Offline Imagery Checks for Remote Drone Usage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
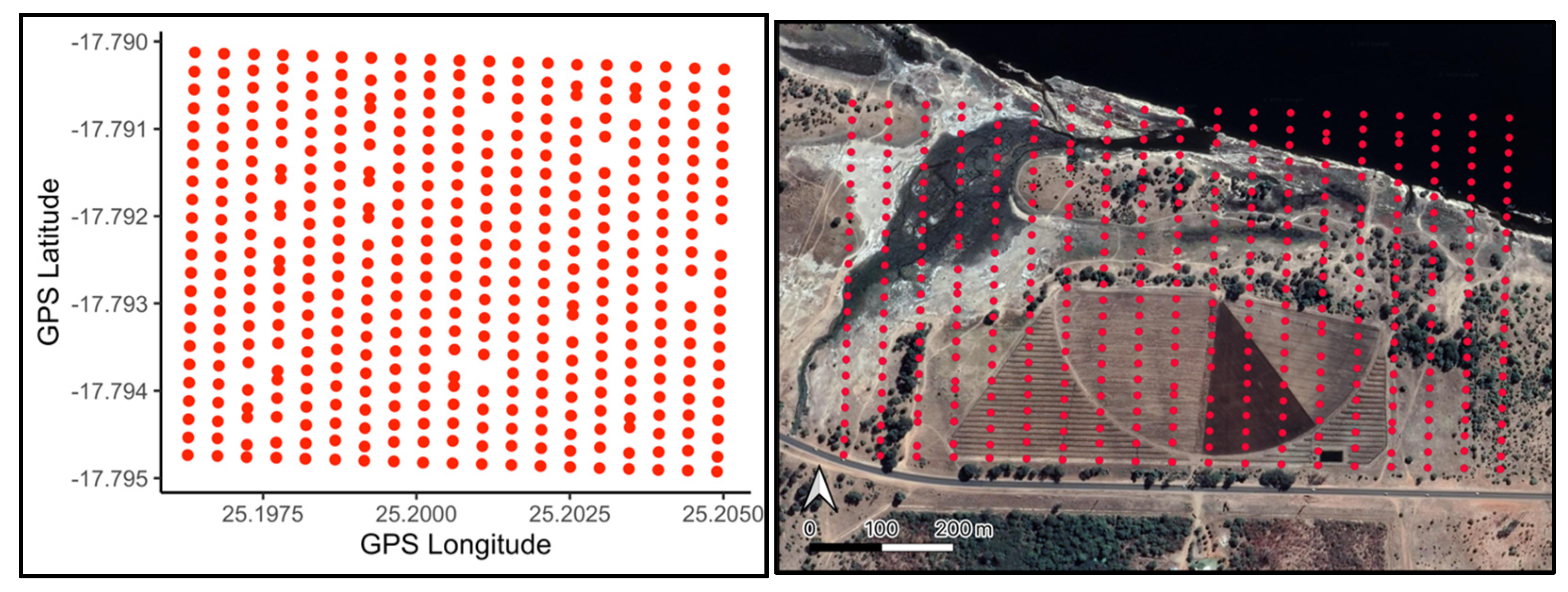
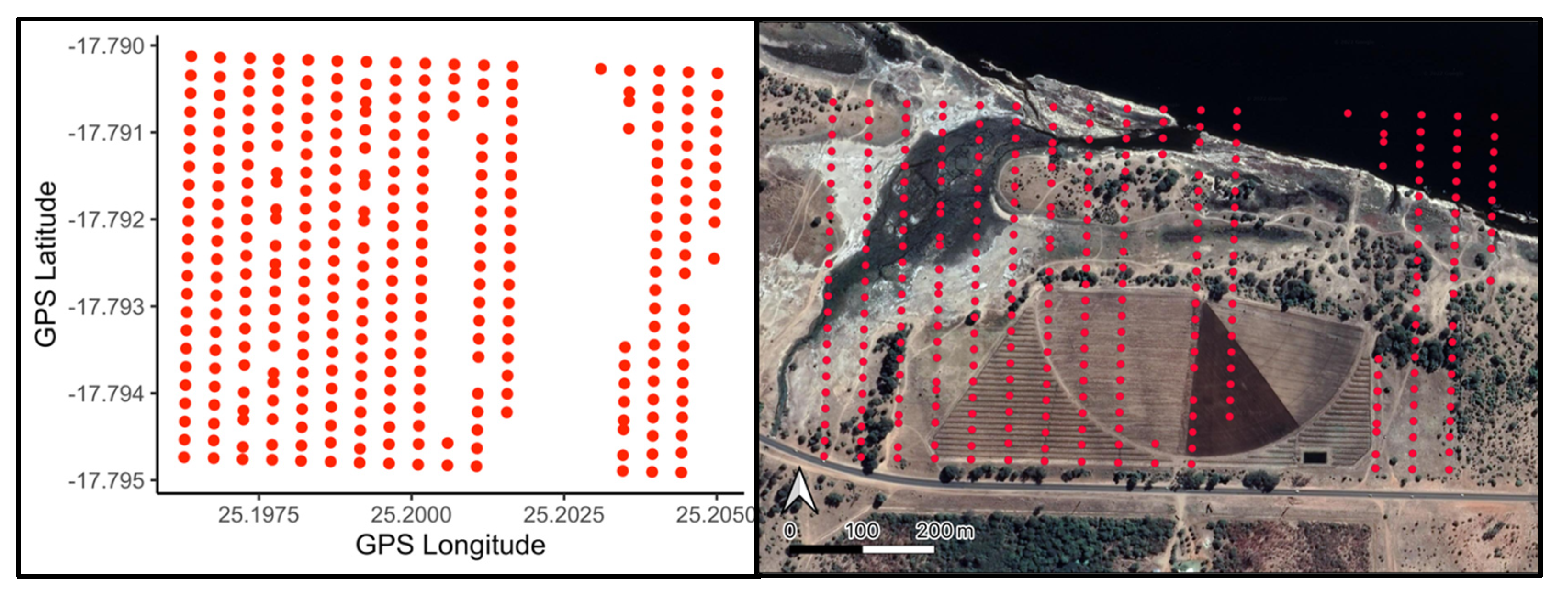
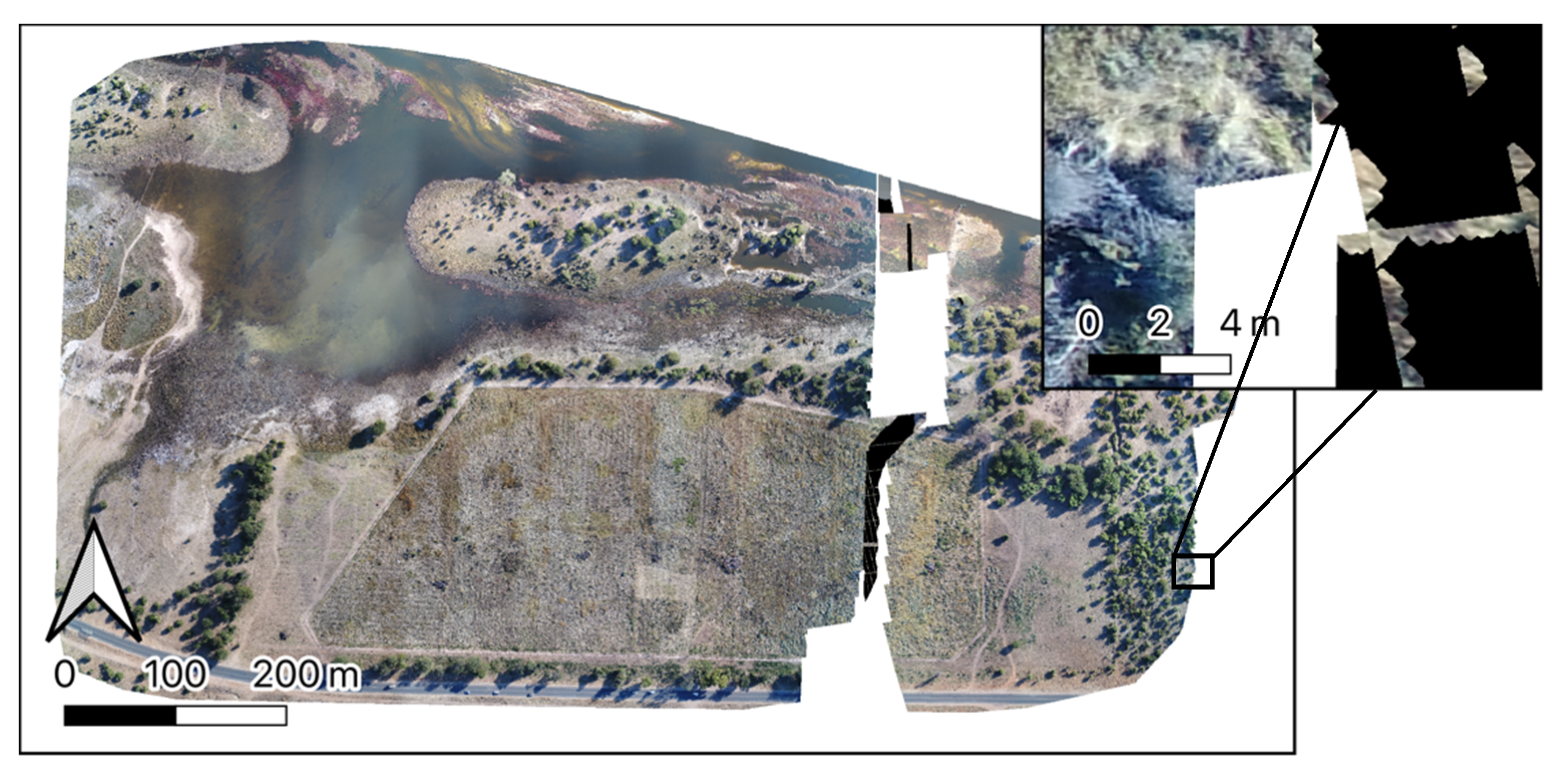
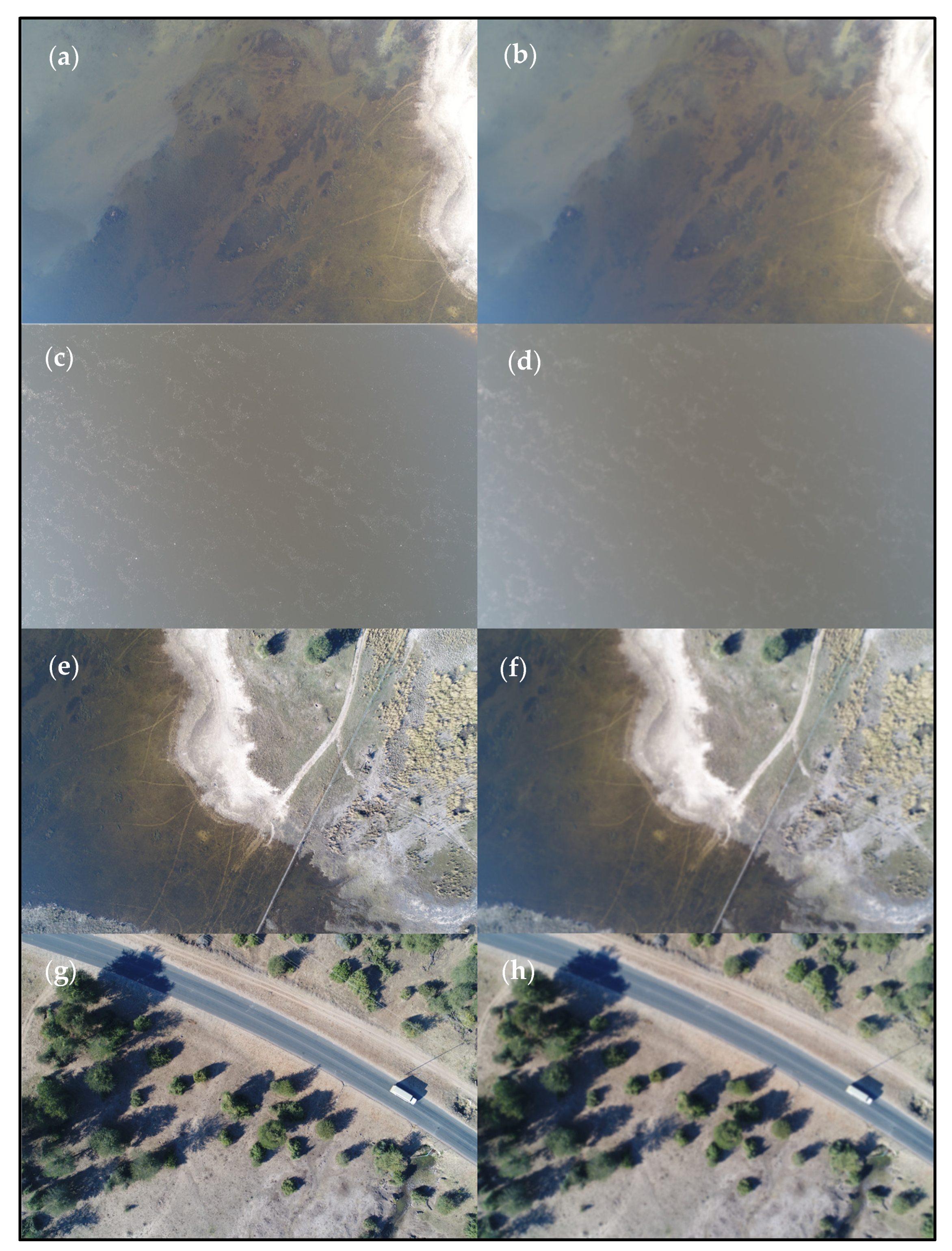
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rocke, B.; Ruffell, A.; Donnelly, L. Drone aerial imagery for the simulation of a neonate burial based on the geoforensic search strategy (GSS). J. Forensic Sci. 2021, 66, 1506–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugler, L. Real-world applications for drones. Commun. ACM 2019, 62, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Sepasgozar, S.M.; Wang, C. A systematic review of smart real estate technology: Drivers of, and barriers to, the use of digital disruptive technologies and online platforms. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, D.; Nehmer, R.A. Using drones in internal and external audits: An exploratory framework. J. Emerg. Technol. Account. 