Elucidation of the Volatilome of Packaged Spanish-Style Green Olives of Conservolea and Halkidiki Varieties Using SPME-GC/MS †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Olive Samples and Preparation
2.2. Volatile Compound Extraction Using Solid Phase Microextraction (SPME)
2.3. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
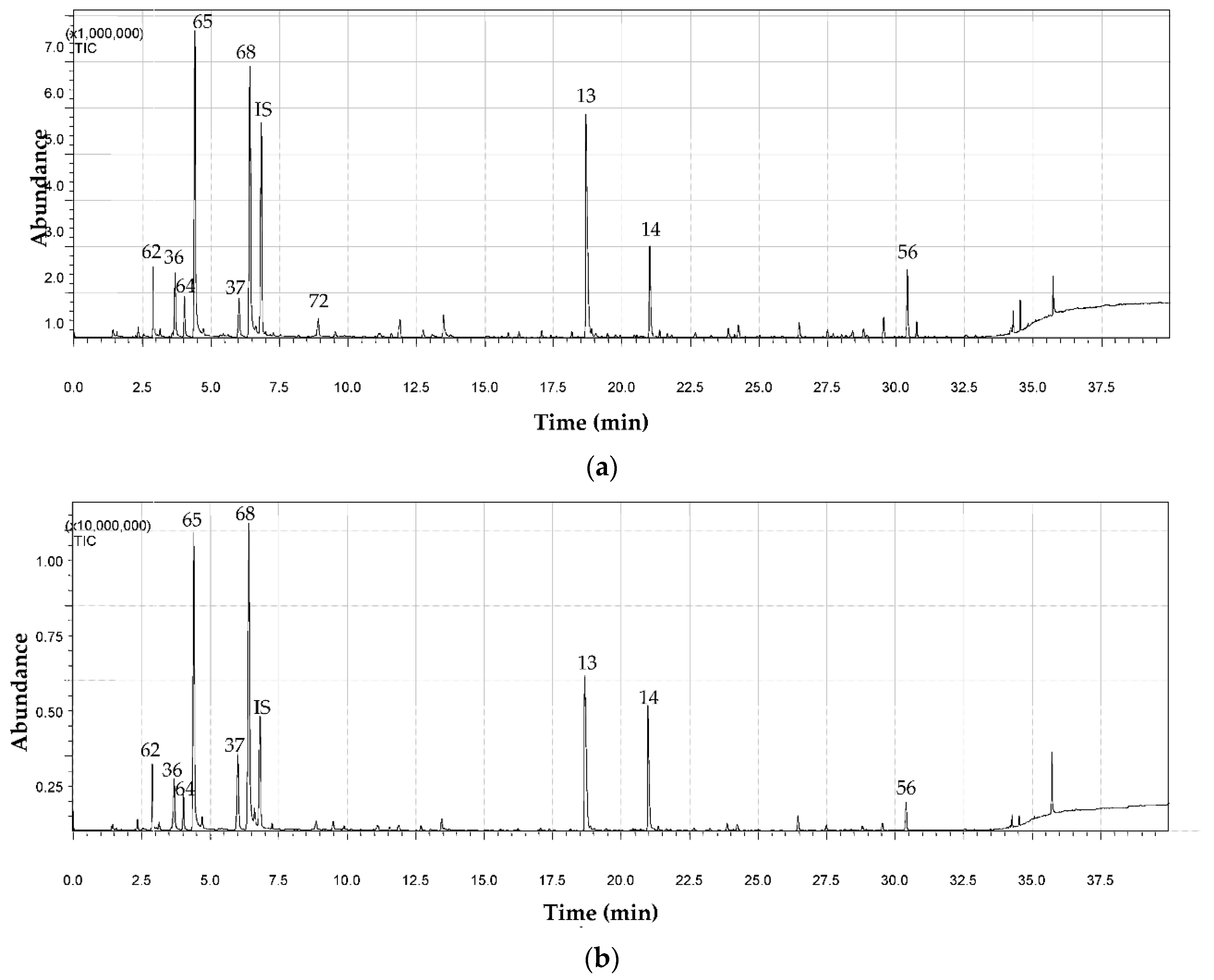
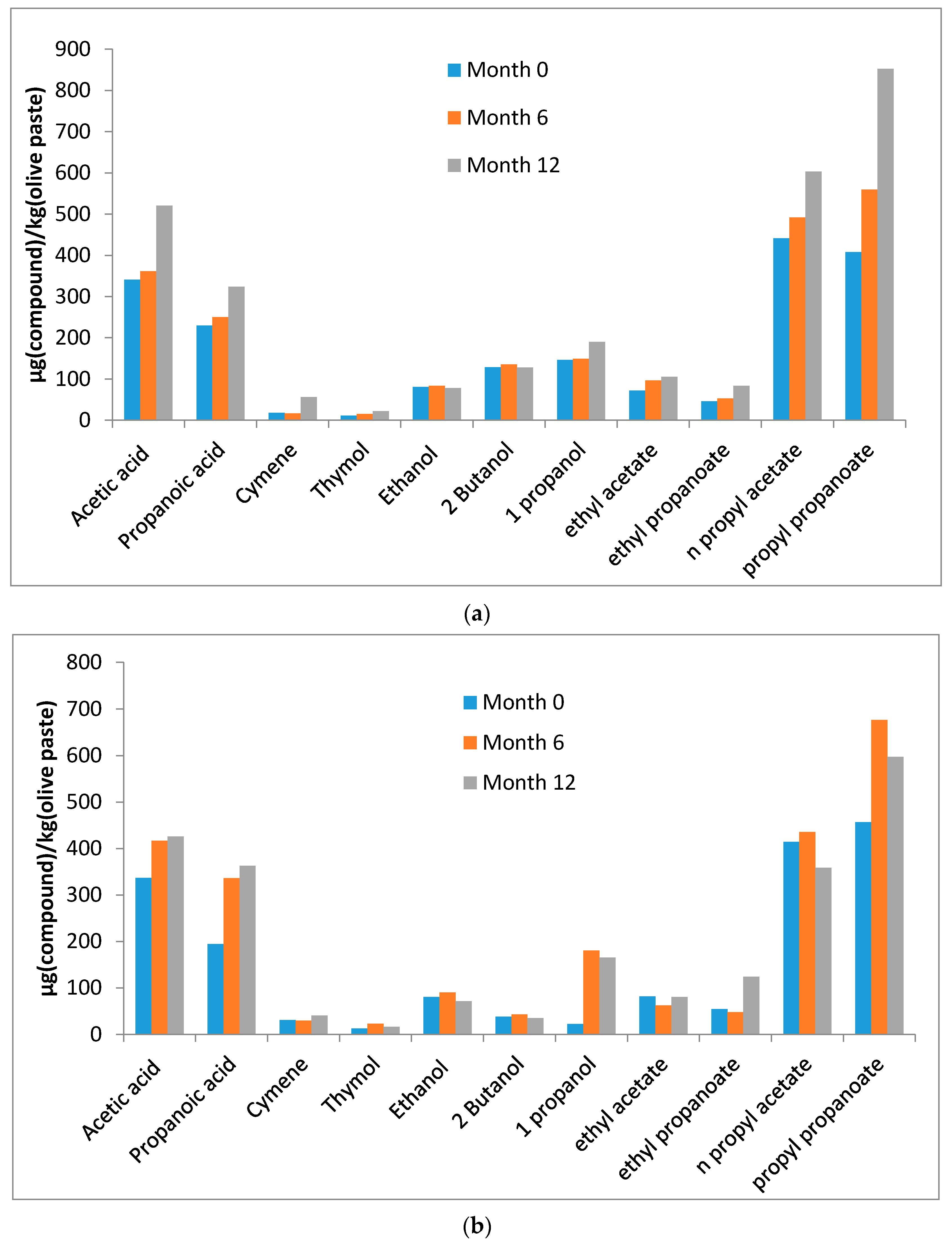
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panagou, E.Z.; Schillingerb, U.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Microbiological and biochemical profile of cv. Conservolea naturally black olives during controlled fermentation with selected strains of lactic acid bacteria. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DOEPEL (Interprofessional Table Olives Association). Greek Table Olives. Our National Treasure. Available online: https://doepel.gr/?page_id=14869&lang=en_US (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Garrido-Fernández, A.; Fernández-Díez, M.J.; Adams, M.R. Table Olives: Production and Processing; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Garrido-Fernández, A.; Montaño, A.; Sánchez-Gómez, A.H.; Cortés-Delgado, A.; López-López, A. Volatile profiles of green Spanish-style table olives: Application of compositional data analysis for the segregation of their cultivars and production areas. Talanta 2017, 169, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Sun, M.; Song, S.; Zhuang, H.; Yao, L. Gas chromatography for food quality evaluation. In Evaluation Technologies for Food Quality; Zhong, J., Wang, X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 219–265. [Google Scholar]
