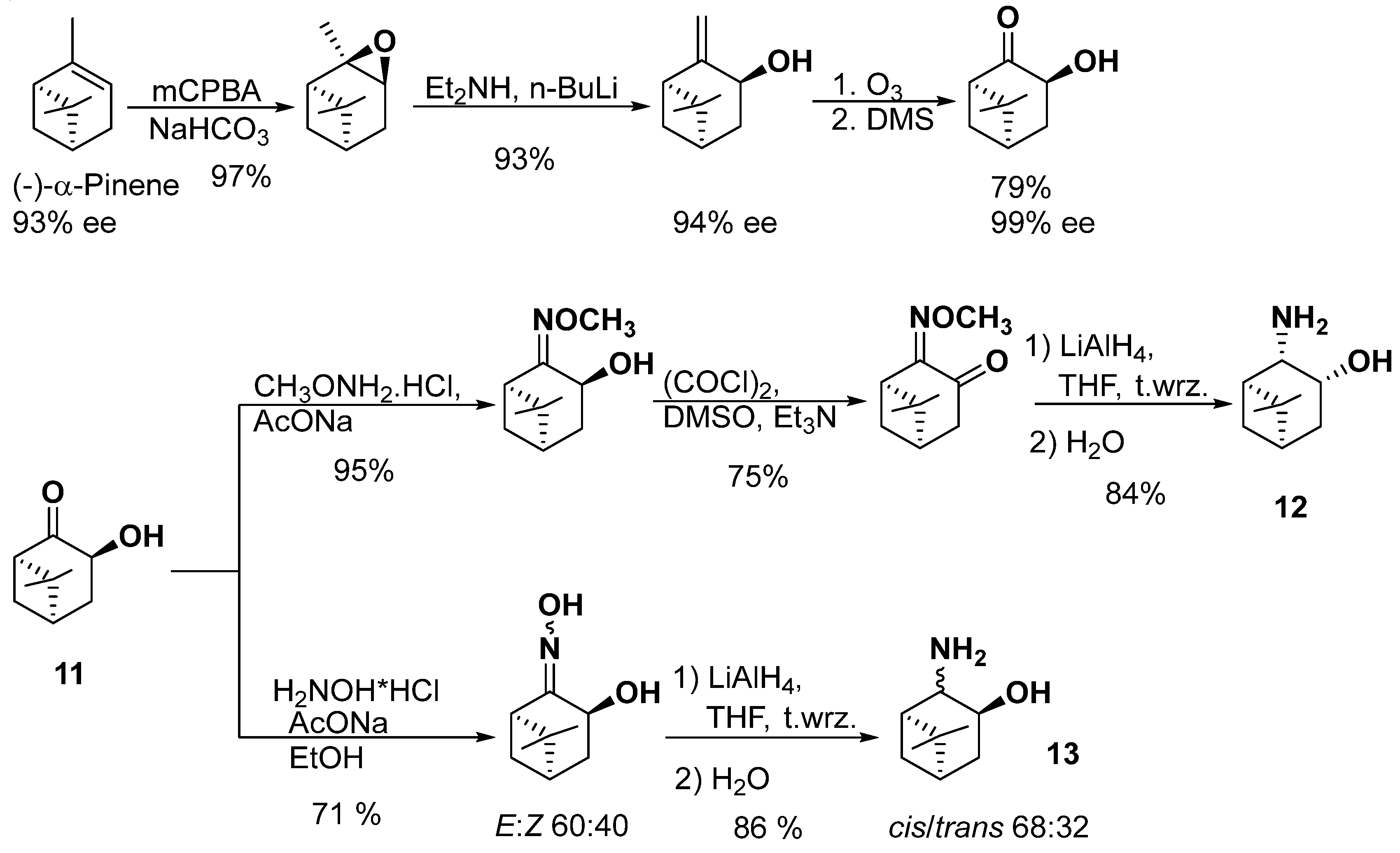
Synthesis of 2-Amino-apopinan-3-ol and Applications of Its Derivatives in Asymmetric Reduction of Ketones †
Abstract
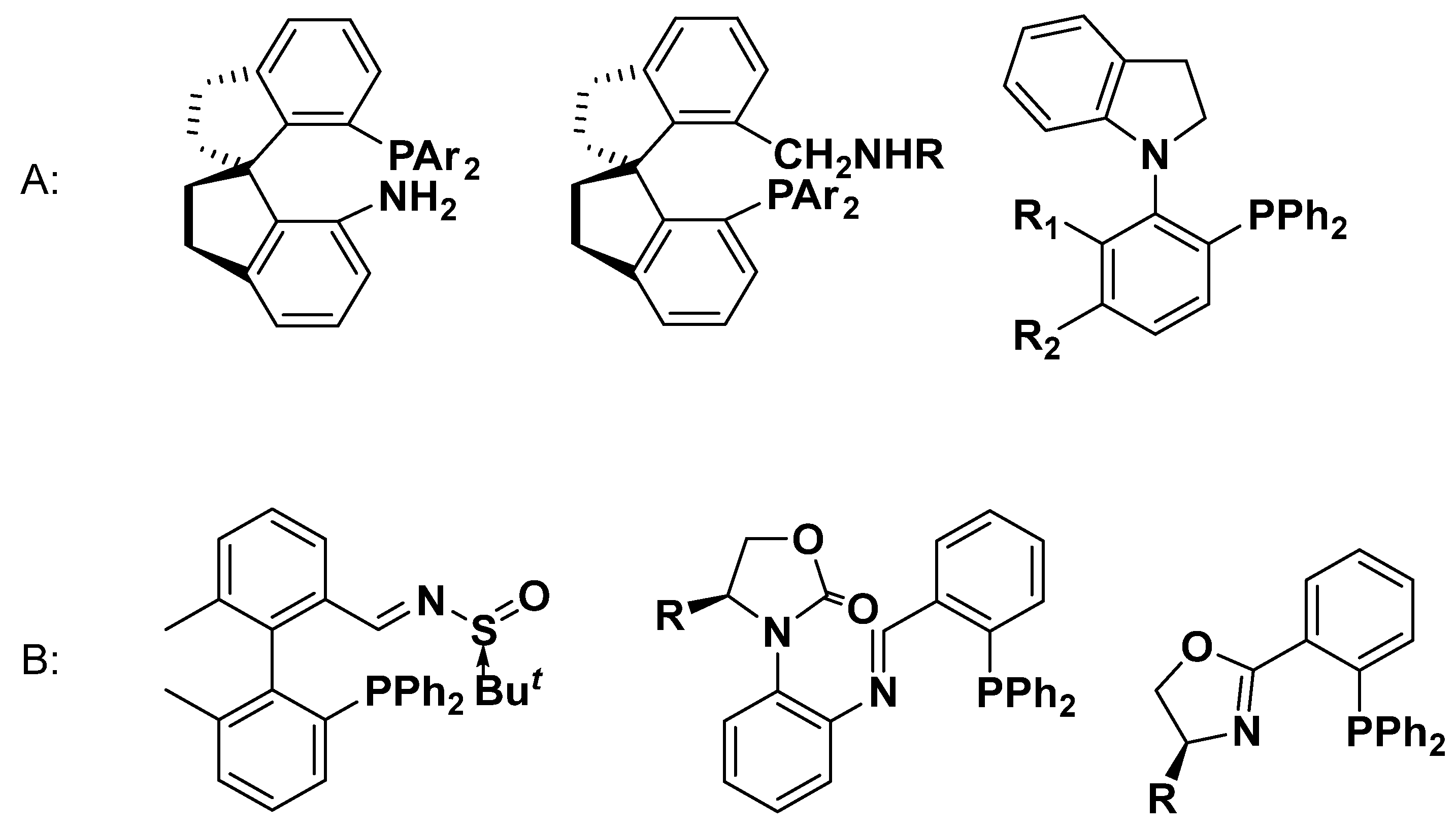
1. Introduction
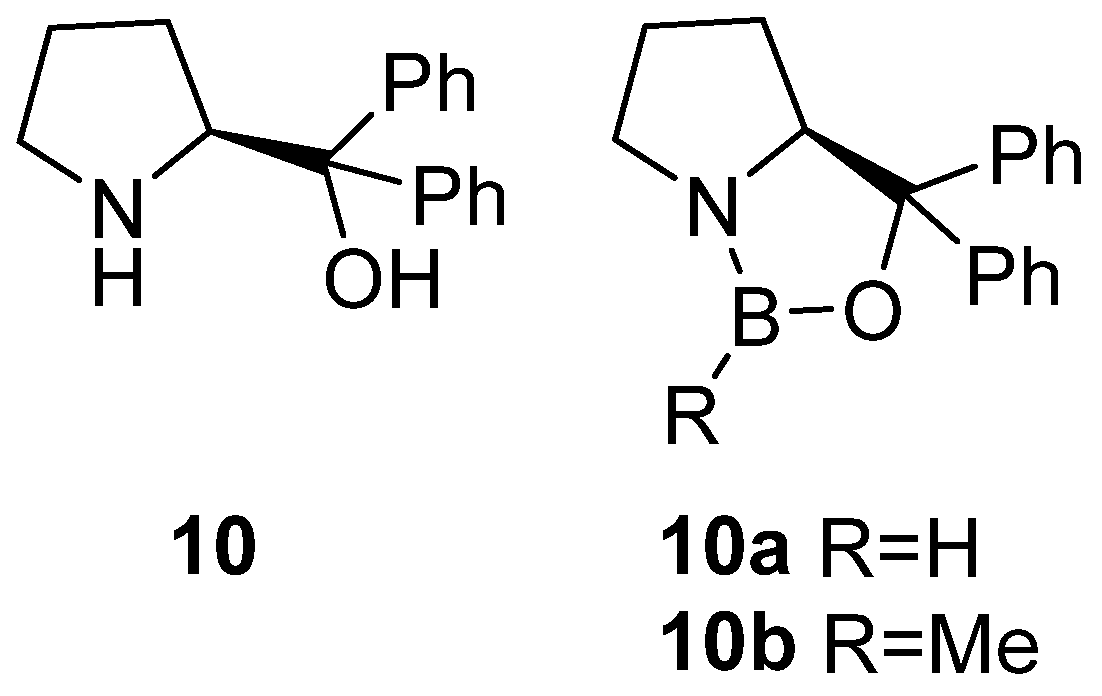
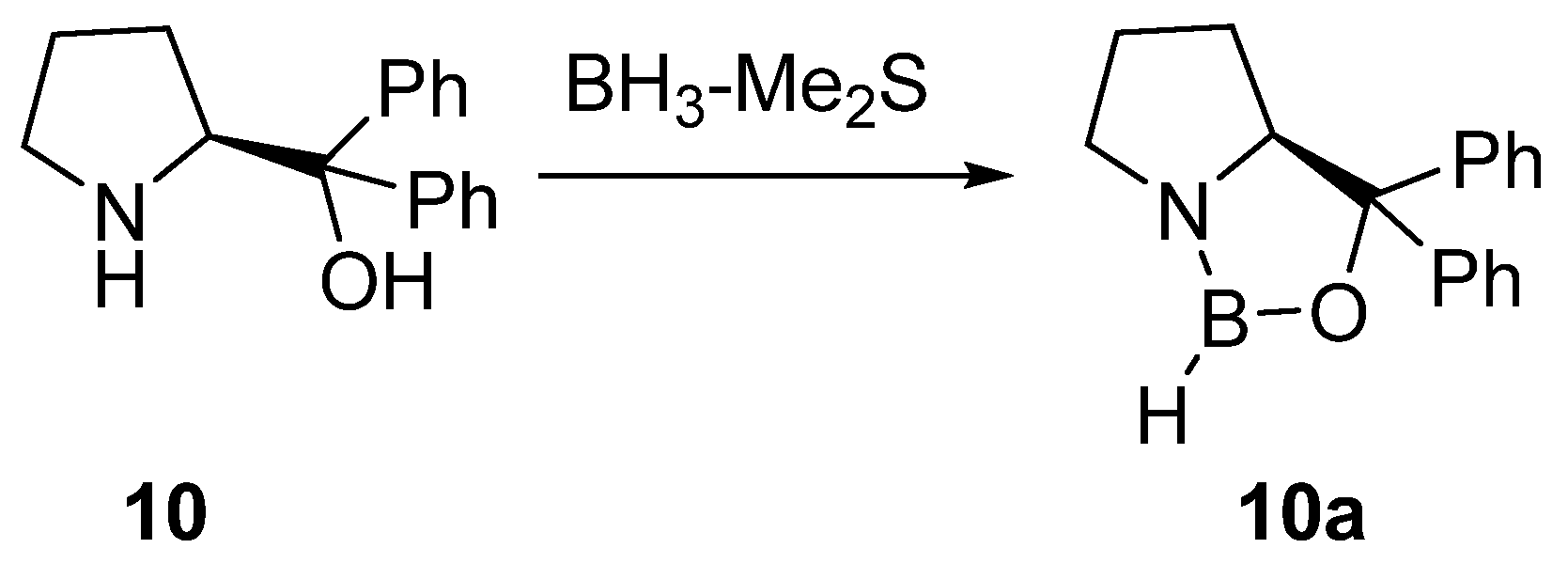
2. Synthesis of β-Amino Alcohols
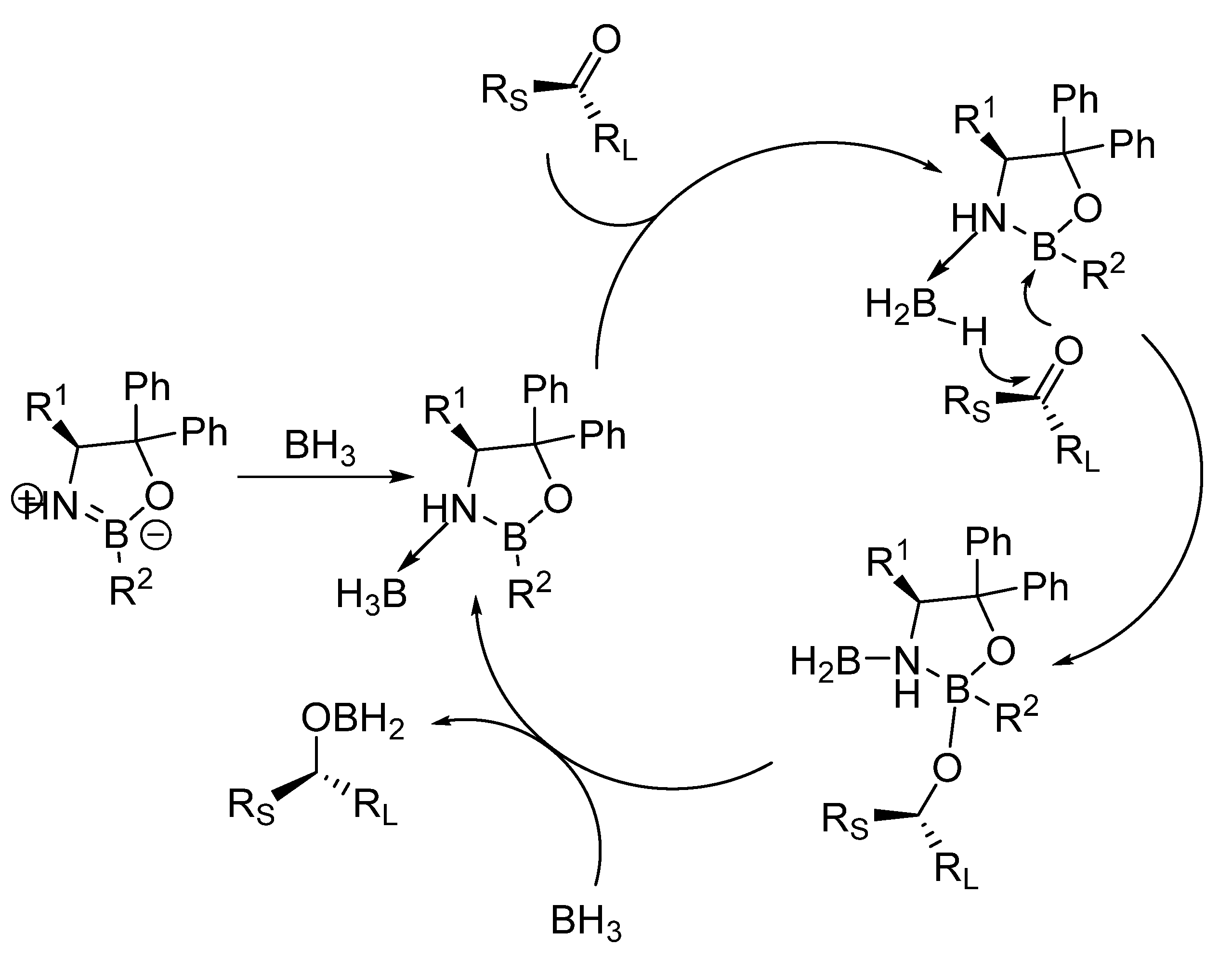
3. Asymmetric Reduction of Aryl-Alkyl Ketones with Borane
4. Conclusions
References
- Carroll, M.P.; Guiry, P.J. P,N ligands in asymmetric catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiry, P.J.; Saunders, C.P. The Development of Bidentate P,N Ligands for Asymmetric Catalysis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 497–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, D.; Graham, T.W.; Guo, R.; Tsang, C.-W.; Abdur-Rashid, K. Aminophosphine catalysts in modern asymmetric synthesis. Aldrichim. Acta 2008, 41, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kostas, I.D. Recent Advances on P,N-Containing Ligands for Transition-Metal Homogeneous Catalysis. Curr. Org. Synth. 2008, 5, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, X.; Kong, W.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q. Highly Enantioselective Hydrogenation of α-Arylmethylene Cycloalkanones Catalyzed by Iridium Complexes of Chiral Spiro Aminophosphine Ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4538–4539. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.-F.; Yu, Y.-B.; Li, S.; Wang, L.-X.; Zhou, Q.-L. Enantioselective Hydrogenation of α-Substituted Acrylic Acids Catalyzed by Iridium Complexes with Chiral Spiro Aminophosphine Ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8872–8875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, M.P.; Guiry, P.J.; Brown, J.M. Meta-analysis in asymmetric catalysis. Influence of chelate geometry on the roles of PN chelating ligands. