Alzheimer’s Disease: A Step Towards Prognosis Using Smart Wearables †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
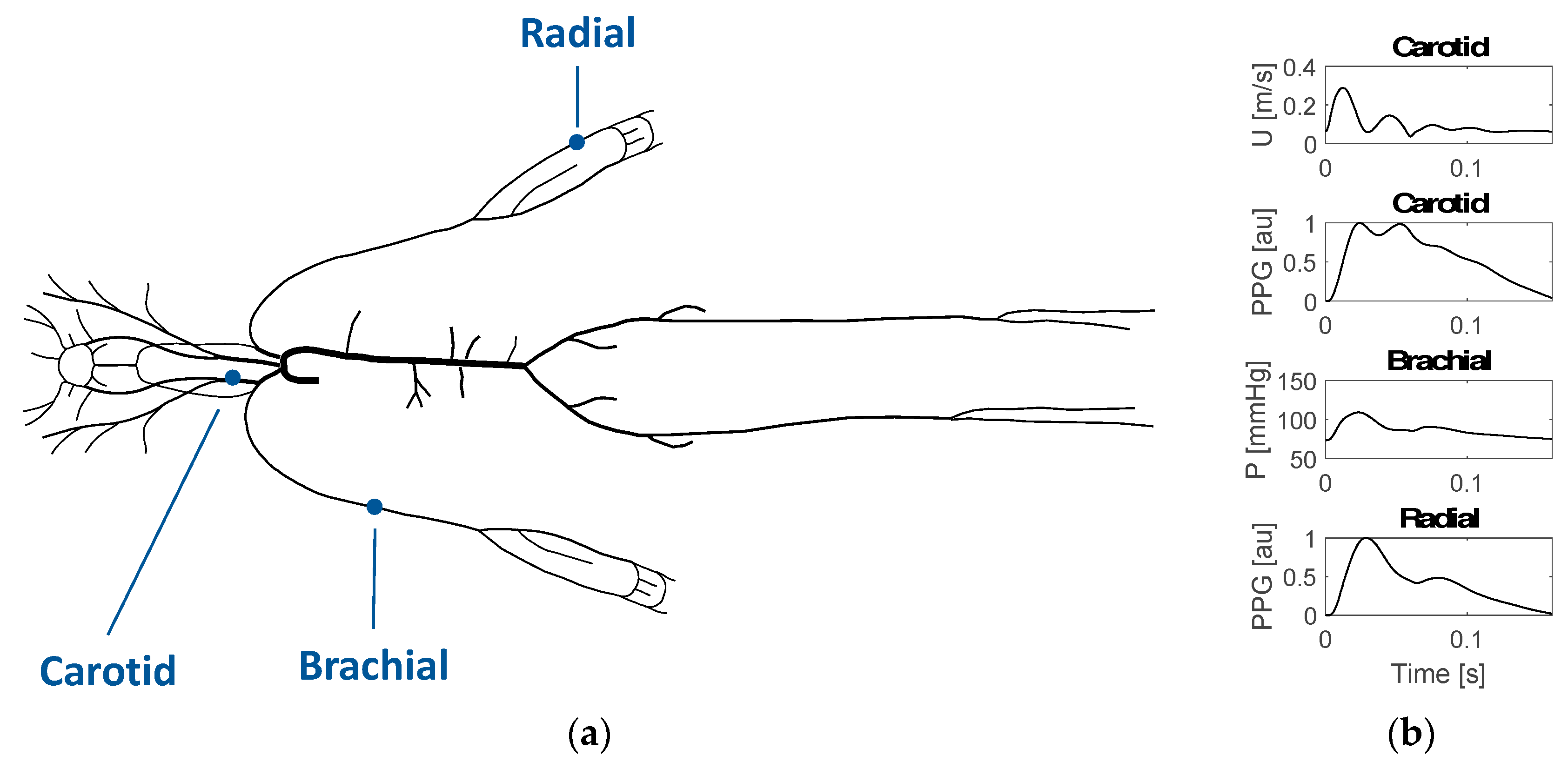
2.1. Simulating Arterial Pulse Waves (PWs)
2.2. Investigating the Impact of Risk Factors on Haemodynamics
2.3. Identifying Pulse Wave (PW) Features Indicative of Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
3. Results and Discussion
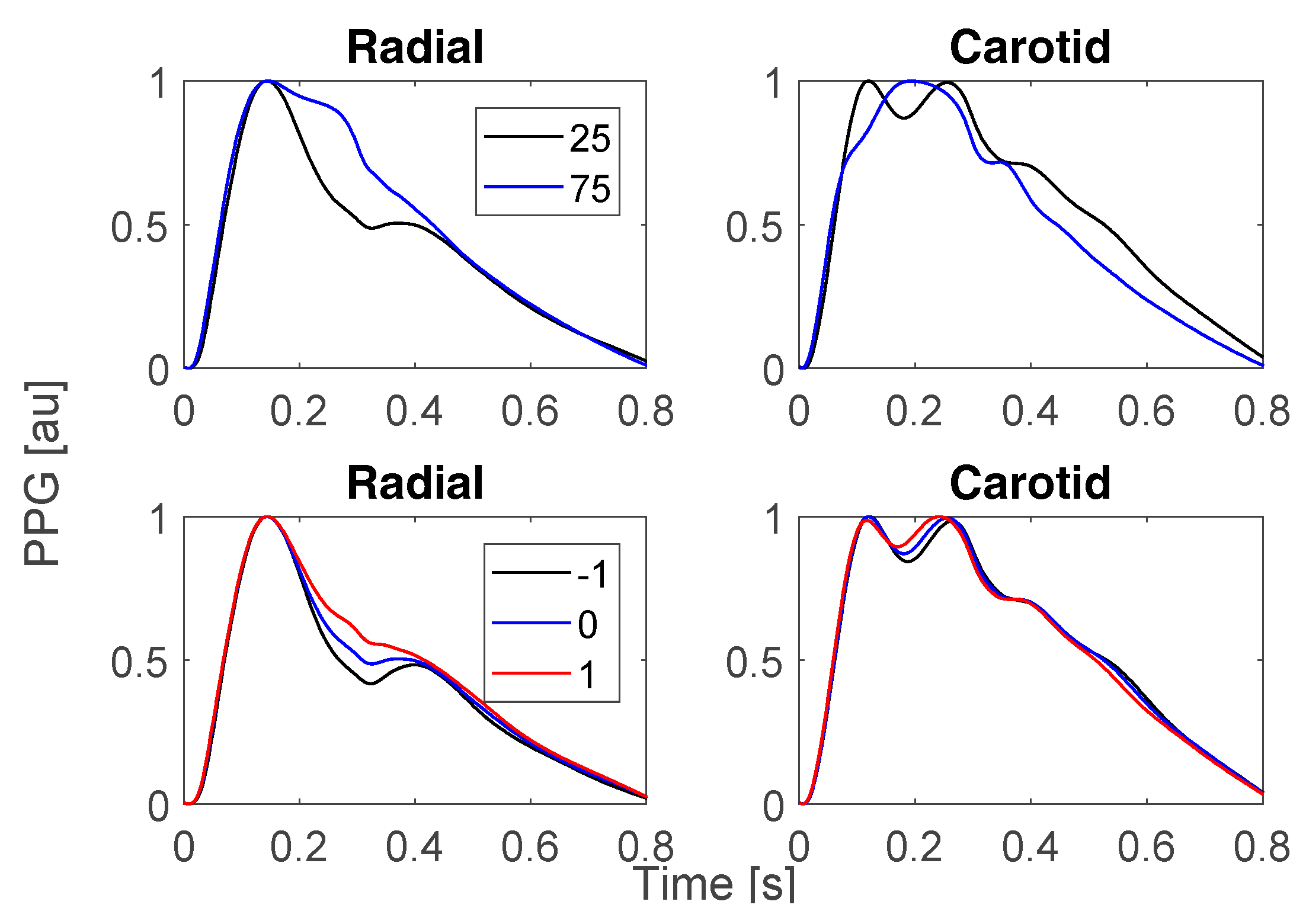
3.1. Changes in Risk Factors for Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
3.2. Towards Pulse Wave Markers of Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
3.3. Relevance for Prognosis
3.4. Limitations and Future Work
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2017 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 325–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winblad, B.; Amouyel, P.; Andrieu, S.; Ballard, C.; Brayne, C.; Brodaty, H.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Dubois, B.; Edvardsson, D.; Feldman, H.; et al. Defeating Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: A priority for European science and society. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 455–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustavsson, A.; Brinck, P.; Bergvall, N.; Kolasa, K.; Wimo, A.; Winblad, B.; Jönsson, L. Predictors of costs of care in Alzheimer’s disease: A multinational sample of 1222 patients. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, S.; Matthews, FE.; Barnes, D.E.; Yaffe, K.; Brayne, C. Potential for primary prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: An analysis of population-based data. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitz, C.; Mayeux, R. Alzheimer disease: Epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, risk factors and biomarkers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pase, M.P.; Herbert, A.; Grima, N.A.; Pipingas, A.; O’Rourke, M.F. Arterial stiffness as a