Applying Nanotechnology to Okara for Developing Soy Protein Gel-Based Foods †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of WG-Treated Okara
2.3. Viscosity
2.4. Particle Size Distribution (PSD)
2.5. Gel Preparations
2.6. Compression Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. PSD, Viscosity, and Dispersion Ability of WG-Treated Okara
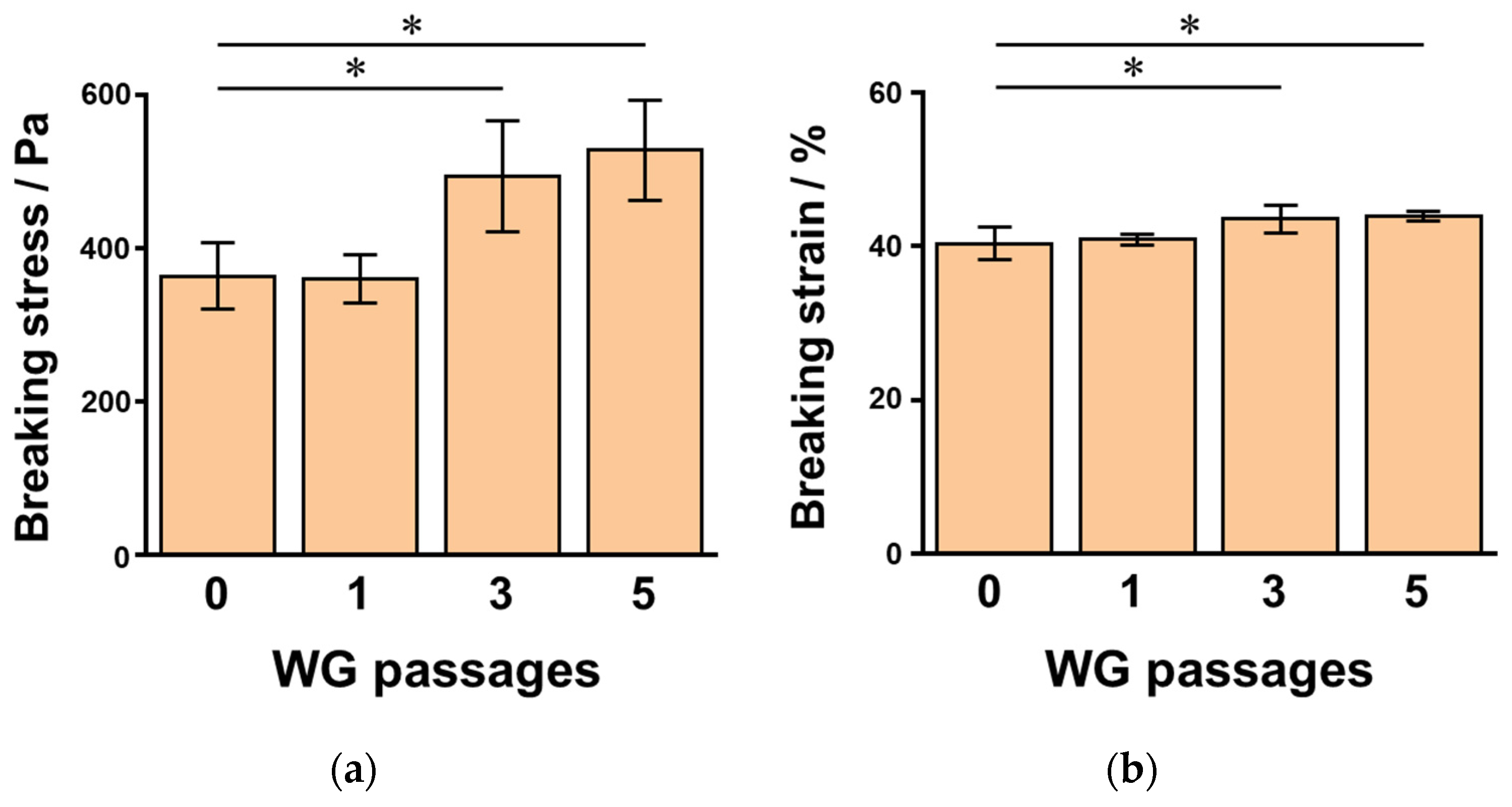
3.2. Effects of Adding WG-Treated Okara on SPI Gels
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajinipriya, M.; Nagalakshmaiah, M.; Robert, M.; Elkoun, S. Importance of agricultural and industrial waste in the field of nanocellulose and recent industrial developments of wood based nanocellulose: A review. ACS Sust. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2807–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, T.; Arai, Y.; Yano, H.; Aoki, T.; Kurihara, S.; Hirano, R.; Nishinari, K. Improved physicochemical and functional properties of okara, a soybean residue, by nanocellulose technologies for food development—A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 105964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y.; Nagano, T.; Guo, S.; Wang, R. Soy as a food ingredient. In Proteins in Food Processing, 2nd ed.; Yada, R.Y., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 149–186. [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto, S.