Insecticidal Activity Evaluation of Phenylazo and Dihydropyrrole-Fused Neonicotinoids Against Cowpea Aphids Using the MLR Approach †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Dataset and Theoretical Molecular Descriptors Calculation
2.2. The Multiple Linear Regression Method
2.3. Model Validation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, L.; Lou, Y.; Chen, N.; Xia, S.; Shao, X.; Xu, X.; Li, Z. Synthesis And Insecticidal Activities Of Tetrahydroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridinones: Further Exploration On Cis-Neonicotinoids. Synth. Commun. 2014, 44, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, R.; Denholm, I. Resistance of Insect Pests to Neonicotinoid Insecticides: Current Status and Future Prospects. Arch. Insect Biochem. 2005, 58, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagabu, S. Chloronicotinyl insecticides discovery, application and future perspective. Rev. Toxicol. 1997, 1, 75–129. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, M.; Béguin, M.; Requier, F.; Rollin, O.; Odoux, J.F.; Aupinel, P.; Aptel, J.; Tchamitchian, S.; Decourtye, A. A common pesticide decreases foraging success and survival in honey bees. Science 2012, 336, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.A.; Lozier, J.D.; Strange, J.P.; Koch, J.B.; Cordes, N.; Solter, L.F.; Griswold, T.L. Patterns of widespread decline in North American bumble bees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xia, S.; Zou, M.; Shao, X. Bridged heterocyclic neonicotinoid analogues: Design, synthesis, and insecticidal activity. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2015, 41, 5293–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbert, A.; Haas, M.; Springer, B.; Thielert, W.; Nauen, R. Applied aspects of neonicotinoid uses in crop protection. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Liang, D.; Yang, X.; Jin, S. A novel halogen bond and a better-known hydrogen bond cooperation of neonicotinoid and insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptor recognition. J. Mol. Model. 2012, 18, 3867–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casida, J.E.; Durkin, K.A. Neuroactive Insecticides: Targets, Selectivity, Resistance, and Secondary Effects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagabu, S.; Nishimura, K.; Naruse, Y.; Ohno, I. Insecticidal and neuroblocking potencies of variants of the thiazolidine moiety of thiacloprid and quantitative relationship study for the key neonicotinoid pharmacophore. J. Pest. Sci. 2008, 33, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ju, X.L.; Jiang, F.C. Pharmacophore model for neonicotinoid insecticides. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2008, 19, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazawa, A.; Akamatsu, M.; Nishiwaki, H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Miyagawa, H.; Nishimura, K.; Ueno, T. Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis of acyclic and cyclic chloronicotinyl insecticides. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2000, 56, 509–515. [Google Scholar]
- Okazawa, A.; Akamatsu, M.; Ohoka, A.; Nishiwaki, H.; Cho, W.-J.; Nakagawa, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Ueno, T. Prediction of the Binding Mode of Imidacloprid and Related Compounds to House-Fly Head Acetylcholine Receptors Using Three-Dimensional QSAR Analysis. Pest. Sci. 1998, 54, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, A.; Sukekawa, M. Quantitative correlation between molecular similarity and receptor-binding activity of neonicotinoid insecticides. Pest. Sci. 1998, 52, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, N.-D.; Jang, S.-C.; Choi, K.-S. CoMFA and CoMSIA on the Neuroblocking Activity of 1-(6-Chloro-3-pyridylmethyl)-2-nitroiminoimidazolidine Analogues. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2006, 27, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Xia, S.; Shao, X.; Cheng, J.; Xu, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, Z.; Qian, X. Design, synthesis, crystal structure analysis, and insecticidal evaluation of Phenylazoneonicotinoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 10615–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Shi, L.; Shao, X.; Xu, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, Z. Pyrrole- and dihydropyrrole-fused Neonicotinoids: Design, synthesis, and insecticidal evaluation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, P.C.D.; Skillman, A.G.; Warren, G.L.; Ellingson, B.A.; Stahl, M.T. Conformer generation with OMEGA: Algorithm and validation using high quality structures from the Protein Databank and Cambridge Structural Database. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, P.C.D.; Nicholls, A. Conformer generation with OMEGA: Learning from the data set and the analysis of failures. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 2919–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Dunn, W.J., III. Multivariate quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR): Conditions for their applicability. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1983, 23, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, N.; Papa, E.; Kovarich, S.; Cassani, S.; Gramatica, P. QSARINS, software for QSAR MLR Model development and validation. QSAR Res. Unit in Environ. Chem. and Ecotox., DiSTA, University of Insubria, Varese, Italy. 2012. Available online: http://www.qsar.it (accessed on 15 May 2018).
