Topographic and Landcover Influence on Lower Atmospheric Profiles Measured by Small Unoccupied Aerial Systems (sUAS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
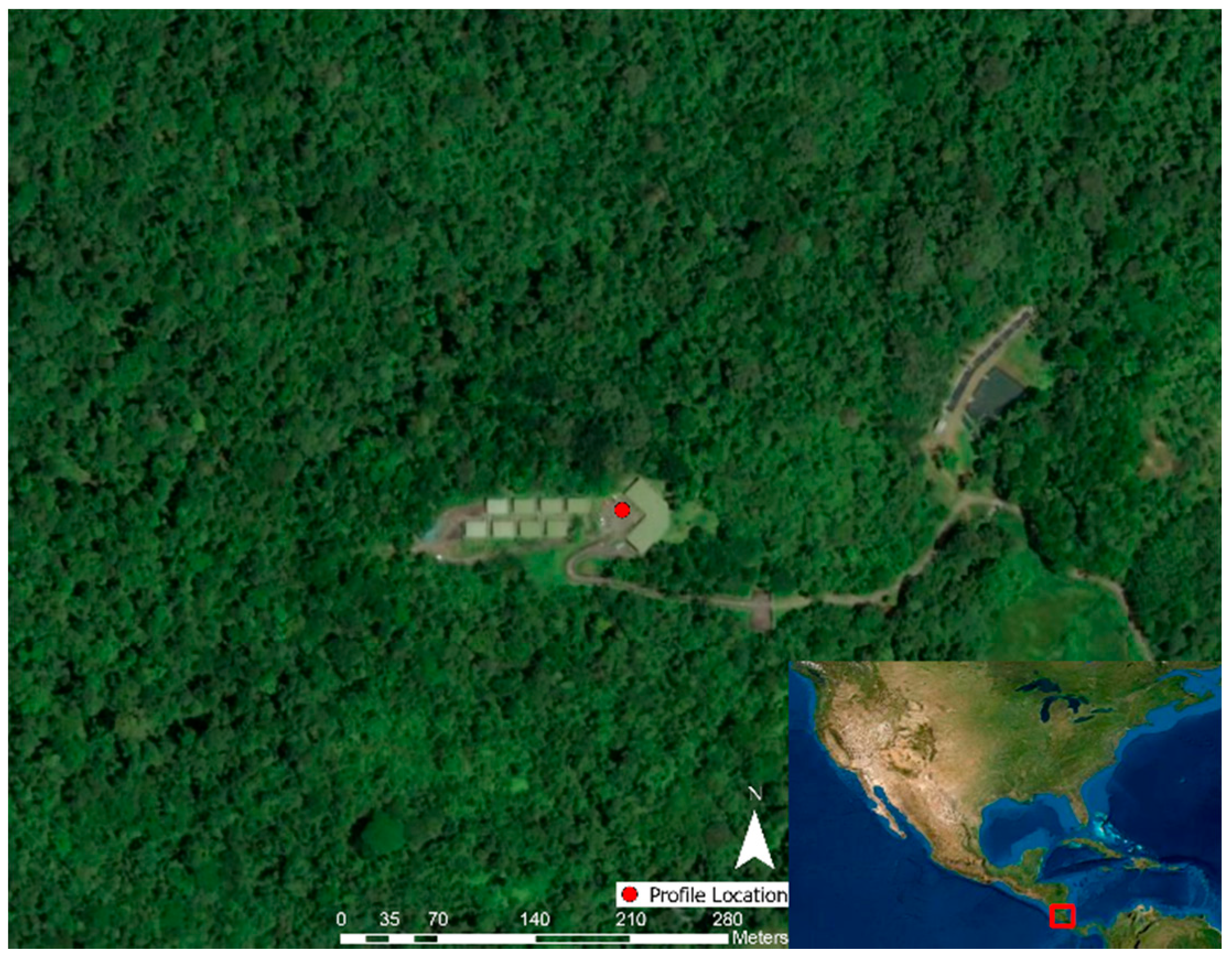
2.1.1. Texas A&M University Soltis Center for Research and Education, Costa Rica
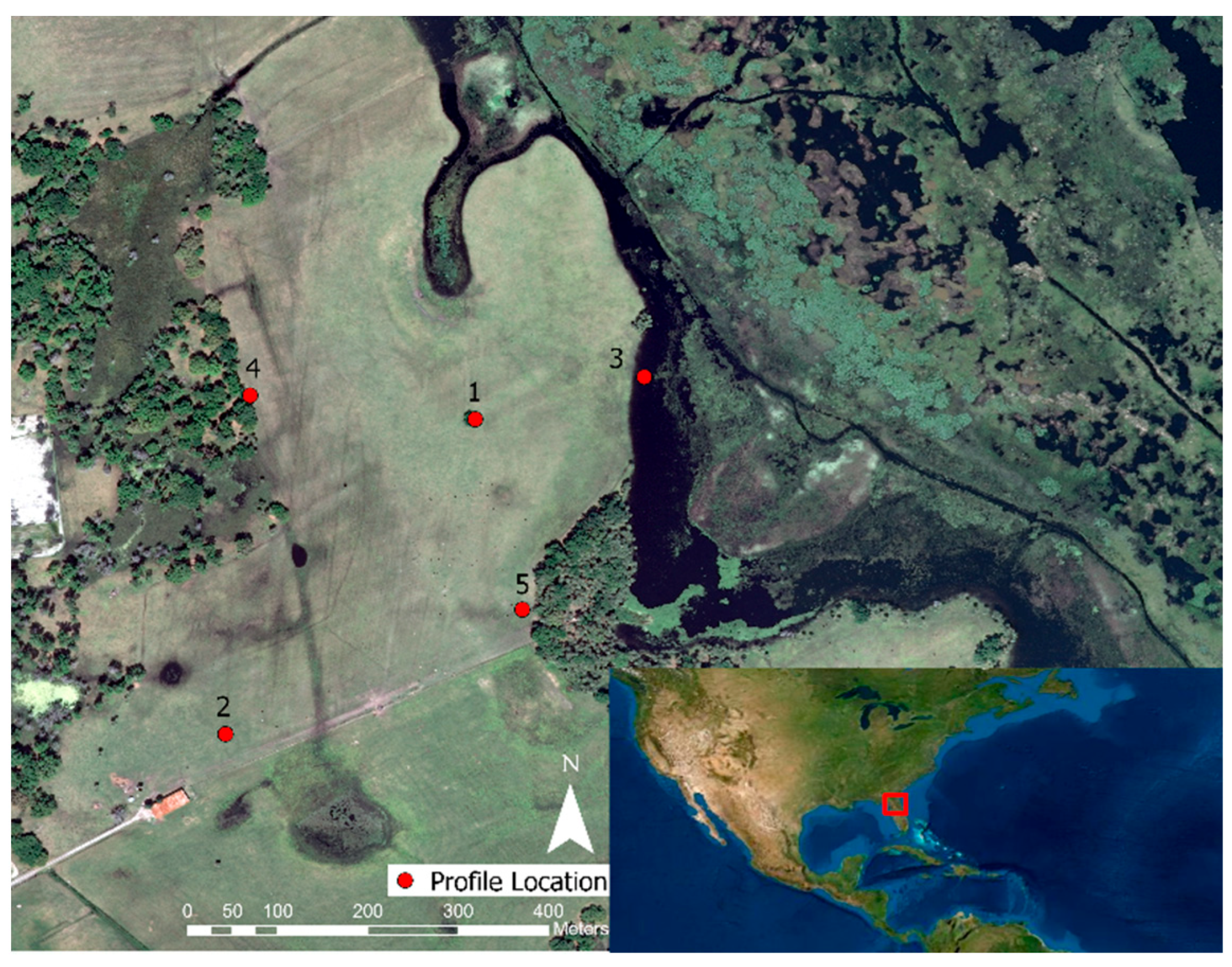
2.1.2. Orange Lake, FL, USA
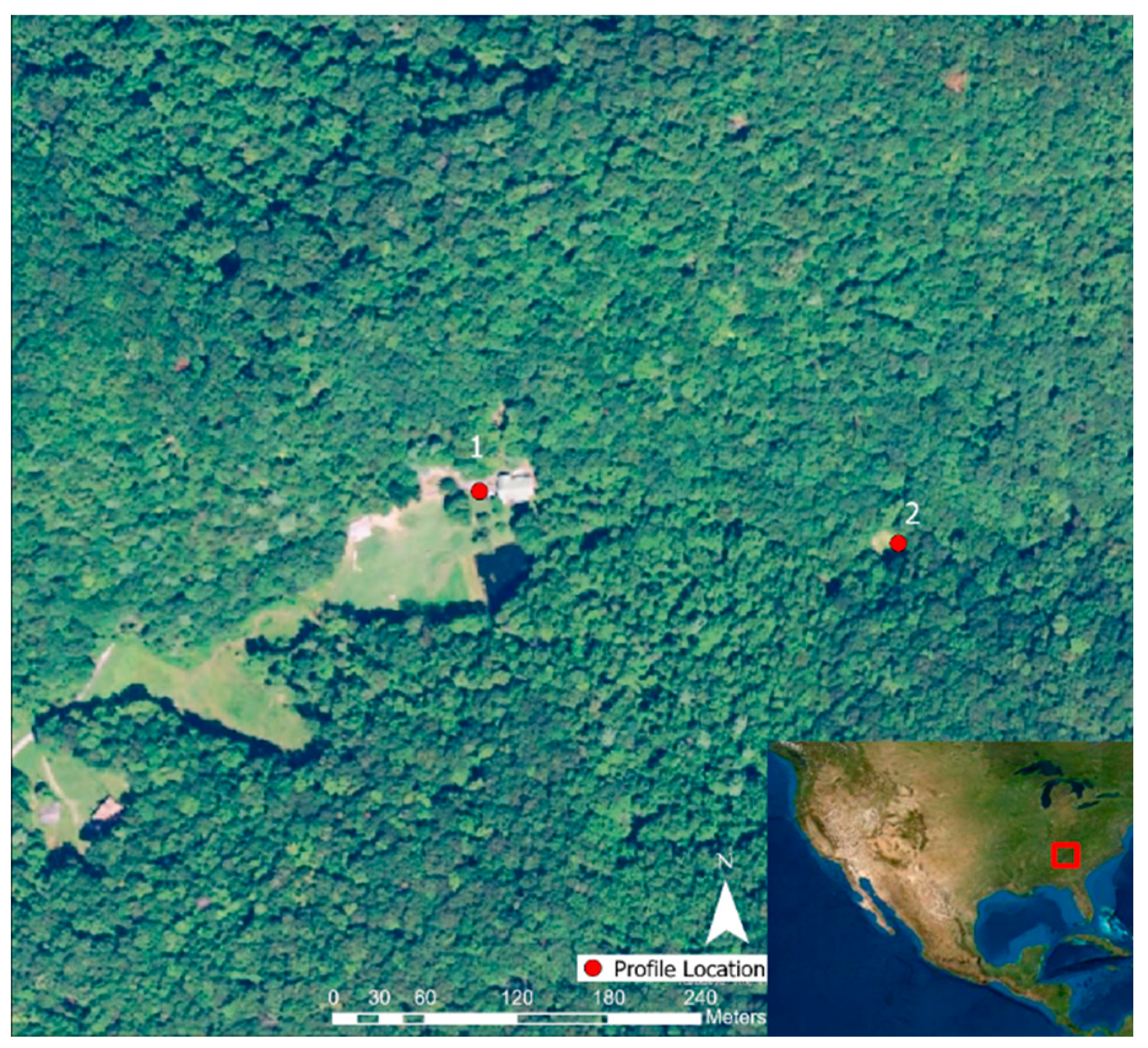
2.1.3. Morganton, GA, USA
2.2. sUAS Setup
2.3. Field Measurements
2.4. Data Processing
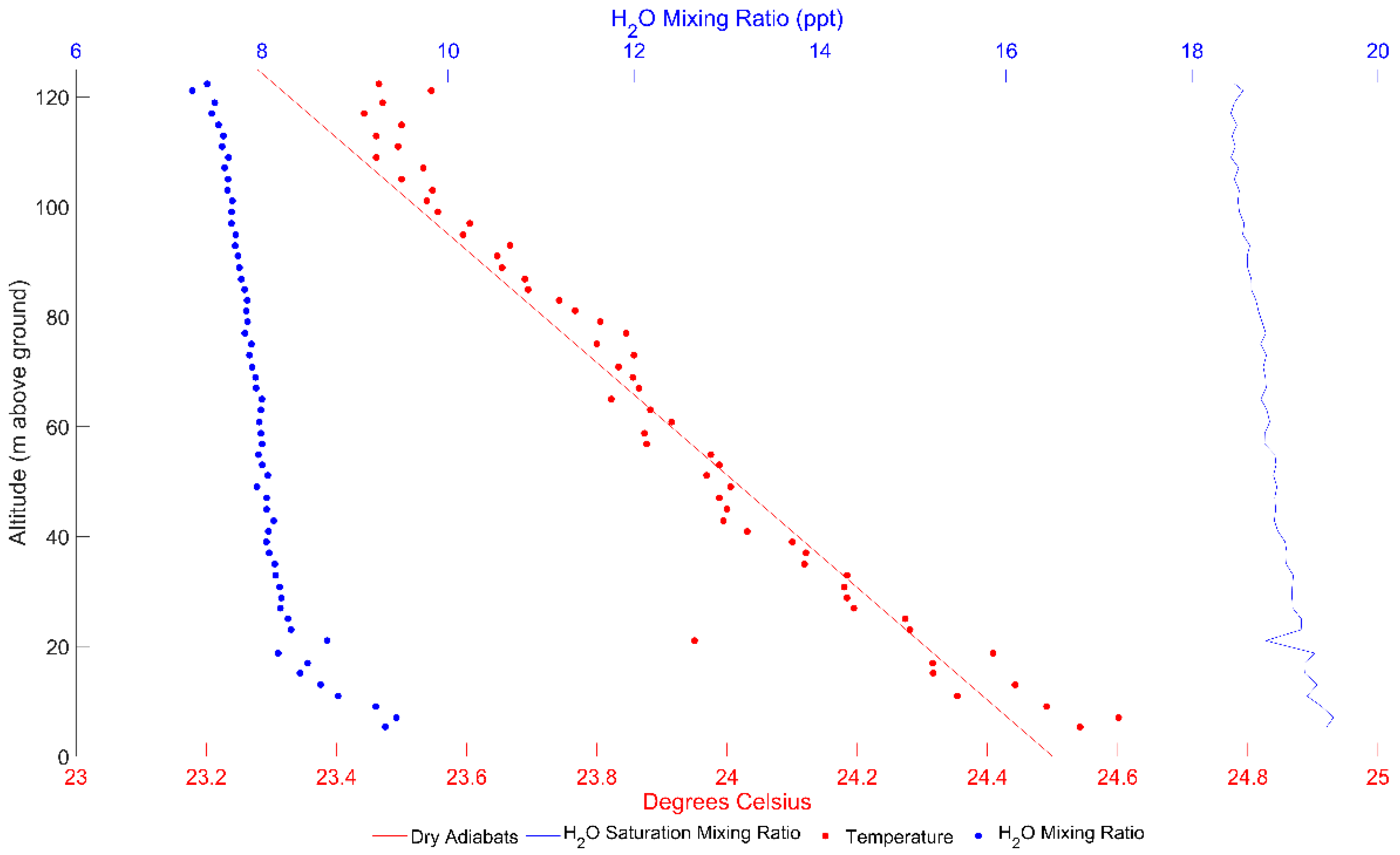
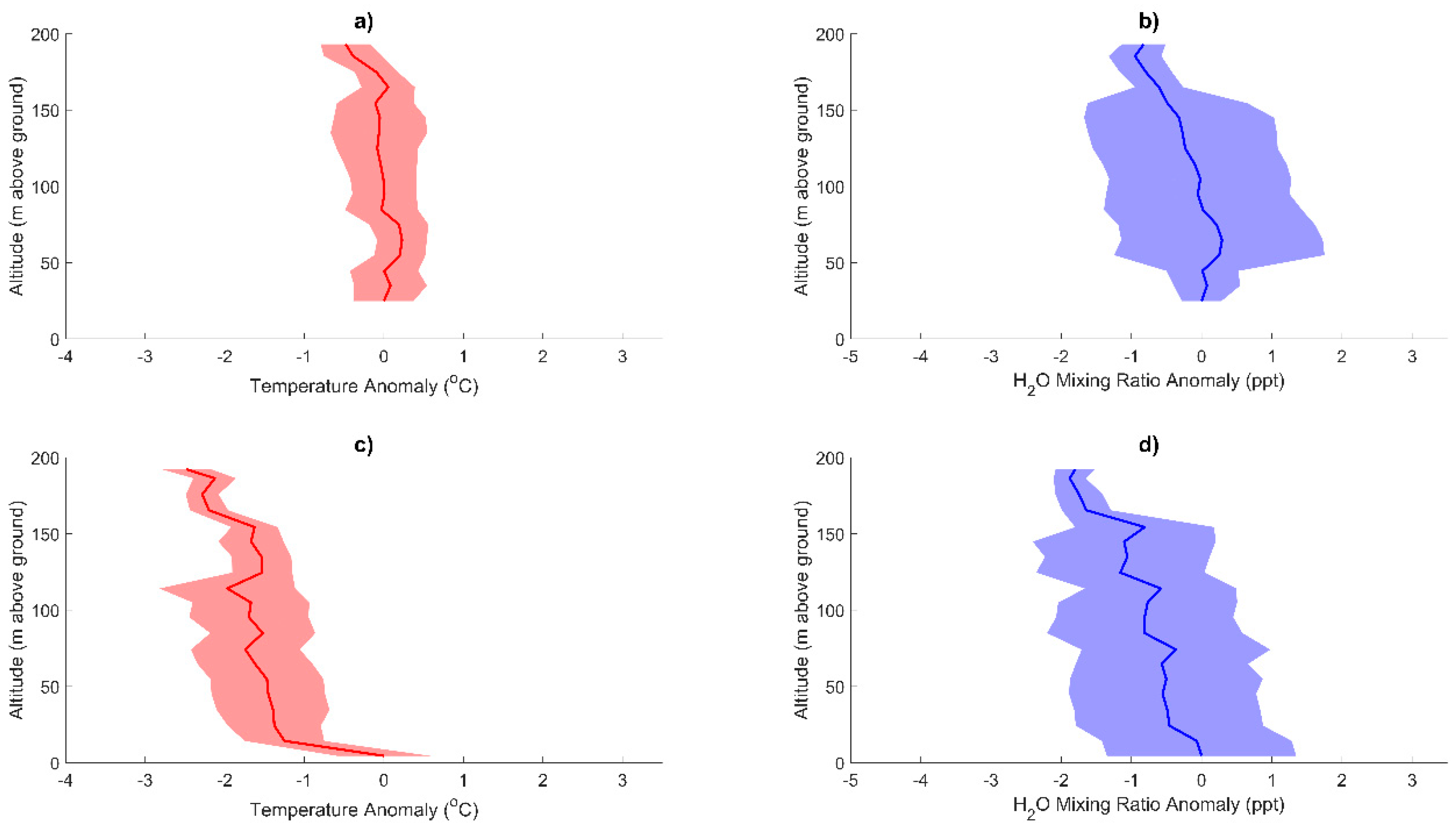
3. Results
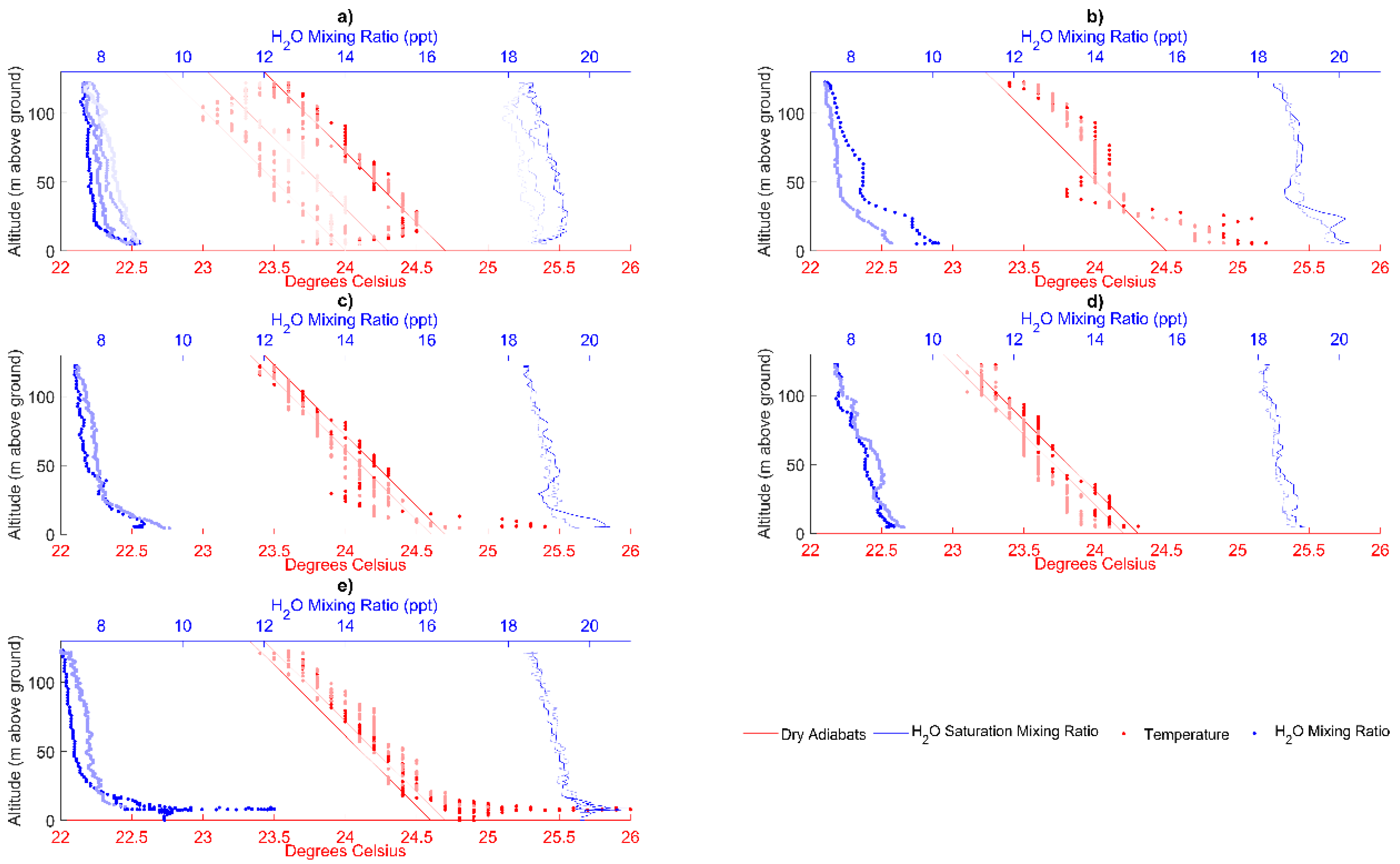
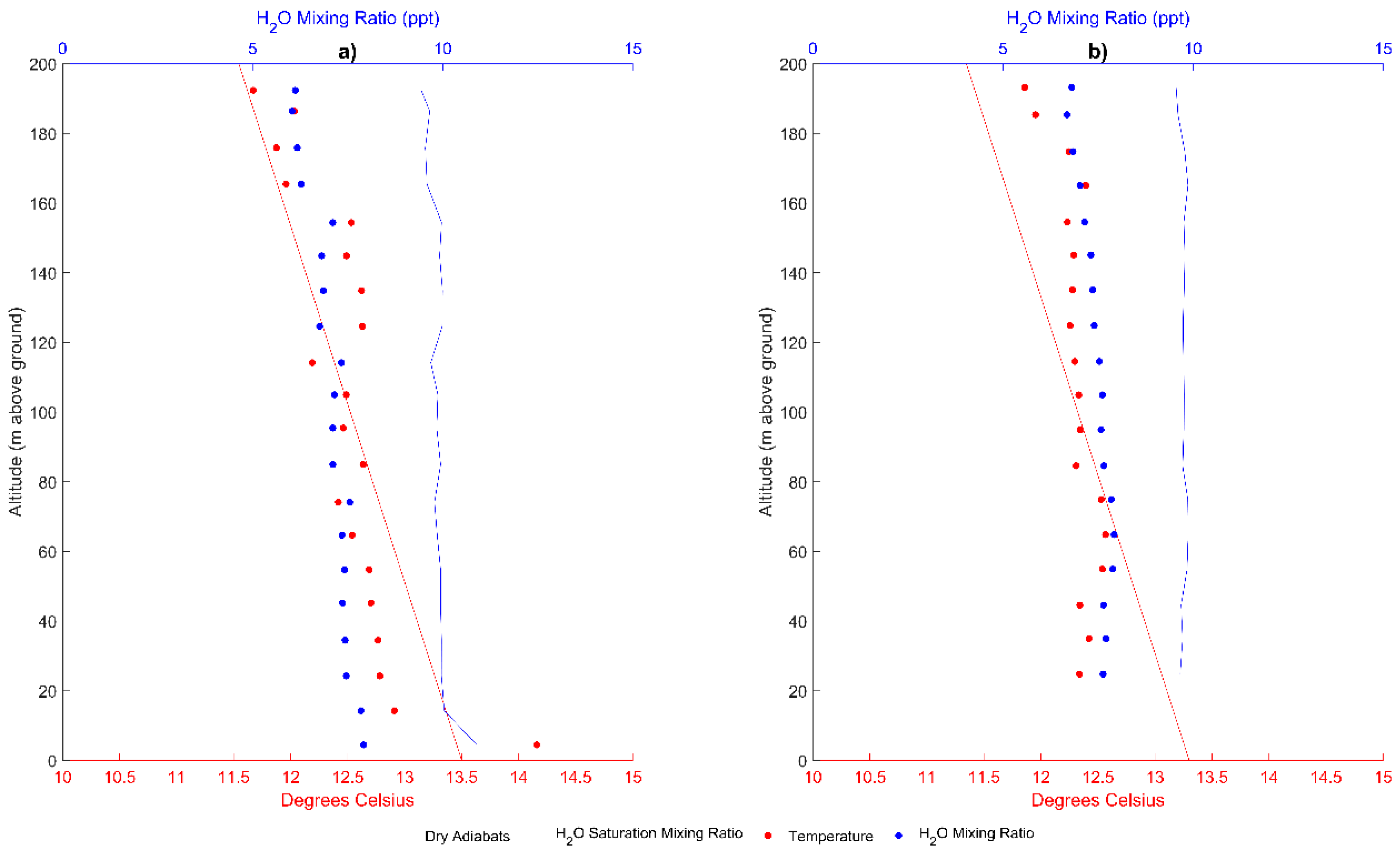
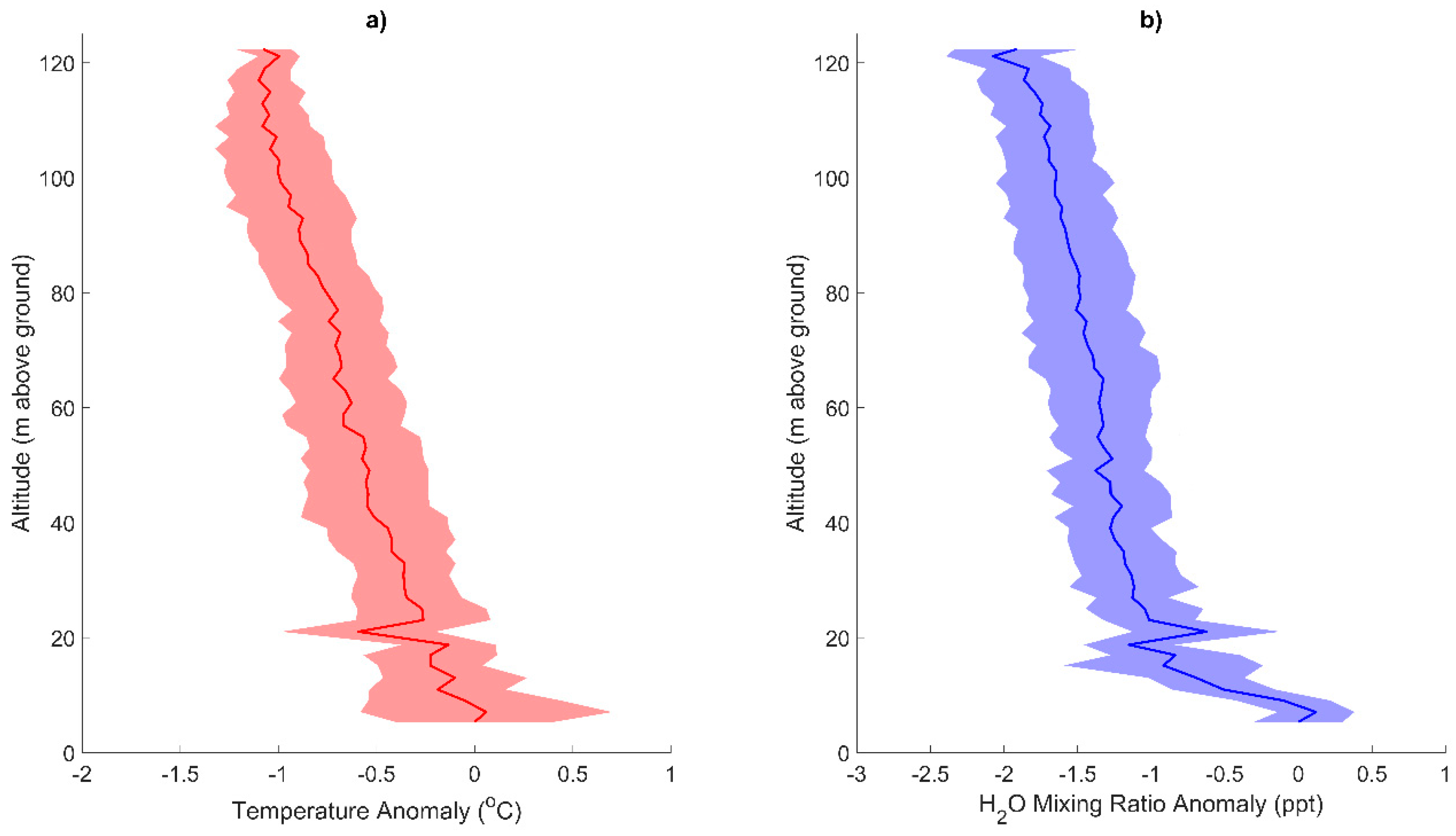
3.1. Texas A&M University Soltis Center for Research and Education, Costa Rica
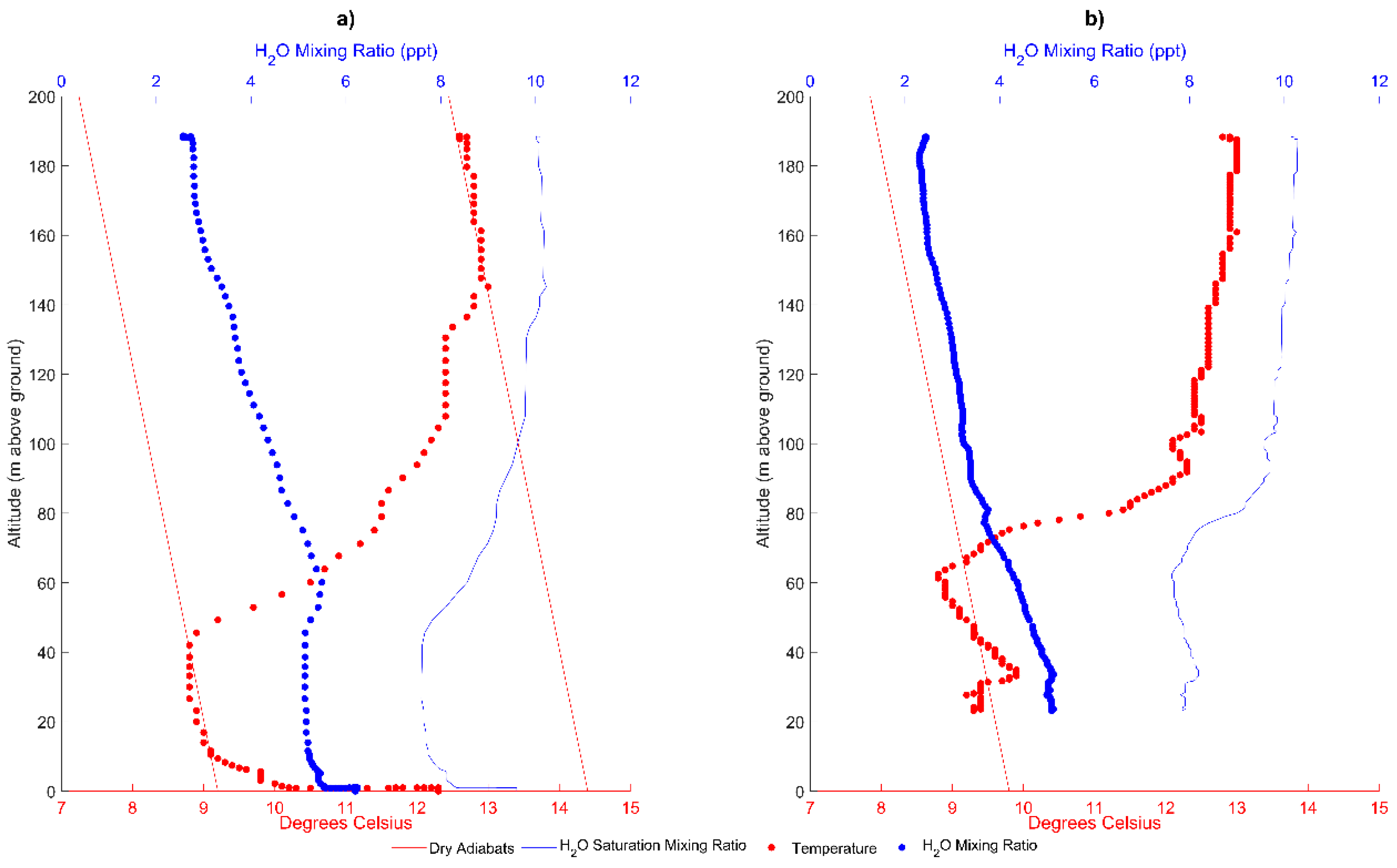
3.2. Orange Lake, FL, USA
3.3. Morganton, GA, USA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine. Thriving on Our Changing Planet: A Decadal Strategy for Earth Observation from Space; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-309-46757-5. [Google Scholar]
- Council, N.R. Observing Weather and Climate from the Ground Up: A Nationwide Network of Networks; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-309-12986-2. [Google Scholar]
- Elston, J.; Argrow, B.; Stachura, M.; Weibel, D.; Lawrence, D.; Pope, D. Overview of Small Fixed-Wing Unmanned Aircraft for Meteorological Sampling. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Bange, J.; Beyrich, F. Meteorological Profiling of the Lower Troposphere Using the Research UAV “M2AV Carolo”. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reuder, J.; Jonassen, M.O.; Ólafsson, H. The Small Unmanned Meteorological Observer SUMO: Recent Developments and Applications of a Micro-UAS for Atmospheric Boundary Layer Research. Acta Geophys. 