Abstract
In this work, a biaxial, piezoelectrically driven resonant MEMS mirror with large design flexibility is presented. After FEM-based design optimization to reduce material stress and thereby maximize the achievable total optical scanning angles, fabricated MEMS mirrors were electrically, mechanically, and optically characterized. While the achievable optical scanning angles were determined using a home-built optical setup, a laser Doppler vibrometer was used to characterize the resonance frequencies of the rotational modes and their respective quality factors. The encapsulation of the mirror by a glass window ensures its operation in vacuum, which increases the Q-factor up to 15,000.
1. Introduction
Multiaxial resonant MEMS mirrors are frequently applied in miniaturized detection or projection systems since they combine the advantages of compactness, speed, and low power consumption [1,2]. The presented design was optimized utilizing finite element method (FEM) simulations with a focus on reducing material stress as well as the realization of resonance frequencies of the torsional modes which are suitable for Lissajous scanning with high frame rates and/or fill factors [3]. The current work focuses on the experimental characterization of these optical MEMS scanners as well as improving the FEM simulations in order to increase the simulation-based prediction capabilities for future designs.
2. Design Concept and FEM Simulations
The design exhibits two separate actuator groups responsible for the rotation of the mirror along two orthogonal axes, which reduces mechanical coupling and thereby the mutual influence of the rotations. The geometry used for the FEM simulations, as presented exemplarily in Figure 1, was built from the real geometry of the lithography masks. Here, the masks for the epitaxially grown polycrystalline Si (Epi-poly Si) etching, the etching from the backside, and the active piezoelectric area were imported into COMSOL Multiphysics. Subsequently, the results of the eigenfrequency study will be compared with experimental results from frequency studies of the MEMS mirrors.
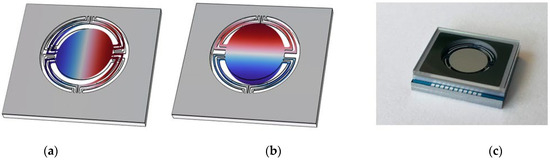
Figure 1.
The results of the FEM-based eigenfrequency study of the active wafer of the MEMS scanner. Presented are the slow rotational mode (a) and fast rotational mode (b). The color code represents the z-component of the deflection in arbitrary units. (c) A photograph of the final optical MEMS scanner.
3. Experimental Results
The characterization of the dynamic modes, the respective resonance frequencies, the quality factors, and the achieved total optical scanning angles was performed using a combination of laser Doppler vibrometry and measurements obtained using a home-built optical setup. The results of the experimental characterization and the comparison with the FEM-simulations are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of the eigenfrequencies from the FEM simulations and the experimental results.
4. Outlook
The replacement of AlN with AlScN, which exhibits an enhanced piezoelectric coefficient, e31,f [4], represents a promising possibility to increase the optical scanning angles of the presented MEMS mirrors. The integration of AlScN is currently underway and will be addressed in future publications.
Author Contributions
All authors: conceptualization, methodology, validation, and writing—review and editing; P.S., J.A., L.W. (Lianzhi Wen), P.R. and L.W. (Lena Wysocki): investigation and data curation; G.W. and E.Y.: resources and data curation; L.W. (Lena Wysocki): writing—original draft preparation, visualization, software, and formal analysis; S.G.-S.: supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research of Germany as part of the research project “MEMS-Scanner basiertes Laserprojektionssystem fuer Maritime Augmented Reality” (project number 03SX472C).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to legal restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gu-Stoppel, S.; Giese, T.; Quenzer, H.J.; Hofmann, U.; Benecke, W. Piezoelectrically Driven and Sensed Micromirrors with Extremely Large Scan Angles and Precise Closed-Loop Control. Proceedings 2017, 1, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, U.; Senger, F.; Janes, J.; Mallas, C.; Stenchly, V.; von Wantoch, T.; Quenzer, H.-J.; Weiss, M. Wafer-level vacuum-packaged two-axis MEMS scanning mirror for pico-projector application. Proc. SPIE 2014, 8977, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki, L.; Ratzmann, L.; Schütt, P.; Albers, J.; Wille, G.; Gu-Stoppel, S. Efficient piezoelectric gimbal-less MEMS-mirror with large design flexibility. Proc. SPIE 2023, 12434, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Fichtner, S.; Wolff, N.; Krishnamurthy, G.; Petraru, A.; Bohse, S.; Lofink, F.; Chemnitz, S.; Kohlstedt, H.; Kienle, L.; Wagner, B. Identifying and overcoming the interface originating c-axis instability in highly Sc enhanced AlN for piezoelectric micro-electromechanical systems. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 035301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).