Changes in the Antioxidant Activity of Peptides Released during the Hydrolysis of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa willd) Protein Concentrate †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Quinoa Protein Solubility Study
2.2.1. Quinoa Protein Solubility
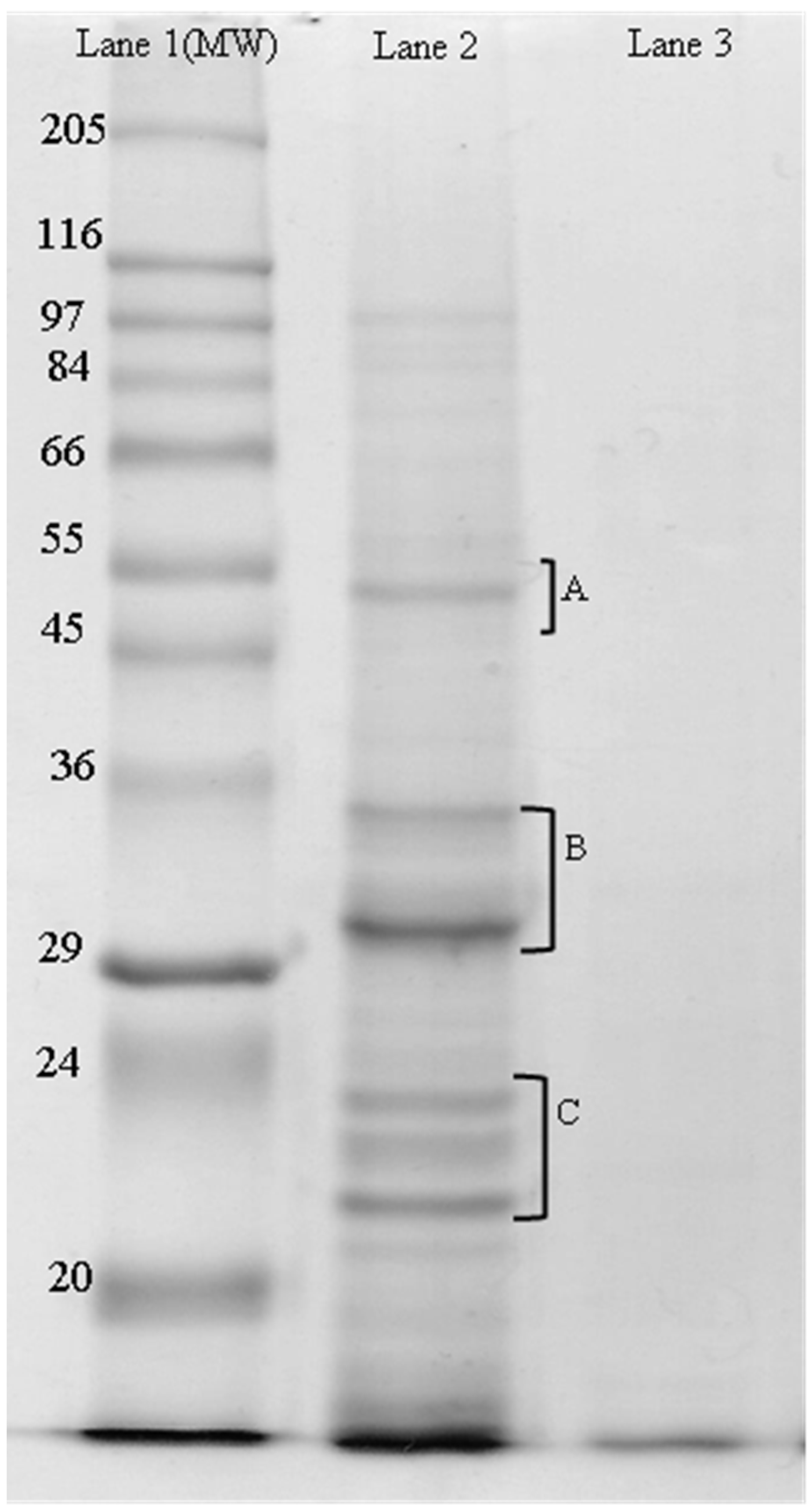
2.2.2. SDS-PAGE
2.3. Quinoa Protein Concentrate (QPC)
2.4. Proteolysis
2.4.1. Hydrolysis Conditions
2.4.2. Protease Activity
2.4.3. Quinoa Protein Hydrolysates (QPH)
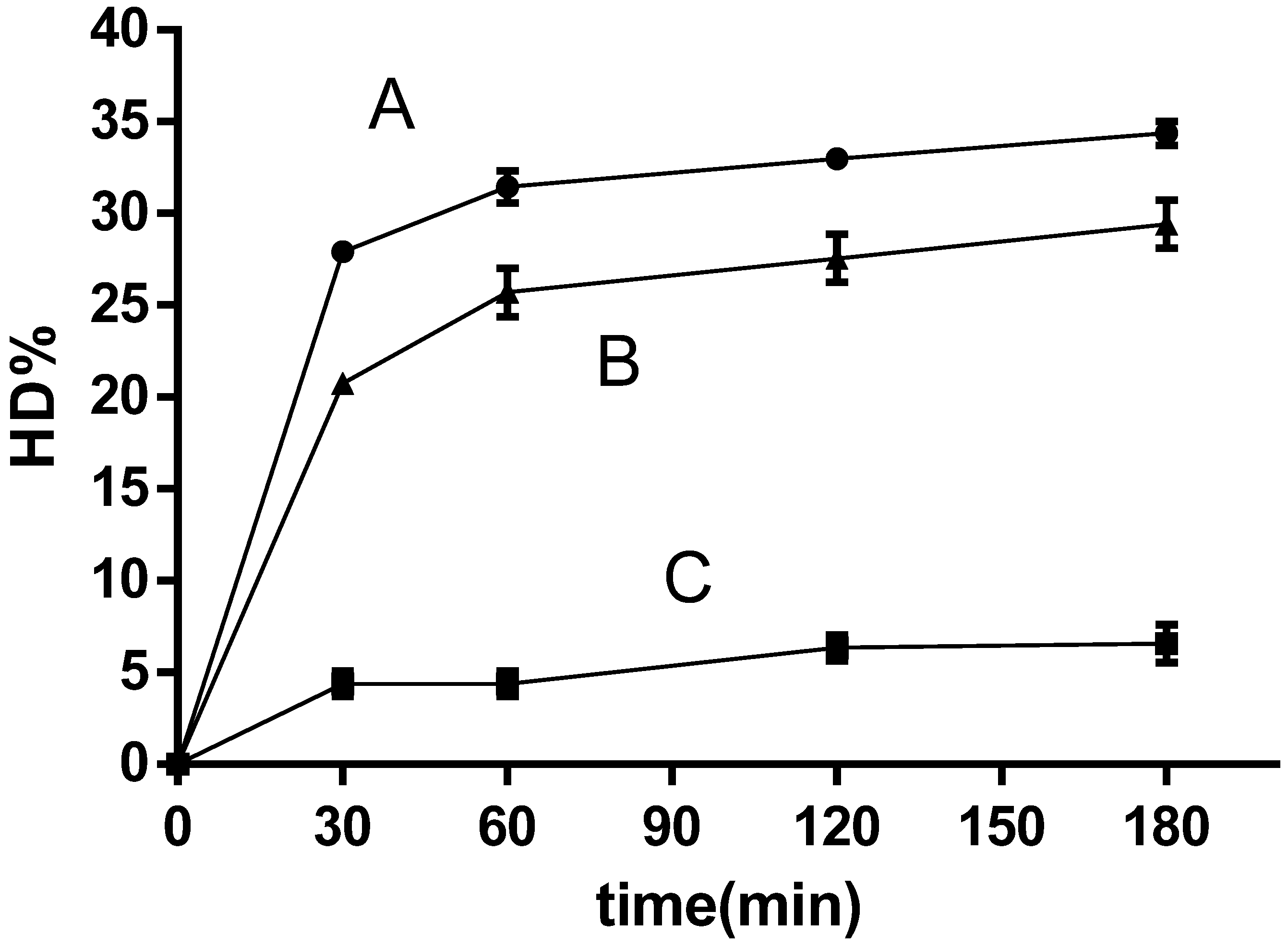
2.4.4. Hydrolysis Degree Calculation
2.5. Antiradical Activity
2.5.1. Inhibition of Radical DPPH
2.5.2. Inhibition of Radical ABTS
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Quinoa Protein Solubility
3.2. Electrophoresis
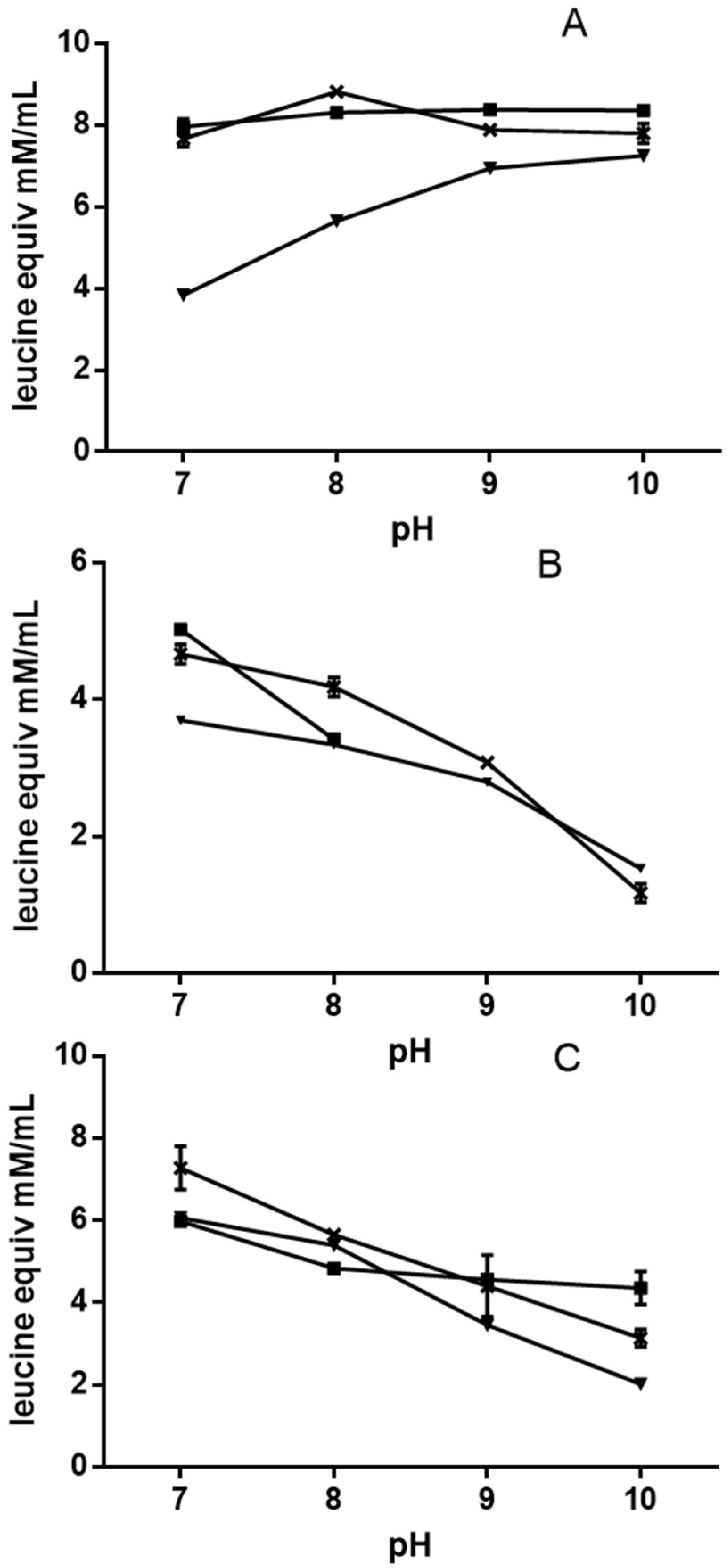
3.3. Hydrolysis Conditions
3.4. Quinoa Protein Hydrolysis
3.5. Antiradical Activity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Vilcacundo, R.; Martínez-Villaluenga, C.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Release of dipeptidyl peptidase IV, α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) during in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; Le Maux, S.; Dubrulle, C.; Barre, C.; FitzGerald, R.J. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) protein hydrolysates with in vitro dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory and antioxidant properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 65, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete del Toro, M.A.; García-Carreño, F.L. Evaluation of the Progress of Protein Hydrolysis. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2003, 10, B2.2.1–B2.2.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schokker, E.P.; van Boekel, A.J.S. Kinetic Modeling of Enzyme Inactivation: Kinetics of Heat Inactivation at 90–110 °C of Extracellular Proteinase from Pseudomonas fluorescens 22F. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 4740–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, C.; Santos, M.; Mauro, R.; Samman, N.; Matos, A.S.; Torres, D.; Castanheira, I. Protein content and amino acids profile of pseudocereals. Food Chem. 2016, 193, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakka, A.K.; Elias, M.; Jini, R.; Sakhare, P.Z.; Bhaskar, N. In-vitro antioxidant and antibacterial properties of fermentatively and enzymatically prepared chicken liver protein hydrolysates. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 8059–8067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsohaimy, S.A.; Refaay, T.M.; Zaytoun, M.A.M. Physicochemical and functional properties of quinoa protein isolate. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2015, 60, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, E.N.; Añón, M.C. Composition and structural characterization of amaranth protein isolates. An electrophoretic and calorimetric study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 2523–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, R.E.; Monu, E. Functional and Bioactive Properties of quinoa seed protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 68, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abugoch, L.E.; Romero, N.; Tapia, C.A.; Silva, J.; Rivera, M. Study of some physicochemical and functional properties of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) protein isolates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4745–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinegar, C.; Goundan, S. Isolation and characterization of chenopodin, the 11S seed storage protein of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Karawita, R.; Heo, S.J.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, S.K.; Jeon, Y.J. Recovery of a novel Ca-binding peptide from Alaska Pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) backbone by pepsinolytic hydrolysis. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 2097–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamnarathip, P.; Jangchud, K.; Jangchud, A.; Nitisinprasert, S.; Tadakittisarn, S.; Vardhanabhuti, B. Extraction and characterisation of Riceberry bran protein hydrolysate using enzymatic hydrolysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Enzyme | Temperature | pH | PU/min |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcalasa | 50 | 8 | 220 |
| Flavoruzyme | 60 | 7 | 125 |
| Protamex | 50 | 7 | 182 |
| Time (min) | Alcalase | Flavourzyme | Protamex | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABTS (asc. ac./mL) | DPPH (% inhib) | ABTS (asc. ac./mL) | DPPH (% inhib) | ABTS (asc. ac./mL) | DPPH (% inhib) | |||||||
| 0 | 20.9 | ±0.2c | 9.3 | ±2.7a | 20.9 | ±0.2a | 9.3 | ±2.7a | 20.9 | ±0.2d | 9.3 | ±2.7a |