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Yano, H. Nano-fibrillation of pulp fibers for the processing of transparent nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. A. 2007, 89, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.H.; Chien, J.T.; Kuo, M.I. Ultra high pressure homogenized soy flour for tofu making. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
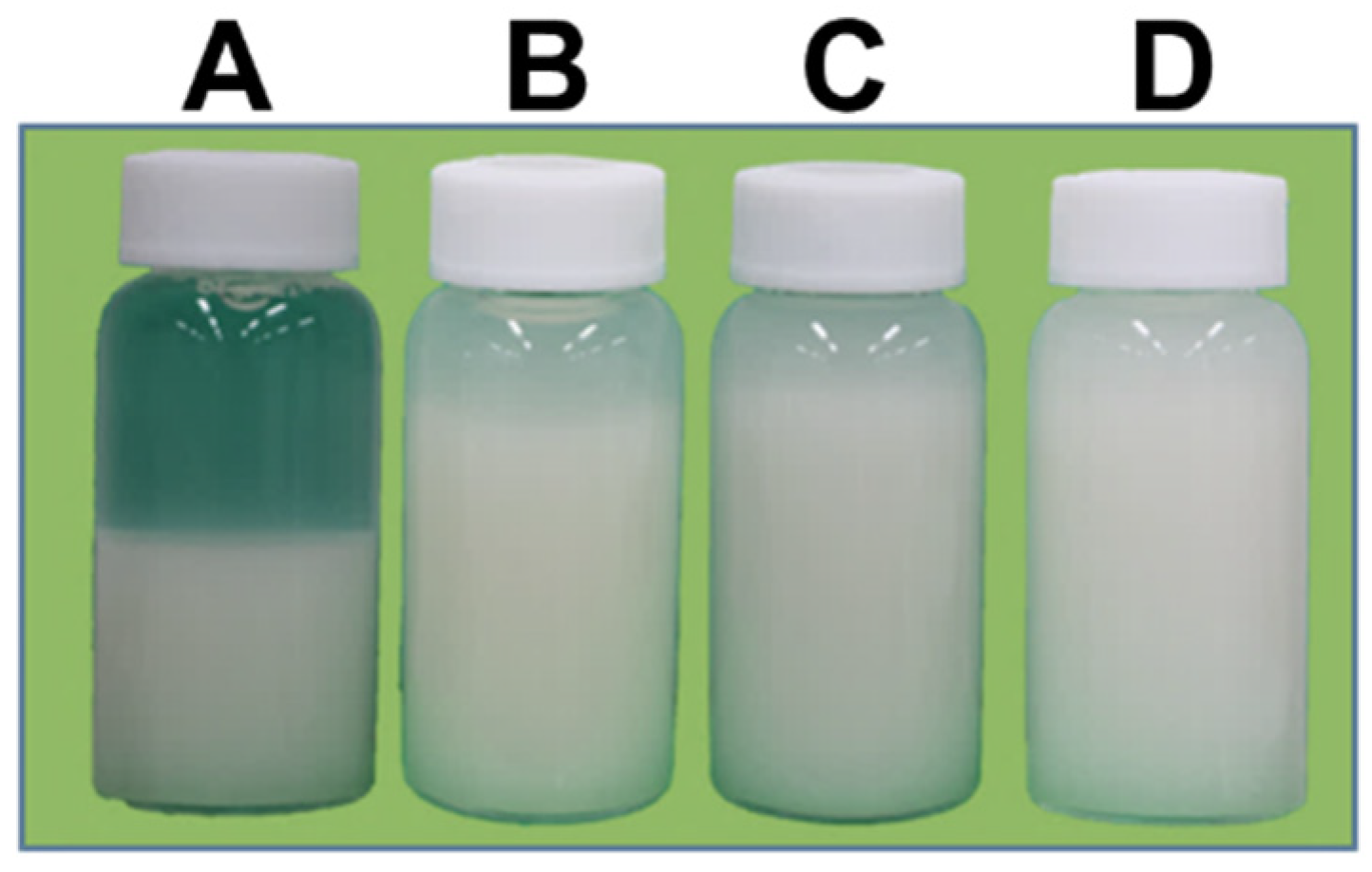
| Untreated | One Passage | Three Passages | Five Passages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median size (μm) | 68.5 | 13.5 | 9.9 | 8.9 |
| Viscosity (mPas) | 10 | 40 | 70 | 120 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arai, Y.; Nishinari, K.; Nagano, T. Applying Nanotechnology to Okara for Developing Soy Protein Gel-Based Foods. Proceedings 2021, 70, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07798
Arai Y, Nishinari K, Nagano T. Applying Nanotechnology to Okara for Developing Soy Protein Gel-Based Foods. Proceedings. 2021; 70(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07798
Chicago/Turabian StyleArai, Yuya, Katsuyoshi Nishinari, and Takao Nagano. 2021. "Applying Nanotechnology to Okara for Developing Soy Protein Gel-Based Foods" Proceedings 70, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07798
APA StyleArai, Y., Nishinari, K., & Nagano, T. (2021). Applying Nanotechnology to Okara for Developing Soy Protein Gel-Based Foods. Proceedings, 70(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07798





