Structural and Functional Annotation of Uncharacterized Protein NCGM946K2_146 of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: An In-Silico Approach †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Retrieval
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization
2.3. Functional Annotation Prediction
2.4. Secondary Structure Prediction
2.5. Tertiary Structure Modeling and Validation
2.6. Sub-Cellular Localization
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization
3.2. Functional Annotation Prediction
3.3. Secondary Structure Prediction
3.4. Binding Sites (Protein–Protein, and Protein-Polynucleotide)
3.5. Sub-Cellular Localization
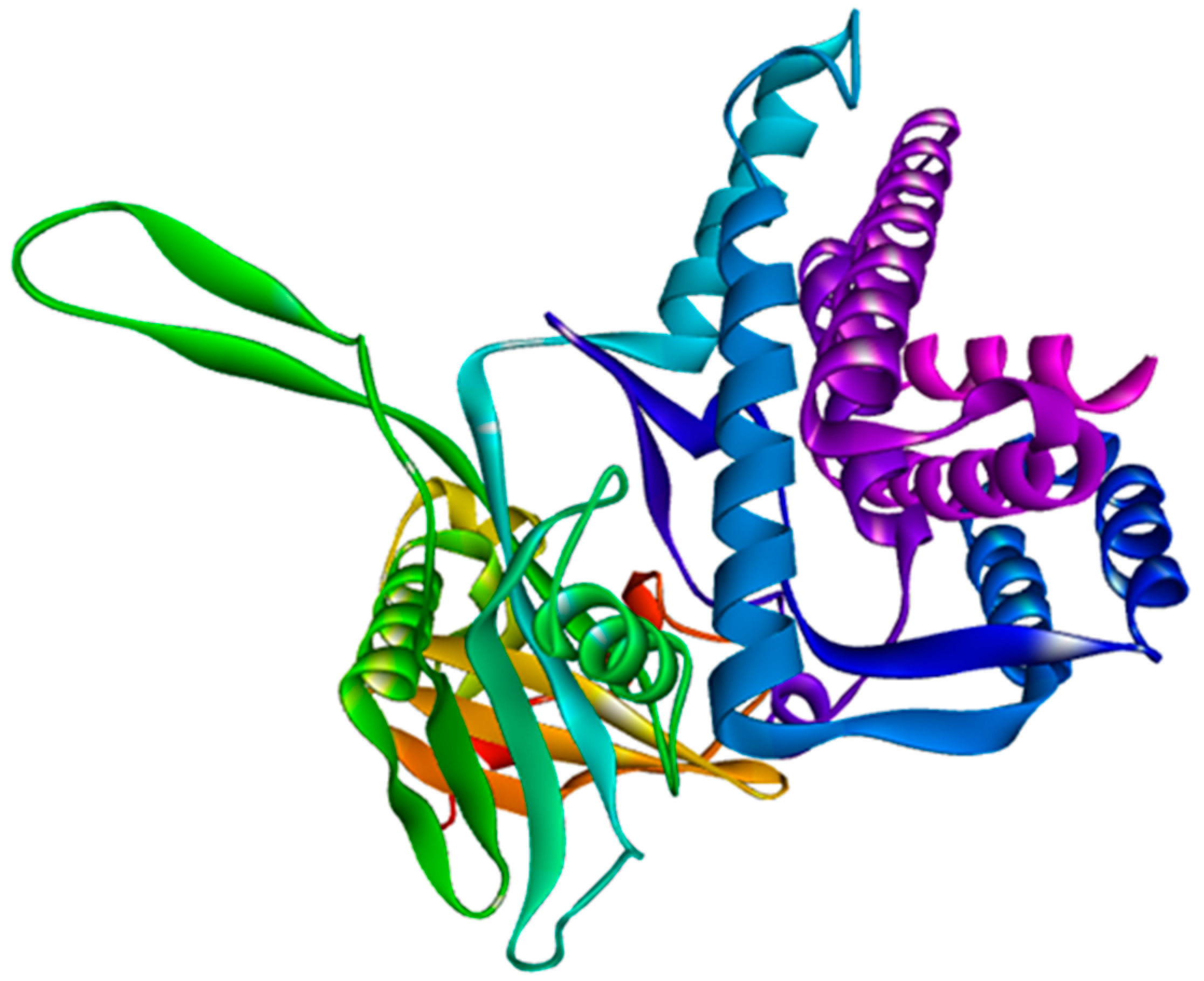
3.6. Modeling and Validation of Tertiary Structures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO|Global Tuberculosis Report 2019. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/ (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- YamuraiBishi, L.; Chaitanya Vedithi, S.L.; Blundell, T.; Mugumbate, G. Computational Deorphaning of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Targets. In Drug Discovery and Development-New Advances; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCBI Resource Coordinators. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D7–D17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Garrity, D.M.; Yao, T. Genomics and Transcriptomics of the Molting Gland (Y-Organ) in the Blackback Land Crab, Gecarcinus Lateralis; Colorado State University, Libraries: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Combet, C.; Blanchet, C.; Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. NPS@: Network protein sequence analysis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T. Protein secondary structure prediction based on position-specific scoring matrices. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 292, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2016, 86, 2.9.1–2.9.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukas, Z.; Stephens, A.; Nam, S.-Z.; Rau, D.; Kübler, J.; Lozajic, M.; Gabler, F.; Söding, J.; Lupas, A.N.; Alva, V. A completely reimplemented MPI bioinformatics toolkit with a new HHpred server at its core. J.Mol.Biol. 2018, 430, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, K.; Bordoli, L.; Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, G.N.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Sasisekharan, V. Stereochemistry of polypeptide chain configurations. J. Mol. Biol. 1963, 7, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthy, R.; Bowie, J.U.; Eisenberg, D. Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature 1992, 356, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodacre, N.F.; Gerloff, D.L.; Uetz, P. Protein domains of unknown function are essential in bacteria. MBio 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.-S.; Lin, C.-J.; Hwang, J.