cause of cognitive decline and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern. Med. J. 2012, 42, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, B.P.; Nair, V.A.; Meier, T.B.; Xu, G.; Rowley, H.A.; Carlsson, C.M.; Johnson, S.C.; Prabhakaran, V. Effects of hypoperfusion in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 26, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Pi, Z.; Liu, B. TROIKA: A general framework for heart rate monitoring using wrist-type photoplethysmographic signals during intensive physical exercise. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alastruey, J.; Parker, K.H.; Sherwin, S.J. Arterial pulse wave haemodynamics. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Pressure Surges, Lisbon, Portugal, 24–26 October 2012; pp. 401–443. [Google Scholar]
- Charlton, P.H.; Mariscal Harana, J.; Vennin, S.; Willemet, M.; Chowienczyk, P.; Alastruey, J. Modelling arterial pulse wave propagation during healthy ageing. In Proceedings of the World Congress of Biomechanics 2018, Dublin, Ireland, 8–12 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Charlton, P.H.; Celka, P.; Farukh, B.; Chowienczyk, P.; Alastruey, J. Assessing mental stress from the photoplethysmogram: A numerical study. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 054001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roher, A.E.; Esh, C.; Kokjohn, T.A.; Kalback, W.; Luehrs, D.C.; Seward, J.D.; Sue, L.I.; Beach, T.G. Circle of Willis atherosclerosis is a risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corder, E.H.; Ervin, J.F.; Lockhart, E.; Szymanski, M.H.; Schmechel, D.E.; Hulette, C.M. Cardiovascular damage in Alzheimer disease: Autopsy findings from the Bryan ADRC. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2005, 2, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.Y.; Snyder, P.J.; Wu, W.-C.; Zhang, M.; Echeverria, A.; Alber, J. Pathophysiologic relationship between Alzheimer’s disease, cerebrovascular disease, and cardiovascular risk: A review and synthesis. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 7, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-W.; Fuh, J.-L. Exposure to general anesthesia and the risk of dementia. J. Pain Res. 2015, 8, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gelman, S. General anesthesia and hepatic circulation. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1987, 65, 1762–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamagata, K.; Motoi, Y.; Hori, M.; Suzuki, M.; Nakanishi, A.; Shimoji, K.; Kyougoku, S.; Kuwatsuru, R.; Sasai, K.; Abe, O.; et al. Posterior hypoperfusion in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia measured with arterial spin labeling MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruitenberg, A.; den Heijer, T.; Bakker, S.L.; van Swieten, J.C.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Hofman, A.; Breteler, M.M. Cerebral hypoperfusion and clinical onset of dementia: The Rotterdam study. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 57, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pontoriero, A.D.; Charlton, P.H.; Alastruey, J. Alzheimer’s Disease: A Step Towards Prognosis Using Smart Wearables. Proceedings 2019, 4, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05742
Pontoriero AD, Charlton PH, Alastruey J. Alzheimer’s Disease: A Step Towards Prognosis Using Smart Wearables. Proceedings. 2019; 4(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05742
Chicago/Turabian StylePontoriero, Antonella D., Peter H. Charlton, and Jordi Alastruey. 2019. "Alzheimer’s Disease: A Step Towards Prognosis Using Smart Wearables" Proceedings 4, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05742
APA StylePontoriero, A. D., Charlton, P. H., & Alastruey, J. (2019). Alzheimer’s Disease: A Step Towards Prognosis Using Smart Wearables. Proceedings, 4(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05742






