Abstract
Current electrolytes for electrochemical energy storage devices are made of solvents, which often present problems of flammability, corrosion and high toxicity. Ionic liquids and mixtures with metal salts are proposed as a good selection for safer electrolytes due to their properties such as, among others, non-flammability, negligible vapor pressure, high ionic conductivity and wide electrochemical window. In this work, the electrical conductivity of solutions of the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium nitrate ([EIm][NO3]) with lithium nitrate salt in three different concentrations is analyzed for liquid and gel states. The temperature and salt concentration dependences of electrical conductivity are studied for liquid and gel states. As expected, an increase in conductivity with temperature and a decrease with salt concentration were observed, except for the case of gel [EIm][NO3] with a salt concentration of 0.5 m, which shows a small increase in conductivity compared to the pure gel. Comparison of the conductivity of the liquid and gel states shows a significant increase for the gel state at low concentrations of the added salt.
1. Introduction
The increasing demand for batteries has led industry and academia to focus on improving the performance, safety and cost of lithium battery technology. Replacing the flammable electrolytes used in current batteries with non-flammable compounds, for example ionic liquids (ILs) doped with inorganic salts containing relevant metals for this electrochemical application [1,2], can be an important step to achieve these improvements.
ILs are nanostructured green compounds considered as a new class of solvents, whose properties can be appropriately tuned (designer solvents) by choosing combinations of cations and anions from the large number of currently known IL moieties.
Recent studies suggest the possibility of using sol–gel electrolytes [3] in electrochemical devices to improve the safety of the electrolyte and facilitate its manipulation, although the behavior of some key properties such as ionic conductivity after gelation have not been studied in depth, with some contradictory results found in the literature.
In this work, the effect of gelation and the influence of lithium salt doping of the ionogel of ethylimidazolium nitrate ionic liquid are analyzed in terms of ionic conductivity against temperature.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
Solutions of IL [EIm][NO3] with lithium salt (LiNO3) were prepared via stirring/mixing at three different concentrations (0.5, 1 and 3 mol·kg−1). Chemical structures and further identification of chemical compounds (CAS registry number, molecular weight, etc.) can be found in Table 1. Furthermore, detailed information on the mixtures can be found in Table 2.

Table 1.
Identification of the chemicals used in this work.

Table 2.
Molality of the studied samples and mass of pure metal salts per 100 g of pure ionic liquid (IL).
[EIm][NO3]–lithium salt mixtures were dried via a vacuum procedure for 24–48 h in order to remove water content. The residual quantity of water was measured using a Karl Fischer titrator, and quantities of water lower than 100 ppm were obtained.
2.2. Gelation Routes
A main procedure for the sol–gel route in order to prepare gel samples was carried out, using an adaptation of the method described by Garaga et al. [4]. A brief description of the selected method is the following:
- The volume proportions of the sample mixtures were 3 parts of EtOH, 0.428 of TEOS and 1 of [EIm][NO3] (or mixture), and then these mixtures were stirred in a round flask for at least 60 min.
- After that, they were transferred to a vial, where the mixture was stored in a furnace at 40 °C until ethanol was completely evaporated (7–8 days).
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Electrical Conductivity
With the purpose of obtaining electrical conductivity (σ), a conductimeter GLP31 from CRISON was used at a constant frequency of 500 Hz. The resolution of this conductivity meter is better than 1% of the measured value; the minimum and maximum values registered by CRISON GLP31 are 0.2 µS·cm−1 and 100 mS·cm−1, respectively. The probe is formed by two parallel flat platinum plates, which can take measurements in the case of liquid or gel samples in a temperature range from 243 to 323 K. A calibrated Julabo F25 thermostat was used to control the temperature of the sample; the error in the temperature was lower than 0.1 K. These measurements need to be taken in an isothermal regime, so the time spent on each measurement was at least 15 min while there was no phase transition. When phase transition took place, the time spent on the measurement was more than 30 min.
4. Results
Figure 1 shows the ionic conductivity of IL–salt mixtures versus temperature for (a) liquid form and (b) gel form. An increase in conductivity with temperature can be seen for all samples. The temperature dependence of the ionic conductivity of all the samples was found to be well described by the Vogel–Fulcher–Tammann (VFT) equation [5]. On the other hand, a clear decrease in conductivity with the salt concentration in liquid state is also observed, and different behavior can be observed for gel form (Figure 1b), characterized by an increase in conductivity until a maximum value around 0.5 molsalt/kg, followed by a decrease with further salt addition.
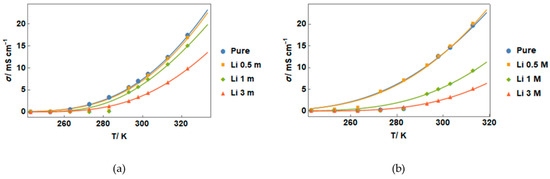
Figure 1.
Electrical conductivity vs. temperature measured in a cooling ramp for (a) liquid and (b) gel forms. Lines in the figure correspond to Vogel–Fulcher–Tammann (VFT) fitting curves in liquid and gel forms.
An increase in conductivity for the lowest studied concentration of salt addition in gel state can be clearly seen in Figure 2, which shows the conductivity vs. molality curves for different temperatures.
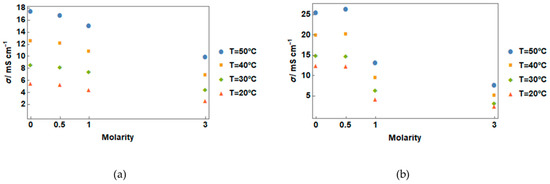
Figure 2.
Electrical conductivity vs. temperature in a cooling ramp for (a) liquid and (b) gel states.
This behavior agrees with Garaga et al. [4], who found an enhancement of ionic mobility after gelation using silica micro-particles, although to our knowledge, studies about the behavior of conductivity with salt addition in gel form have not been previously performed.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness and the FEDER Program through the project MAT2017-89239-C2-1-P, and by the Xunta de Galicia through the GRC ED431C 2016/001 project and the Galician Network of Ionic Liquids (ReGaLIs) ED431D 2017/06. P. Vallet and J. J. Parajó thank funding support from the FPI Program of the Spanish Ministry of Science, Education and Universities and the I2C postdoctoral Program of the Xunta de Galicia, respectively.
References
- Salgado, J.; Parajó, J.J.; Villanueva, M.; Rodríguez, J.R.; Cabeza, O.; Varela, L.M. Liquid range of ionic liquid—Metal salt mixtures for electrochemical applications. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 134, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Tachikawa, N.; Forsyth, M.; Pringle, J.M.; Howlett, P.C.; Elliott, G.D.; Davis, J.H.; Watanabe, M.; Simon, P.; Angell, C.A. Energy applications of ionic liquids. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nègre, L.; Daffos, B.; Turq, V.; Taberna, P.L.; Simon, P. Ionogel-based solid-state supercapacitor operating over a wide range of temperature. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 206, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaga, M.N.; Aguilera, L.; Yaghini, N.; Matic, A.; Persson, M.; Martinelli, A. Achieving enhanced ionic mobility in nanoporous silica by controlled surface interactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 5727–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timachova, K.; Chintapalli, M.; Olson, K.R.; Mecham, S.J.; DeSimone, J.M.; Balsara, N.P. Mechanism of ion transport in perfluoropolyether electrolytes with a lithium salt. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 5389–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).