Macrophage Inflammatory Response Mediated by Intimin and Bundle-Forming Pilus from Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Cloning, Expression and Purification of Recombinant Intimin and BfpA Proteins
2.3. Macrophages
2.4. Activation of BMDM with Intimin or BfpA
2.5. Effect of Intimin and Bfp on BMDM Viability
2.6. Effect of Intimin and BfpA Treatment with Polymyxin B and Proteinase K
2.7. Cytokines Assays
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Intimin and BfpA Had No Effect on BMDM Viability
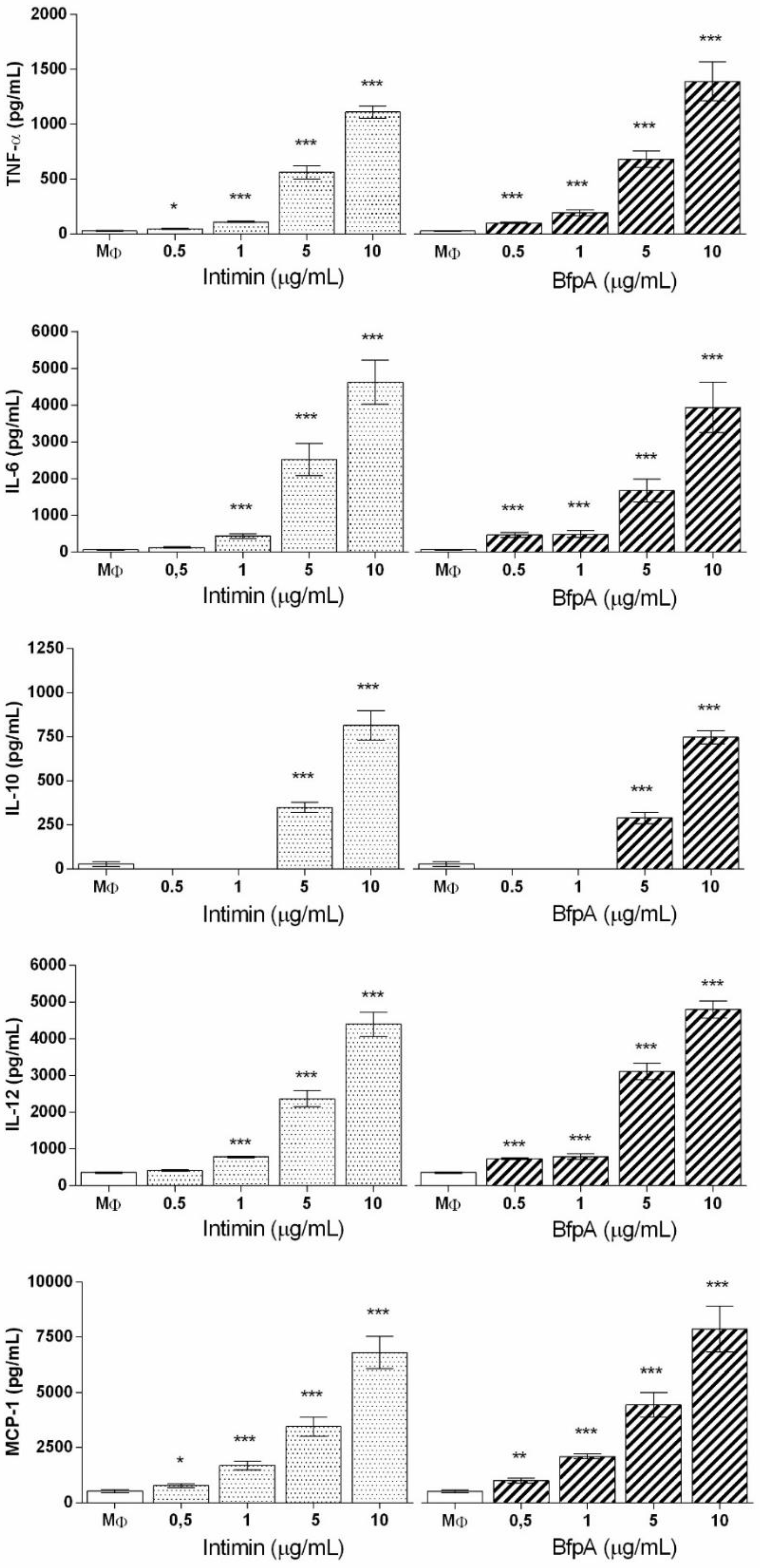
3.2. Role of Intimin and BfpA in BMDM Activation
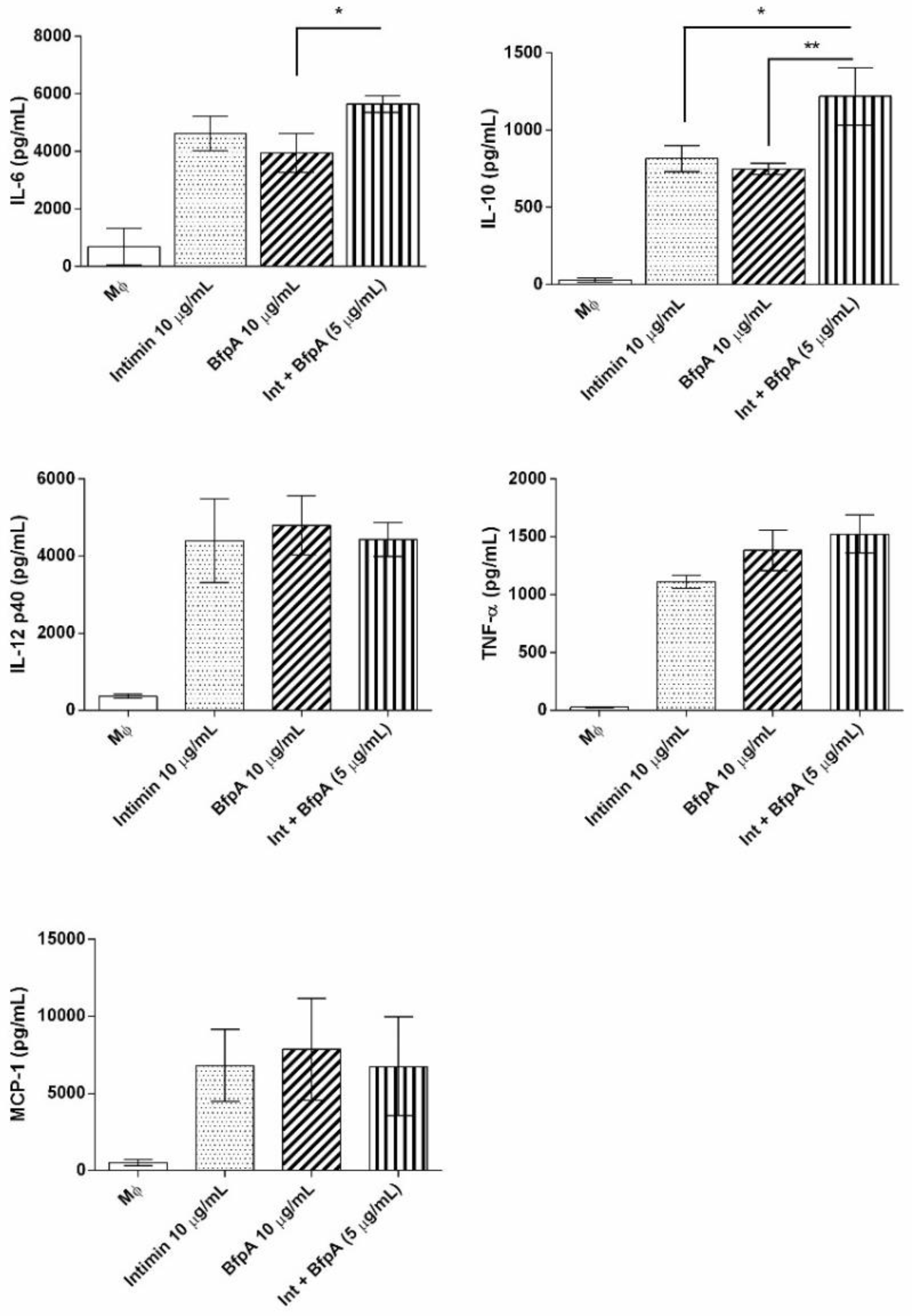
3.3. Intimin and BfpA Do Not Work Synergistically to Activate BMDM
3.4. The Immune Response Mediated by Intimin and BfpA Was Specific
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ochoa, T.J.; Contreras, C.A. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection in children. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 24, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchalingam, S.; Antonio, M.; Hossain, A.; Mandomando, I.; Ochieng, B.; Oundo, J.; Ramamurthy, T.; Tamboura, B.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; Petri, W.; et al. Diagnostic Microbiologic Methods in the GEMS-1 Case/Control Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, S294–S302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, T.A.; Elias, W.P.; Scaletsky, I.C.; Guth, B.E.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Piazza, R.M.; Ferreira, L.C.; Martinez, M.B. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47 (Suppl. 1), 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platts-Mills, J.A.; Liu, J.; Rogawski, E.T.; Kabir, F.; Lertsethtakarn, P.; Siguas, M.; Khan, S.S.; Praharaj, I.; Murei, A.; Nshama, R.; et al. Use of quantitative molecular diagnostic methods to assess the aetiology, burden, and clinical characteristics of diarrhoea in children in low-resource settings: A reanalysis of the MAL-ED cohort study. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e1309–e1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, V.R.; Nakano, V.; Delannoy, S.; Fach, P.; Alberca, G.G.F.; Farfan, M.J.; Piazza, R.M.F.; Avila-Campos, M.J. Prevalence of Enteropathogens and Virulence Traits in Brazilian Children With and Without Diarrhea. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.W.; Whipp, S.C.; Argenzio, R.A.; Levine, M.M.; Giannella, R.A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect. Immun. 1983, 41, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnenberg, M.S.; Kaper, J.B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 3953–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón, J.A.; Ho, A.S.; Schoolnik, G.K. An inducible bundle-forming pilus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Science 1991, 254, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerse, A.E.; Yu, J.; Tall, B.D.; Kaper, J.B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 7839–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, G.; Phillips, A.D.; Novakova, M.; Field, H.; Candy, D.C.; Schauer, D.B.; Douce, G.; Dougan, G. Intimin from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli restores murine virulence to a Citrobacter rodentium eaeA mutant: Induction of an immunoglobulin A response to intimin and EspB. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 5315–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, B.; DeVinney, R.; Stein, M.; Reinscheid, D.J.; Frey, E.A.; Finlay, B.B. Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) transfers its receptor for intimate adherence into mammalian cells. Cell 1997, 91, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, P.; Kenny, B. The effector repertoire of enteropathogenic E. coli: Ganging up on the host cell. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulshen, M.H.; Rollo, J.L. Pathogenesis of Escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man-another mechanism. N. Engl. J. Med. 1980, 302, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Villamil, J.; Navarro-Garcia, F. Role of virulence factors on host inflammatory response induced by diarrheagenic Escherichia coli pathotypes. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 1009–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Girón, J.A.; Torres, A.G.; Crawford, J.A.; Negrete, E.; Vogel, S.N.; Kaper, J.B. Flagellin of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli stimulates interleukin-8 production in T84 cells. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.S.; Finlay, B.B. Bringing down the host: Enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli effector-mediated subversion of host innate immune pathways. Cell Microbiol. 2015, 17, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahida, Y.R. The key role of macrophages in the immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2000, 6, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Sica, A.; Locati, M. New vistas on macrophage differentiation and activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dann, S.M.; Spehlmann, M.E.; Hammond, D.C.; Iimura, M.; Hase, K.; Choi, L.J.; Hanson, E.; Eckmann, L. IL-6-dependent mucosal protection prevents establishment of a microbial niche for attaching/effacing lesion-forming enteric bacterial pathogens. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 6816–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, K.; Huerta, R.; Oswald, E.; Garcia-Tovar, C.; Hernandez, J.M.; Navarro-Garcia, F. Role of EspA and intimin in expression of proinflammatory cytokines from enterocytes and lymphocytes by rabbit enteropathogenic Escherichia coli-infected rabbits. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeis, S.L.; Sherman, M.A.; Kalman, D. Protective and destructive innate immune responses to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and related A/E pathogens. Future Microbiol. 2008, 3, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gea-Sorlí, S.; Closa, D. Role of macrophages in the progression of acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 1, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Kobayashi, K. Macrophages in inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.J.; Wynn, T.A. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2011, 11, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.C.; Whittam, T.S.; Gomes, T.A.; Andrade, J.R.; Trabulsi, L.R. Escherichia coli serogroup O111 includes several clones of diarrheagenic strains with different virulence properties. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 3282–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaris, D.; Sbrogio-Almeida, M.E.; Dib, C.C.; Canhamero, T.A.; Souza, G.O.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; Ferreira, L.C.; Abreu, P.A. Protective Immunity and Reduced Renal Colonization Induced by Vaccines Containing Recombinant Leptospira interrogans Outer Membrane Proteins and Flagellin Adjuvant. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, C.M.; Quintana-Flores, V.M.; Medina-Acosta, E.; Schriefer, A.; Barral-Netto, M.; Dias da Silva, W. Egg yolk anti-BfpA antibodies as a tool for recognizing and identifying enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Scand. J. Immunol. 2003, 57, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcellos, H.L.; Scaramuzzi, K.; Nascimento, I.P.; Da Costa Ferreira, J.M.; Abe, C.M.; Piazza, R.M.; Kipnis, A.; Dias da Silva, W. Generation of recombinant bacillus Calmette-Guérin and Mycobacterium smegmatis expressing BfpA and intimin as vaccine vectors against enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Vaccine 2012, 30, 5999–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, M.A.; Rocha, L.B.; Koga, P.C.; Fernandes, I.; Nara, J.M.; Magalhães, C.A.; Abe, C.M.; Ayala, C.O.; Burgos, Y.K.; Elias, W.P.; et al. Identification of enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli strains by immunoserological detection of intimin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, J.M.; Cianciarullo, A.M.; Culler, H.F.; Bueris, V.; Horton, D.S.; Menezes, M.A.; Franzolin, M.R.; Elias, W.P.; Piazza, R.M. Differentiation of typical and atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli using colony immunoblot for detection of bundle-forming pilus expression. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weischenfeldt, J.; Porse, B. Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages (BMM): Isolation and Applications. CSH Protoc. 2008, 2008, pdb.prot5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperstock, M.S. Inactivation of endotoxin by polymyxin B. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1974, 6, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandri, S.; Rodriguez, D.; Gomes, E.; Monteiro, H.P.; Russo, M.; Campa, A. Is serum amyloid A an endogenous TLR4 agonist? J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleary, J.; Lai, L.C.; Shaw, R.K.; Straatman-Iwanowska, A.; Donnenberg, M.S.; Frankel, G.; Knutton, S. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) adhesion to intestinal epithelial cells: Role of bundle-forming pili (BFP), EspA filaments and intimin. Microbiology 2004, 150, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallance, B.A.; Finlay, B.B. Exploitation of host cells by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8799–8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, R.M.; Armstrong, G.D. Sticky situation: Localized adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to the small intestine epithelium. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1645–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L.A.; Bajaj-Elliott, M.; Klein, N.J.; Murch, S.H.; Phillips, A.D. Bacterial-epithelial contact is a key determinant of host innate immune responses to enteropathogenic and enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.D.; Frankel, G. Intimin-mediated tissue specificity in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli interaction with human intestinal organ cultures. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 1496–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Biswas, S.K.; Galdiero, M.R.; Sica, A.; Locati, M. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J. Pathol. 2013, 229, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Plüddemann, A.; Martinez Estrada, F. Macrophage heterogeneity in tissues: Phenotypic diversity and functions. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 262, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, P.; Morris, V.; Greenbaum, J.A.; Park, Y.; Bjoerheden, U.; Mikulski, Z.; Muffley, T.; Shui, J.W.; Kim, G.; Cheroutre, H.; et al. IL-10-producing intestinal macrophages prevent excessive antibacterial innate immunity by limiting IL-23 synthesis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Tesfay, S.; Tomson, F.L.; Kanteti, R.P.; Viswanathan, V.K.; Hecht, G. Balance of bacterial pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators dictates net effect of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli on intestinal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G685–G694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hine, A.M.; Loke, P. Intestinal Macrophages in Resolving Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosurgi, L.; Cao, Y.G.; Cabeza-Cabrerizo, M.; Tucci, A.; Hughes, L.D.; Kong, Y.; Weinstein, J.S.; Licona-Limon, P.; Schmid, E.T.; Pelorosso, F.; et al. Macrophage function in tissue repair and remodeling requires IL-4 or IL-13 with apoptotic cells. Science 2017, 356, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolasia, K.; Bisht, M.K.; Pradhan, G.; Udgata, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S. TLRs/NLRs: Shaping the landscape of host immunity. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 37, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Miao, E.A.; Ting, J.P. Mechanisms of NOD-like receptor-associated inflammasome activation. Immunity 2013, 39, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltorak, A.; He, X.; Smirnova, I.; Liu, M.Y.; Van Huffel, C.; Du, X.; Birdwell, D.; Alejos, E.; Silva, M.; Galanos, C.; et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: Mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 1998, 282, 2085–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caetano, B.A.; Mourão, D.B.; Abreu, P.A.E.; Monaris, D.; Vasconcellos, H.L.; Luz, D.; Galhardo, C.S.; Menezes, M.A.; Lima, F.A.; Elias, W.P.; et al. Macrophage Inflammatory Response Mediated by Intimin and Bundle-Forming Pilus from Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli . Proceedings 2020, 66, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066021
Caetano BA, Mourão DB, Abreu PAE, Monaris D, Vasconcellos HL, Luz D, Galhardo CS, Menezes MA, Lima FA, Elias WP, et al. Macrophage Inflammatory Response Mediated by Intimin and Bundle-Forming Pilus from Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli . Proceedings. 2020; 66(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066021
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaetano, Bruna A., Daniela B. Mourão, Patrícia A. E. Abreu, Denize Monaris, Halyka L. Vasconcellos, Daniela Luz, Cynthia Soares Galhardo, Marcio A. Menezes, Flávia A. Lima, Waldir P. Elias, and et al. 2020. "Macrophage Inflammatory Response Mediated by Intimin and Bundle-Forming Pilus from Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli " Proceedings 66, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066021
APA StyleCaetano, B. A., Mourão, D. B., Abreu, P. A. E., Monaris, D., Vasconcellos, H. L., Luz, D., Galhardo, C. S., Menezes, M. A., Lima, F. A., Elias, W. P., Borges, M. M., & Piazza, R. M. F. (2020). Macrophage Inflammatory Response Mediated by Intimin and Bundle-Forming Pilus from Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli . Proceedings, 66(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066021