2012, 60, 1454–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, S.; Sandvik, A.; Jonassen, M.O.; Reuder, J. Atmospheric Profiling with the UAS SUMO: A New Perspective for the Evaluation of Fine-Scale Atmospheric Models. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2012, 116, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautenberg, A.; Schön, M.; Zum Berge, K.; Mauz, M.; Manz, P.; Platis, A.; van Kesteren, B.; Suomi, I.; Kral, S.T.; Bange, J. The Multi-Purpose Airborne Sensor Carrier MASC-3 for Wind and Turbulence Measurements in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Sensors 2019, 19, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hemingway, B.L.; Frazier, A.E.; Elbing, B.R.; Jacob, J.D. Vertical Sampling Scales for Atmospheric Boundary Layer Measurements from Small Unmanned Aircraft Systems (SUAS). Atmosphere 2017, 8, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machado, C.R. An Analysis of Meteorological Measurements Using a Miniature Quad-Rotor Unmanned Aerial System. Master’s Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Walther, J.; PytlikZillig, L.; Detweiler, C.; Houston, A. How People Make Sense of Drones Used for Atmospheric Science (and Other Purposes): Hopes, Concerns, and Recommendations. J. Unmanned Veh. Syst. 2019, 7, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbieri, L.; Kral, S.T.; Bailey, S.C.; Frazier, A.E.; Jacob, J.D.; Reuder, J.; Brus, D.; Chilson, P.B.; Crick, C.; Detweiler, C. Intercomparison of Small Unmanned Aircraft System (SUAS) Measurements for Atmospheric Science during the LAPSE-RATE Campaign. Sensors 2019, 19, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segales, A.R.; Greene, B.R.; Bell, T.M.; Doyle, W.; Martin, J.J.; Pillar-Little, E.A.; Chilson, P.B. The CopterSonde: An Insight into the Development of a Smart Unmanned Aircraft System for Atmospheric Boundary Layer Research. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 2833–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Houston, A.L.; Shankar, A.; Detweiler, C. Design and Evaluation of Sensor Housing for Boundary Layer Profiling Using Multirotors. Sensors 2019, 19, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, N.P.; Pinkerman, C.W.; Jacob, J.D. Meteorological Data Collection for Three-Dimensional Forecasting Advancements; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 13 June 2016; p. 4195. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, M.J.; Clements, C.B. Meteorological Profiling in the Fire Environment Using UAS. Fire 2020, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.E.; Fengler, M.; Chilson, P.B.; Elmore, K.L.; Argrow, B.; Andra, D.L., Jr.; Lindley, T. On the Use of Unmanned Aircraft for Sampling Mesoscale Phenomena in the Preconvective Boundary Layer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 2265–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, P.J.; Pinto, J.; González-Rocha, J.; Jensen, A.; Vezzi, C.N.; Bailey, S.C.; De Boer, G.; Diehl, C.; Laurence, R.; Powers, C.W. Coordinated Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) and Ground-Based Weather Measurements to Predict Lagrangian Coherent Structures (LCSs). Sensors 2018, 18, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lampert, A.; Altstädter, B.; Bärfuss, K.; Bretschneider, L.; Sandgaard, J.; Michaelis, J.; Lobitz, L.; Asmussen, M.; Damm, E.; Käthner, R. Unmanned Aerial Systems for Investigating the Polar Atmospheric Boundary Layer—Technical Challenges and Examples of Applications. