Near-Infrared pH Sensor Based on a SPEEK–Polyaniline Polyelectrolyte Complex Membrane †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
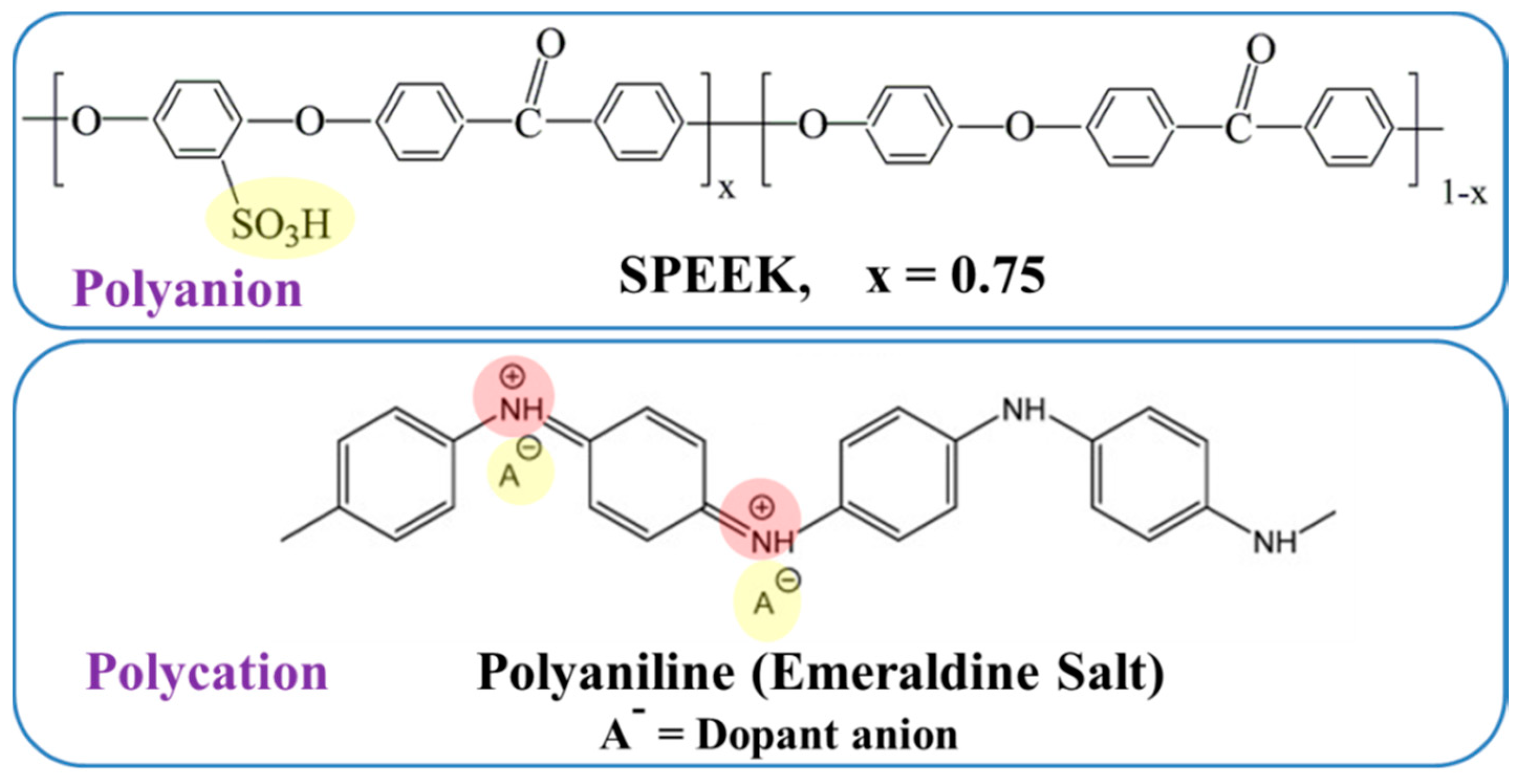
2.2. Preparation of the SPEEK–Polyaniline PEC Membrane
2.3. Sensor Characterization and pH Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
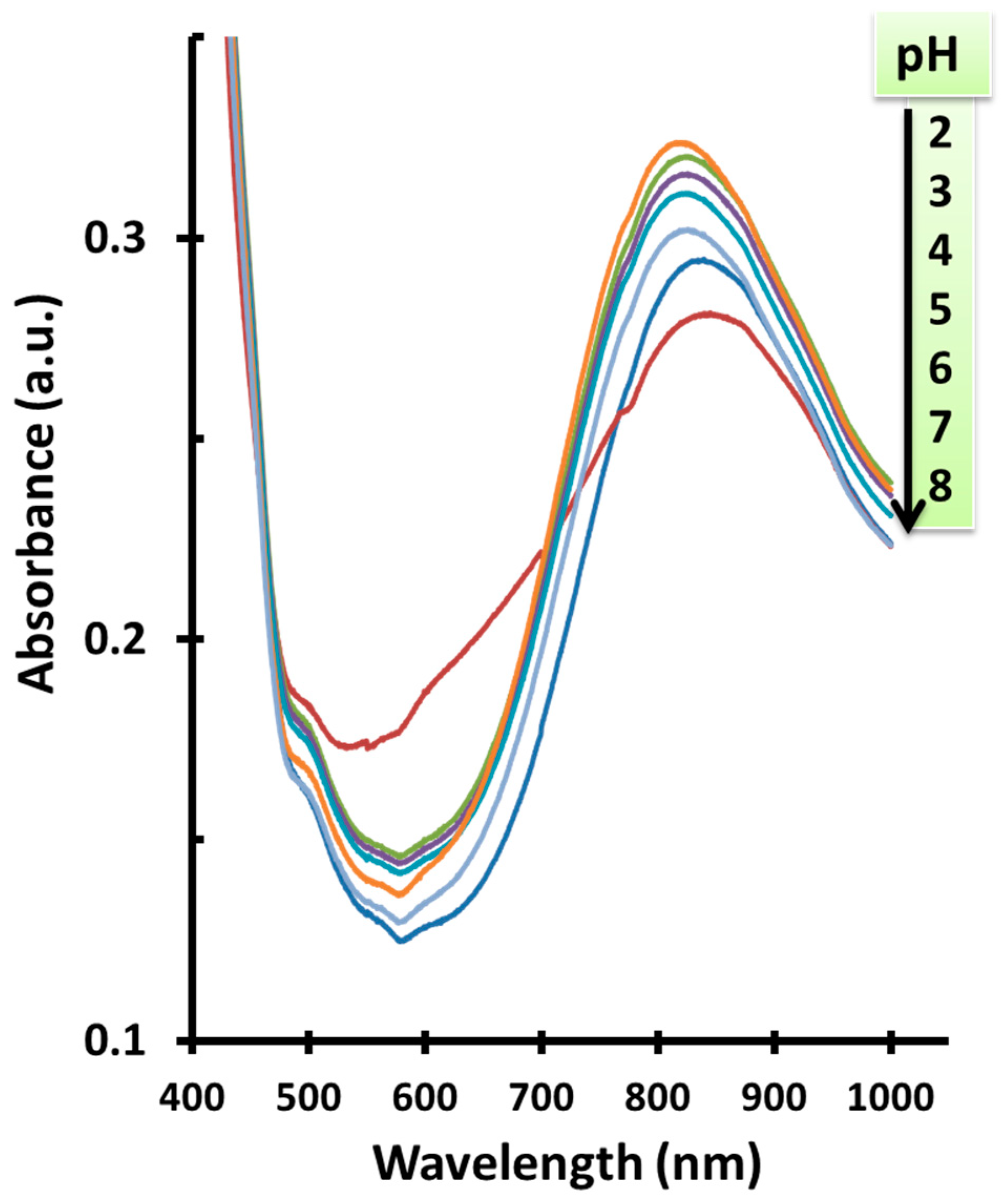
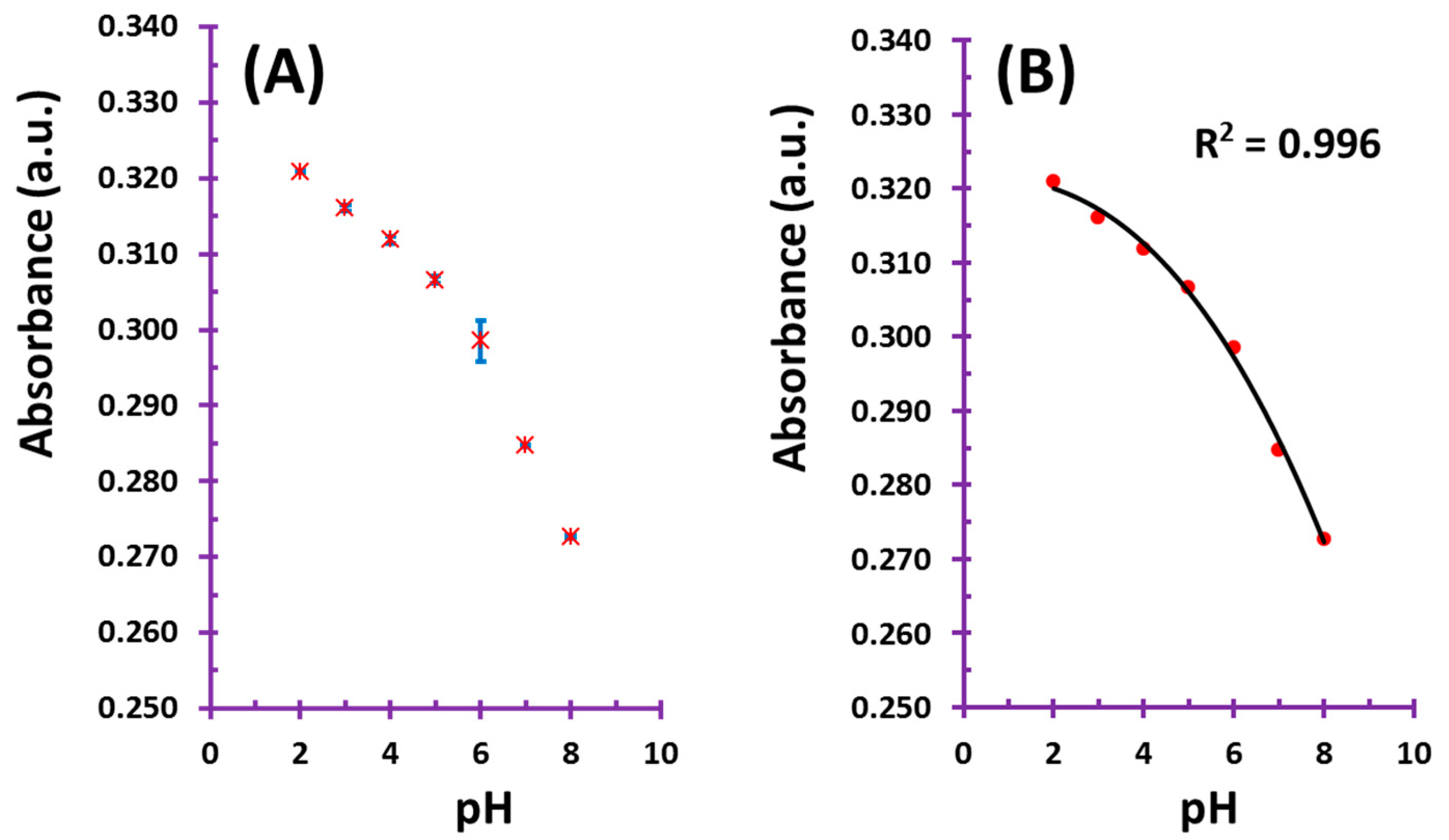
3.1. pH Measurements
3.2. Response Time
3.3. Sensor Stability
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Bucur, C.B.; Sui, Z.; Schlenoff, J.B. Ideal mixing in polyelectrolyte complexes and multilayers: Entropy driven assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13690–13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borukhov, I.; Andelman, D.; Borrega, R.; Cloitre, M.; Leibler, L.; Orland, H. Polyelectrolyte titration: Theory and experiment. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 11027–11034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankerfors, C.; Ondaral, S.; Wågberg, L.; Odberg, L. Using jet mixing to prepare polyelectrolyte complexes: Complex properties and their interaction with silicon oxide surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundall, R.B.; Lawton, J.B.; Murray, D.; Phillips, G.O. Polyelectrolyte complexes, 1. The effect of pH and ionic strength on the stoichiometry of model polycation—Polyanion complexes. Die Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1979, 180, 2913–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Rieser, T.; Lunkwitz, K.; Meier-Haack, J. Polyelectrolyte complex layers: A promising concept for anti-fouling coatings verified by in-situ ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 1999, 20, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönhoff, M. Layered polyelectrolyte complexes: Physics of formation and molecular properties. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, R1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbert, D.L.; Herbert, C.B.; Hubbell, J.A. Thin polymer layers formed by polyelectrolyte multilayer techniques on biological surfaces. Langmuir 1999, 15, 5355–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrai, P.; Guerra, G.D.; Maltinti, S.; Tricoli, M.; Giusti, P.; Petarca, L.; Polacco, G. Physicochemical properties of poly(allylammonium acrylate) complexes obtained by radical template polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 1994, 15, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoilova, O.; Koseva, N.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Polyelectrolyte complex between chitosan and poly(2-acryloylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid). Polym. Bull. 1999, 43, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Thabit, N.Y.; Hamdy, A.S. Stimuli-responsive Polyelectrolyte Multilayers for fabrication of self-healing coatings—A review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 303, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, V.B.V.; Yoshida, C.M.; Franco, T.T. Chitosan/pectin polyelectrolyte complex as a pH indicator. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukdar, H.; Kundu, S. Thin film of polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles for protein sensing. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1942, 080030. [Google Scholar]
- Emmanuel, B.D.; Abu-Thabit, N.Y.; Ngwuluka, N.C. Responsive polyelectrolyte complexes based on natural polysaccharides for drug delivery applications. In Stimuli Responsive Polymeric Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 267–287. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Tian, F.; Yang, J.; He, C.N.; Xing, N.; Li, F. Chitosan and alginate polyelectrolyte complex membranes and their properties for wound dressing application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.M.; Felt, O.; Gurny, R. Structure and interactions in chitosan hydrogels formed by complexation or aggregation for biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; De Feyter, S.; Chen, D.; Aldea, S.; Vandezande, P.; Du Prez, F.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Solvent-resistant nanofiltration membranes based on multilayered polyelectrolyte complexes. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3876–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.Y.; Lee, Y.M. Pervaporation and properties of chitosan-poly(acrylic acid) complex membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 135, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malay, Ö.; Batıgün, A.; Bayraktar, O. pH-and electro-responsive characteristics of silk fibroin–hyaluronic acid polyelectrolyte complex membranes. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 380, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sakiyama, T.; Chu, C.-H.; Fujii, T.; Yano, T. Preparation of a polyelectrolyte complex gel from chitosan and κ-carrageenan and its pH-sensitive swelling. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1993, 50, 2021–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yin, M.; Zhang, A.P.; Prescher, S.; Antonietti, M.; Yuan, J. Hierarchically structured nanoporous poly (ionic liquid) membranes: Facile preparation and application in fiber-optic pH sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5549–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Thabit, N.; Umar, Y.; Ratemi, E.; Ahmad, A.; Abuilaiwi, F.A. A Flexible Optical pH Sensor Based on Polysulfone Membranes Coated with pH-Responsive Polyaniline Nanofibers. Sensors 2016, 16, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Thabit, N.Y. Chemical Oxidative Polymerization of Polyaniline: A Practical Approach for Preparation of Smart Conductive Textiles. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Thabit, N.Y.; Ali, S.A.; Javaid Zaidi, S.M.; Mezghani, K. Novel sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/phosphonated polysulfone polymer blends for proton conducting membranes. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, L.; Fay, C.; Lahiff, E.; Phelan, T.; O’Connor, N.E.; Corcoran, B.; Diamond, D.; Benito-Lopez, F. Dynamic pH mapping in microfluidic devices by integrating adaptive coatings based on polyaniline with colorimetric imaging techniques. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringsheim, E.; Terpetschnig, E.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Optical sensing of pH using thin films of substituted polyanilines. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 357, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Anglada, N.; Kaempgen, M.; Roth, S. Transparent and flexible carbon nanotube/polypyrrole and carbon nanotube/polyaniline pH sensors. Phys. Status Solidi B 2006, 243, 3519–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Thabit, N.; Ahmad, A.; Umar, Y.; Ratemi, E. Polyaniline-Coated Polysulfone Membranes as Flexible Optical pH Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Electronic Conference on Sensors and Applications, Basel, Switzerland, 15–30 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Fu, T.; Shi, Y.; Na, H. Composite membranes based on highly sulfonated PEEK and PBI: Morphology characteristics and performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 308, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, D.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Lu, H.; Na, H. SPEEKK/polyaniline (PANI) composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cell usages. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 275, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.; Rovati, L.; Fabbri, P.; Pilati, F. Disposable Fluorescence Optical pH Sensor for Near Neutral Solutions. Sensors 2013, 13, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Membrane Type | Water Uptake (%) |
|---|---|
| SPEEK | 35.2 |
| SPEEK-PANI | 35.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu-Thabit, N.Y. Near-Infrared pH Sensor Based on a SPEEK–Polyaniline Polyelectrolyte Complex Membrane. Proceedings 2019, 3, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/IOCN_2018-1-05493
Abu-Thabit NY. Near-Infrared pH Sensor Based on a SPEEK–Polyaniline Polyelectrolyte Complex Membrane. Proceedings. 2019; 3(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/IOCN_2018-1-05493
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu-Thabit, Nedal Y. 2019. "Near-Infrared pH Sensor Based on a SPEEK–Polyaniline Polyelectrolyte Complex Membrane" Proceedings 3, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/IOCN_2018-1-05493
APA StyleAbu-Thabit, N. Y. (2019). Near-Infrared pH Sensor Based on a SPEEK–Polyaniline Polyelectrolyte Complex Membrane. Proceedings, 3(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/IOCN_2018-1-05493





