On the Use of Fisher Vector Encoding for Voice Spoofing Detection †
Abstract
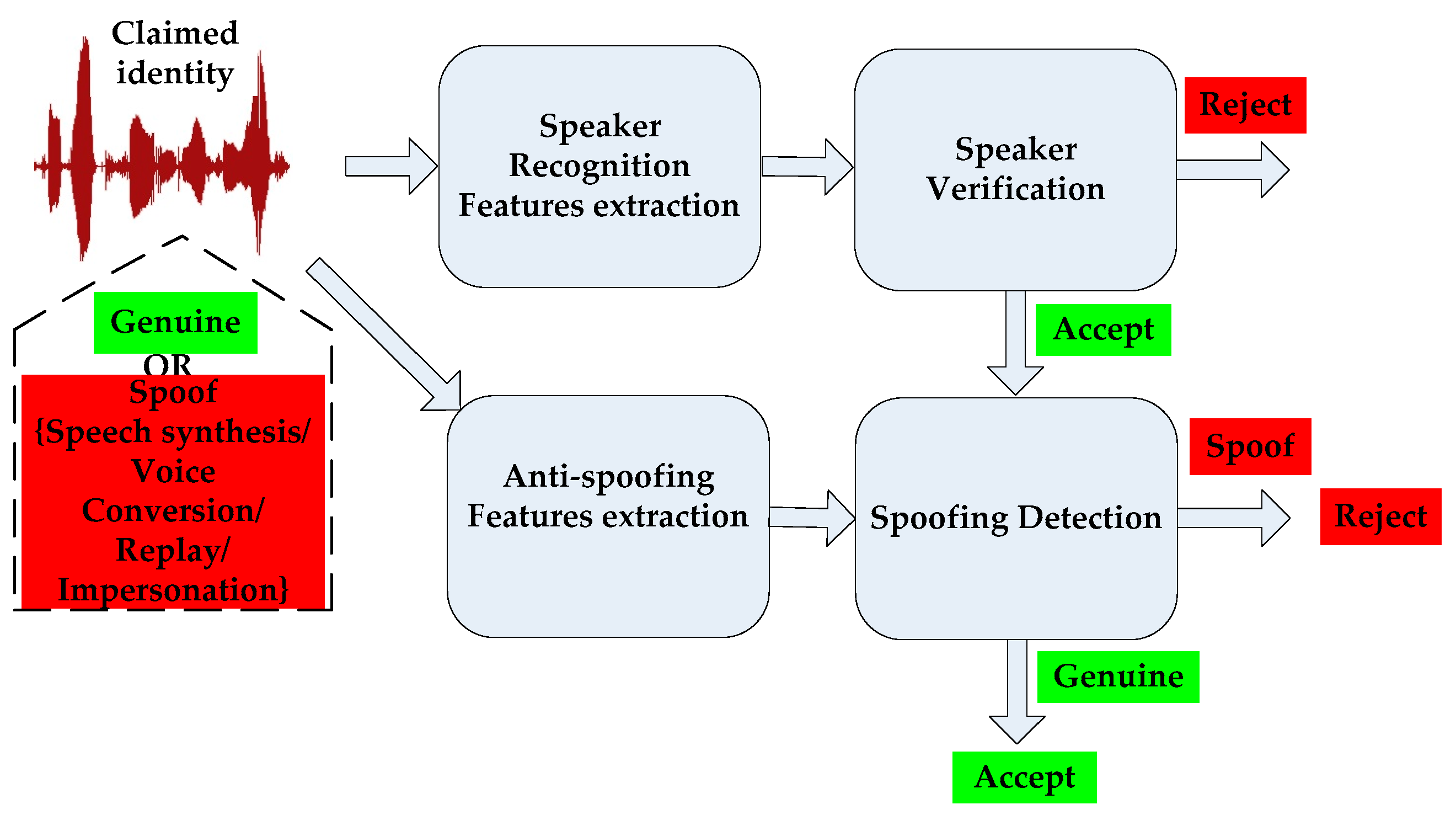
:1. Introduction
2. Low-Level Acoustic Features as Spoofing Countermeasures
3. Baseline Voice Spoofing Detection Systems
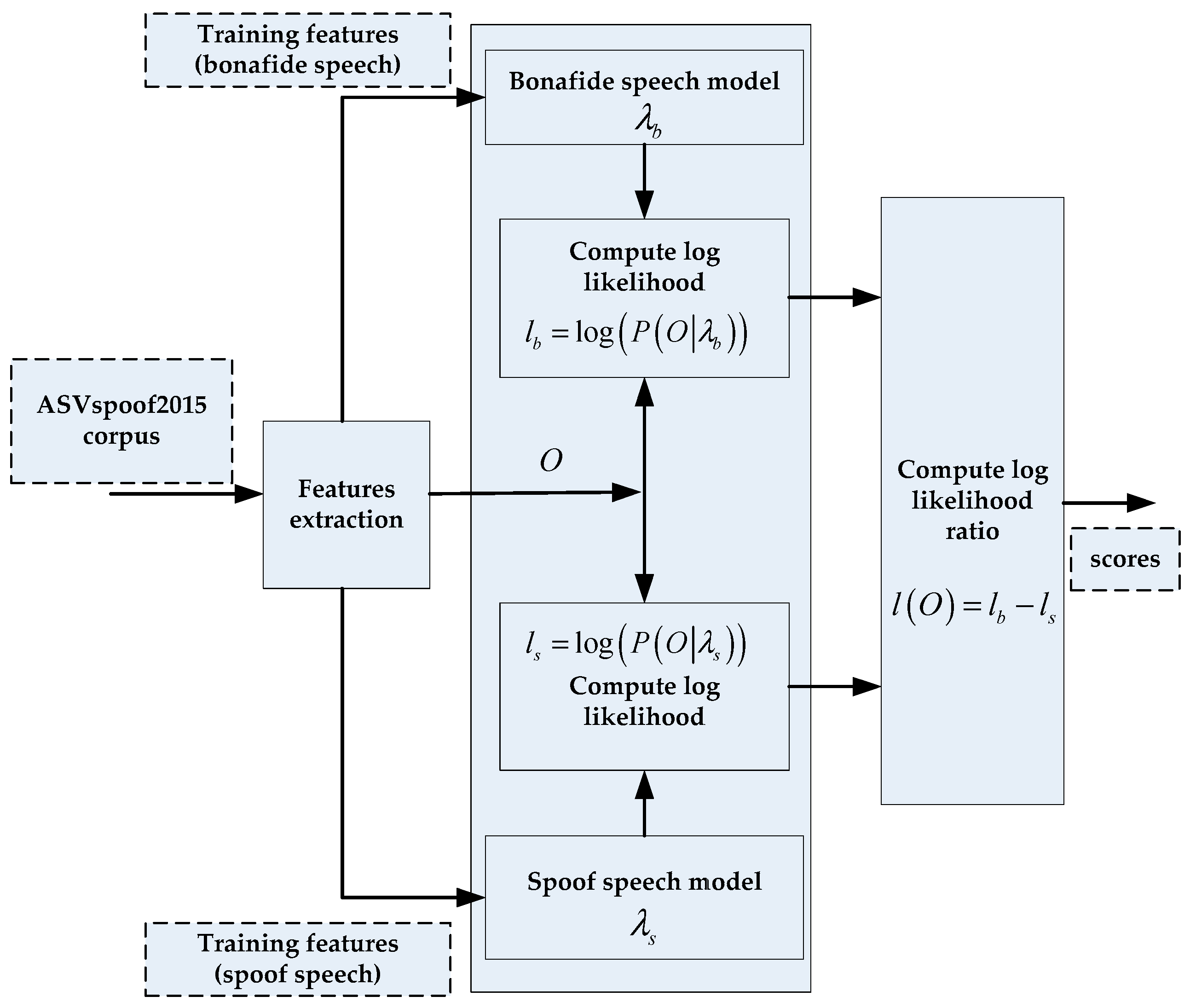
3.1. GMM-Based Framework
3.2. I-vector/PLDA Framework
4. Spoofing Detection using Fisher Vector Encoding
- Train GMMs on the training features (spoof and bonafide GMMs for the first approach and a UBM for the second approach)
- Extract 2560-dimensional raw Fisher vectors (i.e., without L2 + power normalization) from the training data and train a PCA projection matrix on the extracted training Fisher vectors.