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araujo, J.O.; Valente, J.; Kooistra, L.; Munniks, S.; Peters, R.J. Experimental Flight Patterns Evaluation for a UAV-Based Air Pollutant Sensor. Micromachines 2020, 11, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiliński, M.T.; Markowicz, K.M.; Kubicki, M. UAS as a Support for Atmospheric Aerosols Research: Case Study. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 3325–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobziar, L.N.; Pingree, M.R.; Watts, A.C.; Nelson, K.N.; Dreaden, T.J.; Ridout, M. Accessing the Life in Smoke: A New Application of Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) to Sample Wildland Fire Bioaerosol Emissions and Their Environment. Fire 2019, 2, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altstädter, B.; Platis, A.; Wehner, B.; Scholtz, A.; Wildmann, N.; Hermann, M.; Käthner, R.; Baars, H.; Bange, J.; Lampert, A. ALADINA–An Unmanned Research Aircraft for Observing Vertical and Horizontal Distributions of Ultrafine Particles within the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altstädter, B.; Deetz, K.; Vogel, B.; Babić, K.; Dione, C.; Pacifico, F.; Jambert, C.; Ebus, F.; Bärfuss, K.; Pätzold, F. The Vertical Variability of Black Carbon Observed in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer during DACCIWA. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7911–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crazzolara, C.; Ebner, M.; Platis, A.; Miranda, T.; Bange, J.; Junginger, A. A New Multicopter-Based Unmanned Aerial System for Pollen and Spores Collection in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 1581–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bärfuss, K.; Pätzold, F.; Altstädter, B.; Kathe, E.; Nowak, S.; Bretschneider, L.; Bestmann, U.; Lampert, A. New Setup of the UAS ALADINA for Measuring Boundary Layer Properties, Atmospheric Particles and Solar Radiation. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leuenberger, D.; Haefele, A.; Omanovic, N.; Fengler, M.; Martucci, G.; Calpini, B.; Fuhrer, O.; Rossa, A. Improving High-Impact Numerical Weather Prediction with Lidar and Drone Observations. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E1036–E1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilgan, K.; Stauffer, R.; Meindl, M.; Geiger, A. Comparison of Tropospheric Parameters from Meteodrone Measurements with GNSS Estimates from Ground-Based Stations. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 2812–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.R.; Dumas, E.J.; Buban, M.S.; Baker, C.B.; Neuhaus, J.; Rogers, M.; Chappelle, N.; Marwine, C.; Swanson, M.; Amaral, C. Improved Sampling of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Using Small Unmanned Aircraft Systems: Results from the Avon Park Experiment; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lauer, J.; Fengler, M. Meteodrones-Meteorological Planetary Boundary Layer Measurements by Vertical Drone Soundings. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2017; p. 2983. [Google Scholar]
- Chilson, P.B.; Bell, T.M.; Brewster, K.A.; de Azevedo, G.B.H.; Carr, F.H.; Carson, K.; Doyle, W.; Fiebrich, C.A.; Greene, B.R.; Grimsley, J.L. Moving towards a Network of Autonomous UAS Atmospheric Profiling Stations for Observations in the Earth’s Lower Atmosphere: The 3D Mesonet Concept. Sensors 2019, 19, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, T.M.; Greene, B.R.; Klein, P.M.; Carney, M.; Chilson, P.B. Confronting the Boundary Layer Data Gap: Evaluating New and Existing Methodologies of Probing the Lower Atmosphere. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 3855–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W.; Orozco, G.; Aparecido, L.M.; Miller, G.R. Upscaling Transpiration in Diverse Forests: Insights from a Tropical Premontane Site. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Miller, G.R.; Cahill, A.T.; Aparecido, L.M.T.; Moore, G.W. Modeling Profiles of Micrometeorological Variables in a Tropical Premontane Rainforest Using Multi-Layered CLM (CLM-ML). J. Adv. Modeling Earth Syst. 2021, 13, e2020MS002259. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, R.S. The Temporal Variation of Vertical Micrometeorological Profiles in a Lower Montane Tropical Forest. Master’s Thesis, Texas A & M University, Bizzell St, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aparecido, L.M.; Miller, G.R.; Cahill, A.T.; Moore, G.W. Leaf Surface Traits and Water Storage Retention Affect Photosynthetic Responses to Leaf Surface Wetness among Wet Tropical Forest and Semiarid Savanna Plants. Tree Physiol. 2017, 37, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teale, N.G.; Mahan, H.; Bleakney, S.; Berger, A.; Shibley, N.; Frauenfeld, O.W.; Quiring, S.M.; Rapp, A.D.; Roark, E.B.; Washington-Allen, R. Impacts of Vegetation and Precipitation on Throughfall Heterogeneity in a Tropical Pre-montane Transitional Cloud Forest. Biotropica 2014, 46, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindinger, J.G.; Davis, J.B.; Flocks, J.G. High-Resolution Single-Channel Seismic Reflection Surveys of Orange Lake and Other Selected Sites of North Central Florida; US Geological Survey, Center for Coastal Geology: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Pirkle, E.; Brooks, H. Origin and Hydrology of Orange Lake, Santa Fe Lake, and Levys Prairie Lakes of North-Central Peninsular Florida. J. Geol. 1959, 67, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, C.O.D.; Dinerstein, E.; Weakley, A.; Noss, R.; Stritholt, J.K. Wolfe Appalachian-Blue Ridge Forests. Available online: https://www.worldwildlife.org/ecoregions/na0403 (accessed on 3 March 2019).
