Abstract
Consumers are being encouraged to increase their protein and fibre consumption through convenient and healthy food products. Six samples of extruded rice snacks were developed by substituting rice flour with cowpea flour and whey protein concentrate (WPC). Texture and colour were assessed instrumentally, and sensory analysis was conducted by an untrained panel (N = 70) who rated overall liking using the nine-point hedonic scale, and a check-all-that-apply (CATA) question with 37 attributes and emotions. Hedonic scores of the texture, taste and overall liking were significantly different across samples (p < 0.05). The crispy and crunchy CATA attributes were associated with 10–15% cowpea and 5% WPC. Correlations between mechanical and sensory texture and colour were non-significant (p > 0.05). A principal component analysis (PCA) revealed the positive associations between the groups, crispiness and L* value, and hardness b* and a* values, respectively. The results of the present study will help to guide innovative high-protein and high-fibre plant food designs and formulations.
1. Introduction
Extrusion has become a preferred food processing technology, which creates highly expanded products with a wide variety of textures and mouth feelings, with convenience. It offers an excellent avenue to combine different ingredients in ready-to-eat snacks and breakfast cereals. In recent times, research has been focused on enriching the nutrition value of extruded snacks with protein and fibre, through the addition of legumes, fruits, vegetables and food industry by-products [1,2,3]. These additions reduce carbohydrate-rich, high-glycaemic products, and improve bioactive components in snacks [4,5]. Simultaneously, considerable interest in the nutritional profile of cereal-based ready-to-eat snacks has been shown by consumers. In this regard, the industry challenge is to produce nutritionally fortified snacks with acceptable physical and sensory properties.
Various researchers have strived to enhance the nutritional profiles of different extruded products by combining cereals, legumes and food sources. Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) is a food legume which contains 24.2% protein, 63.5% carbohydrates, 14.4% dietary fibre and 2.5% fat on a dry matter basis, and has a complementary amino acid pattern to cereal grains [6]. The chemical profile of cowpea includes several bioactive compounds leading to antidiabetic, antihypertensive, anti-hypocholesterolaemia, anticancer and anti-inflammatory effects [7,8,9]. This study aimed to assess the instrumental and sensory properties of extruded ready-to-eat snacks rich in fibre and protein using three different ingredients: rice, cowpea and whey protein concentrate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Extrusion Processing
Rice flour and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) seeds were obtained from Yogijis Food Mart (Christchurch, New Zealand), and whey protein concentrate (WPC) was obtained from Kiwi Nutrition and Health Ltd. (Wellington, New Zealand). Whole grain cowpea seeds were ground in a lab-scale mill (Disc mill, 3310 Perten) with a 1 mm screen size. Rice flour (100–50):cowpea flour(CPF) (10–30):WPC (05–20) composites were prepared by using a lab-scale food mixer, and the flours were then stored at 4 °C until extruded. A co-rotating twin-screw extruder (Clextral BC21 twin-screw co-rotating, self-wiping extruder Clextral; Firminy Cedex, France), was used to obtain rice-based extrudates containing cowpea and WPC in five different combinations and rice was used as a control. Process conditions were screw speed at 252 rpm, die temperature at 111.5 °C, feed rate at 7.98 kg h−1, water rate at 90.67 kg h−1 and die diameter was 3 mm.
2.2. Colour Analysis
The colour of the extruded snack samples was measured in terms of L* (brightness), a* (redness) and b* (yellowness) by using a tristimulus colour analyser (Minolta Chroma Meter CR 210, Minolta Camera Co., Japan). The instrument was calibrated using a standard white tile (L* = 98.03, a* = −0.23, b* = 0.25). Prior to colour analysis, the extrudates were ground using a lab-scale grinder. Total colour change (∆E) and the browning index (BI) were calculated according to the following equations [10].
2.3. Texture Analysis
The crispiness and hardness of extruded snacks were evaluated using a 5-blade Kramer shear cell (HDP/KS5) texture analyser (TA.XT2; Stable Micro Systems, Godalming, UK) equipped with a 50 kg load cell. The shear cell was filled to 50%. The test speed was set at test speed: 2.0 mm/s, and distance: 48 mm. The hardness (maximum force) and crispiness (number of peaks) were recorded [11].
