Functionalisation of Pectin by Ultra High Pressure Homogenisation †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Sample Preparation and UHPH Treatment
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2.2. UHPH Treatment
2.2.3. Gel Preparation
2.3. Pectin Characterization
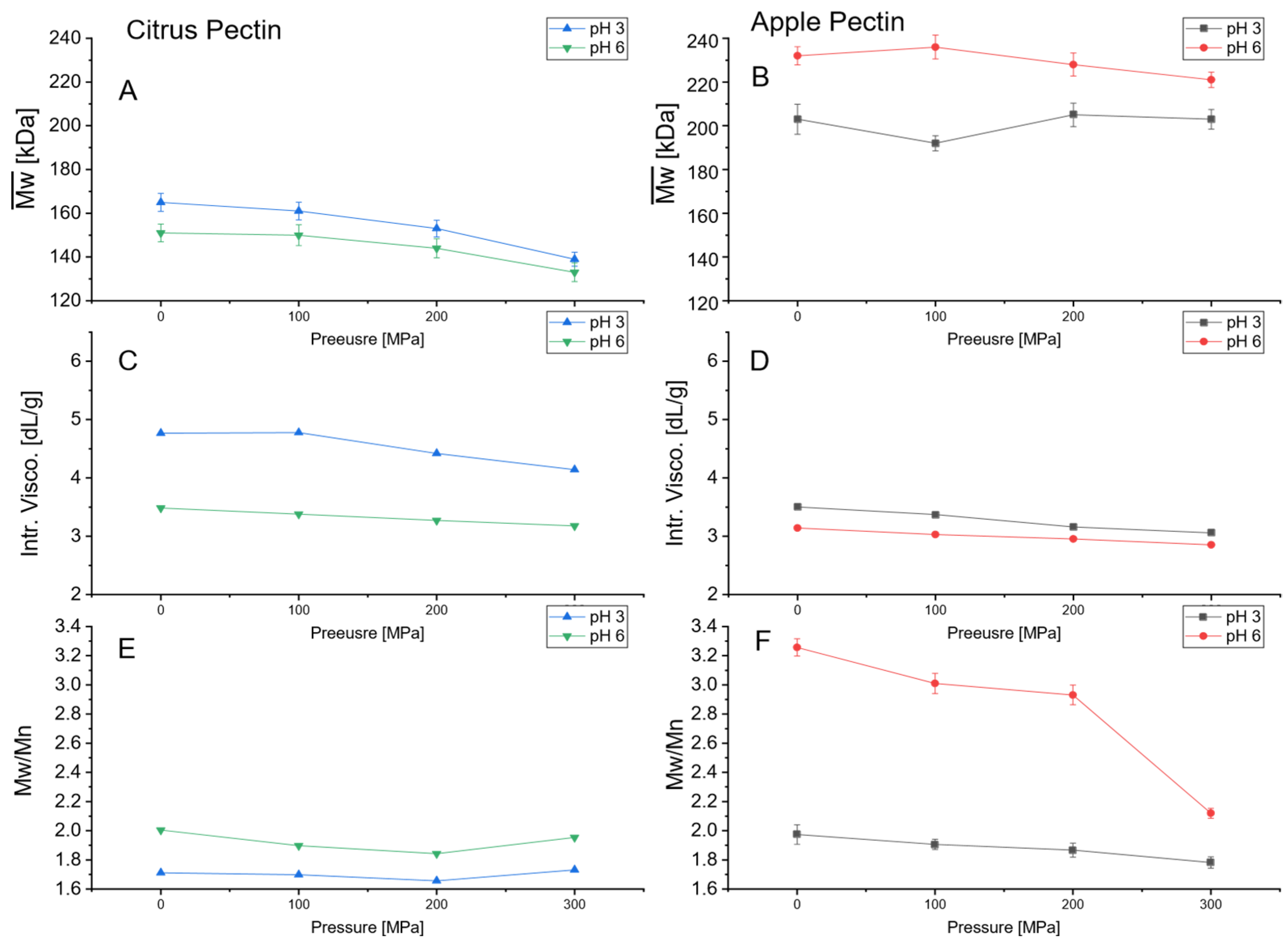
2.3.1. Molecular Weight, Dispersity and Intrinsic Viscosity Measurements
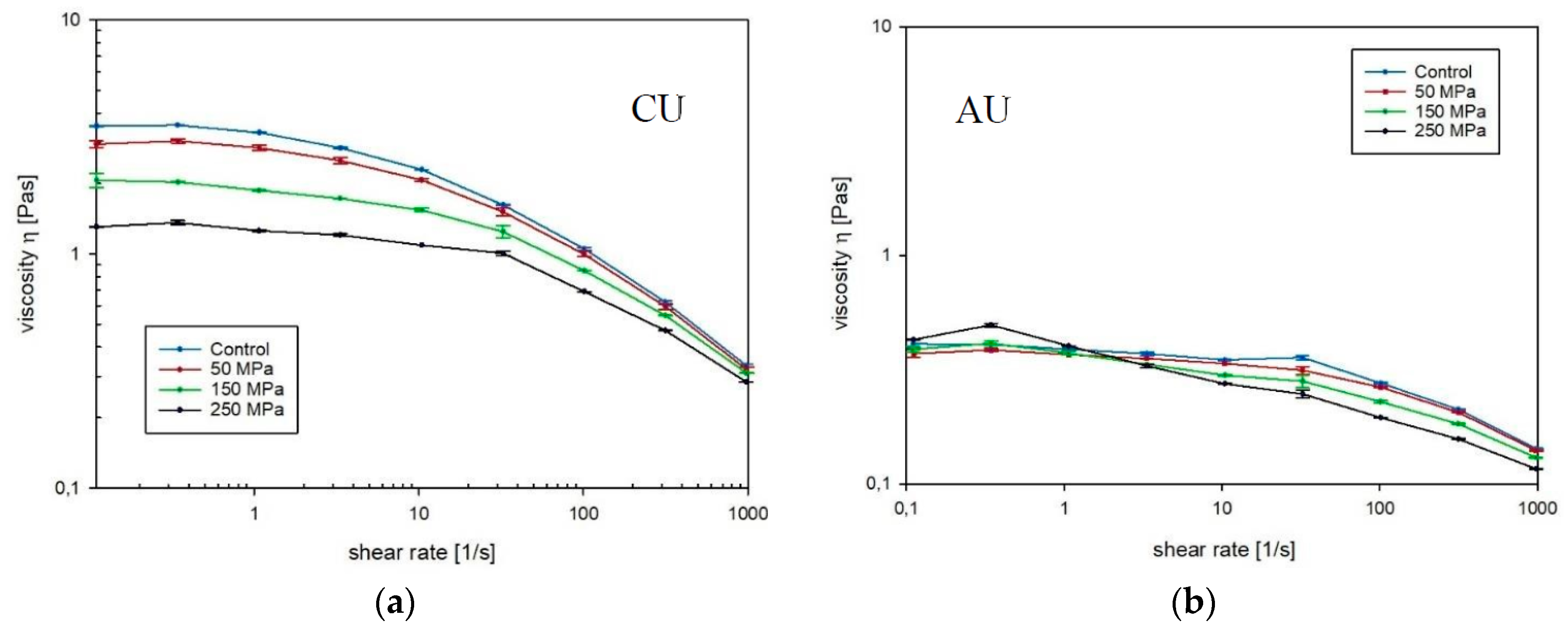
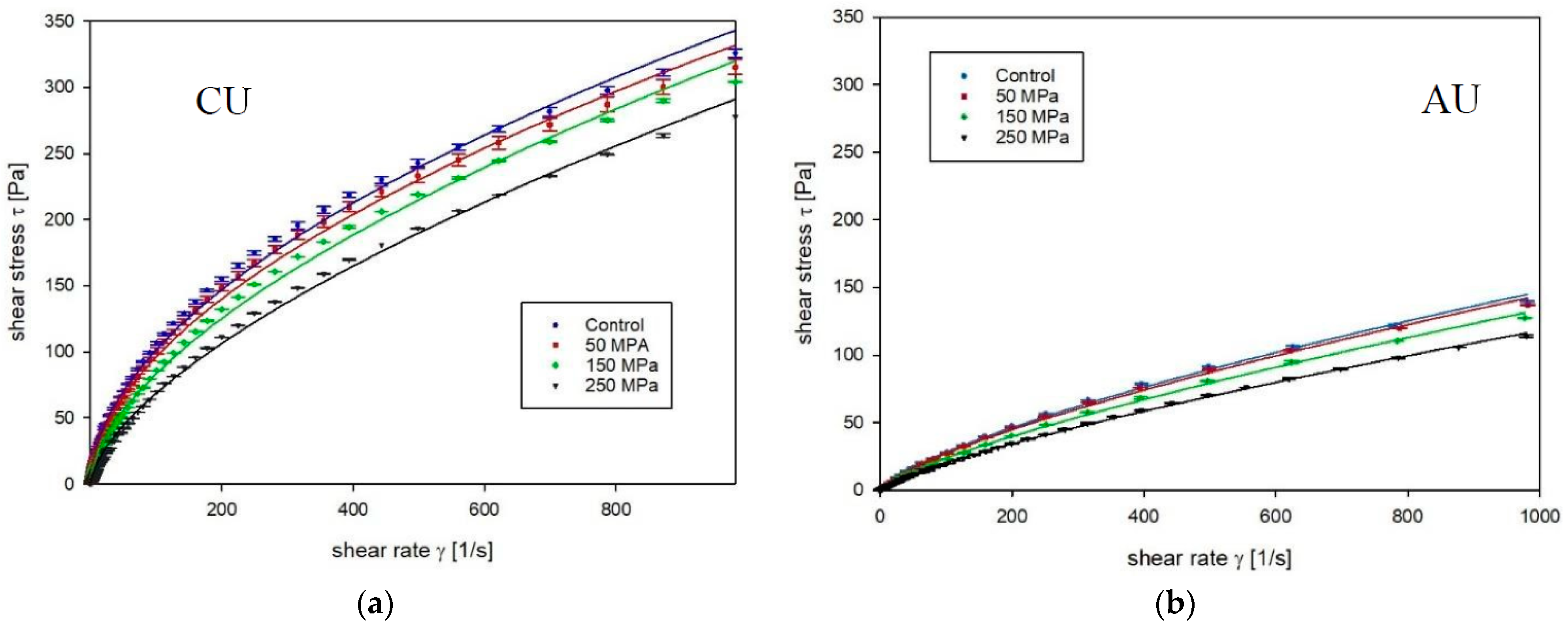
2.3.2. Apparent Viscosity
2.3.3. Gel Strenght
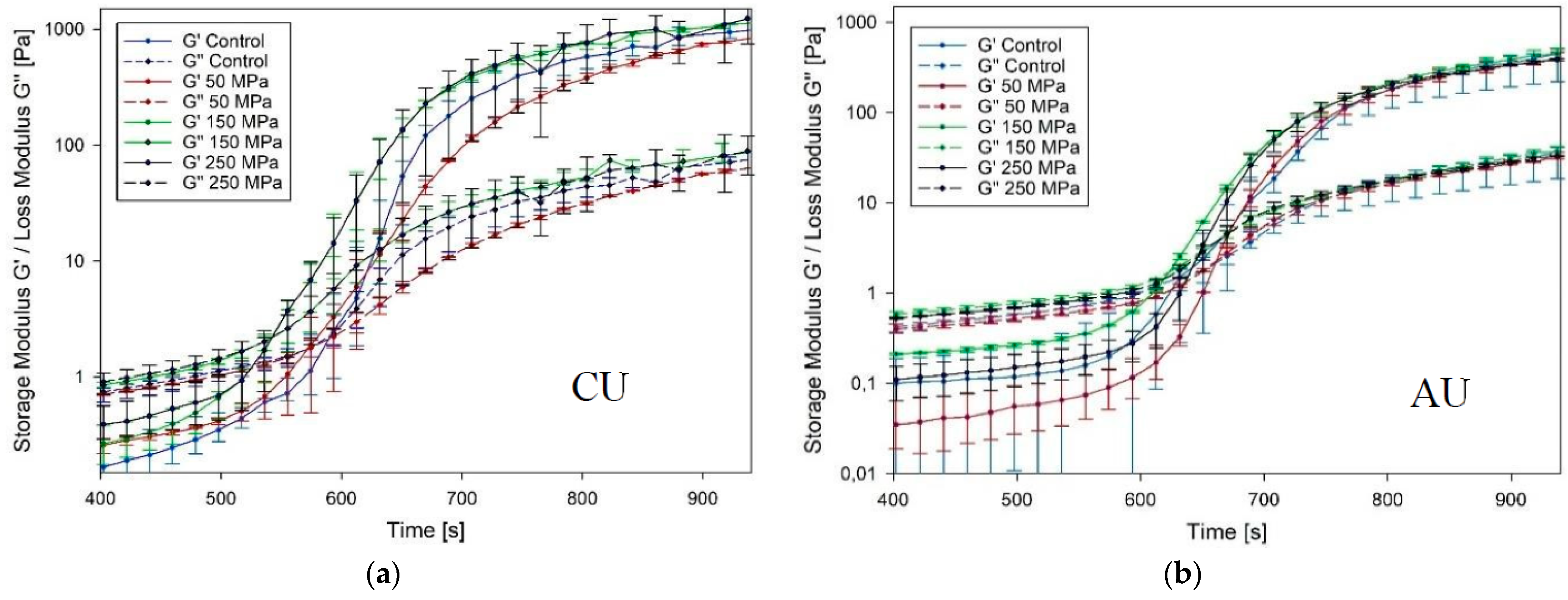
2.3.4. Gelation Speed and Melting Point (Sol-Gel-Sol Transition)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Apparent Viscosity
3.2. Impact of UHPH at pH 3 and pH 6 on Pectin Molecular Characteristics
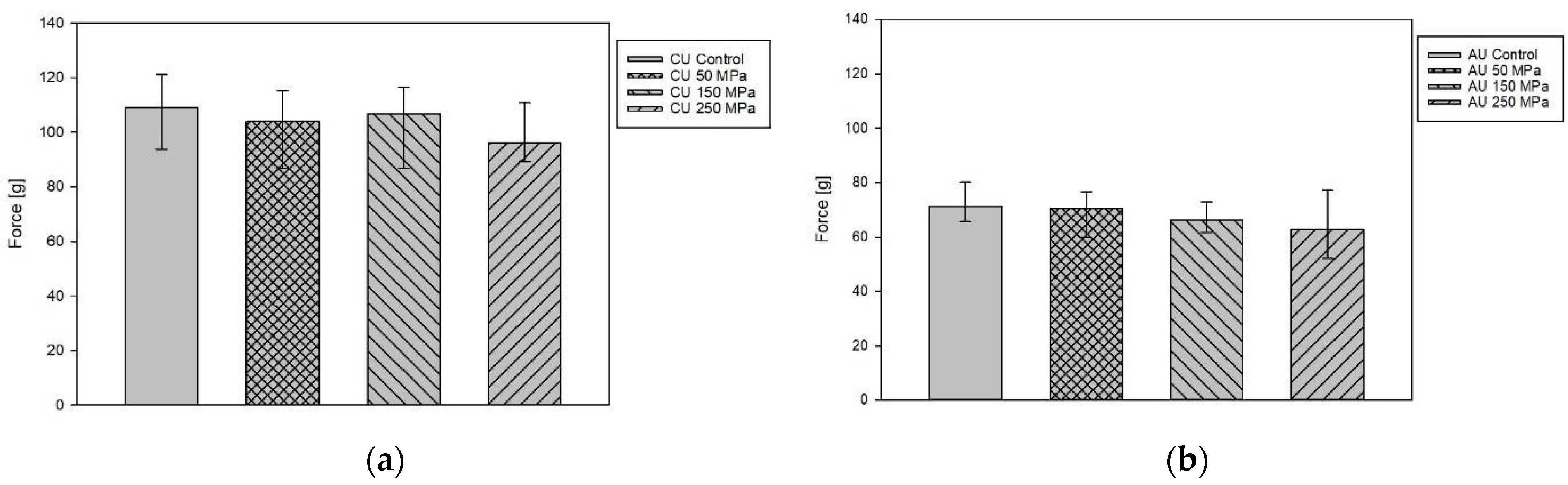
3.3. Gel Strenght
3.4. Gelation Speed and Melting Point
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B

References