-K. Predicting subcellular localization of proteins for Gram-negative bacteria by support vector machines based on n-peptide compositions. Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiederstein, M.; Sippl, M.J. ProSA-web: Interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35 (Suppl. 2), W407–W410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guruprasad, K.; Reddy, B.V.B.; Pandit, M.W. Correlation between stability of a protein and its dipeptide composition: A novel approach for predicting in vivo stability of a protein from its primary sequence. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1990, 4, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotriffer, C.; Klebe, G. Identification and mapping of small-molecule binding sites in proteins: Computational tools for structure-based drug design. Il Farmaco. 2002, 57, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Kellogg, G.E. A novel and efficient tool for locating and characterizing protein cavities and binding sites. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinf. 2010, 78, 825–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.S.; Calafell, S.J.; Thomas, D.Y.; Hallett, M.T. Refining protein subcellular localization. PLoSComput. Biol. 2005, 1, 0518–0528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smet, K.A.L.; Weston, A.; Brown, I.N.; Young, D.B.; Robertson, B.D. Three pathways for trehalose biosynthesis in mycobacteria. Microbiology 2000, 146, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Physio-Chemical Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of amino acids | 455 |
| Molecular weight | 49,889.11 |
| Theoretical isoelectric point (pI) | 5.06, 4.82* |
| Aliphatic index | 88.62 |
| Instability index | 38.05 |
| Extinction coefficients (all pairs of Cys residues form cystines) | 69,455 |
| Extinction coefficients (all Cys residues are reduced) | 69,330 |
| Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu) | 61 |
| Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys) | 46 |
| Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) | −0.185 |
| Secondary Structure Elements | Values (%) |
|---|---|
| Alpha helix (Hh) | 51.21 |
| 310 helix (Gg) | 0.00 |
| Pi helix (Ii) | 0.00 |
| Beta bridge (Bb) | 0.00 |
| Extended strand (Ee) | 11.21 |
| Beta turn (Tt) | 3.74 |
| Bend region (Ss) | 0.00 |
| Random coil (Cc) | 33.85 |
| Ambiguous states | 0.00 |
| Other states | 0.00 |
| S. No. | Amino Acids | No. of Amino Acids | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ala (A) | 60 | 13.2 |
| 2 | Arg (R) | 39 | 8.6 |
| 3 | Asn (N) | 9 | 2.0 |
| 4 | Asp (D) | 31 | 6.8 |
| 5 | Cys (C) | 3 | 0.7 |
| 6 | Gln (Q) | 15 | 3.3 |
| 7 | Glu (E) | 30 | 6.6 |
| 8 | Gly (G) | 33 | 7.3 |
| 9 | His (H) | 7 | 1.5 |
| 10 | Ile (I) | 12 | 2.6 |
| 11 | Leu (L) | 47 | 10.3 |
| 12 | Lys (K) | 7 | 1.5 |
| 13 | Met (M) | 4 | 0.9 |
| 14 | Phe (F) | 15 | 3.3 |
| 15 | Pro (P) | 25 | 5.5 |