- Prior, E.M.; Brumbelow, K.; Miller, G.R. Measurement of Above-canopy Meteorological Profiles Using Unmanned Aerial Systems. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 34, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAA. Code of Federal Regulations (14 CFR) Part 107; FAA: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dingman, S.L. Physical Hydrology, 3rd ed.; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2015; ISBN 1-4786-2807-3. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jiboori, M.H.; Fei, H.U. Surface Roughness around a 325-m Meteorological Tower and Its Effect on Urban Turbulence. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 22, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Acevedo, O.C.; Araùjo, A.; Artaxo, P.; Barbosa, C.G.; Barbosa, H.; Brito, J.; Carbone, S.; Chi, X.; Cintra, B. The Amazon Tall Tower Observatory (ATTO): Overview of Pilot Measurements on Ecosystem Ecology, Meteorology, Trace Gases, and Aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10723–10776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Aircraft 1 | Aircraft 2 | Sensor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company: | Autel Robotics, Bothell, WA, USA | DJI, Shenzhen, China | Kestrel Meters, Boothwyn, PA, USA |
| Model: | Autel Robotics X-Star Premium | DJI Phantom 4 Pro V2.0 | Kestrel DROP D3FW Fire Weather Monitor |
| Mass: | 1452 g | 1380 g | 34 g |
| Dimensions: | 352 mm diagonal | 350 mm diagonal | 24 mm × 46 mm × 60 mm |
| Flight Number | Start Time | Parking Lot | Forest |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 July 2018 15:13 | X | |
| 2 | 6 July 2018 13:43 | X | X |
| 3 | 6 July 2018 16:03 | X | X |
