Abstract
The Southern Ocean waters exchange freshwater, nutrients, carbon, heat, and salt to the Equator and influence the global carbon budget. Therefore, it is essential to understand the variations in Southern Ocean circulation during the last deglacial period to comprehend its changes with climate change. To understand the spread of the Southern Ocean Antarctic Intermediate and Subantarctic Mode Waters during the last deglaciation (from about 19 to 11 thousand years before the present (kyr BP)), this modeling study employs a synchronously coupled general circulation model. The results show that the Southern Hemisphere’s low-level winds overlap with the zone of maximum mixed layer depth, signifying the influence of westerlies in the Southern Ocean waters. The results also indicate that the Southern Ocean Antarctic Intermediate and Subantarctic Mode Waters are fresher, warmer, and about 2.4 times deeper during the early Holocene compared to Heinrich-1. The model simulated the Antarctic sea ice edge (grid points in the ice model have a sea ice concentration above ten percent) overlapping with the poleward edge of the Antarctic Intermediate Waters, and the Southern Ocean mixed layers. Additionally, the simulated quasi-permanent Antarctic sea ice edge (grid points in the ice model have a sea ice concentration above eighty percent) and the surface distribution of Antarctic Intermediate and Subantarctic Mode Waters shifted poleward by about 5° and 10°, respectively, during the early Holocene compared to the Heinrich-1. Therefore, this study highlights a close linkage between the Southern Ocean Antarctic Intermediate and Subantarctic Mode Waters with the Antarctic sea ice distribution throughout the last deglacial period.
1. Introduction
The Southern Ocean (SO) (the ocean body south of 30° S) dynamically links the atmosphere (Southern Hemisphere westerly winds), ocean, and Antarctic sea ice and ventilates a significant part of the global ocean. Through biogeochemical processes, including primary surface productivity, remineralization at depth, and upwelling of carbon-rich water masses, the SO has played a significant role in the Earth’s climate system by directly connecting the deep ocean carbon storage. Although the SO occupies less than one-third of the global ocean and 14% of the Earth’s surface, it has absorbed about 43% of total oceanic anthropogenic carbon dioxide and 75% of heat [1]. In addition, the upwelled SO water exchanges freshwater, nutrients, carbon, heat, and salt with the Equator. Therefore, it contributes to the ocean’s biological productivity and affects the global carbon budget.
The wind and buoyancy-driven SO Circumpolar Deep Water upwelling brings nutrients and carbon onto the ocean surface poleward of the Antarctic Polar Front. The Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW), which is formed around the Antarctic coast, is created when a portion of this upwelled water travels south, loses heat and buoyancy, and sinks. The other share of this upwelled water gets Ekman transported equatorward along the ocean surface and mixes with Antarctic surface water. The densest form of this water subducts to form Antarctic Intermediate Water (AAIW), which is characterized by salinity minimum [2] and can be traced northward beyond the Equator. Further north of AAIW production, Antarctic surface water mixes with subtropical surface water to form Subantarctic Mode Water (SAMW). The SAMW originates in the thick wintertime mixed layers surrounding the Southern Ocean [3].
Currently, the understanding of the SO dynamics is still developing. Paleoclimate scientists acknowledge the SO overturning circulation to be predominantly wind-driven [4,5]. However, numerous studies have demonstrated that variations in buoyant flux caused by freshwater outflow [6,7], ocean eddies [8], topography [7], and Antarctic sea ice feedback [9,10,11,12,13,14] contribute to the SO dynamical changes during the last deglacial time. Therefore, understanding how the distribution of Antarctic sea ice affects the surface distribution and transport of AAIW and SAMW movement is crucial.
The Southern Hemisphere sub-tropical gyres depend on the AAIW and SAMW of the Southern Ocean for the transportation of freshwater, heat, and nutrients. The SO’s AAIW and SAMW are essential components of equatorward freshwater, nutrient, and heat transport, which distributes in all southern hemisphere subtropical gyres and even spans the Equator [3]. Therefore, it is essential to understand the change in atmospheric, oceanic, and cryosphere dynamics affecting Southern Ocean water transport. Moreover, a change in the volume transport of AAIW and SAMW transport can affect the eastern equatorial productivity primary productivity and carbon budget [15,16,17].
