Social Conflicts Studied by Statistical Physics Approach and Monte Carlo Simulations †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Two-Group Dynamics
2.1. Model: Time-Dependent Mean-Field Theory
2.2. Monte Carlo Simulation
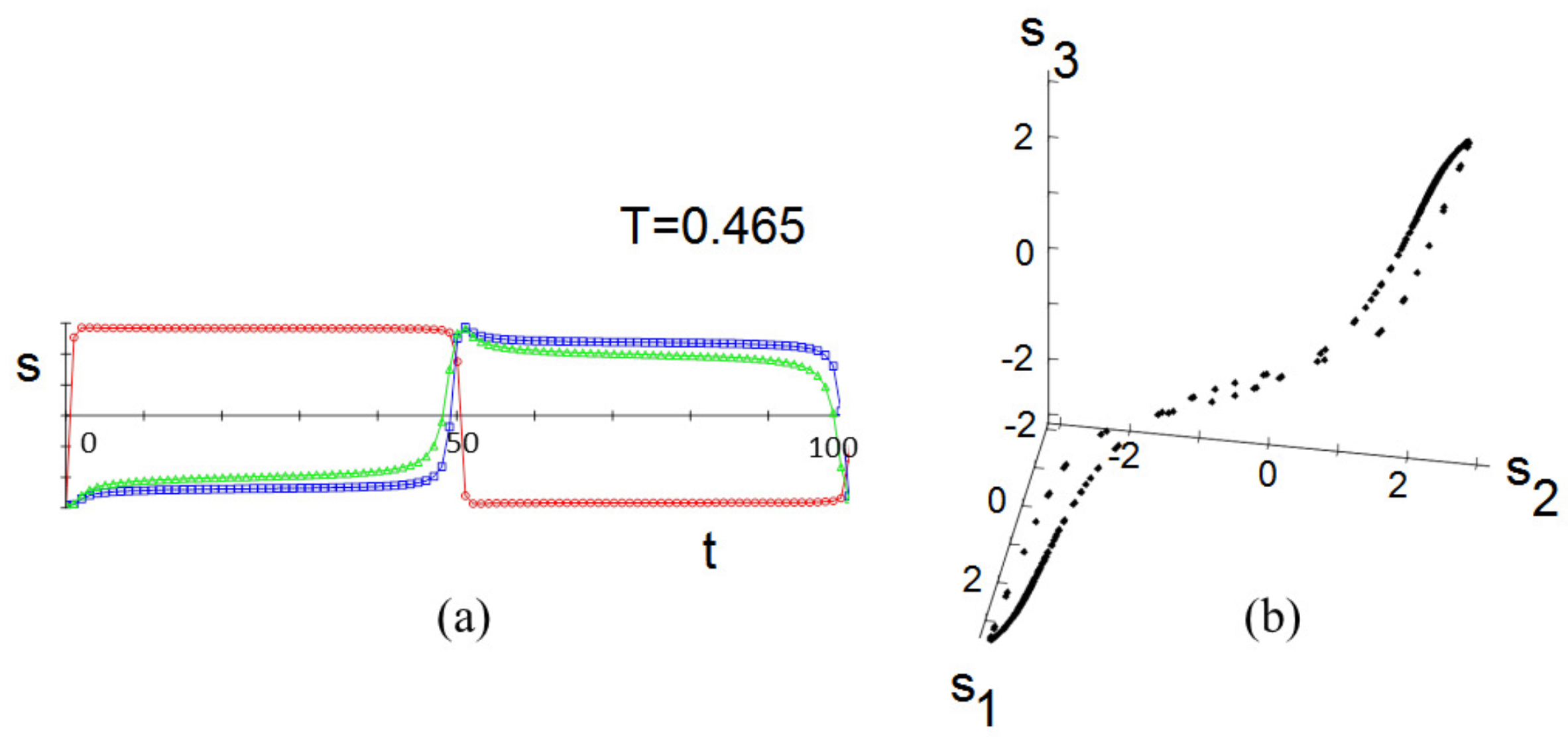
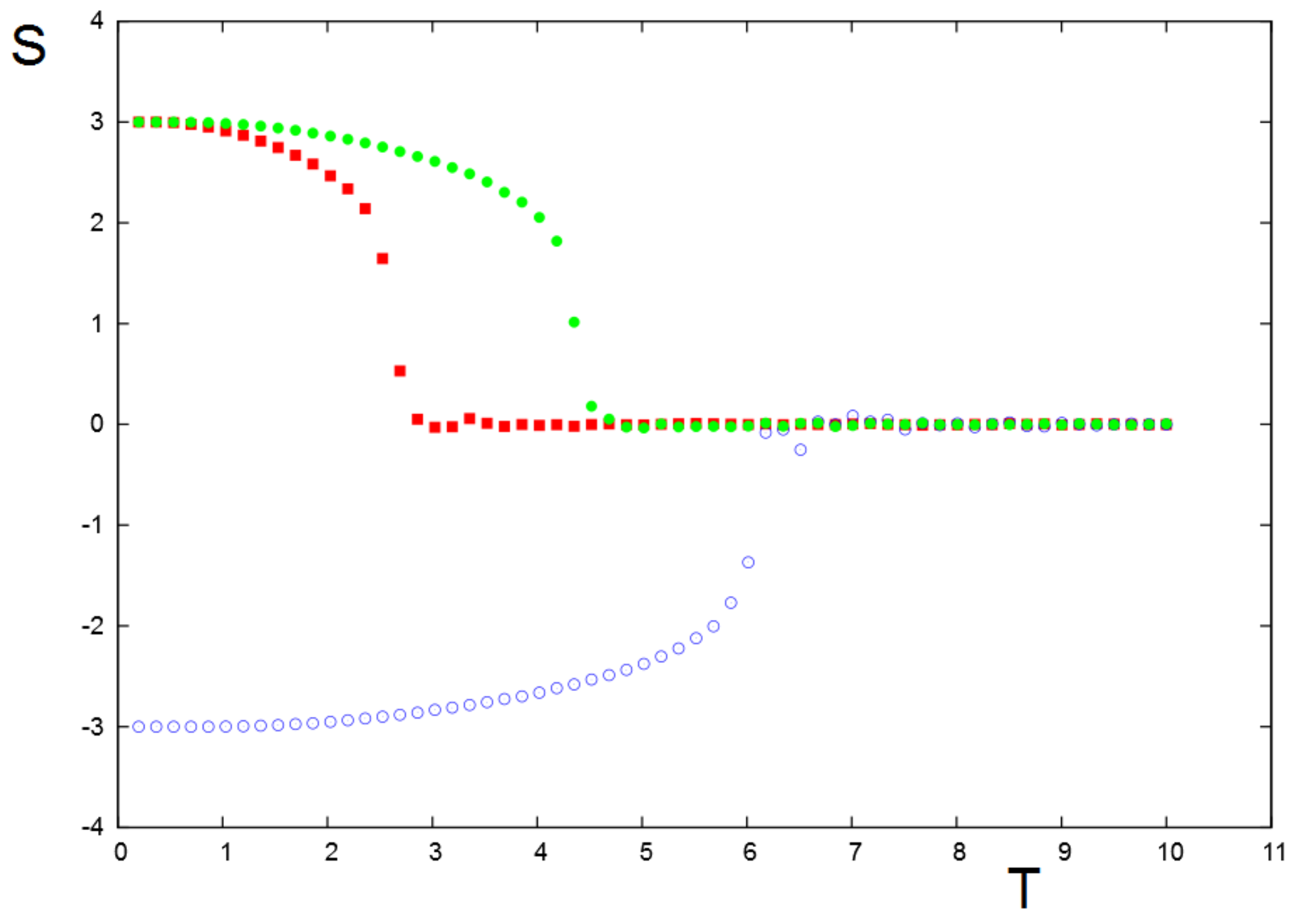
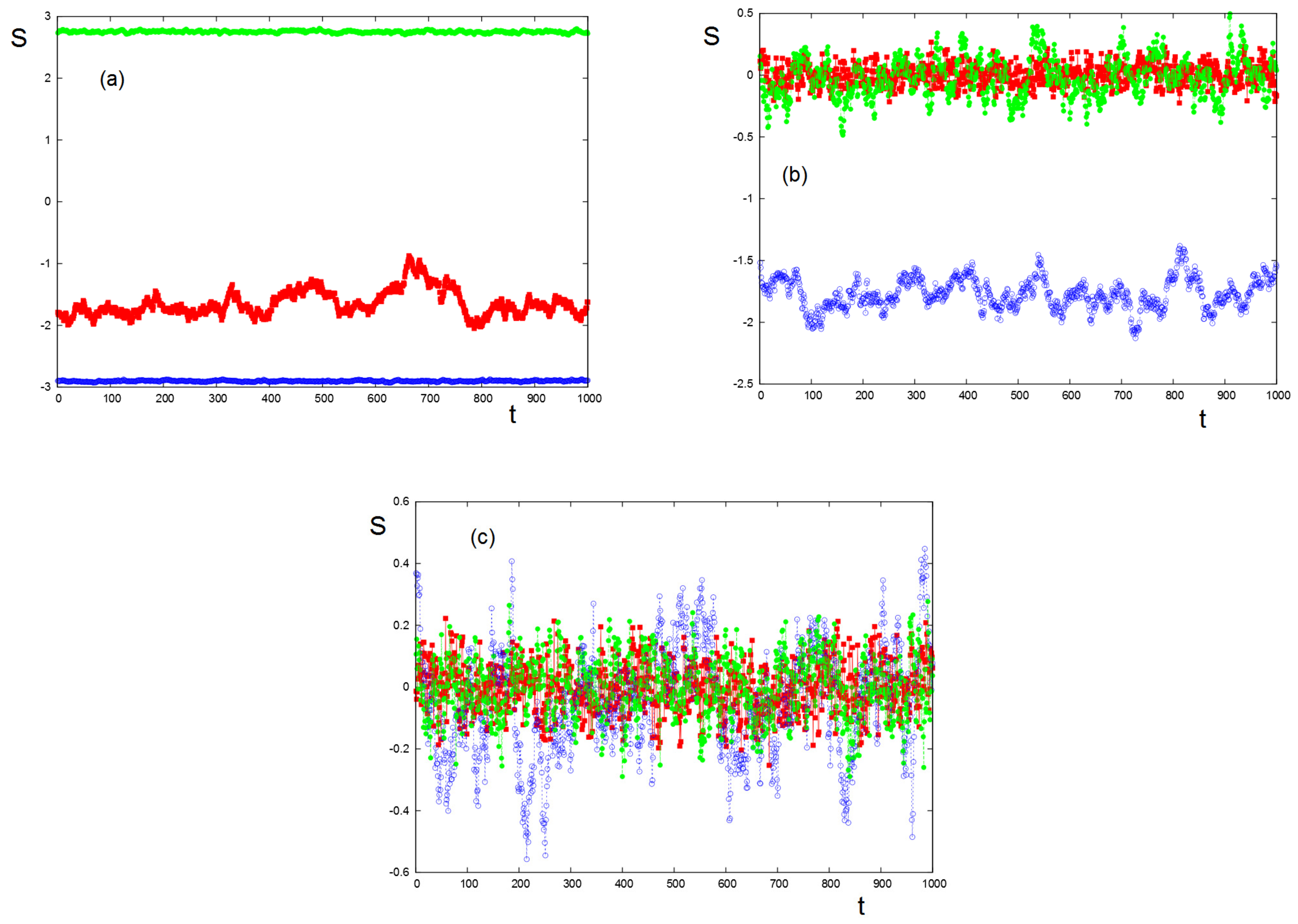
3. Three-Group Dynamics
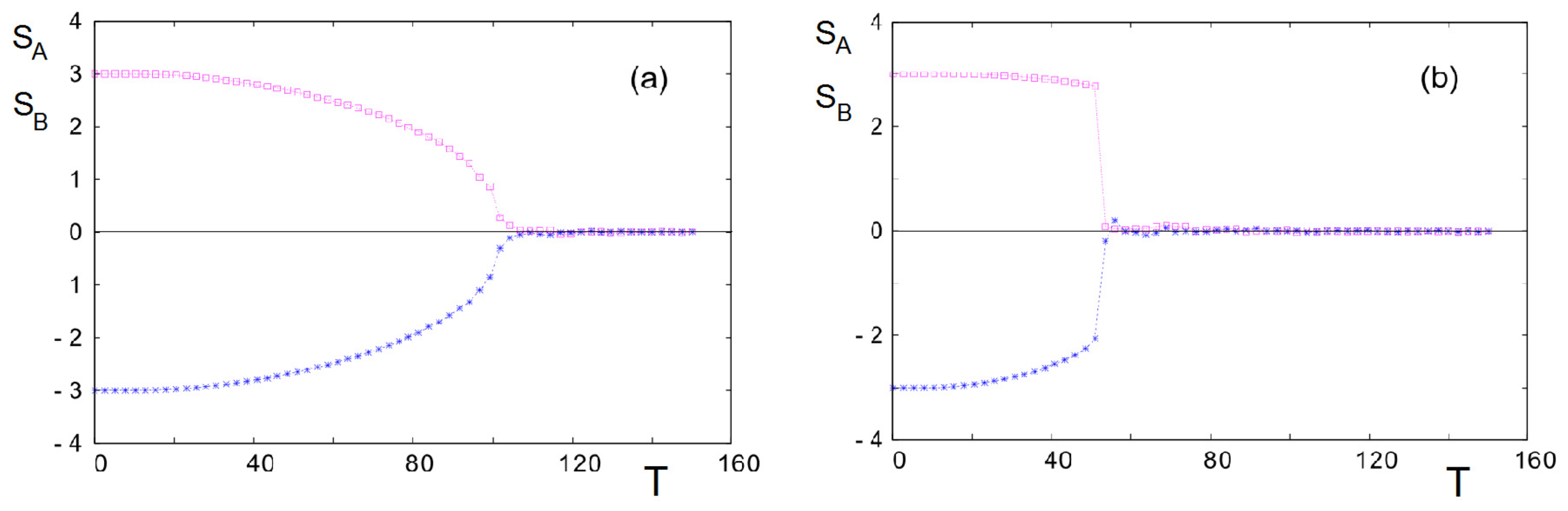
3.1. Mean-Field Results
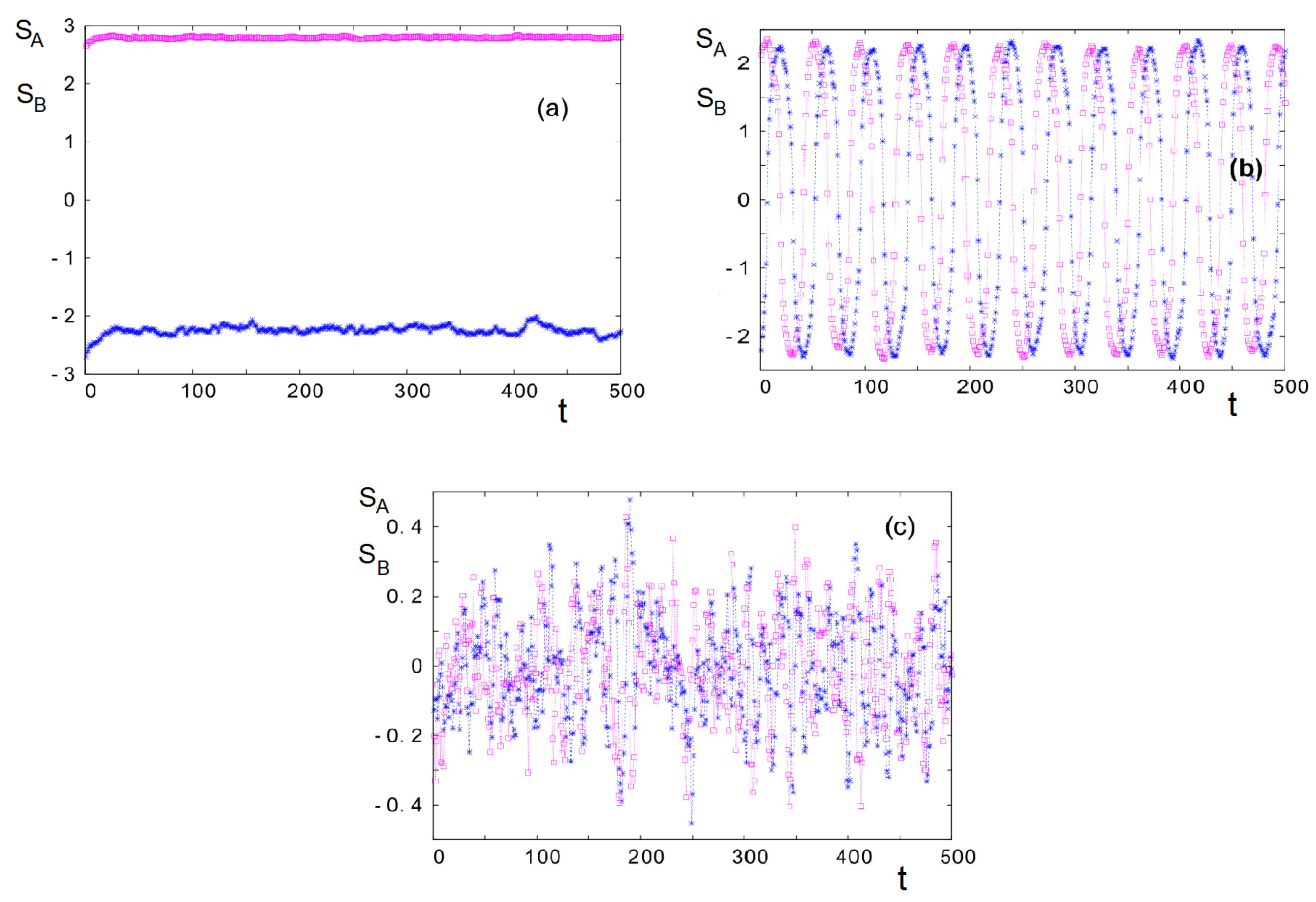
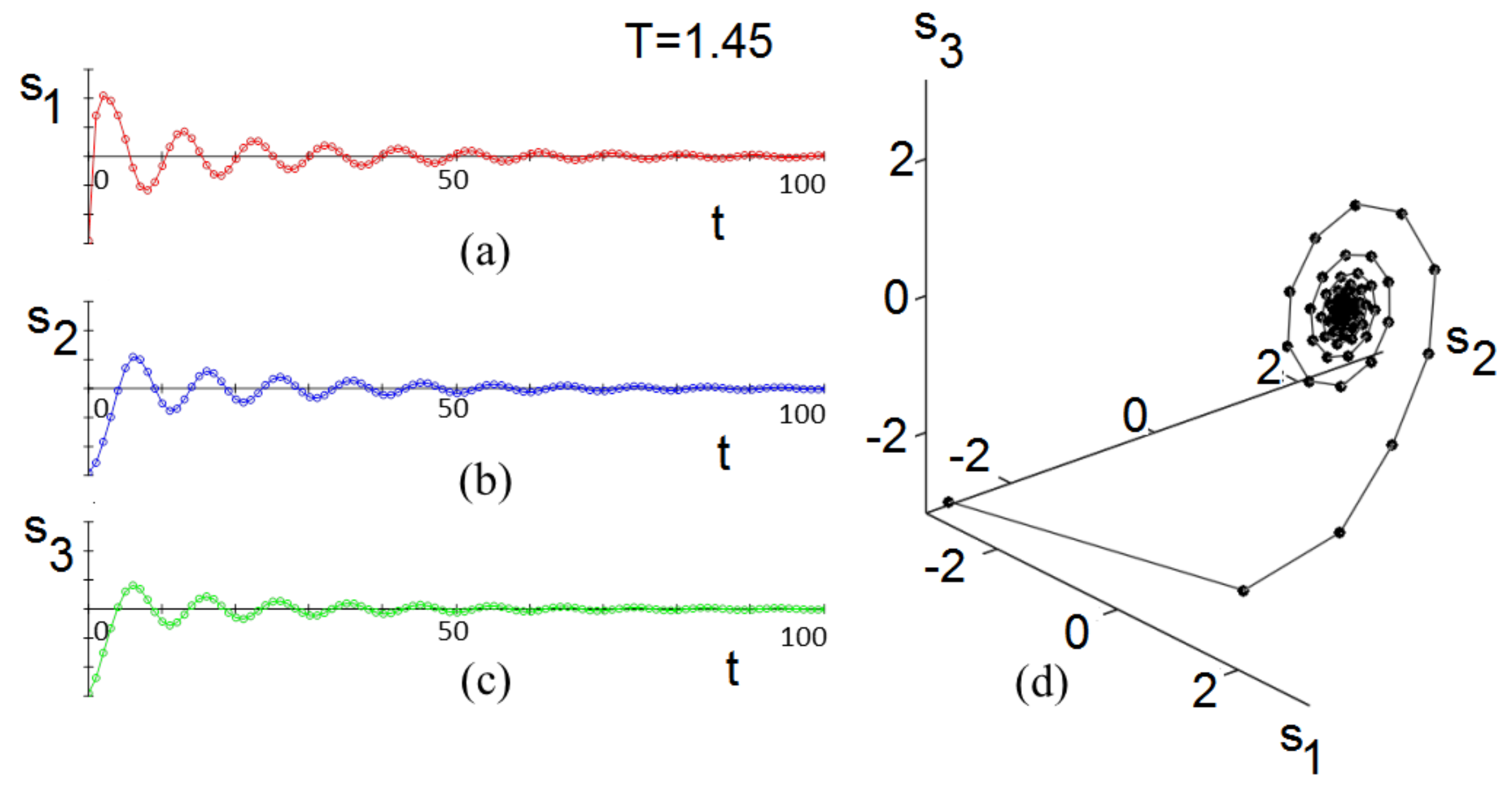
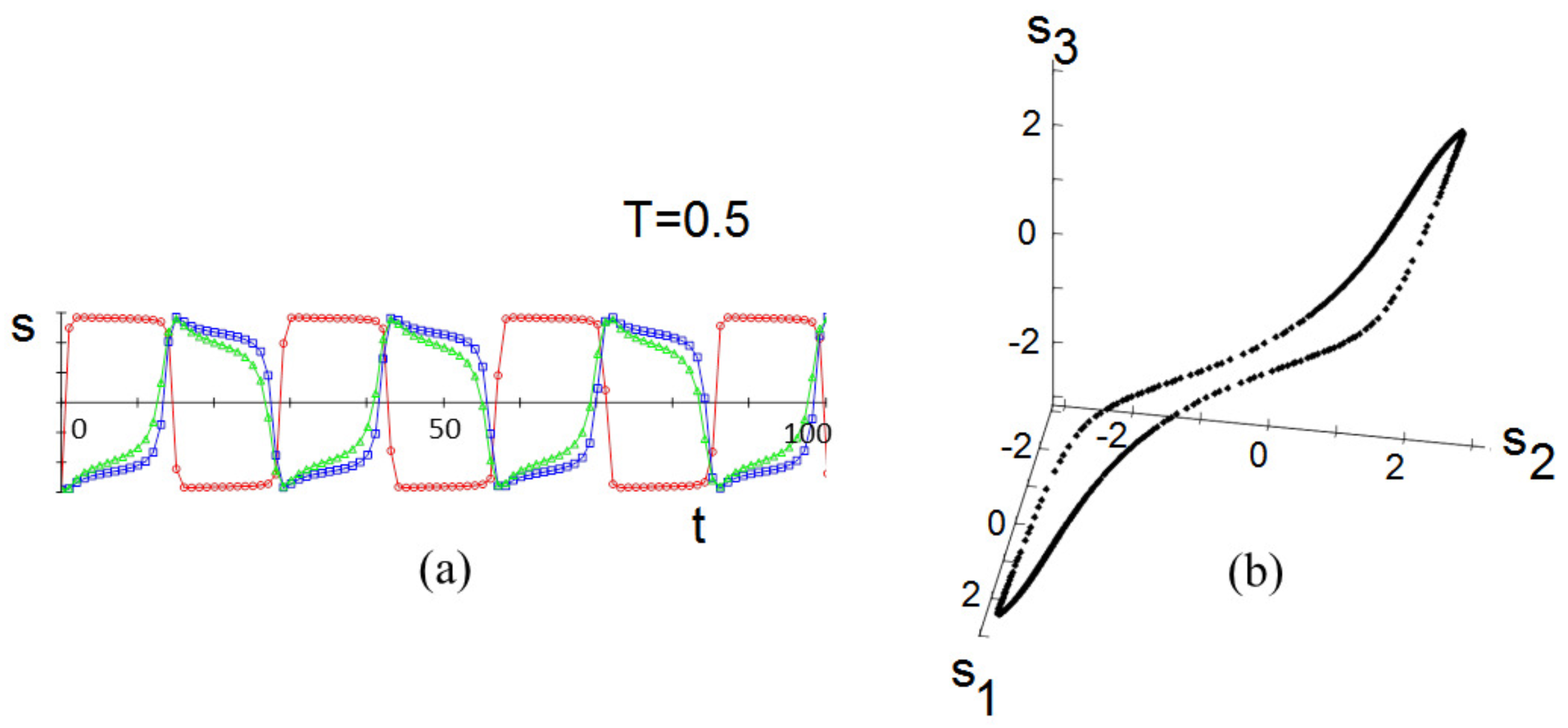
