AVIRIS-NG Data for Geological Applications in Southeastern Parts of Aravalli Fold Belt, Rajasthan †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions:
- ➢
- In the present study, mineral endmembers are identified from AVIRIS-NG hyperspectral images by using spectral and spatial data dimensionality reduction techniques.
- ➢
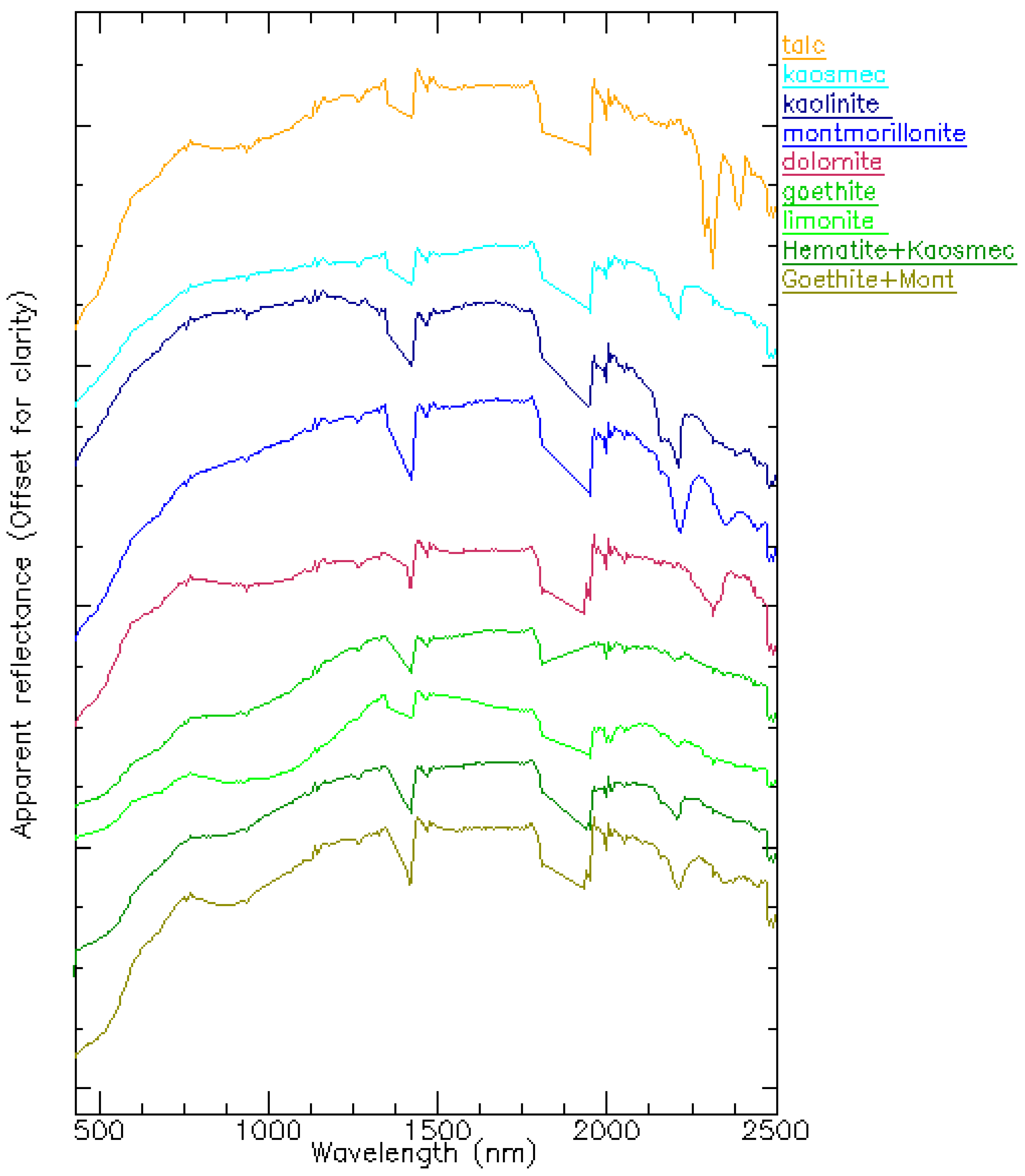
- Because of the contiguous nature of AVIRIS-NG data, it has become possible to study the shape, size, and accurate location of spectral features, which in turn helps in identifying and discriminating various minerals, in particular phyllosilicate, carbonate, and iron bearing minerals.