- Willats, W.; Knox, J.; Mikkelsen, J. Pectin: New insights into an old polymer are starting to gel. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marić, M.; Grassino, A.; Zhu, Z.; Barba, F.; Brnčić, M.; Rimac Brnčić, S. An overview of the traditional and innovative approaches for pectin extraction from plant food wastes and by-products: Ultrasound-, microwaves-, and enzyme-assisted extraction. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 76, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.; Okun, Z.; Shpigelman, A. High-Pressure Homogenization: Principles and Applications beyond Microbial Inactivation. Food Eng. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhang, W.; Lan, X.; Gong, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure and high pressure homogenization processing on characteristics of potato peel waste pectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shpigelman, A.; Kyomugasho, C.; Christiaens, S.; Van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M. The effect of high pressure homogenization on pectin: Importance of pectin source and pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Bi, J.; Yi, J.; Peng, J.; Ning, C.; Wellala, C.; Zhang, B. Effects of high pressure homogenization on pectin structural characteristics and carotenoid bioaccessibility of carrot juice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirug, L.; Okun, Z.; Ramon, O.; Shpigelman, A. Iron ions as mediators in pectin-flavonols interactions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelatine.org. 2020. Available online: https://www.gelatine.org/fileadmin/user_upload/gme_content/GME_Statements/GME_S_Monograph_Standardised_Methods_for_the_Testing_of_Edible_Gelatine.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Kravtchenko, T.; Voragen, A.; Pilnik, W. Analytical comparison of three industrial pectin preparations. Carbohydr. Polym. 1992, 18, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Consistency Index K [Pasn] | Flow Index n [-] | R² [-] |
|---|---|---|---|
