Techno-Functional Properties of New Andean Ingredients: Maca (Lepidium meyenii) and Amaranth (Amaranthus caudatus) †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
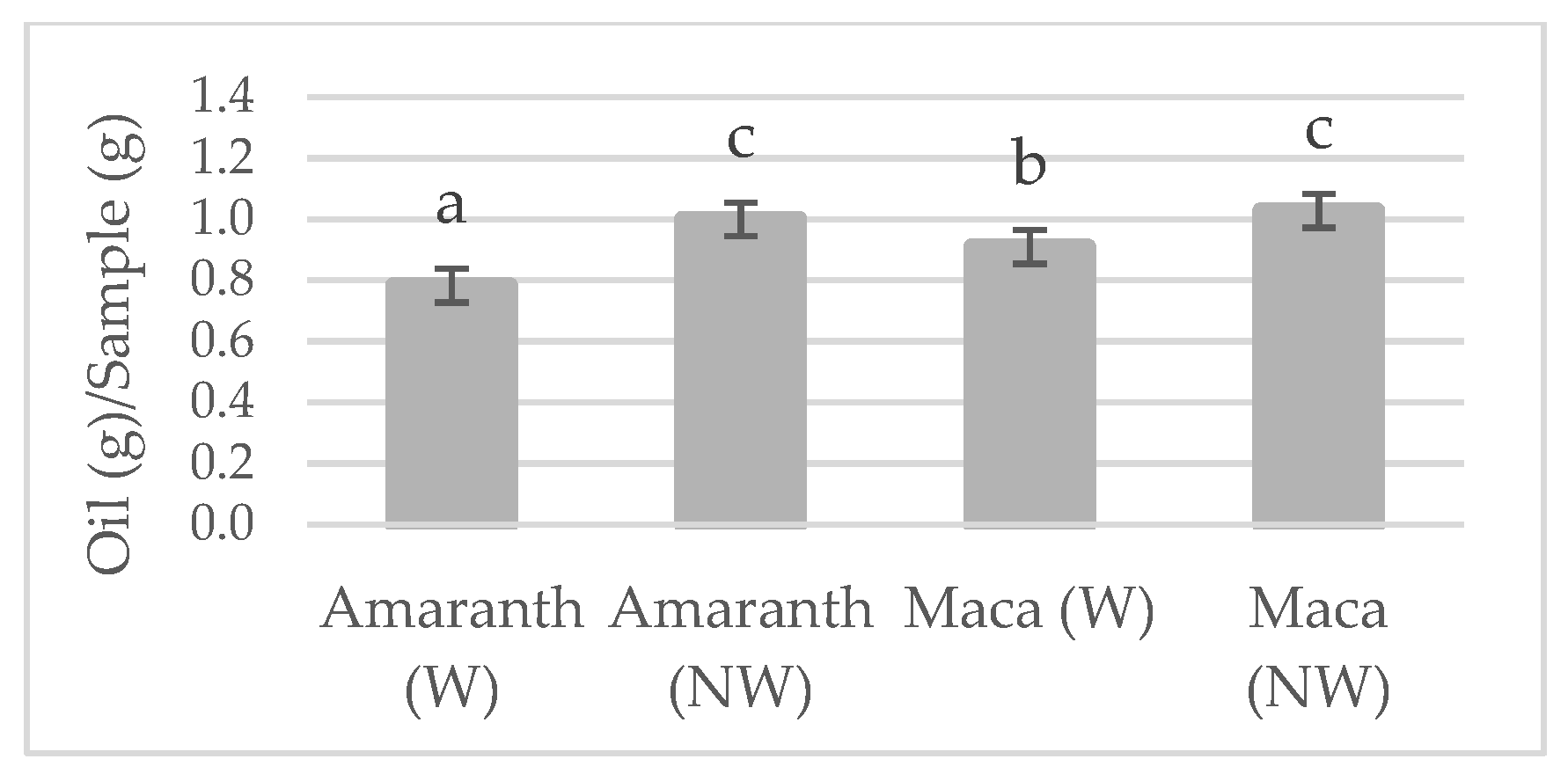
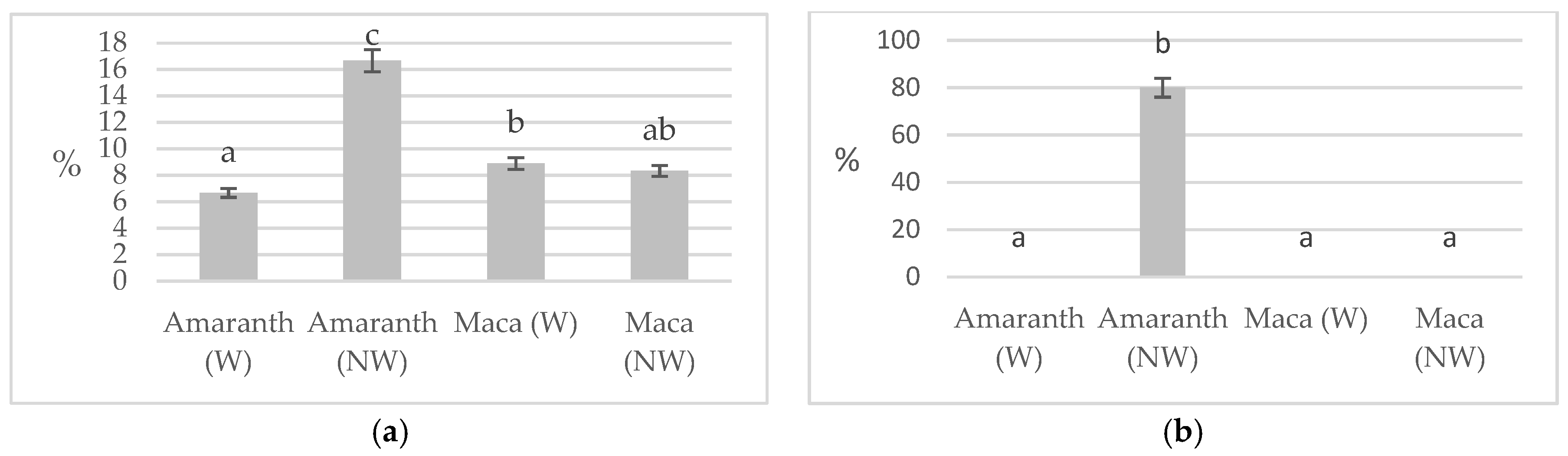
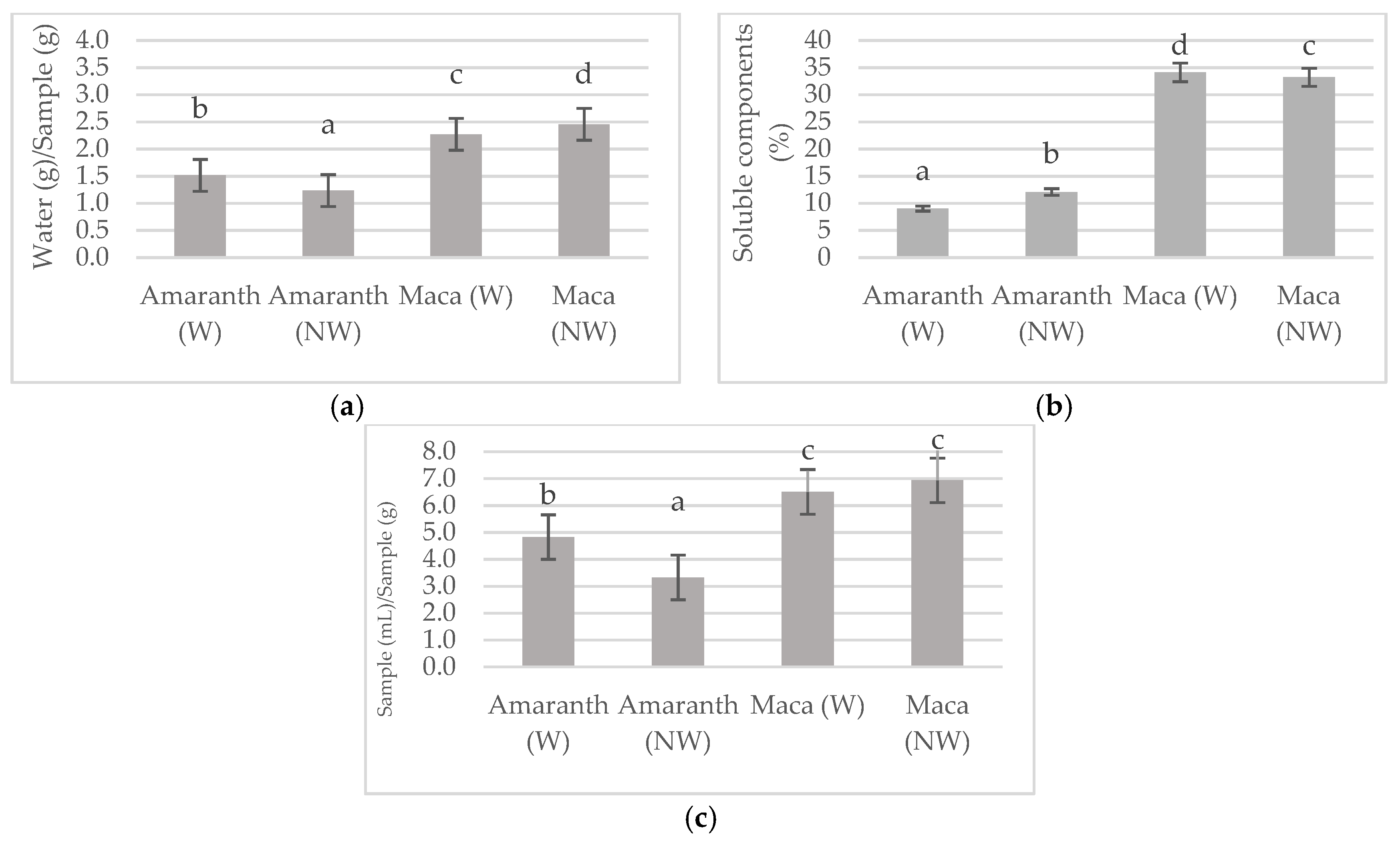
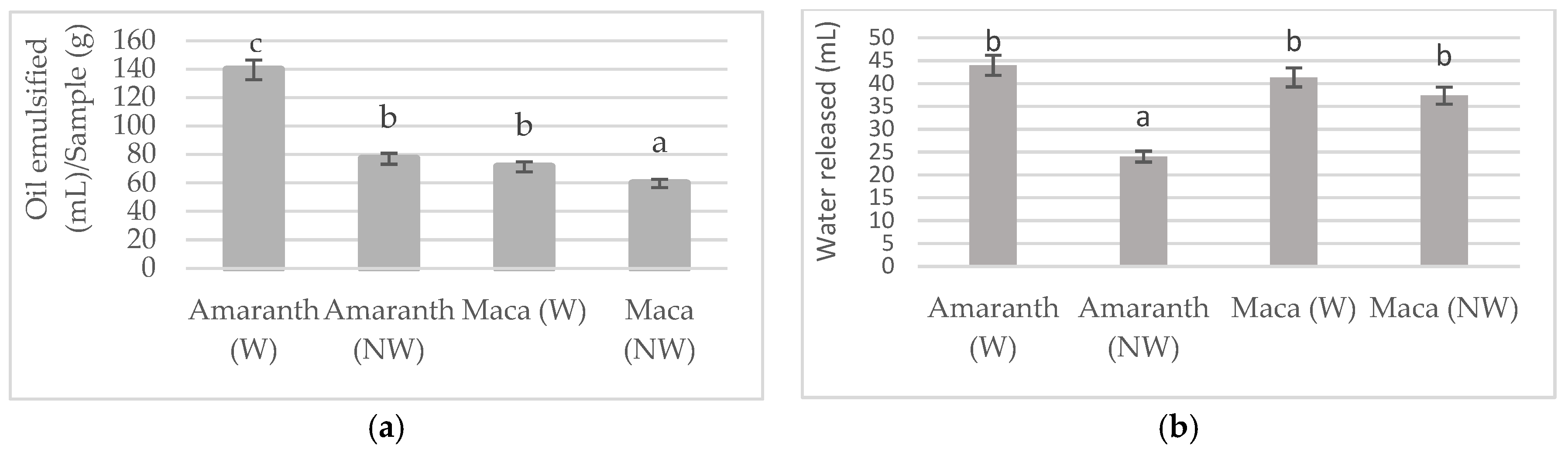
2.2. Techno-Functional Properties
2.3. Particle Size
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loyer, J.; Knight, C. Selling the “Inca superfood”: Nutritional primitivism in superfoods books and maca marketing. Food Cult. Soc. 2018, 21, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A.; Rana, J.C. Physicochemical, Pasting, and Functional Properties of Amaranth Seed Flours: Effects of Lipids Removal. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C1271–C1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chain, F.E.; Grau, A.; Martins, J.; Catalan, C.A. Macamides from wild ‘Maca’, Lepidium meyenii Walpers (Brassicaceae). Phytochem. Lett. 2014, 8, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Muhammad, I.; Dunbar, D.C.; Mustafa, J.; Khan, I.A. New Alkamides from Maca (Lepidium meyenii). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corke, H.; Cai, Y.Z.; Wu, H.X. Amaranth: Overview. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Duan, Z.; Zhu, S.; Fan, L. The Composition Analysis of Maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.) from Xinjiang and Its Antifatigue Activity. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 2904951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, F. Chemical composition and health effects of maca (Lepidium meyenii). Food Chem. 2019, 288, 422–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, S. Antioxidants in Maca (Lepidium meyenii) as a Supplement in in Nutrition. In Antioxidants in Foods and Its Applications; Shalaby, E., Ghada, G., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 137–154. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Fan, L. The Nutritional Composition of Maca in Hypocotyls (Lepidium meyenii Walp.) Cultivated in Different Regions of China. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 3749627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachiguma, N.A.; Mwase, W.; Maliro, M.; Damaliphetsa, A. Chemical and Mineral Composition of Amaranth (Amaranthus L.) Species Collected from Central Malawi. J. Food Res. 2015, 4, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamsen, M.; Shekarchizadeh, H.; Soltanizadeh, N. Evaluation of wheat flour substitution with amaranth flour on chicken nugget properties. LWT 2018, 91, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Singh, P.; Shevkani, K.; Virdi, A.S. Amaranth: Potential Source for Flour Enrichment. In Flour and Breads and Their Fortification in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, M.; Xin, X.; Lai, F.; Wu, H. Physicochemical and functional properties of a protein isolate from maca (Lepidium meyenii) and the secondary structure and immunomodulatory activity of its major protein component. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2894–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.A.; De Monredon, F.D.; Dysseler, P.; Guillon, F.; Amado, R.; Thibault, J.-F. Hydration Properties of Dietary Fibre and Resistant Starch: A European Collaborative Study. LWT 2000, 33, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, S.K.; Salunkhe, D.K. Functional Properties of the Great Northern Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Proteins: Emulsion, Foaming, Viscosity, and Gelation Properties. J. Food Sci. 1981, 46, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A.; Rana, J.C. Structural and functional characterization of kidney bean and field pea protein isolates: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Saxena, D.; Singh, S. Total dietary fibre and antioxidant activity of gluten free cookies made from raw and germinated amaranth (Amaranthus spp.) flour. LWT 2015, 63, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, F.; Novillo, G.; Villacrés, E.; Rosell, C.M. Evaluation of the physicochemical and nutritional changes in two amaranth species (Amaranthus quitensis and Amaranthus caudatus) after germination. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes-López, O.; Schevenin, M.L.; Hernández-López, D.; Cárabez-Trejo, A. Amaranth Starch—Isolation and Partial Characterization. Starch Stärke 1989, 41, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Rana, J.C.; Kaur, A. Relationship between physicochemical and functional properties of amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) protein isolates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 49, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, L.; Zha, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, B. Physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fiber from maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.) liquor residue. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, M.; Lucas-Gonzales, R.; Ricci, A.; Fontecha, J.; Fernández-López, J.