2017, 14, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Cour-Harbo, A. Mass threshold for ‘harmless’ drones. Int. J. Micro Air Veh. 2017, 9, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsan, M.; Somantri, L.; Sugito, N.; Himayah, S.; Affriani, A. The Comparison of Stage and Result Processing of Photogrammetric Data Based on Online Cloud Processing. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hinge, L.; Gundorph, J.; Ujang, U.; Azri, S.; Anton, F.; Rahman, A.A. Comparative analysis of 3D photogrammetry modeling software packages for drones survey. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. Digital inequalities in rural Australia: A double jeopardy of remoteness and social exclusion. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 54, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleye, N.; Eboagu, C. Evaluation of ICT development and economic growth in Africa. Netnomics Econ. Res. Electron. Netw. 2019, 20, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bánhidi, Z. The impact of broadband networks on growth and development in South America. Period. Polytech. Soc. Manag. Sci. 2021, 29, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.B.; Brandis, K.J.; Murray, N.J.; Wilshire, J.H.; McCann, J.A.; Kingsford, R.T.; Callaghan, C.T. Monitoring large and complex wildlife aggregations with drones. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujičić, M.D.; Kennell, J.; Stankov, U.; Gretzel, U.; Vasiljević, Đ.A.; Morrison, A.M. Keeping up with the drones! Techno-social dimensions of tourist drone videography. Technol. Soc. 2022, 68, 101838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez López, J.; Mulero-Pázmány, M. Drones for conservation in protected areas: Present and future. Drones 2019, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemerly, E.M. Automatic georeferencing of images acquired by UAV’s. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2014, 11, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancin-Murguzur, F.J.; Munoz, L.; Monz, C.; Hausner, V.H. Drones as a tool to monitor human impacts and vegetation changes in parks and protected areas. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 6, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, I.-K.; Unger, D.; Kulhavy, D.; Zhang, Y. Positional precision analysis of orthomosaics derived from drone captured aerial imagery. Drones 2019, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PIX4D. Troubleshooting—PIX4Dcapture. Troubleshooting 2021. Available online: https://support.pix4d.com/hc/en-us/articles/115004119343-Troubleshooting-PIX4Dcapture (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Drone Deploy, Drone Deploy. California, United States. 2022.