- Pawliszyn, J. Solid Phase Microextraction: Theory and Practice; Wiley: New Jersey, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Vas, G.; Vekey, K. Solid-phase microextraction: A powerful sample preparation tool prior to mass spectrometric analysis. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 39, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatini, N.; Marsilio, V. Volatile compounds in table olives (Olea Europaea L., Nocellara del Belice cultivar). J. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.H.; De Castro, A.; Lopez-Lopez, A.; Cortes-Delgado, A.; Beato, V.M.; Montano, A. Retention of color and volatile compounds of Spanish-style green table olives pasteurized and stored in plastic containers under conditions of constant temperature. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, R.F. Fermentation microorganisms and flavor changes in fermented foods. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagou, E.Z.; Hondrodimou, O.; Mallouchos, A.; Nychas, G.-J.E. A study on the implications of NaCl reduction in the fermentation profile of Conservolea natural black olives. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano, A.; Sanchez, A.H.; Casado, F.J.; De Castro, A.; Rejano, L. Chemical profile of industrially fermented green olives of different varieties. J. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, N.; Perri, E.; Marsilio, V. An investigation on molecular partition of aroma compounds in fruit matrix and brine medium of fermented table olives. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagou, E.Z.; Tassou, C.C. Changes in volatile compounds and related biochemical profile during controlled fermentation of cv. Conservolea green olives. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassou, C.C.; Panagou, E.Z.; Katsaboxakis, K.Z. Microbiological and physicochemical changes of naturally black olives fermented at different temperatures and NaCl levels in the brines. Food Microbiol. 2002, 19, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, H.P.; Etchells, J.L.; Bell, T.A. Vapor analysis of fermented Spanish-type green olives by gas chromatography. J. Food Chem. 1969, 34, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nanou, A.; Mallouchos, A.; Panagou, E.Z. Elucidation of the Volatilome of Packaged Spanish-Style Green Olives of Conservolea and Halkidiki Varieties Using SPME-GC/MS. Proceedings 2021, 70, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07629
Nanou A, Mallouchos A, Panagou EZ. Elucidation of the Volatilome of Packaged Spanish-Style Green Olives of Conservolea and Halkidiki Varieties Using SPME-GC/MS. Proceedings. 2021; 70(1):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07629
Chicago/Turabian StyleNanou, Alexandra, Athanasios Mallouchos, and Efstathios Z. Panagou. 2021. "Elucidation of the Volatilome of Packaged Spanish-Style Green Olives of Conservolea and Halkidiki Varieties Using SPME-GC/MS" Proceedings 70, no. 1: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07629
APA StyleNanou, A., Mallouchos, A., & Panagou, E. Z. (2021). Elucidation of the Volatilome of Packaged Spanish-Style Green Olives of Conservolea and Halkidiki Varieties Using SPME-GC/MS. Proceedings, 70(1), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07629