2.4. Sensory Analysis
This research protocol was approved by the Lincoln University Human Ethics Committee (2020-30). The consumer study was conducted at Lincoln University in partitioned booths under cool natural fluorescent lighting. Computerised questionnaires were administered (RedJade® Sensory Solutions, LLC, CA, USA). Consumers (N = 70) were recruited from the staff and postgrad students. Each panellist was served five pieces of six extruded snack formulations, labelled with three-digit codes, following a counter-balanced presentation order. Unsalted crackers and water were provided for palate cleansing.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Check-all-that-apply (CATA) data, penalty analysis (just above right, JAR) and correspondence analysis were performed using XLSTAT statistical software (Addinsoft, NY, USA). Analysis of variance (ANOVA), and Tukey’s tests (p < 0.05) were carried out to determine whether differences existed among treatments in terms of colour, texture and sensory liking scores.
3. Results and Discussion
Instrumental Texture and Colour Analysis
According to Table 1, cowpea and WPC additions yielded instrumental colour changes in the snacks, based on significantly (p < 0.05) different L* a* b* values across treatments. Extrusion treatment affected the colour by decreasing lightness (L*) and increasing the redness or greenness (a*), and yellowness or blueness (b*) in snacks. The browning index was increasing accordingly with the cowpea flour and WPC substitution. The L* was highest for control (75.92) and lowest for 30% CPF + 20% WPC addition (65.75). All cowpea- and whey protein concentrate-added samples were significantly darker than control. A decrease in lightness can be explained by the Maillard reaction between the carbonyl components of the reducing sugars and amines from the protein at high temperatures [12]. Protein aggregation and the formation of disulphides in the same samples correlated with the increasing red colour in snacks formulations [13]. The addition of 10–25% cowpea and 5–15% WPC resulted in no significant differences (p < 0.05) in crispiness compared to control. On the other hand, hardness was increased significantly (p < 0.05) in treatments with 15–30% cowpea incorporations. When increasing the proportion of legume, fibre is also increased in extrudates accordingly, since it interferes with air bubble formation and increases the thickness of the air cell walls, resulting in a harder product [14].

Table 1.
Mean values (and standard deviations) of colour and texture parameters.
The mean scores of sensory likings for extrudates are given in Table 2. Based on the hedonic rating of 1–9, mean scores for sensory attributes >5 were obtained, indicating that appearance, colour, aroma, overall flavour, texture, aftertaste, and overall acceptability attributes were moderately liked by panellists. Overall, cowpea and WPC addition improved the sensory liking scores of the extrudates compared to the control. The results show that there were no significant differences (p < 0.05) in appearance, colour, aroma and overall flavour of all extrudates. In terms of sensory liking scores, 15% CPF and 5% WPC incorporation resulted in more favourable appearance (5.97), colour (6.19), aroma (5.73) and overall flavour (5.89) than the other combinations and the control. Overall flavour scores were indicative that consumers did not detect the beany flavours. This may be due to desirable nutty smells due to browning reactions during the extrusion process and removal of beany flavour from legumes by extrusion [11]. In general, the moderate sensory scores from this study were indicative of the acceptability of cowpea- and WPC-based snack products to consumers.

Table 2.
Mean scores (and standard deviations) of consumer responses based on a 9-point hedonic scale for sensory attributes.
In this case, to find out the degree of correlation between instrumental and sensory attributes, Pearson correlation coefficients were obtained (Supplementary Table S1). There were no significant correlations between instrumental colour and sensory colour (r = 0.68 and 0.87) and crispiness and hardness with sensory texture (r = 0.48 and 0.49). Significant correlations were found between hardness and b* value (r = 0.86, p < 0.05) and crispiness and L* value (R- = 0.64, p > 0.05), respectively. Some studies have shown that instrumental texture analysis correlates better with sensory results of extruded snacks [15]. The texture of a product is a critical sensory attribute of an extruded snack. This outcome may be due to the variation between the selected instrumental technique and the way consumers perceive food characteristics, because the mouthfeel of texture and detecting colour are highly variable among individuals and those factors are strongly influenced by the environment [15]. The principal component analysis (PCA) (Figure 1a) allowed us to discriminate between the formulations and instrumental/sensory variables. The addition of cowpea flour (20–30%) and WPC (10–20%) to the snack promoted an increase in hardness, and a* and b* colour parameters. The snack with substitutions of 10–15% cowpea flour and 5% WPC showed the most liked texture and hedonic scores for most of the sensory attributes.
