Ultrasonically-Extracted Marine Polysaccharides as Potential Green Antioxidant Alternatives †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
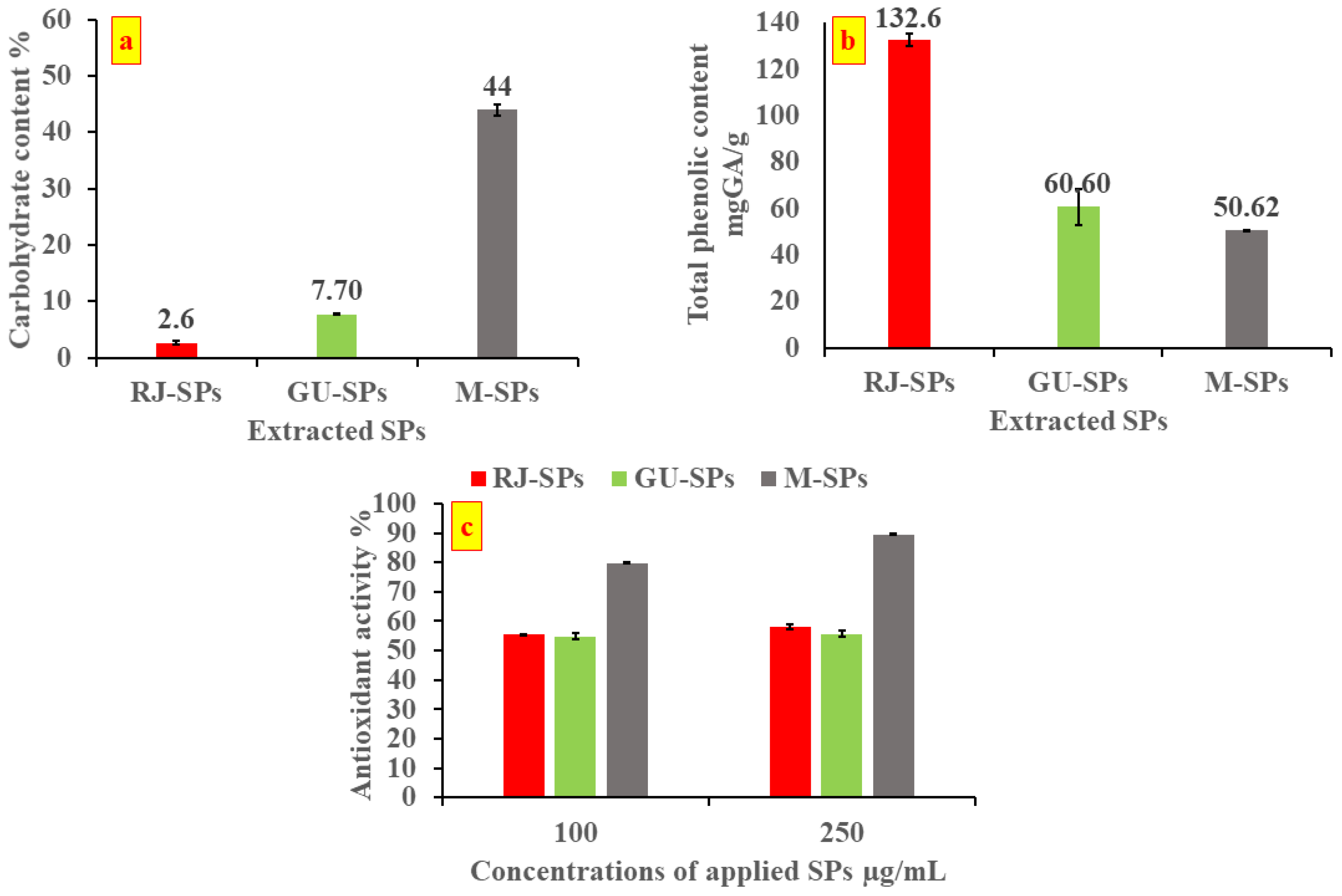
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdullah, S.A.; Omar, H.H.; Bahabri, F.S. Health Benefits of Edible Seaweeds and Their Nano-Applications. J. Am. Sci. 2020, 16, 40–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman, J. SAS Survival Handbook; Harvill Secker: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Chiavaroli, A.; Sinan, K.I.; Zengin, G.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Sadeer, N.B.; Etienne, O.K.; Cziáky, Z.; Jekő, J.; Glamocilja, J.; Sokovic, M.; et al. Identification of Chemical Profiles and Biological Properties of Rhizophora racemosa G. Mey. Extracts Obtained by Different Methods and Solvents. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatoi, H.N.; Patra, J.K.; Das, S.K. Free radical scavenging and antioxidant potential of mangrove plants: A review. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Azm, N.A.; Fleita, D.; Rifaat, D.; Mpingirika, E.Z.; Amleh, A.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Production of bioactive compounds from the sulfated polysaccharides extracts of Ulva lactuca: Post-extraction enzymatic hydrolysis followed by ion-exchange chromatographic fractionation. Molecules 2019, 24, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jime’nez-Escrig, A.; Jime´nez-Jime´nez, I.; Pulido, R.; Saura-Calixto, F. Antioxidant activity of fresh and processed edible seaweeds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rez, P.R.; Ahrazem, O.; Leal, J.A. Potential Antioxidant Capacity of Sulfated Polysaccharides from the Edible Marine Brown Seaweed Fucus vesiculosus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 840–845. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.-J.; Zhang, W.-W.; Li, X.-M.; Wang, B.-G. Evaluation of antioxidant property of extract and fractions obtained from a red alga, Polysiphonia urceolata. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara, I.; Yoon, N.Y.; Kim, S.K. Phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava (Phaeophyceae): Biological activities and potential health benefits. Biofactors 2010, 36, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essa, H.; Fleita, D.; Rifaat, D.; Samy, S.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Towards optimizing the conventional and ultrasonic-assisted extraction of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 464, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, H.L.; Abdelfattah, M.S.; Marzouk, A.S.; Guirguis, H.A.