- Extract 600-dimensional normalized Fisher vectors from all data using extracted local descriptors, trained GMMs and PCA projection matrix.
- Perform binary classification using PLDA classifiers (or backend).
- Perform score level fusion (for Figure 4 only).
Motivation behind Using Fisher Vector Encoding for Spoofing Detection
5. Experiments and Results
5.1. ASVspoof2015 Corpus
5.2. Experimental Setup
5.3. Evaluation Metrics
5.4. Implementation
5.5. Results and Discussion
- CQCC-GMM512: GMM-based spoofing detection system with 512-Gaussian components diagonal covariance GMMs on the top of 40-dimensional CQCC features.
- CQCC-GMM512 (FC): Same as CQCC-GMM512 but with full covariance GMMs.
- CQCC-GMM32: Same as CQCC-GMM512 but employs 32-Gaussian components GMMs.
- CQCC-GMM32 (FC): Same as CQCC-GMM512 (FC) but uses 32-Gaussian components GMMs.
- FV1-PLDA: Fisher vector-based spoofing detection system as presented in Figure 4.
- FV1-PLDA (no norm): Same as FV1-PLDA but without using L2 and power normalization methods.
- FV2-PLDA: Fisher vector-based spoofing detection system employing a UBM as presented in Figure 5.
- i-vector/PLDA: In this system, 400-dimensional i-vectors extracted with a 512-Gaussian component diagonal covariance UBM and CQCC features.
- Fused: Equal weighted score level fusion (i.e., sum fusion) of CQCC-GMM512, FV1-PLDA, FV2- PLDA and i-vector/PLDA systems.
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Evans, N.; Kinnunen, T.; Yamagishi, J.; Wu, Z.; Alegre, F.; de Leon, P. Speaker recognition anti-spoofing. In Handbook of Biometric Anti-Spoofing; Marcel, S., Li, S., Nixon, M., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen, T.; Wu, Z.; Lee, K.A.; Sedlak, F.; Chng, E.S.; Li, H. Vulnerability of speaker verification systems against voice conversion spoofing attacks: The case of telephone speech. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Kyoto, Japan, 25–30 March 2012; pp. 4401–4404. [Google Scholar]
- de Leon, P.L.; Pucher, M.; Yamagishi, J. Evaluation of the vulnerability of speaker verification to synthetic speech. In Proceedings of the IEEE Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop (Odyssey), Brno, Czech Republic, 28 June–1 July 2010; pp. 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Kinnunen, T.; Evans, N.; Yamagishi, J.; Hanilçi, C.; Sahidullah, M.; Sizov, A. ASVspoof 2015: The First ASV Spoofing and Countermeasures Challenge. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH 2015, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015; Available online: http://www.spoofingchallenge.org/is2015_asvspoof.pdf (accessed on 01 July 2019).