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A.; Viuda-Martos, M. Chemical, fatty acid, polyphenolic profile, techno-functional and antioxidant properties of flours obtained from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) seeds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 111, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.E.A. Chapter 1 Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 58, pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, N.; Ureta, M.M.; Guerrero-Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Zavaglia, A. Nutritional and technological properties of a quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) spray-dried powdered extract. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alarcón-García, M.A.; Perez-Alvarez, J.A.; López-Vargas, J.H.; Pagán-Moreno, M.J. Techno-Functional Properties of New Andean Ingredients: Maca (Lepidium meyenii) and Amaranth (Amaranthus caudatus). Proceedings 2021, 70, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07744
Alarcón-García MA, Perez-Alvarez JA, López-Vargas JH, Pagán-Moreno MJ. Techno-Functional Properties of New Andean Ingredients: Maca (Lepidium meyenii) and Amaranth (Amaranthus caudatus). Proceedings. 2021; 70(1):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07744
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlarcón-García, Miguel Angel, Jose Angel Perez-Alvarez, Jairo Humberto López-Vargas, and Maria Jesús Pagán-Moreno. 2021. "Techno-Functional Properties of New Andean Ingredients: Maca (Lepidium meyenii) and Amaranth (Amaranthus caudatus)" Proceedings 70, no. 1: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07744
APA StyleAlarcón-García, M. A., Perez-Alvarez, J. A., López-Vargas, J. H., & Pagán-Moreno, M. J. (2021). Techno-Functional Properties of New Andean Ingredients: Maca (Lepidium meyenii) and Amaranth (Amaranthus caudatus). Proceedings, 70(1), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07744