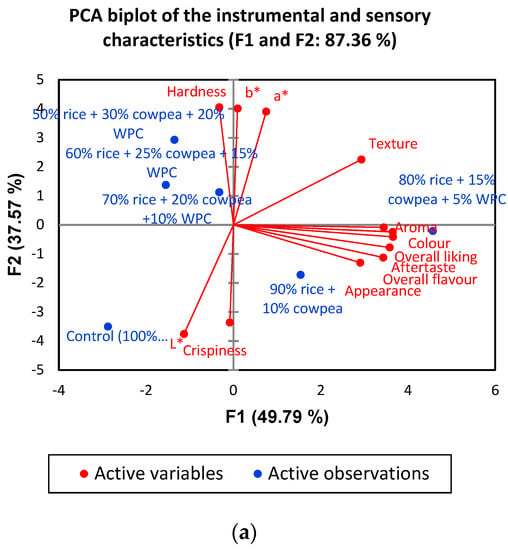
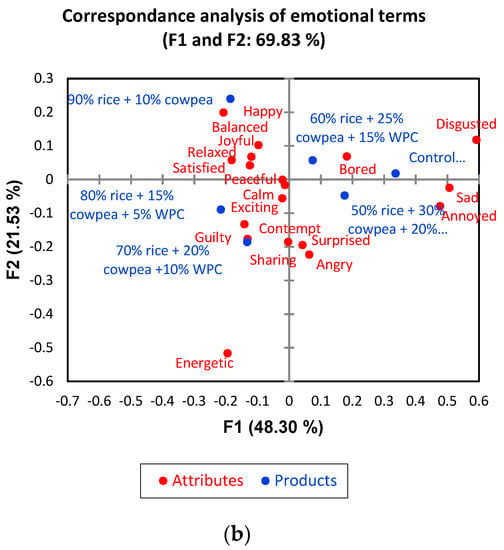
Figure 1.
(a) Principal component analysis (PCA) for the levels of substitution of rice flour by cow−pea flour and WPC (5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and 30% w/w) in relation to the instrumental colour, texture and sensory scores, (b) a bi−plot drawn by the correspondence analysis for check−all−that−apply (CATA) emotions.
A bi-plot of the correspondence analysis (Figure 1b), explaining 69.83% of the total variance, illustrates the associations between samples and the emotional attributes. More specifically, 10–15% cowpea and 5% WPC incorporated into snacks were associated with “happy”, “balanced”, “joyful”, “relaxed”, “satisfied”, “peaceful”, “calm” and “exciting”. Based on the CATA emotional terms selected by panellists, extruded snacks samples could be classified into two groups, i.e., (1) 10–20% cowpea and 5–10% WPC, and (2) 25–30% cowpea and 15–20% WPC, mainly by the X-axis (F1) that explains 48.30% of the total variance. According to principal coordinate analysis (PCoA; Figure 2), overall liking was associated with the attributes firm, crispy, crunchy and sticky.
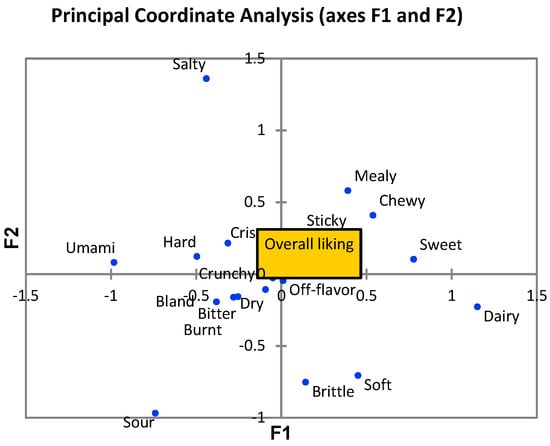
Figure 2.
Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) for overall liking and CATA attributes.