- Gramatica, P.; Chirico, N.; Papa, E.; Cassani, S.; Kovarich, S. QSARINS: A new software for the development, analysis, and validation of QSAR MLR models. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2121–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.M.; Fang, H.; Tong, W.; Wu, J.; Perkins, R.; Blair, R.M.; Branham, W.S.; Dial, S.L.; Moland, C.L.; Sheehan, D.M. QSAR models using a large diverse set of estrogens. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2001, 41, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüürmann, G.; Ebert, R.U.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Kühne, R. External validation and prediction employing the predictive squared correlation coefficient test set activity mean vs training set activity mean. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2008, 48, 2140–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, V.; Ballabio, D.; Todeschini, R. Comments on the definition of the Q2 parameter for QSAR validation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, N.; Gramatica, P. Real External Predictivity of QSAR Models: How to Evaluate It? Comparison of Different Validation Criteria and Proposal of Using the Concordance Correlation Coefficient. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2320–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirico, N.; Gramatica, P. Real External Predictivity of QSAR Models. Part 2. New Intercomparable Thresholds for Different Validation Criteria and the Need for Scatter Plot Inspection. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 2044–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Mitra, I. On the Use of the Metric as an Effective Tool for Validation of QSAR Models in Computational Drug Design and Predictive Toxicology. Min.-Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 491–504. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, L.; Johansson, E.; Kettaneh-Wold, N.; Wold, S. Multi and Megavariate Data Analysis: Principles and Applications; Umetrics AB: Umea, Sweden, 2001; pp. 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Goodarzi, M.; Deshpande, S.; Murugesan, V.; Katti, S.B.; Prabhakar, Y.S. Is Feature Selection Essential for ANN Modeling? QSAR Comb. Sci. 2009, 28, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todeschini, R.; Consonni, V.; Maiocchi, A. The K correlation index: Theory development and its application in chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. 1999, 46, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, H.R.; Massart, D.L.; Brans, J.P. Multicriteria decision making: A case study. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1991, 11, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
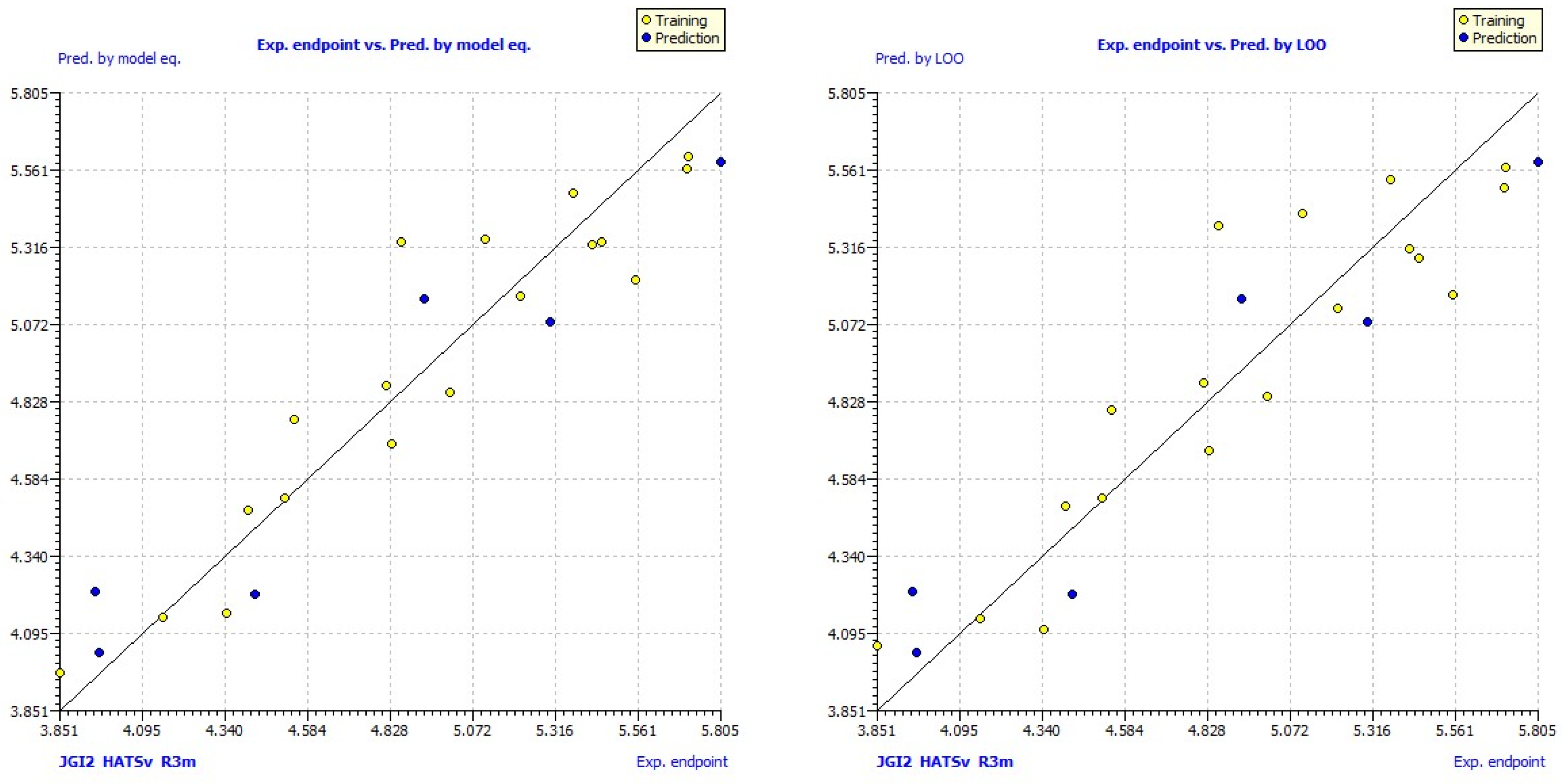

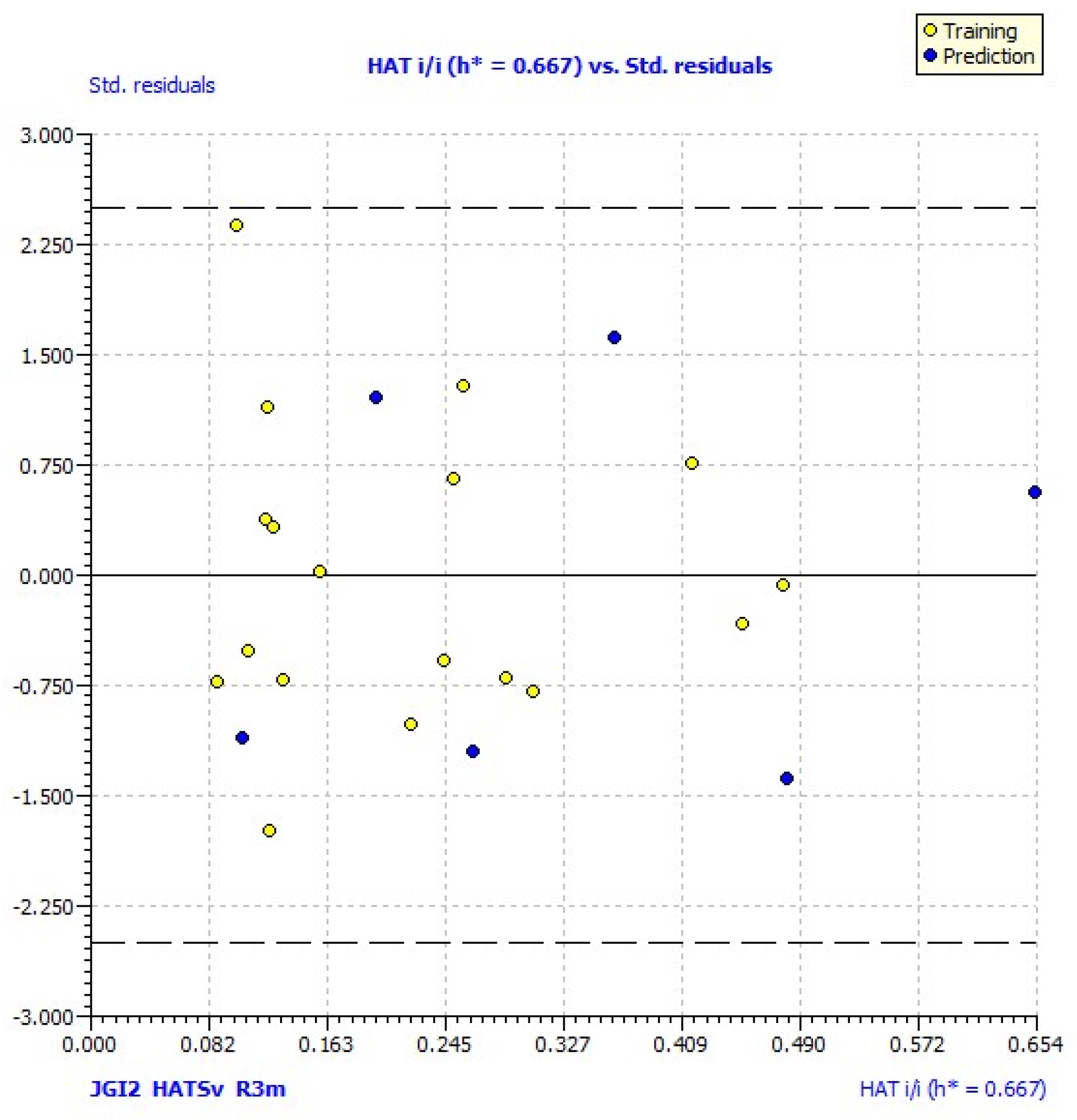
| No | Structure | pLC50exp | pLC50pred | No | Structure | pLC50exp | pLC50pred |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 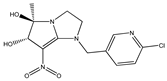 | 5.21 | 5.16 | 13 * | 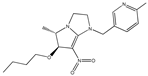 | 3.97 | 4.04 |
| 2 | 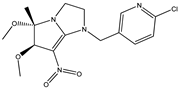 | 5.70 | 5.57 | 14 * |  | 4.43 | 4.22 |
| 3* |  | 5.80 | 5.59 | 15 | 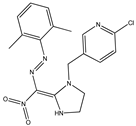 | 5.37 | 5.49 |