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Nano-Formulations of Copper Species Coated with Sulfated Polysaccharide Extracts and Assessment of Their Phytotoxicity on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Seedlings in Seed Germination, Foliar and Soil Applications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleita, D.; El-Sayed, M.M.H.; Rifaat, D. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of enzymatically-hydrolyzed sulfated polysaccharides extracted from red algae; Pterocladia capillacea. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blois, M.S. Antioxidant determination by the use of a stable free radical. Nature 1985, 181, 1199–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rafie, H.M.; El-Rafie, M.H.; Zahran, M.K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using polysaccharides extracted from marine macro algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthi, S.; Balaji Raghavendran, H.R.; Sunil, A.; Gayathri, V.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Vasanthi, H.R. In vitro antioxidant and in vivo anti-inflammatory potential of crude polysaccharide from Turbinaria ornata (Marine Brown Alga). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Wavelength, cm−1 | Functional Groups | RJ-SPs | GU-SPs | M-SPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3500–3400 | OH group | √ | √ | √ |
| 1600–1420 | Uronic acid and phenolic groups | √ | √ | √ |
| 1260–1258 | Ester Sulfate group | × | √ | √ |
| 1088–1012 | Acidic polysaccharide | √ | √ | √ |
| 963–927 | Glycosidic linkage | √ | √ | √ |
| 850–845 | Galactose sulfate group | √ | √ | × |
| Types of Monosaccharides | RJ-SPs | GU-SPs | M-SPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | 94.04 | 6.55 | 24.51 |
| Galactose | 0.10 | 3.53 | 17.46 |
| Glucuronic acid | 0.16 | 89.92 | 7.65 |
| Xylose | 2.14 | NA | 1.29 |
| Mannose | 3.51 | NA | 0.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Essa, H.L.; Guirguis, H.A.; El-Sayed, M.M.H.; Rifaat, D.; Abdelfattah, M.S. Ultrasonically-Extracted Marine Polysaccharides as Potential Green Antioxidant Alternatives. Proceedings 2020, 67, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2020-07606
Essa HL, Guirguis HA, El-Sayed MMH, Rifaat D, Abdelfattah MS. Ultrasonically-Extracted Marine Polysaccharides as Potential Green Antioxidant Alternatives. Proceedings. 2020; 67(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2020-07606
Chicago/Turabian StyleEssa, Hanaa L., Hania A. Guirguis, Mayyada M. H. El-Sayed, Dalia Rifaat, and Mohamed S. Abdelfattah. 2020. "Ultrasonically-Extracted Marine Polysaccharides as Potential Green Antioxidant Alternatives" Proceedings 67, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2020-07606
APA StyleEssa, H. L., Guirguis, H. A., El-Sayed, M. M. H., Rifaat, D., & Abdelfattah, M. S. (2020). Ultrasonically-Extracted Marine Polysaccharides as Potential Green Antioxidant Alternatives. Proceedings, 67(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2020-07606