Li et al. [18] have shown changes in the depth and position of the AAIW during the onset of the last deglaciation. They hypothesized that variations in Antarctic Intermediate Water depth were caused by Antarctic sea ice growth and the weakening hydrological cycle, highlighting the importance of Antarctic sea ice in SO circulation. Additionally, it is essential to remember that the physical processes responsible for the SO dynamics during the most recent deglacial period still apply today. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the SAMW and AAIW transport during the last deglacial period to help us understand the present and future changes.
As a result of global warming, the oceans are currently warming, and the waters off the Antarctic shelf are becoming fresher [19,20]. This study aims to comprehend the SO processes and transport of nutrient-rich SAMW and AAIW export using an atmosphere-ocean-ice-land surface coupled earth system climate model that would contribute to understanding the global carbon budget. Moreover, this study highlights the association of Antarctic sea ice distribution with the SAMW and AAIW transport, which is vital to understanding the present and future climate projections.
2. Materials and Methods
This study employs a synchronously coupled ocean-atmosphere-ice-land surface general circulation model (TraCE-21ka). The TraCE-21ka experiment includes a T31_gx3v5 resolution version of the Community Climate System Model (CCSM3) from the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). The Community Atmosphere Model version 3 (CAM3), Community Sea Ice Model version 5 (CSIM5), the Parallel Ocean Program version (POP), and the Community Land Surface Model version 3 (CLM3) are all included in the TraCE-21ka experiment [21]. Realistic transient variations in the meltwater fluxes in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, incoming solar radiation, retreating continental ice sheet topography, which is denoted by the rise in eustatic sea level, and atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations were used as boundary conditions for the TraCE-21ka experiment. The TraCE-21ka model output data are publicly available at https://www.earthsystemgrid.org/project/trace.html (most recent access was on 27 October 2022).
The Community Atmospheric Model 3 (CAM3), run at a T31 (around 3.75 degrees) resolution and a vertical resolution of 26 hybrid coordinate levels, served as the atmospheric model for the TraCE-21ka experiment. The Parallel Ocean Program (POP) and NCAR Community Sea Ice Model version 5 (CSIM5) output data from the TraCE-21ka experiment have similar resolutions (gx3v5). The model output data have about 3.6 degrees resolution in the longitudinal and a variable resolution in the latitudinal direction, such that it is about 0.9 degrees close to the Equator. As a result, the output data from the ocean and ice models were interpolated to a resolution of 3.75 degrees, just like the data from the atmospheric model. The ocean model employs the parameterization of ocean eddies and comes with a vertical z coordinate that has 25 depth levels [22]. A subgrid-scale distribution of ice thickness was also added to the CSIM5 model.
Sloyan and Kamenkovich [23] showed that the GFDLCM2.1, CCSM3, MIROC3.2, and CNRM-CM3 climate models well simulate the AAIW and SAMW volume and temperature transport. Sloyan and Kamenkovich [23] adopted the definitions used by Sloyan and Rintoul [24] and simulated the volume transport of for the CCSM3 climate model between neutral densities ranging between 26.0 to 27.4 kg m−3. In this study, we have analyzed the TraCE-21ka experiment model outputs, which employ the CCSM3 climate model. Therefore, we have followed Sloyan and Kamenkovich [23] and Sloyan and Rintoul [24] and calculated the AAIW and SAMW volume transport between potential densities ranging between 26.0 to 27.4 kg m−3.
This study examined the time evolution of the AAIW and SAMW transport and Antarctic sea ice coverage from about 19 to 9 kyr BP. We have selected three millennial timescales: (a) H1 (Heinrich 1 event; from 17.3 to 16.3 kyr BP), (b) YD (Younger Dryas event; 12.5 to 11.5 kyr BP), and (c) O_H (early Holocene period; 10 to 9 kyr BP), to highlight the variability during the last deglacial period.