- ➢
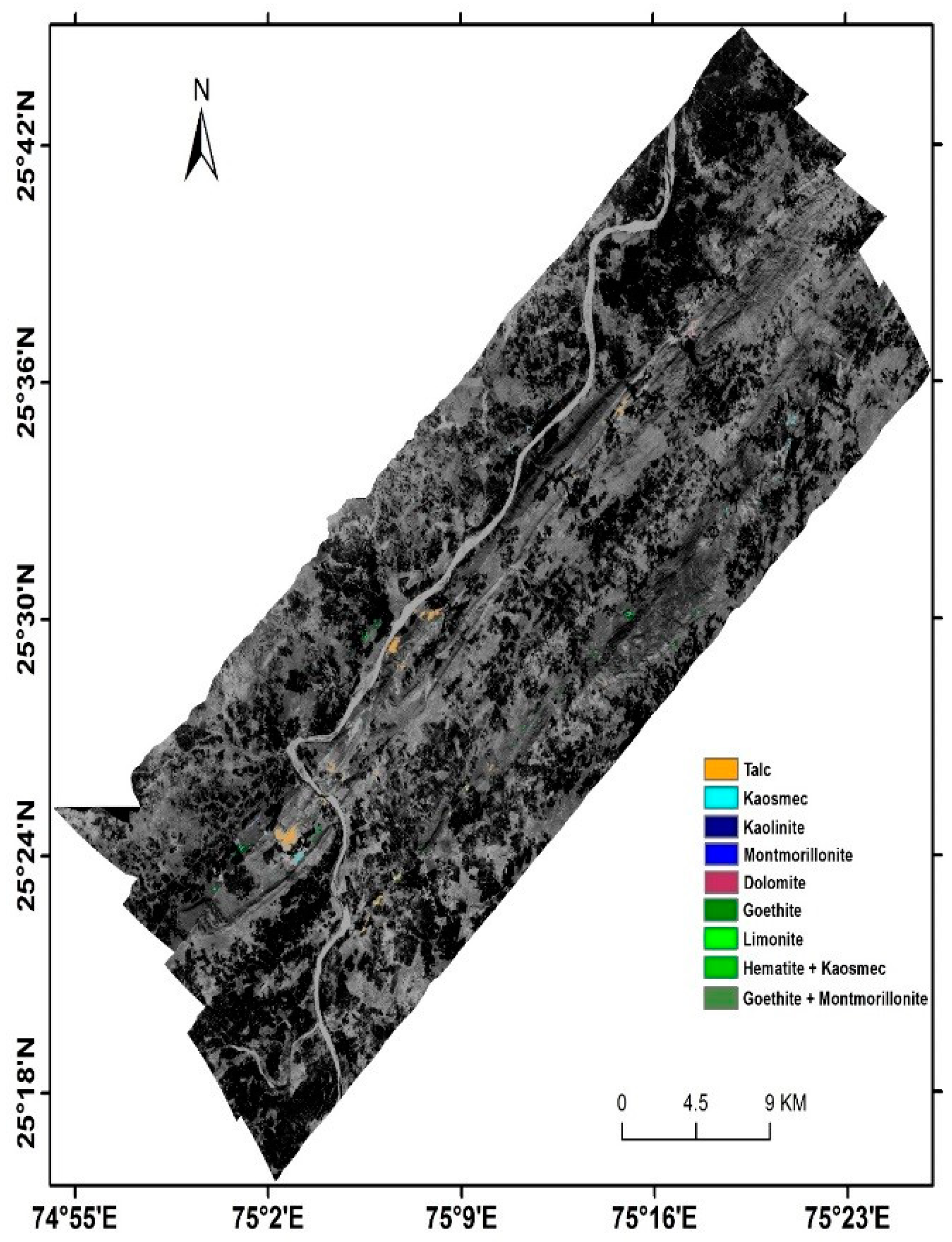
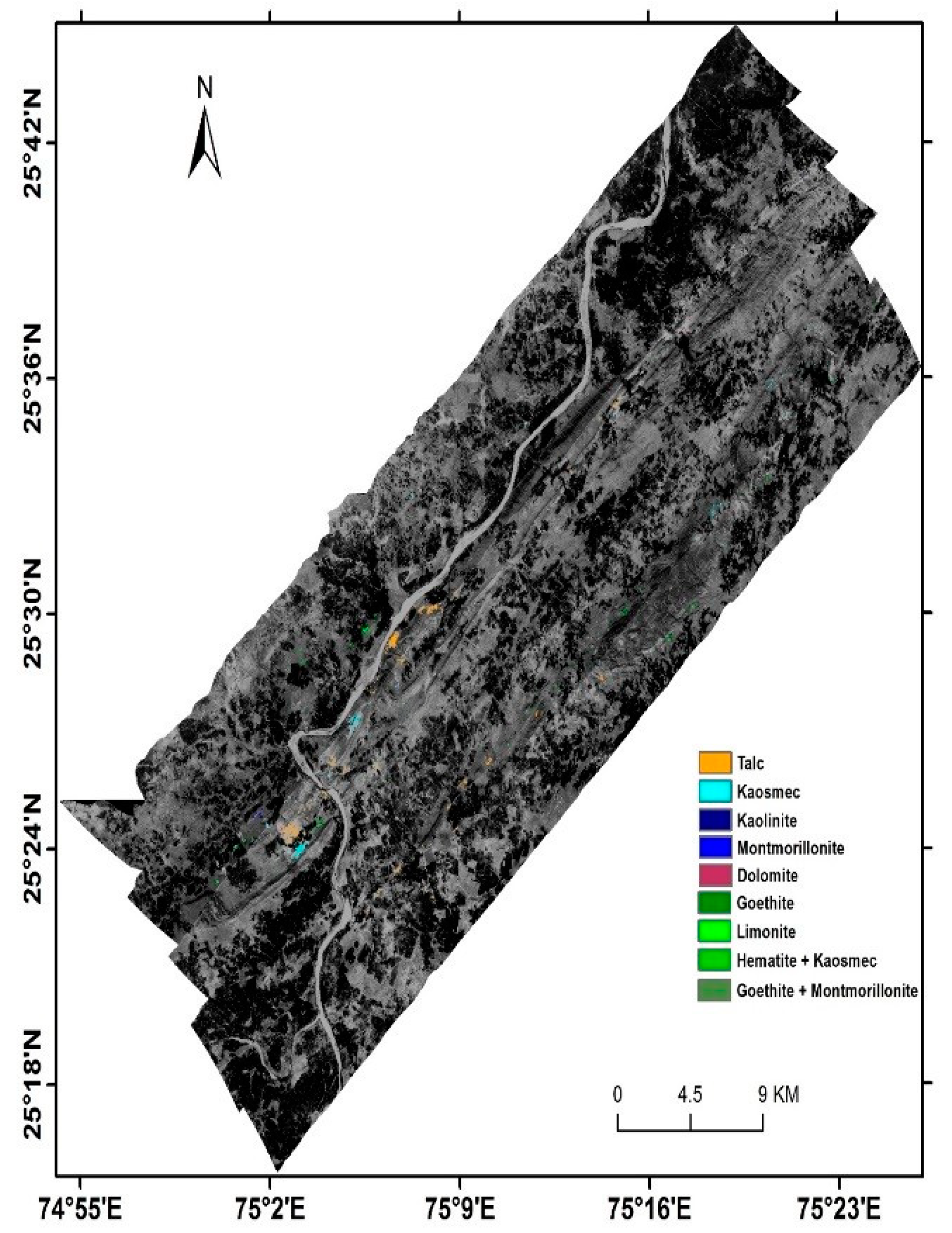
- Thus it can be calculated that AVIRIS-NG data, with high spectral and spatial resolution, can be very efficiently used for the identification and mapping of altered and clay components.
- ➢
- Accuracy assessment of mineral maps, by using SAM and ACE techniques, revealed that SAM produces better result.
