Biaxial Piezoelectrically Driven MEMS Mirror with Large Design Flexibility †
Abstract
1. Introduction
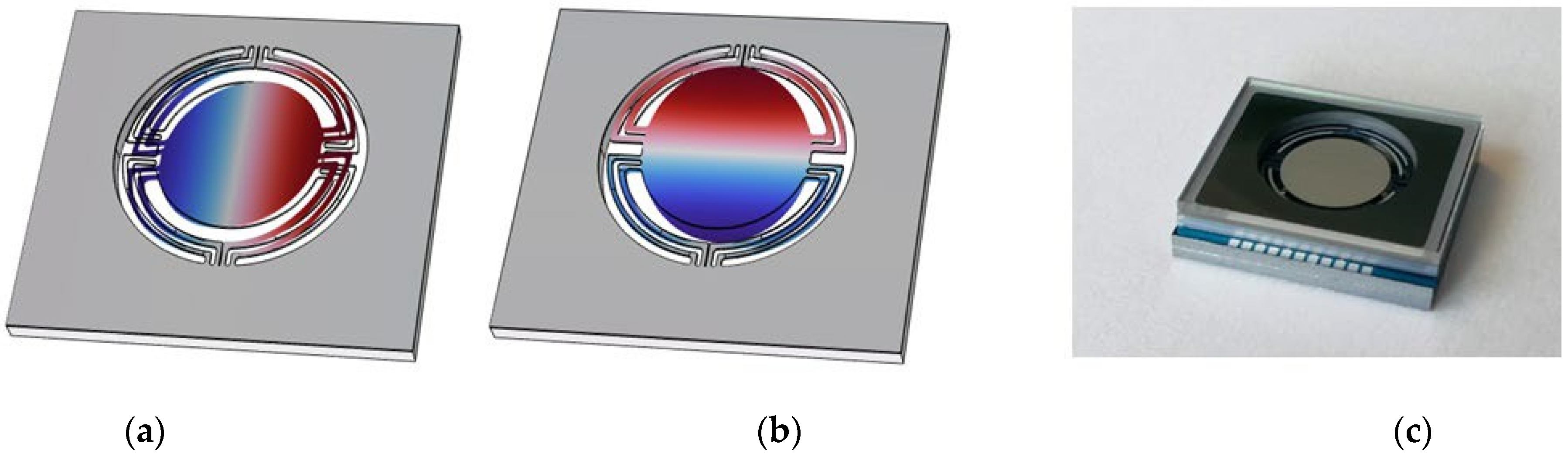
2. Design Concept and FEM Simulations
3. Experimental Results
4. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu-Stoppel, S.; Giese, T.; Quenzer, H.J.; Hofmann, U.; Benecke, W. Piezoelectrically Driven and Sensed Micromirrors with Extremely Large Scan Angles and Precise Closed-Loop Control. Proceedings 2017, 1, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, U.; Senger, F.; Janes, J.; Mallas, C.; Stenchly, V.; von Wantoch, T.; Quenzer, H.-J.; Weiss, M. Wafer-level vacuum-packaged two-axis MEMS scanning mirror for pico-projector application. Proc. SPIE 2014, 8977, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki, L.; Ratzmann, L.; Schütt, P.; Albers, J.; Wille, G.; Gu-Stoppel, S. Efficient piezoelectric gimbal-less MEMS-mirror with large design flexibility. Proc. SPIE 2023, 12434, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Fichtner, S.; Wolff, N.; Krishnamurthy, G.; Petraru, A.; Bohse, S.; Lofink, F.; Chemnitz, S.; Kohlstedt, H.; Kienle, L.; Wagner, B. Identifying and overcoming the interface originating c-axis instability in highly Sc enhanced AlN for piezoelectric micro-electromechanical systems. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 035301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Design | Simulated Frequencies (Slow and Fast) | Mean of Measured Frequencies (Slow and Fast) | Quality Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.7 kHz; 3.8 kHz | 2.3 kHz; 3.2 kHz | 15,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wysocki, L.; Schütt, P.; Albers, J.; Wille, G.; Yarar, E.; Raschdorf, P.; Wen, L.; Gu-Stoppel, S. Biaxial Piezoelectrically Driven MEMS Mirror with Large Design Flexibility. Proceedings 2024, 97, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097139
Wysocki L, Schütt P, Albers J, Wille G, Yarar E, Raschdorf P, Wen L, Gu-Stoppel S. Biaxial Piezoelectrically Driven MEMS Mirror with Large Design Flexibility. Proceedings. 2024; 97(1):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097139
Chicago/Turabian StyleWysocki, Lena, Patrick Schütt, Jörg Albers, Gunnar Wille, Erdem Yarar, Paul Raschdorf, Lianzhi Wen, and Shanshan Gu-Stoppel. 2024. "Biaxial Piezoelectrically Driven MEMS Mirror with Large Design Flexibility" Proceedings 97, no. 1: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097139
APA StyleWysocki, L., Schütt, P., Albers, J., Wille, G., Yarar, E., Raschdorf, P., Wen, L., & Gu-Stoppel, S. (2024). Biaxial Piezoelectrically Driven MEMS Mirror with Large Design Flexibility. Proceedings, 97(1), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097139