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 4591–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Kumada, M. Asymmetric synthesis catalyzed by transition-metal complexes with functionalized chiral ferrocenylphosphine ligands. Acc. Chem. Res. 1982, 15, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, D. Novel chiral copper complexes of N,P-ferrocenyl ligands with central and planar chirality as efficient catalyst for asymmetric addition of diethylzinc to imines. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2005, 16, 2531–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mino, T.; Wakui, K.; Oishi, S.; Hattori, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Fujita, T. Kinetic resolution of allylic esters in palladium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic alkylations using C–N bond axially chiral aminophosphine ligands. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2008, 19, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Bohle, D.S.; Li, C. Synthesis of a new chiral amino phosphine ligand and its application in the asymmetric allylic alkylation (AAA) reaction. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2007, 18, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Takale, V.B.; Sarkar, M.S.; Kim, Y. Highly enantioselective Pd-catalyzed allylic alkylation using new chiral ferrocenylphosphinoimidazolidine ligands. Chem. Commun. 2006, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noel, T.; Bert, K.; Van der Eycken, E.; Van der Eycken, J. Imidate–Phosphanes as Highly Versatile N,P Ligands and Their Application in Palladium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation Reactions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 2010, 4056–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, F.; Wu, R.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q.-R.; Xu, Y.