- PIX4D SA PIX4Dcapture. 2019. Available online: https://www.pix4d.com/product/pix4dcapture (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Vacca, G. WEB Open Drone Map (WebODM) a Software Open Source to Photogrammetry Process. In Proceedings of the Fig Working Week 2020—Smart Surveyors for Land and Water Management, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 10–14 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schofield, G.; Katselidis, K.A.; Lilley, M.K.; Reina, R.D.; Hays, G.C. Detecting elusive aspects of wildlife ecology using drones: New insights on the mating dynamics and operational sex ratios of sea turtles. Funct. Ecol. 2017, 31, 2310–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, G.P.; Clarke, L.E.; Stone, M.; Wood, M.J. Can drones count gulls? Minimal disturbance and semiautomated image processing with an unmanned aerial vehicle for colony-nesting seabirds. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 12322–12334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R.; Kingsford, R.; Brandis, K. Using drones and citizen science counts to track colonial waterbird breeding, an indicator for ecosystem health on the Chobe River, Botswana. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 38, e02231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.J.; Jones, T.H.; Pang, K.; Saimin, S.; Goossens, B. Spatial ecology of estuarine crocodile (Crocodylus porosus) nesting in a fragmented landscape. Sensors 2016, 16, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. Foundation for Statistical Computing. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; 4.1.0; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dunnington, D.H.; Harvey, P. exifr: EXIF Image Data in R; R Package Version 0.3.2; 2021; Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/exifr/exifr.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Ooms, J. magick: Advanced Graphics and Image-Processing in R; R Package Version 2.7.3; 2021; Available online: https://ropensci.org/blog/2017/08/15/magick-10/ (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- PIX4D SA PIX4Dmapper. 2022. Available online: https://www.pix4d.com/product/pix4dmapper-photogrammetry-software (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Junda, J.; Greene, E.; Bird, D.M. Proper flight technique for using a small rotary-winged drone aircraft to safely, quickly, and accurately survey raptor nests. J. Unmanned Veh. Syst. 2015, 3, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, R.J.; Yadav, K. Drone Routing Techniques for Surveying in Urban Areas. Rev. Int. Geogr. Educ. Online 2021, 11, 4157–4167. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, M.; Brandis, K.; Wilshire, J.; Murray, N.; McCann, J.; Kingsford, R.; Callaghan, C. A protocol for using drones to assist monitoring of large breeding bird colonies. EcovoRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Jiménez, S.I.; Ojeda-Bustamante, W.; Marcial-Pablo, M.d.J.; Enciso, J. Digital terrain models generated with low-cost UAV photogrammetry: Methodology and accuracy. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieberth, T.; Wackrow, R.; Chandler, J. Motion blur disturbs—The influence of motion-blurred images in photogrammetry. Photogramm. Rec. 2014, 29, 434–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Miklavcic, S.J. An automatic field plot extraction method from aerial orthomosaic images. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinzmann, T.; Schönberger, J.L.; Pollefeys, M.; Siegwart, R. Mapping on the fly: Real-time 3D dense reconstruction, digital surface map and incremental orthomosaic generation for unmanned aerial vehicles. In Field and Service Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, R.J.; Lyons, M.B.; Kingsford, R.T.; Brandis, K.J. Counting mixed breeding aggregations of animal species using drones: Lessons from waterbirds on semi-automation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, D.; Francis, C.M. Computer-automated bird detection and counts in high-resolution aerial images: A review. J. Field Ornithol. 2016, 87, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Lachs, L.; Pygas, D.R.; Humanes, A.; Sommer, B.; Figueira, W.F.; Edwards, A.J.; Bythell, J.C.; Guest, J.R. Photogrammetry as a tool to improve ecosystem restoration. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2021, 36, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francis, R.J.; Brandis, K.J.; McCann, J.A. Offline Imagery Checks for Remote Drone Usage. Drones 2022, 6, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones6120395
Francis RJ, Brandis KJ, McCann JA. Offline Imagery Checks for Remote Drone Usage. Drones. 2022; 6(12):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones6120395
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancis, Roxane J., Kate J. Brandis, and Justin A. McCann. 2022. "Offline Imagery Checks for Remote Drone Usage" Drones 6, no. 12: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones6120395
APA StyleFrancis, R. J., Brandis, K. J., & McCann, J. A. (2022). Offline Imagery Checks for Remote Drone Usage. Drones, 6(12), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones6120395