3. Results
We analyzed the TraCE-21ka near-surface winds (950 mb) and ocean data from about 19 to 9 kyr BP to understand the evolution of the ocean mixed layer depths and the spatial distribution of the SAMW and AAIW waters in the SO. Figure 1 shows that the Southern Hemisphere’s low-level winds overlap with the zone of mixed layer depth in the Southern Ocean waters. The southernmost point of the AAIW distribution can be seen in the isopycnals 27.4 (values are reported after deducting 1000. Hence a potential density of 27.4 kg m−3 represents the 1027.4 kg m−3 isopycnals). Figure 1 illustrates that the southward extent of AAIW and mixed layer depths closely follow during the latter part of the last deglacial period.
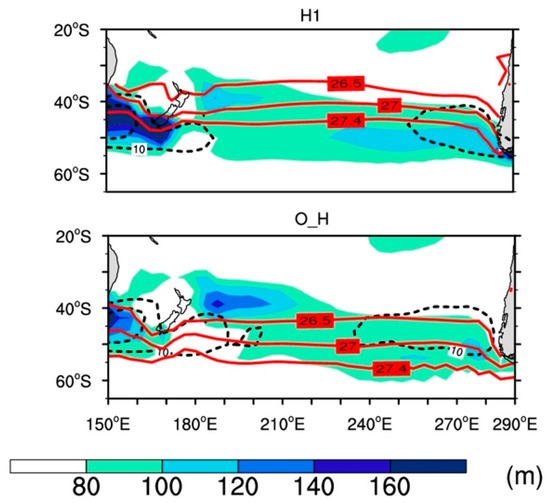
Figure 1.
The depths of the mixed layer in the Southern Ocean on an annual average (color-shaded; meters (m)). It is overlain with near surface 950 mb winds (black, dashed; contour lines) and surface isopycnals (red, solid; contour lines) during the early part of deglaciation (H1) and early Holocene (O_H).
We further analyzed the TraCE-21ka Antarctic sea ice distribution. Figure 2 shows the SO mixed layer depth and the spatial distribution of AAIW and SAMW. It also shows the Antarctic sea ice boundary (green dashed contour line) and Antarctic quasi-permanent sea ice boundary (blue dashed contour line) in the Southern Ocean waters.
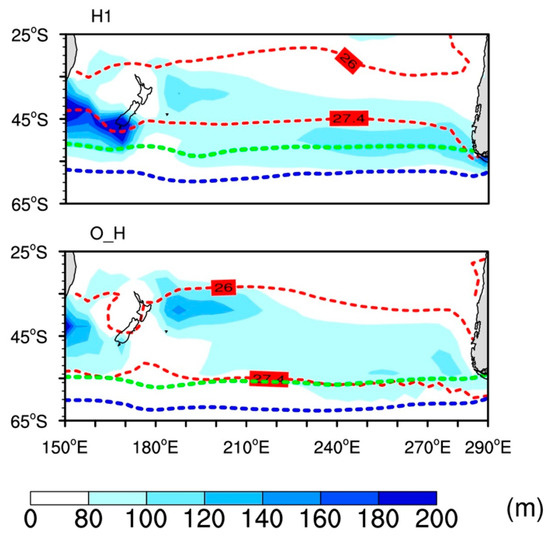
Figure 2.
The depths of the mixed layer in the Southern Ocean on an annual average (color-shaded; meters (m)). It overlays surface isopycnals 26 and 27.4 (red, dashed; contour lines), showing the spatial extent of SAMW and AAIW waters. Additionally, the quasi-permanent sea ice edge, defined as the grid points in the ice model that have a sea ice concentration above eighty percent, and Antarctic sea ice edge, defined as the grid points in the ice model which have a sea ice concentration above ten percent during the early part of deglaciation (H1) and early Holocene (O_H) periods.
Figure 2 also illustrates that the southward extent of AAIW and mixed layer depths closely follow during the latter part of the last deglacial period. The Antarctic sea ice edge (grid points in the ice model have a sea ice concentration above ten percent) overlaps with the southward position of the AAIW and the SO mixed layers. Additionally, the quasi-permanent sea ice edge (grid points in the ice model have a sea ice concentration above eighty percent) and the zone of SAMW and AAIW shifted southward during the early Holocene compared to H1.
Figure 3 shows the Southern Hemisphere depth latitude section of the SAMW and AAIW during the early part of deglaciation (H1) and early Holocene (O_H). It highlights that the simulated AAIW and SAMW are deeper and equatorward shifted during the early Holocene than H1.