| 30 | 105.1 | ±3.7b | 20.0 | ±4.0b | 10.9 | ±0.3b | 9.6 | ±1.0a | 42.8 | ±1.4c | 11.3 | ±3.0a |
| 60 | 110.9 | ±1.3ab | 11.78 | ±1.4ab | 15.1 | ±0.5b | 9.4 | ±0.5a | 50.0 | ±1.2c | 12.3 | ±3.3a |
| 120 | 102.9 | ±2.4b | 10.8 | ±2.5a | 15.3 | ±0.6b | 4.0 | ±0.9a | 60.1 | ±2.6b | 14.1 | ±0.7a |
| 180 | 119.19 | ±8.7a | 7.6 | ±6.2a | 12.7 | ±2.0b | 14.8 | ±2.4b | 75.7 | ±0.6a | 12.5 | ±1.3a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rueda, J.; Lobo, M.O.; Sammán, N. Changes in the Antioxidant Activity of Peptides Released during the Hydrolysis of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa willd) Protein Concentrate. Proceedings 2020, 53, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020053012
Rueda J, Lobo MO, Sammán N. Changes in the Antioxidant Activity of Peptides Released during the Hydrolysis of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa willd) Protein Concentrate. Proceedings. 2020; 53(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020053012
Chicago/Turabian StyleRueda, Julio, Manuel Oscar Lobo, and NornmaCristina Sammán. 2020. "Changes in the Antioxidant Activity of Peptides Released during the Hydrolysis of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa willd) Protein Concentrate" Proceedings 53, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020053012
APA StyleRueda, J., Lobo, M. O., & Sammán, N. (2020). Changes in the Antioxidant Activity of Peptides Released during the Hydrolysis of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa willd) Protein Concentrate. Proceedings, 53(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020053012