| CU untreated | 8.659 ± 0.236 | 0.534 ± 0.004 | 0.996 |
| CU 50 | 7.914 ± 0.23 | 0.542 ± 0.005 | 0.995 |
| CU 150 | 5.507 ± 0.154 | 0.590 ± 0.005 | 0.996 |
| CU 250 | 3.710 ± 0.098 | 0.633 ± 0.004 | 0.997 |
| AU untreated | 0.337 ± 0.005 | 0.816 ± 0.002 | 0.999 |
| AU 50 | 0.291 ± 0.004 | 0.829 ± 0.002 | 0.999 |
| AU 150 | 0.218 ± 0.004 | 0.855 ± 0.003 | 0.999 |
| AU 250 | 0.171 ± 0.003 | 0.871 ± 0.003 | 0.999 |
| Indicators | Sample Name | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CU Untreated | CU 50 | CU 150 | CU 250 | |
| Gelation Temperature [°C] | 59.2 ± 1.10 | 63.2 ± 1.23 | 62.4 ± 0.87 | 62.5 ± 1.07 |
| Gelation time [s] | 586.4 ± 14.58 | 572.1 ± 28.12 | 547.7 ± 10.52 | 546.9 ± 13.29 |
| Gelation Temperature [°C] | AU Untreated | AU 50 | AU 150 | AU 250 |
| 54.8 ± 1.7 | 52.1 ± 0.066 | 57 ± 0.435 | 54.7 ± 0.528 | |
| Gelation time [s] | 639.2 ± 21.02 | 656.5 ± 2.59 | 616.4 ± 2.16 | 644.6 ± 2.885 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zdravkovic, M.; Ebert, E.; Panz, C.; Okun, Z.; Endreß, H.-U.; Shpigelman, A.; Aganovic, K. Functionalisation of Pectin by Ultra High Pressure Homogenisation. Proceedings 2021, 70, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07752
Zdravkovic M, Ebert E, Panz C, Okun Z, Endreß H-U, Shpigelman A, Aganovic K. Functionalisation of Pectin by Ultra High Pressure Homogenisation. Proceedings. 2021; 70(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07752
Chicago/Turabian StyleZdravkovic, Milena, Edward Ebert, Chen Panz, Zoya Okun, Hans-Ulrich Endreß, Avi Shpigelman, and Kemal Aganovic. 2021. "Functionalisation of Pectin by Ultra High Pressure Homogenisation" Proceedings 70, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07752
APA StyleZdravkovic, M., Ebert, E., Panz, C., Okun, Z., Endreß, H.-U., Shpigelman, A., & Aganovic, K. (2021). Functionalisation of Pectin by Ultra High Pressure Homogenisation. Proceedings, 70(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07752