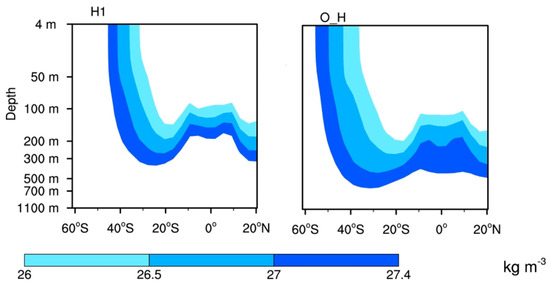
Figure 3.
The depth-latitude section of AAIW and SAMW waters (color-shaded; kilogram per cubic meters (kg m−3)) in the SO. The AAIW and SAMW are calculated between a potential density ranging from 26 and 27.4 kg m−3 isopycnals during the early part of deglaciation (H1) and early Holocene (O_H).
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Recent publications employing the TraCE-21ka experiment model simulations have highlighted the relationship between Antarctic sea ice and SO processes [7,9,10]. The SO upwelling was made stronger by an increase in freshwater discharge brought on by Antarctic sea ice melting [6,10]. Studies have also shown changes in the depth and position of the Antarctic Intermediate Water during the onset of the last deglaciation [18]. They emphasized the importance of Antarctic sea ice in the SO and proposed that variations in Antarctic Intermediate Water depth were caused by Antarctic sea ice expansion and the weakening hydrological cycle.
The study shows that the near-surface winds overlap with the mixed layer depth in the SO, demonstrating the influence of Southern Hemisphere westerlies in the SO dynamics (Figure 1). The findings show that the modeled AAIW during the early Holocene is warmer, fresher, and roughly 2.4 times deeper (Figure 3) than during the early portion of the deglaciation (H1 event). The Antarctic sea ice edge overlaps with the southward edge of the Antarctic Intermediate Waters and the mixed layers in the SO.
The results also highlight that the modeled quasi-permanent Antarctic sea ice edge and AAIW and SAMW surface distribution shift southward by about 5° and 10°, respectively, during the early Holocene compared to the early portion of the deglaciation (H1). Therefore, this study highlights the association between AAIW and SAMW surface distribution and the SO sea ice distribution during the most recent deglacial period (Figure 2).
But it’s important to remember that the same physical processes that governed SO dynamics during the last glacial period would apply today. For instance, recent research has discovered that the freshening of the Antarctic shelf waters caused by sea ice melt regulates the changes in heat and salt in the upper meridional overturning circulation [25]. Studies have also revealed salinity [19] and meltwater [20] variations in the Antarctic waters. Consequently, it is crucial to comprehend the distribution of SAMW, AAIW, and Antarctic sea ice in the SO to comprehend the present and future estimates of nutrient export and climate.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: G.M. and S.-Y.L.; visualization: G.M.; formal analysis: G.M.; methodology: G.M.; investigation: G.M.; supervision: S.-Y.L. and J.-Y.Y.; writing—original draft preparation: G.M.; writing—review and editing: G.M.; funding acquisition: S.-Y.L. and G.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Gagan Mandal and Shih-Yu Lee received funding #111-2811-M-001-021 from Taiwan’s Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The TraCE-21ka experiment model output data are accessible in the public domain (https://www.earthsystemgrid.org/project/trace.html (accessed on 27 October 2022)).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Frölicher, T.L.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Paynter, D.J.; Dunne, J.P.; Krasting, J.P.; Winton, M. Dominance of the Southern Ocean in Anthropogenic Carbon and Heat Uptake in CMIP5 Models. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 862–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartin, C.A.; Fine, R.A.; Sloyan, B.M.; Talley, L.D.; Chereskin, T.K.; Happell, J. Formation rates of Subantarctic mode water and Antarctic intermediate water within the South Pacific. In Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 58, pp. 524–534. [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento, J.L.; Gruber, N.; Brzezinski, M.A.; Dunne, J.P. High-latitude controls of thermocline nutrients and low latitude biological productivity. Nature 2004, 427, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menviel, L.; Spence, P.; Yu, J.; Chamberlain, M.A.; Matear, R.J.; Meissner, K.J.; England, M.H. Southern Hemisphere westerlies as a driver of the early deglacial atmospheric CO2 rise. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.F.; Ali, S.; Bradtmiller, L.I.; Nielsen, S.H.H.; Fleisher, M.Q.; Anderson, B.E.; Burckle, L.H. Wind-Driven Upwelling in the Southern Ocean and the Deglacial Rise in Atmospheric CO2. Science 2009, 323, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernathey, R.P.; Cerovecki, I.; Holland, P.R.; Newsom, E.; Mazloff, M.; Talley, L.D. Water-mass transformation by sea ice in the upper branch of the Southern Ocean overturning. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, S. The Driving Mechanisms on Southern Ocean Upwelling Change during the Last Deglaciation. Geosciences 2021, 11, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauderdale, J.M.; Williams, R.G.; Munday, D.R.; Marshall, D.P. The impact of Southern Ocean residual upwelling on atmospheric CO2 on centennial and millennial timescales. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 1611–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, G.; Lee, S.-Y.; Yu, J.-Y. The Roles of Wind and Sea Ice in Driving the Deglacial Change in the Southern Ocean Upwelling: A Modeling Study. Sustainability 2021, 13, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, G.; Yu, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-Y. The Roles of Orbital and Meltwater Climate Forcings on the Southern Ocean Dynamics during the Last Deglaciation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzocchi, A.; Jansen, M.F. Connecting Antarctic sea ice to deep-ocean circulation in modern and glacial climate simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 6286–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.F.; Nadeau, L.-P. The Effect of Southern Ocean Surface Buoyancy Loss on the Deep-Ocean Circulation and Stratification. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2016, 46, 3455–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Jansen, M.F.; Adkins, J.F.; Burke, A.; Stewart, A.L.; Thompson, A.F. Antarctic sea ice control on ocean circulation in present and glacial climates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8753–8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, K.; Timmermann, A.; Kwon, E.Y.; Friedrich, T. Timing and magnitude of Southern Ocean sea ice/carbon cycle feedbacks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4498–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, K.M.; Jacobel, A.W.; McManus, J.F.; Anderson, R.F.; Winckler, G.; Thiagarajan, N. Productivity patterns in the equatorial Pacific over the last 30,000 years. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2017, 31, 850–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, E.; Pelejero, C.; Pena, L.D.; Cacho, I.; Logan, G.A. Eastern equatorial pacific productivity and related-CO2 changes since the last glacial period. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5537–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, L.D.; Goldstein, S.L.; Hemming, S.R.; Jones, K.M.; Calvo, E.; Pelejero, C.; Cacho, I. Rapid changes in meridional advection of Southern Ocean intermediate waters to the tropical Pacific during the last 30kyr. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 368, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, C.; He, C.; Otto-Bliesner, B. Shallowing Glacial Antarctic Intermediate Water by Changes in Sea Ice and Hydrological Cycle. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL094317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haumann, F.A.; Gruber, N.; Munnich, M.; Frenger, I.; Kern, S. Sea-ice transport driving Southern Ocean salinity and its recent trends. Nature 2016, 537, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronselaer, B.; Winton, M.; Griffies, S.M.; Hurlin, W.J.; Rodgers, K.B.; Sergienko, O.V.; Stouffer, R.J.; Russell, J.L. Change in future climate due to Antarctic meltwater. Nature 2018, 564, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Otto-Bliesner, B.L.; He, F.; Brady, E.C.; Tomas, R.; Clark, P.U.; Carlson, A.E.; Lynch-Stieglitz, J.; Curry, W.; Brook, E.; et al. Transient simulation of last deglaciation with a new mechanism for Bolling-Allerod warming. Science 2009, 325, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, P.R.; McWilliams, J.C. Isopycnal Mixing in Ocean Circulation Models. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1990, 20, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloyan, B.M.; Kamenkovich, I.V. Simulation of Subantarctic Mode and Antarctic Intermediate Waters in Climate Models. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5061–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloyan, B.M.; Rintoul, S.R. Circulation, Renewal, and Modification of Antarctic Mode and Intermediate Water. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 1005–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, S.; Döös, K.; Campino, A.A.; Nycander, J. The Water Mass Transformation in the Upper Limb of the Overturning Circulation in the Southern Hemisphere. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2021JC017330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).