- Chen, N.; Qian, Y.; Dinkel, H.; Chen, B.; Yu, K. Robust Deep Feature for Spoofing Detection—The SJTU System for ASVspoof 2015 Challenge. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2015, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- van den Oord, A.; Dieleman, S.; Zen, H.; Simonyan, K.; Vinyals, O.; Graves, A.; Kalchbrenner, N.; Senior, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Wavenet: A generative model for raw audio. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.03499. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Skerry-Ryan, R.; Stanton, D.; Wu, Y.; Weiss, R.J.; Jaitly, N.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Bengio, S.; et al. Tacotron: Towards end-to-end speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2017, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 4006–4010. [Google Scholar]
- Tamamori, A.; Hayashi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Takeda, K.; Toda, T. Speaker-dependent WaveNet vocoder. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2017, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 1118–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, T.; Kameoka, H.; Hojo, N.; Ijima, Y.; Hiramatsu, K.; Kashino, K. Generative adversarial network-based postfilter for statistical parametric speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the 2017 ICASSP, New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 4910–4914. [Google Scholar]
- Todisco, M.; Delgado, H.; Evans, N. Constant Q Cepstral Coefficients: A Spoofing Countermeasure for Automatic Speaker Verification. Comput. Speech Lang. 2017, 45, 516–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, J.; Kenny, P. Spoofing Detection Employing Infinite Impulse Response—Constant Q Transform-based Feature Representations. In Proceedings of the EUSIPCO, Kos Island, Greece, 28 August–2 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, J.; Kenny, P.; Gupta, V.; Stafylakis, T. Spoofing Detection on the ASVSpoof2015 Challenge Corpus Employing Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Odyssey Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop, Bilbao, Spain, 21–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, J.; Kenny, P.; Bhattacharya, G.; Stafylakis, T. Development of CRIM System for the Automatic Speaker Verification Spoofing and Countermeasures Challenge 2015. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2015, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015; Available online: https://www.asvspoof.org/asvspoof2015/CRIM.pdf (accessed on 01 July 2019).
- Patel, T.B.; Patil, H.A. Combining Evidences from Mel Cepstral, Cochlear Filter Cepstral and Instantaneous Frequency Features for Detection of Natural vs. Spoofed Speech. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2015, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Tian, X.; Du, S.; Xu, H.; Chng, E.S.; Li, H. Spoofing Speech Detection Using High Dimensional Magnitude and Phase Features: The NTU Approach for ASVspoof 2015 Challenge. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2015, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, X.; Chng, E.S.; Li, H. Spoofing detection from a feature representation perspective. In Proceedings of the ICASSP, Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, T.; Patil, H. Effectiveness of fundamental frequency (F0) and strength of excitation (SOE) for spoofed speech detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP, Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jaakkola, T.; Haussler, D. Exploiting generative models in discriminative classifiers. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 30 November–5 December 1998; pp. 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Perronnin, F.; Dance, C. Fisher kernels on visual vocabularies for image categorization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Perronnin, F.; Liu, Y.; Sanchez, J.; Poirier, H. Large-scale Image Retrieval with Compressed Fisher Vectors. In Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 3384–3391. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, H.; Karpov, A.; Salah, A.A. Fisher Vectors with Cascaded Normalization for Paralinguistic Analysis. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2015, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sahidullah, M.; Kinnunen, T.; Hanilçi, C. A Comparison of Features for Synthetic Speech Detection. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2015, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dehak, N.; Kenny, P.J.; Dehak, R.; Dumouchel, P.; Ouellet, P. Front-end factor analysis for speaker verification. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2011, 19, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povey, D.; Ghoshal, A.; Boulianne, G.; Burget, L.; Glembek, O.; Goel, N.; Hannemann, M.; Motlicek, P.; Qian, Y.; Schwarz, P.; et al. The kaldi speech recognition toolkit. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2011 workshop on automatic speech recognition and understanding, IEEE Signal Processing Society, Big Island, HI, USA, 11–15 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, D.; Yamamoto, K.; Minematsu, N.; Hirose, K. One-to-many voice conversion based on tensor representation of speaker space. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2011, Florence, Italy, 27–31 August 2011; pp. 653–656. [Google Scholar]
- The MARY TTS—An Open-Source, Multilingual Text-To-Speech Synthesis System. (the first version was released on 14 February 2006). Available online: http://mary.dfki.de.