| 4 | 6 July 2018 18:02 | X | X |
| 5 | 7 July 2018 11:58 | X | X |
| 6 | 8 July 2018 10:52 | X | X |
| 7 | 8 July 2018 12:48 | X | X |
| 8 | 8 July 2018 16:36 | X | X |
| 9 | 9 July 2018 6:57 | X | X |
| 10 | 9 July 2018 10:29 | X |
| Flight Number | Start Time | 1 Ridge | 2 Pasture | 3 Lake | 4 Next to Forest Furthest from the Lake | 5 Next to Forest near the Lake |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13 Mar 2018 16:42 | X | X | |||
| 2 | 13 Mar 2018 17:11 | X | X | |||
| 3 | 13 Mar 2018 17:40 | X | X |
| Flight Number | Start Time | Parking Lot | Forest Clearing |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 28 Dec 2018 18:16 | X | X |
| 2 | 1 Jan 2019 12:00 | X | X |
| 3 | 1 Jan 2019 16:03 | X | X |
| 4 | 2 Jan 2019 9:49 | X | X |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prior, E.M.; Miller, G.R.; Brumbelow, K. Topographic and Landcover Influence on Lower Atmospheric Profiles Measured by Small Unoccupied Aerial Systems (sUAS). Drones 2021, 5, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones5030082
Prior EM, Miller GR, Brumbelow K. Topographic and Landcover Influence on Lower Atmospheric Profiles Measured by Small Unoccupied Aerial Systems (sUAS). Drones. 2021; 5(3):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones5030082
Chicago/Turabian StylePrior, Elizabeth M., Gretchen R. Miller, and Kelly Brumbelow. 2021. "Topographic and Landcover Influence on Lower Atmospheric Profiles Measured by Small Unoccupied Aerial Systems (sUAS)" Drones 5, no. 3: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones5030082
APA StylePrior, E. M., Miller, G. R., & Brumbelow, K. (2021). Topographic and Landcover Influence on Lower Atmospheric Profiles Measured by Small Unoccupied Aerial Systems (sUAS). Drones, 5(3), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones5030082