| 4 | 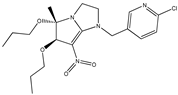 | 5.71 | 5.61 | 16 * | 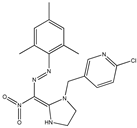 | 5.30 | 5.08 |
| 5 |  | 5.11 | 5.34 | 17 |  | 5.43 | 5.33 |
| 6 | 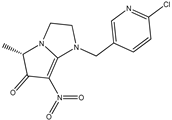 | 3.85 | 3.97 | 18 | 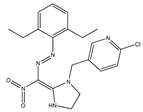 | 5.55 | 5.21 |
| 7 | 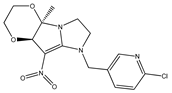 | 4.55 | 4.77 | 19 | 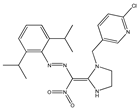 | 4.86 | 5.34 |
| 8 |  | 4.52 | 4.53 | 20 | 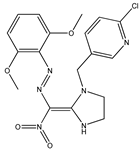 | 5.00 | 4.86 |
| 9 | 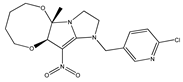 | 4.41 | 4.49 | 21 | 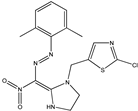 | 5.46 | 5.33 |
| 10 | 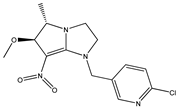 | 4.35 | 4.16 | 22 | 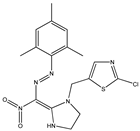 | 4.82 | 4.88 |
| 11* |  | 3.96 | 4.23 | 23* | 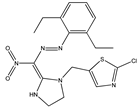 | 4.93 | 5.16 |
| 12 | 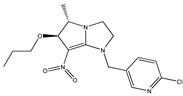 | 4.16 | 4.15 | 24 | 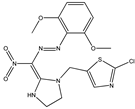 | 4.83 | 4.70 |
| Model | RMSEtr | MAEtr | CCCtr | SEE | F | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLR1 | 0.880 | 0.827 | 0.806 | 0.855 | 0.185 | 0.147 | 0.936 | 0.176 | −0.404 | 0.210 | 34.295 |
| MLR2 | 0.865 | 0.793 | 0.774 | 0.837 | 0.196 | 0.164 | 0.928 | 0.174 | −0.396 | 0.222 | 30.000 |
| MLR3 | 0.854 | 0.777 | 0.755 | 0.822 | 0.205 | 0.172 | 0.921 | 0.178 | −0.390 | 0.232 | 27.208 |
| MLR4 | 0.854 | 0.790 | 0.772 | 0.823 | 0.204 | 0.161 | 0.921 | 0.177 | −0.397 | 0.232 | 27.333 |
| Model | RMSEext | MAEext | CCCext | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLR1 | 0.904 | 0.844 | 0.945 | 0.211 | 0.202 | 0.945 |
| MLR2 | 0.801 | 0.676 | 0.889 | 0.304 | 0.293 | 0.889 |