-C.; Jiang, L. ‘Evans Auxiliary’ Based P–N Ligands for Pd-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation Reactions. Synlett 2012, 23, 1805–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bert, K.; Noel, T.; Kimpe, W.; Goeman, J.L.; Van der Eycken, J. Chiral imidate–ferrocenylphosphanes: Synthesis and application as P,N-ligands in iridium(i)-catalyzed hydrogenation of unfunctionalized and poorly functionalized olefins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 8539–8550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprinz, J.; Helmchen, G. Phosphinoaryl- and phosphinoalkyloxazolines as new chiral ligands for enantioselective catalysis: Very high enantioselectivity in palladium catalyzed allylic substitutions. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 1769–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Matt, P.; Pfaltz, A. Chiral Phosphinoaryldihydrooxazoles as Ligands in Asymmetric Catalysis: Pd-Catalyzed Allylic Substitution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1993, 32, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, G.J.; Frost, C.G.; Williams, J.M.J.; Coote, S.J. Asymmetric palladium catalysed allylic substitution using phosphorus containing oxazoline ligands. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 3149–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, H.A.; Guiry, P.J. Recent Developments in the Application of Oxazoline-Containing Ligands in Asymmetric Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4151–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargaden, G.C.; Guiry, P.J. Recent Applications of Oxazoline-Containing Ligands in Asymmetric Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2505–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, E.; Pouliot, M.-F.; Courtemanche, M.-A.; Paquin, J.-F. Design, Synthesis, and Applications of Potential Substitutes of t-Bu-Phosphinooxazoline in Pd-Catalyzed Asymmetric Transformations and Their Use for the Improvement of the Enantioselectivity in the Pd-Catalyzed Allylation Reaction of Fluorinated Allyl Enol Carbonates. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 77, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Shen, Q. Bis(perfluoroalkyl) Phosphino-Oxazoline: A Modular, Stable, Strongly π-Accepting Ligand for Asymmetric Catalysis. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 7957–7967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behenna, D.C.; Stoltz, B.M. The Enantioselective Tsuji Allylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15044–15045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, C.M.; Eidamshaus, C.; Kimand, J.; Stoltz, B.M. Enantioselective Construction of α-Quaternary Cyclobutanones by Catalytic Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6718–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, K.; Behenna, D.C.; McFadden, R.M.; Stoltz, B.M. A Facile and Modular Synthesis of Phosphinooxazoline Ligands. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 2529–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrems, M.G.; Pfaltz, A. NeoPHOX—An easily accessible P,N-ligand for iridium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation: Preparation, scope and application in the synthesis of demethyl methoxycalamenene†. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6210–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ding, K. Spiro[4,4]-1,6-nonadiene-Based Phosphine–Oxazoline Ligands for Iridium-Catalyzed Enantioselective Hydrogenation of Ketimines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5345–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Peng, Q.; Dong, D.; Hou, X.; Wu, Y. J. Am. A dramatic switch of enantioselectivity in asymmetric Heck reaction by benzylic substituents of ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backvall, J.E. Transition metal hydrides as active intermediates in hydrogen transfer reactions. J. Organomet. Chem. 2002, 652, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladiali, S.; Alberico, E. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation: Chiral ligands and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyori, R.; Yamakawa, M.; Hashiguchi, S. Metal−Ligand Bifunctional Catalysis: A Nonclassical Mechanism for Asymmetric Hydrogen Transfer between Alcohols and Carbonyl Compounds. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 7931–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, M.; Ito, H.; Noyori, R. The Metal−Ligand Bifunctional Catalysis: A Theoretical Study on the Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed Hydrogen Transfer between Alcohols and Carbonyl Compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyori, R.; Hashiguchi, S. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation Catalyzed by Chiral Ruthenium Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samec, J.S.M.; Bäckvall, J.-E.; Andersson, P.G.; Brandt, P. Mechanistic aspects of transition metal-catalyzed hydrogen transfer reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, T.; Helmchen, G. Highly efficient new catalysts for enantioselective transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 1381–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmieciak, A.; Krzemiński, M. Chiral terpene auxiliaries IV: New monoterpene PHOX ligands and their application in the catalytic asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Tetrahedron Asymmery 2017, 28, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, A.; Itsuno, S.; Nakahama, S.; Yamazaki, N. Asymmetric reduction of aromatic ketones with chiral alkoxy-amineborane complexes. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1981, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itsuno, S.; Hirao, A.; Nakahama, S.; Yamazaki, N. Asymmetric synthesis using chirally modified borohydrides. Part 1. Enantioselective reduction of aromatic ketones with the reagent prepared from borane and (S)-valinol. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1983, 1, 1673–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itsuno, S.; Ito, A.; Hirao, A.; Nakahama, S. Asymmetric reduction of aliphatic ketones with the reagent prepared from (S)-(−)-2-amino-3-methyl-1,1-diphenylbutan-1-ol and borane. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, E.J.; Bakshi, R.K.; Shibata, S. Highly enantioselective borane reduction of ketones catalyzed by chiral oxazaborolidines. Mechanism and synthetic implications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 5551–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, E.J.; Helal, C.J. Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds with Chiral Oxazaborolidine Catalysts: A New Paradigm for Enantioselective Catalysis and a Powerful New Synthetic Method. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 1986–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualich, G.; Woodall, T.M. In Situ Oxazaborolidines, Practical Enantioselective Hydride Reagents. Synlett 1993, 12, 929–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, E.J.; Bakshi, R.K.; Shibata, S.; Chen, C.-P.; Singh, V.K. A stable and easily prepared catalyst for the enantioselective reduction of ketones. Applications to multistep syntheses. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 7925–7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathre, D.J.; Jones, T.K.; Xavier, L.C.; Blacklock, T.J.; Reamer, R.A.; Mohan, J.J.; Jones, E.T.T.; Hoogsteen, K.; Baum, M.W.; Grabowski, E.J.J. A practical enantioselective synthesis of.alpha.,.alpha.-diaryl-2-pyrrolidinemethanol. Preparation and chemistry of the corresponding oxazaborolidines. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.K.; Liotta, D.C.; Shinkai, I.; Mathre, D.J. Origins of the enantioselectivity observed in oxazaborolidine-catalyzed reductions of ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, J.X. (S)-2-Aryl-4,4-diphenyl-3,1,2-oxazaboro[3.3.0]octanes: Efficient catalysts for the asymmetric borane reduction of electron-deficient ketones. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2006, 244, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzemiński, M.; Wojtczak, A. Chiral terpene auxiliaries. Part 1: Highly enantioselective reduction of ketones with borane catalyzed by an oxazaborolidine derived from (−)-β-pinene. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 8299–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavallée, P.; Bouthillier, G.J. Efficient conversion of (1R,5R)-(+)-.alpha.-pinene to (1S,5R)-(−)-nopinone. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, J.K.; Crawley, L.C. Base-induced rearrangement of epoxides to allylic alcohols: Trans-pinocarveol. Org. Synth. 1973, 53, 17. [Google Scholar]


 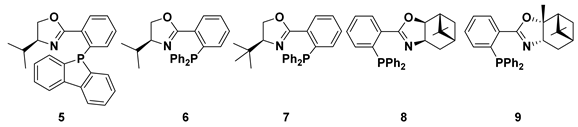 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate. | Ligand | Time [min.] | Conv. [%} | Ee [%] | Ref. |
 | [RuCl25(PPh3)] | 1 | 71 | 87 (R) | 35 |
| 3 | 80 | 78 (R) | 35 | ||
| [RuCl2(PPh3)3] + 5 | 1 | 9 | 91 (R) | 35 | |
| 30 | 37 | 88 (R) | 35 | ||
| 60 | 49 | 86 (R) | 35 | ||
| [RuCl2(PPh3)3] + 6 | 5 | 24 | 94 (R) | 35 | |
| 30 | 74 | 86 (R) | 35 | ||
| 60 | 83 | 73 (R) | 35 | ||
| [RuCl2(PPh3)3] + 7 | 30 | 81 | 85 (R) | 35 | |
| 60 | 84 | 79 (R) | 35 | ||
| [RuCl2(PPh3)3] + 8 | 30 | 98 | 90 (S) | 36 | |
| [RuCl2(PPh3)3] + 9 | 30 | 72 | 37 (R) | 36 | |
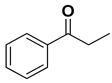 | [RuCl25(PPh3)] | 4 | 50 | 91 (R) | 35 |
| 10 | 85 | 87 (R) | 35 | ||
| [RuCl2(PPh3)3] + 8 | 30 | 88 | 90 (S) | 36 | |
| [RuCl2(PPh3)3] + 9 | 30 | 93 | 51 (R) | 36 | |
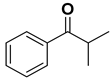 | [RuCl25(PPh3)] | 4 | 56 | 93 (R) | 35 |
| 10 | 74 | 93 (R) | 35 | ||
| 30 | 87 | 92 (R) | 35 | ||
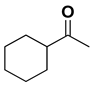 | [RuCl25(PPh3)] | 2 | 70 | 60 (S) | 35 |
| [RuCl2(PPh3)3] + 6 | 60 | 88 | 58 (S) | 35 | |
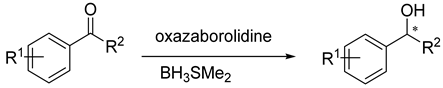 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ketone | |||||||