References
- Goetz, A.F.H.; Vane, G.; Solomon, J.E.; Rock, B.N. Imaging spectrometry for earth remote sensing. Science 1985, 228, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, G.R. Spectral signatures of particulate minerals in the visible and near infrared. Geophysics 1977, 42, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.R.; Salisbury, J.W. Visible and near-infrared spectra of minerals and rocks: I silicate minerals. Mod. Geol. 1970, 1, 283–300. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, G.R. Spectroscopic properties of rocks and minerals. In Handbook of Physical Properties Of rocks; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1982; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.J.B.; Hauff, P.L.; Robitaille, A. Alteration mapping in exploration: Application of short-wave infrared (SWIR) spectroscopy. Soc. Econ. Geol. Newsl. 1999, 39, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutis, E.A. Hyperspectral geological remote sensing: Evaluation of analytical techniques. Int. Jour. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 2215–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabins, F.F. Remote sensing for mineral exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 1999, 14, 157–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A. Identification and mapping of minerals in drill core using hyperspectral image analysis of infrared reflectance spectra. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, F.; de Jong, S. (Eds.) Imaging Spectrometry: Basic Principles and Prospective Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer, F.D.; van der Werff, H.M.A.; van Ruitenbeek, F.J.A.; Hecker, C.A.; Bakker, W.H.; Noomen, M.F.; van der Meijde, M.; Carranza, E.J.M.; de Smeth, J.B.; Woldai, T. Multi- and hyperspectral geologic remote sensing: A review. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 14, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, F.D. Imaging spectrometry for geological remote sensing. Neth. J. Geosci. 1999, 77, 137–151. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meer, F.D. Remote sensing image analysis and geostatistics. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5644–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A.; Boardman, J.W.; Huntington, J.F. Evaluation and validation of EO-1 hyperion for mineral mapping. Ieee Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1388–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A. Mapping surface mineralogy using imaging spectrometry. Geomorphology 2012, 137, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, A.F.H.; Chabrillat, S.; Lu, Z. Field reflectance spectrometry for detection of swelling clays at construction sites. Field Anal. Chem. Technol. 2001, 5, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, F.H.A.; Curtiss, B.; Shiley, D.A. Rapid gangue mineral concentration measurement over conveyors by NIR reflectance spectroscopy. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Seccombe, P.K.; Yang, K. Application of IR spectroscopy to define alteration zones associated with Elura zinc–lead–silver deposit NSW Australia. J. Geochem. Explor. 2001, 73, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, D.; Kusuma, K.N. (), Marine clays and its impact on the rapid urbanization developments: A case study of Mumbai area using EO-1-Hyperion data. Hyperspectral Remote Sens. Spectr. Signat. Appl. 2008, 2008, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan, D.; Bharti, R.; Singh, K.D.; Nithya, M. Thermal inertia mapping and its application in mineral exploration: Results from Mamandur polymetal prospect, India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 122, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pour, A.B.; Hashim, M. The application of ASTER remote sensing data to porphyry copper and epithermal gold deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2012, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, B.K.; Green, R.O.; Rao, S.; Saxena, M.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, K.A.; Srinivasulu, P.; Sharma, S.; Dhar, D.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; et al. An overview of AVIRIS-NG airborne hyperspectral science campaign over India. Curr. Sci. 2019, 116, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.A.; Berman, M.; Switzer, P.; Craig, M.D. A transformation for ordering multispectral data in terms of image quality with implications for noise removal. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A.; Lefkoff, A.B.; Boardman, J.W.; Heidebrecht, K.B.; Shapiro, A.T.; Barloon, P.J.; Goetz, A.F.H. The spectral image processing system (SIPS)—Interactive visualization and analysis of imaging spectrometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 44, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mapping Method | Scene 1 (%) | Scene 2 (%) | Scene 3 (%) | Scene 4 (%) | Scene 5 (%) | Overall Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral Angle Mapper | 85.714 | 87.500 | 87.804 | 85.589 | 87.500 | 86.821 |
| Adaptive Coherence Estimator | 71.428 | 79.166 | 77.235 | 77.611 | 83.333 | 77.754 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mishra, S.; Chattoraj, S.L.; Benny, A.; Sharma, R.U.; Ray, P.K.C. AVIRIS-NG Data for Geological Applications in Southeastern Parts of Aravalli Fold Belt, Rajasthan. Proceedings 2019, 24, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECG2019-06212
Mishra S, Chattoraj SL, Benny A, Sharma RU, Ray PKC. AVIRIS-NG Data for Geological Applications in Southeastern Parts of Aravalli Fold Belt, Rajasthan. Proceedings. 2019; 24(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECG2019-06212
Chicago/Turabian StyleMishra, Sameeksha, Shovan L. Chattoraj, Alen Benny, Richa U. Sharma, and P. K. Champati Ray. 2019. "AVIRIS-NG Data for Geological Applications in Southeastern Parts of Aravalli Fold Belt, Rajasthan" Proceedings 24, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECG2019-06212
APA StyleMishra, S., Chattoraj, S. L., Benny, A., Sharma, R. U., & Ray, P. K. C. (2019). AVIRIS-NG Data for Geological Applications in Southeastern Parts of Aravalli Fold Belt, Rajasthan. Proceedings, 24(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECG2019-06212