| Known | Unknown | Average | All | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CQCC-GMM512 | 0.2375 | 0.796 | 0.517 | 0.836 |
| CQCC-GMM512 (FC) | 0.034 | 0.365 | 0.199 | 0.433 |
| Known | Unknown | Average | All | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FV1-PLDA | 0.114 | 1.223 | 0.668 | 1.048 |
| FV1-PLDA (no norm) | 0.228 | 5.697 | 2.963 | 3.935 |
| Known | Unknown | Average | All | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CQCC-GMM32 | 0.489 | 1.138 | 0.814 | 1.084 |
| CQCC-GMM32 (FC) | 0.164 | 0.669 | 0.417 | 0.618 |
| FV1-PLDA | 0.114 | 1.223 | 0.668 | 1.048 |
| FV2-PLDA | 0.597 | 3.664 | 2.131 | 2.951 |
| CQCC-GMM512 | 0.2375 | 0.796 | 0.517 | 0.836 |
| CQCC (A)-GMM512 [10] | 0.048 | 0.462 | 0.255 | - |
| CQCC-GMM512 (FC) | 0.034 | 0.365 | 0.199 | 0.434 |
| i-vector/PLDA | 0.161 | 4.017 | 2.089 | 2.826 |
| Fused | 0.0243 | 0.307 | 0.165 | 0.456 |
| Known Attacks | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | |
| CQCC-GMM32 | 0.124 | 1.203 | 0.043 | 0.0465 | 1.0286 |
| CQCC-GMM32 (FC) | 0.047 | 0.373 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.396 |
| FV1-PLDA | 0.069 | 0.253 | 0.019 | 0.017 | 0.208 |
| FV2-PLDA | 0.664 | 1.036 | 0.276 | 0.300 | 0.709 |
| CQCC-GMM512 | 0.062 | 0.609 | 0.008 | 0.0184 | 0.489 |
| CQCC (A)-GMM512 [10] | 0.005 | 0.106 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.130 |
| CQCC-GMM512 (FC) | 0.010 | 0.064 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.074 |
| i-vector/PLDA | 0.141 | 0.318 | 0.053 | 0.047 | 0.244 |
| Fused | 0.015 | 0.069 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.037 |
| Unknown attacks | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | |
| CQCC-GMM32 | 1.011 | 0.366 | 2.495 | 0.584 | 1.237 |
| CQCC-GMM32 (FC) | 0.313 | 0.254 | 1.436 | 0.280 | 1.062 |
| FV1-PLDA | 0.244 | 0.064 | 1.892 | 0.151 | 3.760 |
| FV2-PLDA | 0.995 | 0.389 | 2.242 | 0.458 | 14.236 |
| CQCC-GMM512 | 0.455 | 0.227 | 2.015 | 0.323 | 0.961 |
| CQCC (A)-GMM512 [10] | 0.098 | 0.064 | 1.033 | 0.053 | 1.065 |
| CQCC-GMM512 (FC) | 0.089 | 0.046 | 1.165 | 0.0558 | 0.469 |
| i-vector/PLDA | 0.331 | 0.285 | 12.345 | 0.329 | 6.795 |
| Fused | 0.057 | 0.027 | 0.692 | 0.037 | 0.720 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alam, J. On the Use of Fisher Vector Encoding for Voice Spoofing Detection. Proceedings 2019, 31, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031037
Alam J. On the Use of Fisher Vector Encoding for Voice Spoofing Detection. Proceedings. 2019; 31(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031037
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlam, Jahangir. 2019. "On the Use of Fisher Vector Encoding for Voice Spoofing Detection" Proceedings 31, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031037
APA StyleAlam, J. (2019). On the Use of Fisher Vector Encoding for Voice Spoofing Detection. Proceedings, 31(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019031037