| Oxazaborolidine | 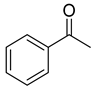 |  | 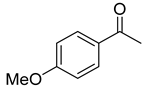 | Ref. | |||
| % ee | Conv. [%[ | % ee | Conv. [%] | % ee | Conv. [%] | ||
 | 96.5 | 100% | 96.7 | 100% | 99 | 100% | 41 |
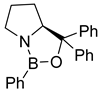 | 97 | 100 | 98 | 100 | 98 | 100 | 46 |
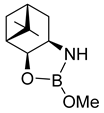 | 98 | 98 | 93 | 99 | 97 | 97 | 47 |
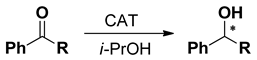 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ketone | CAT [% mol] | BASE | Time [h] | Yield [%] | Ee [%] | Conf. |
 | 0.1 | NaOH | 1 | 75 | 87 | R |
| 0.1 | t-BuOK | 1 | 73 | 93 | ||
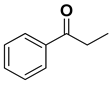 | 0.1 | NaOH | 1 | 64 | 92 | R |
| 0.1 | t-BuOK | 1 | 69 | 96 | ||
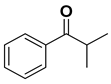 | 0.1 | NaOH | 1.5 | 8 | 58 | R |
| 0.1 | t-BuOK | 1.5 | 22 | 86 | ||
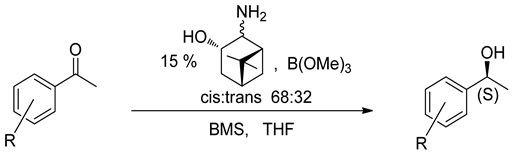 | ||
|---|---|---|
| R | Product | |
| Yield, % | Ee, % | |
| H | 94 | 96 |
| 2-OCH3 | 95 | 94 |
| 3-OCH3 | 89 | 97 |
| 4-OCH3 | 89 | 97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kmieciak, A.; Krzemiński, M.P. Synthesis of 2-Amino-apopinan-3-ol and Applications of Its Derivatives in Asymmetric Reduction of Ketones. Proceedings 2019, 41, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06509
Kmieciak A, Krzemiński MP. Synthesis of 2-Amino-apopinan-3-ol and Applications of Its Derivatives in Asymmetric Reduction of Ketones. Proceedings. 2019; 41(1):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06509
Chicago/Turabian StyleKmieciak, Anna, and Marek P. Krzemiński. 2019. "Synthesis of 2-Amino-apopinan-3-ol and Applications of Its Derivatives in Asymmetric Reduction of Ketones" Proceedings 41, no. 1: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06509
APA StyleKmieciak, A., & Krzemiński, M. P. (2019). Synthesis of 2-Amino-apopinan-3-ol and Applications of Its Derivatives in Asymmetric Reduction of Ketones. Proceedings, 41(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-23-06509