The penalty analysis performed for colour, crispiness and hardness (Supplementary Figure S1) with JAR scale values of 1–3 categorised them as “Too Little,” “Just About Right” and “Too Much,” respectively. Overall, the percentage of consumers that rated the attributes as just about right increased in all categories with cowpea and WPC addition. Similarly, for hedonic scores, 15% cowpea flour and 5% WPC addition achieved the highest percentages for JAR colour and crispiness, with 89% for hardness.
4. Conclusions
A cowpea–WPC-based gluten-free extruded snack containing 10–15% cowpea flour and 5% WPC was found to exhibit the most desirable consumer acceptability properties. The study demonstrated that extrusion cooking could be used to develop acceptable and nutritious composite snacks from protein-rich legumes. Cowpea flours and whey protein concentrate considerably increased the protein, fibre and mineral content in the snack when compared to extruded plain rice snacks. Thus, ingredient complementation can be strategically applied in the development of extruded bean-based food products to boost nutritional quality and sensory acceptability.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2504-3900/70/1/95/s1, Table S1: Correlation values between instrumental and sensory attributes, Figure S1: JAR results from consumer acceptance test for extrudates for (a) colour; (b) crispiness; (c) hardness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, supervision, review and editing: C.S.B., M.A.B. and D.D.T.; conceptualization, conducting experiments, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation: H.N.N.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Human Ethics Committee of Lincoln University (Approval: 2020-30).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Beck, S.M.; Knoerzer, K.; Foerster, M.; Mayo, S.; Philipp, C.; Arcot, J. Low moisture extrusion of pea protein and pea fibre fortified rice starch blends. J. Food Eng. 2018, 231, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, M.; Pathania, S.; Sharma, A. LWT—Food Science and Technology Optimization of the extrusion process for development of high fi bre soybean-rice ready-to-eat snacks using carrot pomace and cauli fl ower trimmings. LWT 2016, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojceska, V.; Ainsworth, P.; Plunkett, A.; Ibanoǧlu, Ş. The advantage of using extrusion processing for increasing dietary fibre level in gluten-free products. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, C.; Pereira, E.; Barros, L.; Alves, M.J.; Calhelha, R.C.; Guillamón, E.; Pedrosa, M.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Healthy novel gluten-free formulations based on beans, carob fruit and rice: Extrusion effect on organic acids, tocopherols, phenolic compounds and bioactivity. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, C.; Brennan, M.; Derbyshire, E.; Tiwari, B.K. Effects of extrusion on the polyphenols, vitamins and antioxidant activity of foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Cabrejas, M. Legumes: Nutritional Quality, Processing and Potential Health Benefits; Martín-Cabrejas, M., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, S. Nutrition and the prevention of cancer. J. Fam. Health Care 2006, 16, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hachibamba, T.; Dykes, L.; Awika, J.; Minnaar, A.; Duodu, K.G. Effect of simulated gastrointestinal digestion on phenolic composition and antioxidant capacity of cooked cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) varieties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 2638–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojwang, L.O.; Banerjee, N.; Noratto, G.D.; Angel-Morales, G.; Hachibamba, T.; Awika, J.M.; Mertens-Talcott, S.U. Polyphenolic extracts from cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) protect colonic myofibroblasts (CCD18Co cells) from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation-modulation of microRNA 126. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, S.A.; Kumar, P. Influence of different mixtures of ingredients on the physicochemical, nutritional and pasting properties of extruded snacks. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2016, 10, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto, M.; Farroni, A.; Rodríguez, S.D.; Schoenlechner, R.; Schleining, G.; del Pilar Buera, M. Assessing changes in enriched maize flour formulations after extrusion by means of FTIR, XRD, and chemometric analysis. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, S. Amino acids, peptides, and proteins. In Food Chemistry, 3rd ed.; CRC press Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 412–413. [Google Scholar]
- Kristiawan, M.; Chaunier, L.; Della Valle, G.; Ndiaye, A.; Vergnes, B. Trends in Food Science & Technology Modeling of starchy melts expansion by extrusion. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 48, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Robin, F.; Dubois, C.; Curti, D.; Schuchmann, H.P.; Palzer, S. Effect of wheat bran on the mechanical properties of extruded starchy foams. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2880–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, A.M.; Conti-Silva, A.C. Texture profile and correlation between sensory and instrumental analyses on extruded snacks. J. Food Eng. 2014, 121, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).