| 16 | Ser (S) | 25 | 5.5 |
| 17 | Thr (T) | 29 | 6.4 |
| 18 | Trp (W) | 8 | 1.8 |
| 19 | Tyr (Y) | 17 | 3.7 |
| 20 | Val (V) | 39 | 8.6 |
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) | Localization | Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Amino acid Comp. | Cytoplasmic | 0.931 |
| N-peptide Comp. | Cytoplasmic | 0.825 |
| Partitioned seq. Comp. | Membrane | 0.577 |
| Physicochemical Comp. | Cytoplasmic | 0.817 |
| Neighboring seq. Comp. | Cytoplasmic | 0.820 |
| Subcellular Localization Predictor (CELLO) value | Cytoplasmic | 3.791 * |
| Membrane | 1.016 | |
| Extracellular | 0.177 | |
| Cell Wall | 0.017 |
| Servers | Ramachandran Plot Calculation | Value (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Modeller | Residues in most favored regions [A,B,L] | 95.2 |
| Residues in additional allowed regions [a,b,l,p] | 4.8 | |
| Residues in generously allowed regions [~a,~b,~l,~p] | 0.0 | |
| Residues in disallowed regions | 0.0 | |
| Phyre2 | Residues in most favored regions [A,B,L] | 93.6 |
| Residues in additional allowed regions [a,b,l,p] | 6.1 | |
| Residues in generously allowed regions [~a,~b,~l,~p] | 0.0 | |
| Residues in disallowed regions | 0.3 | |
| Swiss Model | Residues in most favored regions [A,B,L] | 94.2 |
| Residues in additional allowed regions [a,b,l,p] | 5.3 | |
| Residues in generously allowed regions [~a,~b,~l,~p] | 0.4 | |
| Residues in disallowed regions | 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saikat, A.S.M.; Islam, R.; Mahmud, S.; Imran, M.A.S.; Alam, M.S.; Masud, M.H.; Uddin, M.E. Structural and Functional Annotation of Uncharacterized Protein NCGM946K2_146 of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: An In-Silico Approach. Proceedings 2020, 66, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066013
Saikat ASM, Islam R, Mahmud S, Imran MAS, Alam MS, Masud MH, Uddin ME. Structural and Functional Annotation of Uncharacterized Protein NCGM946K2_146 of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: An In-Silico Approach. Proceedings. 2020; 66(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066013
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaikat, Abu Saim Mohammad, Rabiul Islam, Shahriar Mahmud, Md. Abu Sayeed Imran, Mohammad Shah Alam, Mahmudul Hasan Masud, and Md. Ekhlas Uddin. 2020. "Structural and Functional Annotation of Uncharacterized Protein NCGM946K2_146 of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: An In-Silico Approach" Proceedings 66, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066013
APA StyleSaikat, A. S. M., Islam, R., Mahmud, S., Imran, M. A. S., Alam, M. S., Masud, M. H., & Uddin, M. E. (2020). Structural and Functional Annotation of Uncharacterized Protein NCGM946K2_146 of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: An In-Silico Approach. Proceedings, 66(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066013







