
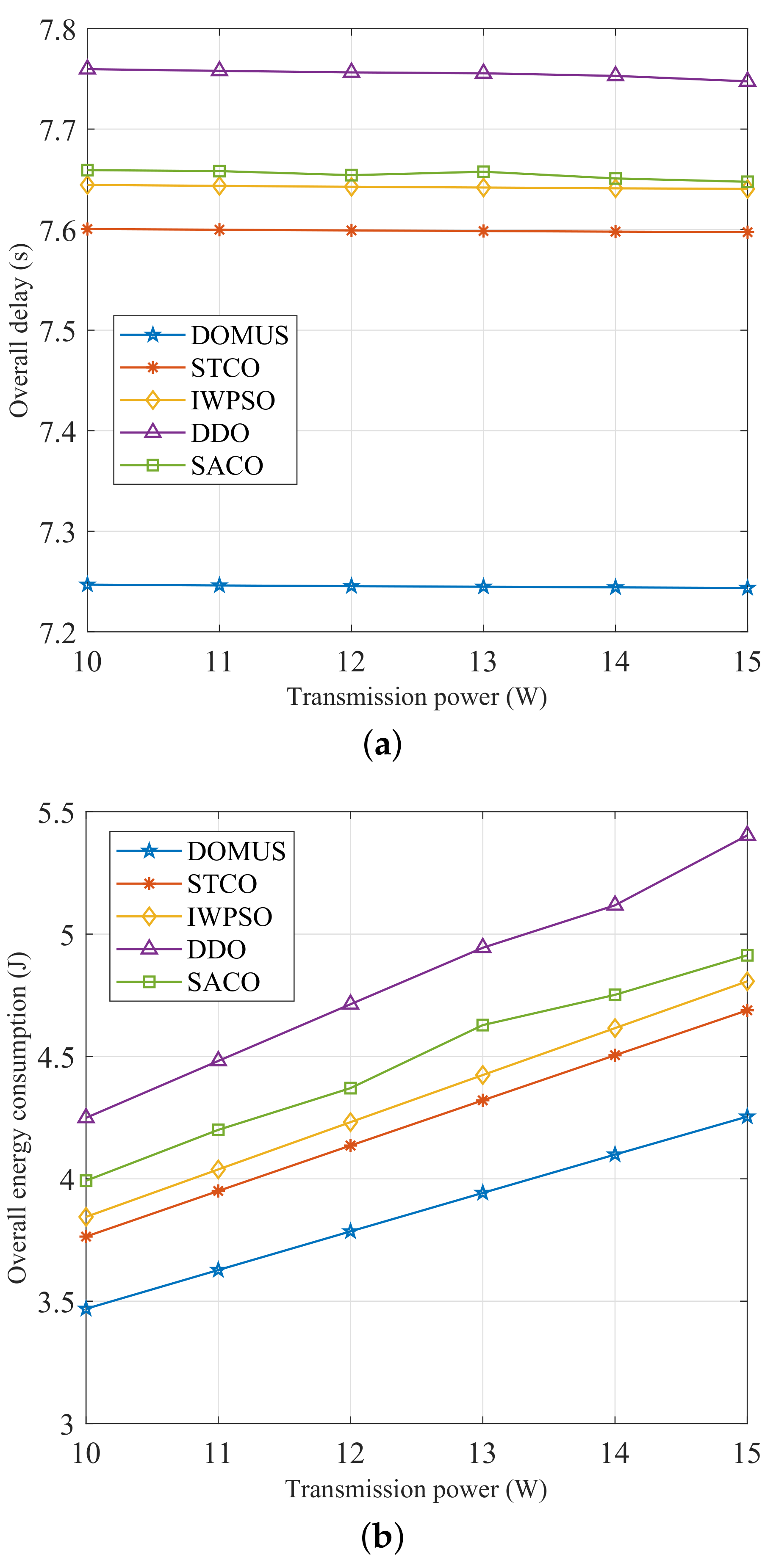
6.5. Performance Comparison
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, M.; Su, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, N. Vehicle Assisted Computing Offloading for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Smart City. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 1932–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Shen, L.; Zhao, S.; Cong, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, D.; Jia, S.; Xiang, X. Mission-Oriented Miniature Fixed-Wing UAV Swarms: A Multilayered and Distributed Architecture. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 1588–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigala, A.; Langhals, B. Applications of Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS): A Delphi Study projecting future UAS missions and relevant challenges. Drones 2020, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Hanly, S.V.; Collings, I.B. Optimal Transmit Power and Flying Location for UAV Covert Wireless Communications. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 3321–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhang, R.; Yang, J.; Chen, L. Development Status and Key Technologies of Plant Protection UAVs in China: A Review. Drones 2022, 6, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazid, Y.; Ez-Zazi, I.; Guerrero-González, A.; El Oualkadi, A.; Arioua, M. UAV-enabled mobile edge-computing for IoT based on AI: A comprehensive review. Drones 2021, 5, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhu, A.; Guo, S.; Yang, Y. Intelligent Network Selection Algorithm for Multiservice Users in 5G Heterogeneous Network System: Nash Q-Learning Method. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 11877–11890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, K.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Leung, V.C.M. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Energy-Efficient Computation Offloading in Mobile-Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 1517–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchali, S.; Sharma, A.; Harrison, J.; Elhafsi, A.; Kang, D.; Pergament, E.; Cidon, E.; Katti, S.; Pavone, M. Network offloading policies for cloud robotics: A learning-based approach. Auton. Robot. 2021, 45, 997–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Ma, M.; Guo, S.; Yu, S.; Yi, L. Adaptive Multi-Access Algorithm for Multi-Service Edge Users in 5G Ultra-Dense Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 2807–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, Y. Mobile Data Offloading Efficiency: A Stochastic Analytical View. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Kansas City, MO, USA, 20–24 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, S.; Jiao, J.; Lin, X.H.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Q. Energy-Efficient Task Offloading of Edge-Aided Maritime UAV Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Liang, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L. Hagp: A heuristic algorithm based on greedy policy for task offloading with reliability of mds in mec of the industrial internet. Sensors 2021, 21, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T.; Gong, C. New Method of Task Offloading in Mobile Edge Computing for Vehicles Based on Simulated Annealing Mechanism. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2022, 44, 3220–3230. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X. Distributed Offloading in Overlapping Areas of Mobile-Edge Computing for Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 13837–13847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Yao, Z.; Li, Y.; Mao, S. Online Distributed Offloading and Computing Resource Management With Energy Harvesting for Heterogeneous MEC-Enabled IoT. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 6743–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, N.; Zeng, D.; Fan, P. Stackelberg-Game-Based Computation Offloading Method in Cloud-Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 16510–16520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Shen, B. An Evolutionary Game Based Computation Offloading for an UAV Network in MEC. In Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference, WASA 2022, Dalian, China, 24–26 November 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 586–597. [Google Scholar]