3.2. Monte Carlo Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diep, H.T. Statistical Physics: Fundamentals and Application to Condensed Matter; World Scientific: Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, M. The Social Atom; Bloomsbury: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Galam, S. Sociophysics: A Physicist’s Modeling of Psycho-Political Phenomena; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Castellano, C.; Fortunato, S.; Loreto, V. Statistical physics of social dynamics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coser, L.A. The Functions of Social Conflict; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 1956; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Druckman, D. Human Factors in International Negotiations: A Survey of Research on Social-psychological Aspects of International Conflict; Schweppe Research and Education Fund, Academy for Educational Development: Washington, DC, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt, D.G. Social Conflict; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schelling, T.C. The Strategy of Confict; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, H.W. Persuasion in social conflicts: A critique of prevailing conceptions and a framework for future research. Commun. Monogr. 1972, 39, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, H.T.; Kaufman, M.; Kaufman, S. Dynamics of two-group conflicts: A statistical physics model. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2017, 469, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, M.; Kaufman, S.; Diep, H.T. Scenarios of Social Conflict Dynamics on Duplex Networks. J. Policy Complex Syst. 2017, 3, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galam, S. The Trump phenomenon an explanation from sociophysics. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.03933v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, M.; Diep, H.T.; Kaufman, S. Sociophysics of intractable conflicts: Three-group dynamics. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 517, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, K.; Heermann, D.W. Monte Carlo Simulation in Statistical Physics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Diep, H.T.; Desgranges, G. Dynamics of Price Behavior in Stock Markets: A Statistical Physics Approach. 2019. in preparation. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diep, H.T.; Kaufman, M.; Kaufman, S. Social Conflicts Studied by Statistical Physics Approach and Monte Carlo Simulations. Proceedings 2020, 46, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecea-5-06661
Diep HT, Kaufman M, Kaufman S. Social Conflicts Studied by Statistical Physics Approach and Monte Carlo Simulations. Proceedings. 2020; 46(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecea-5-06661
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiep, Hung T., Miron Kaufman, and Sanda Kaufman. 2020. "Social Conflicts Studied by Statistical Physics Approach and Monte Carlo Simulations" Proceedings 46, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecea-5-06661
APA StyleDiep, H. T., Kaufman, M., & Kaufman, S. (2020). Social Conflicts Studied by Statistical Physics Approach and Monte Carlo Simulations. Proceedings, 46(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecea-5-06661






