1. Introduction
In recent years, works have shown that probiotics have beneficial localized effects. Probiotic treatment is effective against diseases and infections of the skin and mucous membranes [1]. Several studies on the probiotic Lactobacillus Reuteri (L. Reuteri) have demonstrated anti-inflammatories and antimicrobials effects [2].
2. Materials and Methods
A 48-year-old female patient with non-plaque and tartar gingival papilla swelling between the upper incisors 1.1–1.2, went to our observation (Figure 1). She takes drugs for hypertension and vitamin D supplement, suffers from periodontal diseases in a good state of maintenance and was subjected to professional oral hygiene sessions every 4 months. It was decided to perform a biopsy, scheduled 2 weeks later. To restore the oral probiotic microbiota L. Reuteri have been suggested. Tablets of Lactobacillus Reuteri DSM 17938 ATCC PTA 5289 have been prescribed as home therapy twice a day, for two weeks, dissolving them slowly in the mouth after careful oral hygiene, taking care to rub the tablet with the tongue against the swollen papilla. At the check the gum appeared during the normalization phase, so the treatment was prolonged for another two weeks, and the biopsy has been postponed (Figure 2).
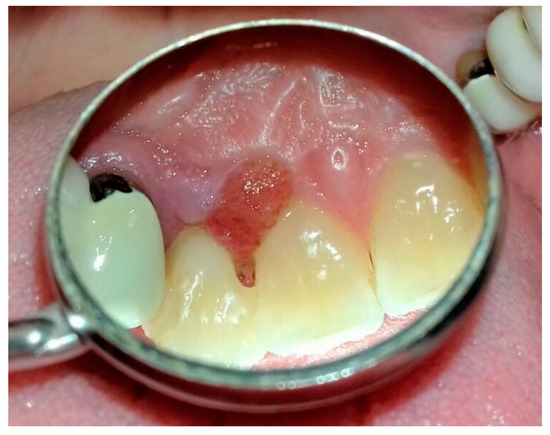
Figure 1.
Patient before using probiotics L. Reuteri DSM 17938 ATCC PTA 5289.
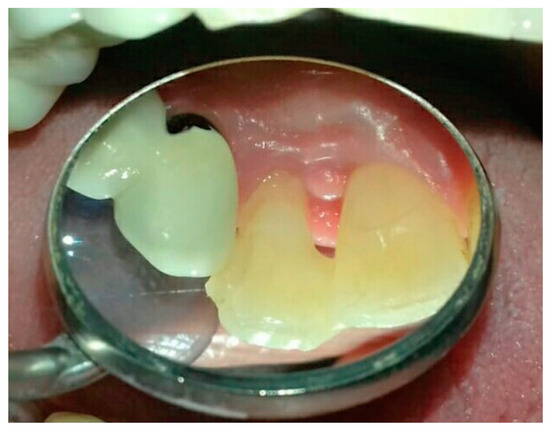
Figure 2.
Patient 4 weeks after therapy with L. Reuteri DSM 17938 ATCC PTA 5289.
3. Results
4 weeks of follow-up were carried out. The gingival papilla is completely healed after treatment with L. Reuteri.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Oral treatment with tablets containing the probiotic strain of L. Reuteri induces in most patients a significant reduction in the proinflammatory cytokine response and an improvement in clinical parameters [3]. L. Reuteri is known for its secretion of 2 bacteriocins, reuterine and reutericiclina, which inhibit the growth of a wide variety of pathogens; it also has a strong ability to adhere to host tissues with localized anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects [2]. Probiotics present a new ray of hope in periodontal therapy with a proven track record of safety and efficacy [2,3]. The use of topical probiotics in the treatment of gingival hypertrophy could be considered a valid alternative to conventional treatments. Further studies must be performed to confirm this starting result.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Friedrich, A.D.; Paz, M.L.; Leoni, J.; González Maglio, D.H. Message in a Bottle: Dialog between Intestine and Skin Modulated by Probiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laleman, I.; Pauwels, M.; Quirynen, M.; Teughels, W. A dual strain Lactobacilli reuteri probiotic improves the treatment of residual pockets: a randomized controlled-clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penala, S.; Kalakonda, B.; Pathakota, K.R.; Jayakumar, A.; Koppolu, P.; Lakshmi, B.V.; Pandey, R.; Mishra, A. Efficacy of local use of probiotics as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in chronic periodontitis and halitosis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Res. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 5, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).