- You, Q.; Tang, B. Efficient task offloading using particle swarm optimization algorithm in edge computing for industrial internet of things. J. Cloud Comput. 2021, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; He, S.; Liu, M.; Li, N.; Fang, C. Intelligent Computation Offloading Mechanism of UAV in Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Frontiers of Electronics, Information and Computation Technologies (ICFEICT), Wuhan, China, 19–21 August 2022; pp. 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Asaamoning, G.; Mendes, P.; Rosário, D.; Cerqueira, E. Drone swarms as networked control systems by integration of networking and computing. Sensors 2021, 21, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliatsios, D.; Goudos, S.K.; Lagkas, T.; Argyriou, V.; Boulogeorgos, A.A.A.; Sarigiannidis, P. Drone-base-station for next-generation internet-of-things: A comparison of swarm intelligence approaches. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2021, 3, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amponis, G.; Lagkas, T.; Zevgara, M.; Katsikas, G.; Xirofotos, T.; Moscholios, I.; Sarigiannidis, P. Drones in B5G/6G networks as flying base stations. Drones 2022, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, T.; Zhang, S.; Liu, A. Deep reinforcement learning for computation offloading in mobile edge computing environment. Comput. Commun. 2021, 175, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cao, L.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, T.; Du, J.; Jiang, K. Task offloading method of edge computing in internet of vehicles based on deep reinforcement learning. Clust. Comput. 2022, 25, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, D.; Gu, W.; Chen, Y. Uav-assisted task offloading for iot in smart buildings and environment via deep reinforcement learning. Build. Environ. 2022, 222, 109218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vhora, F.; Gandhi, J.; Gandhi, A. Q-TOMEC: Q-Learning-Based Task Offloading in Mobile Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the Futuristic Trends in Networks and Computing Technologies: Select Proceedings of Fourth International Conference on FTNCT 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Li, T.; Tian, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Geng, L.; Sun, J. Speed-aware and customized task offloading and resource allocation in mobile edge computing. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2683–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, P.; Du, C.; Li, Y. Energy-Efficient Edge Caching and Task Deployment Algorithm Enabled by Deep Q-Learning for MEC. Electronics 2022, 11, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naouri, A.; Wu, H.; Nouri, N.A.; Dhelim, S.; Ning, H. A novel framework for mobile-edge computing by optimizing task offloading. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13065–13076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, A.; Chakarbarty, C. Task offloading in fog computing for using smart ant colony optimization. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 127, 1683–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, J. Collaborative computation offloading for multiaccess edge computing over fiber–wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 4514–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekaslan, D.; Wagner, C.; Garibaldi, J.M. ADONiS-Adaptive Online Nonsingleton Fuzzy Logic Systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 2302–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Jiang, X.; Luo, Q.; Guo, B.; Sun, X.; Sun, F.; Meng, L. AQROM: A quality of service aware routing optimization mechanism based on asynchronous advantage actor-critic in software-defined networks. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiadou, G.E.; Fytampanis, P.; Zarbouti, D.A.; Tsoulos, G.V.; Gkonis, P.K.; Kaklamani, D.I. Radio network planning towards 5G mmWave standalone small-cell architectures. Electronics 2020, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garroppo, R.G.; Volpi, M.; Nencioni, G.; Wadatkar, P.V. Experimental Evaluation of Handover Strategies in 5G-MEC Scenario by using AdvantEDGE. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Mediterranean Conference on Communications and Networking (MeditCom), Athens, Greece, 5–8 September 2022; pp. 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, H.N.; Wang, Q.; Imran, M.; Guizani, N. Wireless powering Internet of Things with UAVs: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE Netw. 2022, 36, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Liu, H.; Yao, Y.; Cao, D.; Zhao, M. Latency-aware offloading for mobile edge computing networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2673–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, T.; Chen, X.; He, S.; Guo, D.; Wu, J. Reverse auction-based computation offloading and resource allocation in mobile cloud-edge computing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y. Altitude Optimization and Task Allocation of UAV-Assisted MEC Communication System. Sensors 2022, 22, 8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Gui, X.; Ren, D.; Li, D. Energy-Latency Tradeoff for Computation Offloading in UAV-Assisted Multiaccess Edge Computing System. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 6709–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Sun, Z.; Li, D.; Luo, J.; Wan, S. User-centric computation offloading for edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 12559–12568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Symbols | Definition |
|---|---|
| Set of UAVs | |
| Set of servers | |
| Task of UAV | |
| Data size of | |
| Computation resources required by task | |
| , | Offloading decisions |
| Computational capability of UAV | |
| Computational capability of server | |
| Execution time in local computing | |
| Energy consumption in local computing | |
| Energy consumption coefficient per CPU cycle | |
| , | Transmission rate via cellular and Wi-Fi networks, respectively |
| , | Allocated bandwidth to the UAV u from cellular and Wi-Fi networks, respectively |
| , | Transmission power of the UAV u via cellular and Wi-Fi connectivities, respectively |
| , | Channel gain over cellular and Wi-Fi networks, respectively |
| , | Noise power of the channel over cellular and Wi-Fi networks, respectively |
| Distance between the UAV u and the server m | |
| Task transmission time in the MEC offloading | |
| Task execution time on the server | |
| Transmission energy consumption in the MEC offloading | |
| Total time in the MEC offloading | |
| Maximum energy constraint of the UAV u | |
| , , | Tolerable upper bound values for delay, BER, and PLR, respectively |
| , | Balance factors for delay and energy consumption, respectively |
| Computation capacity of the server m | |
| Utility of the UAV u | |
| Fuzzy logic processor | |
| Packet loss rate generated in the data transmission | |
| Bit error rate generated in the data transmission | |
| Offloading probability |
| Symbol | Value | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (MHz) | 4 | (MHz) | 5 |
| (dBm) | (W) | 10 | |
| (Gcycles/s) | (Gcycles/s) | ||
| (Gcycles) | ≥1 | ||
| (MB) | (Gcycles) | ||
| (J/cycles) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, M.; Wang, Z. Distributed Offloading for Multi-UAV Swarms in MEC-Assisted 5G Heterogeneous Networks. Drones 2023, 7, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7040226
Ma M, Wang Z. Distributed Offloading for Multi-UAV Swarms in MEC-Assisted 5G Heterogeneous Networks. Drones. 2023; 7(4):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7040226
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Mingfang, and Zhengming Wang. 2023. "Distributed Offloading for Multi-UAV Swarms in MEC-Assisted 5G Heterogeneous Networks" Drones 7, no. 4: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7040226
APA StyleMa, M., & Wang, Z. (2023). Distributed Offloading for Multi-UAV Swarms in MEC-Assisted 5G Heterogeneous Networks. Drones, 7(4), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7040226