| MLR3 | 0.818 | 0.704 | 0.896 | 0.291 | 0.281 | 0.896 |
| MLR4 | 0.744 | 0.583 | 0.858 | 0.345 | 0.309 | 0.858 |
| Model | MCDM all | Descriptors included in the MLR model * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLR1 | 0.824 | 0.867 | JGI2 HATSv R3m |
| MLR2 | 0.795 | 0.814 | BEHp2 JGI2 R3m |
| MLR3 | 0.791 | 0.812 | JGI2 Mor06m R3m |
| MLR4 | 0.720 | 0.786 | JGI2 R3m R8m+ |
| JGI2 | HATSv | R3m | Std. coeff. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JGI2 | 1 | 0.967 | ||
| HATSv | −0.278 | 1 | 0.321 | |
| R3m | −0.121 | 0.623 | 1 | −0.617 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Funar-Timofei, S.; Bora, A. Insecticidal Activity Evaluation of Phenylazo and Dihydropyrrole-Fused Neonicotinoids Against Cowpea Aphids Using the MLR Approach. Proceedings 2019, 9, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05664
Funar-Timofei S, Bora A. Insecticidal Activity Evaluation of Phenylazo and Dihydropyrrole-Fused Neonicotinoids Against Cowpea Aphids Using the MLR Approach. Proceedings. 2019; 9(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05664
Chicago/Turabian StyleFunar-Timofei, Simona, and Alina Bora. 2019. "Insecticidal Activity Evaluation of Phenylazo and Dihydropyrrole-Fused Neonicotinoids Against Cowpea Aphids Using the MLR Approach" Proceedings 9, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05664
APA StyleFunar-Timofei, S., & Bora, A. (2019). Insecticidal Activity Evaluation of Phenylazo and Dihydropyrrole-Fused Neonicotinoids Against Cowpea Aphids Using the MLR Approach. Proceedings, 9(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-22-05664






