Preliminary High-Temperature Tests of Textile Reinforced Concrete (TRC) †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
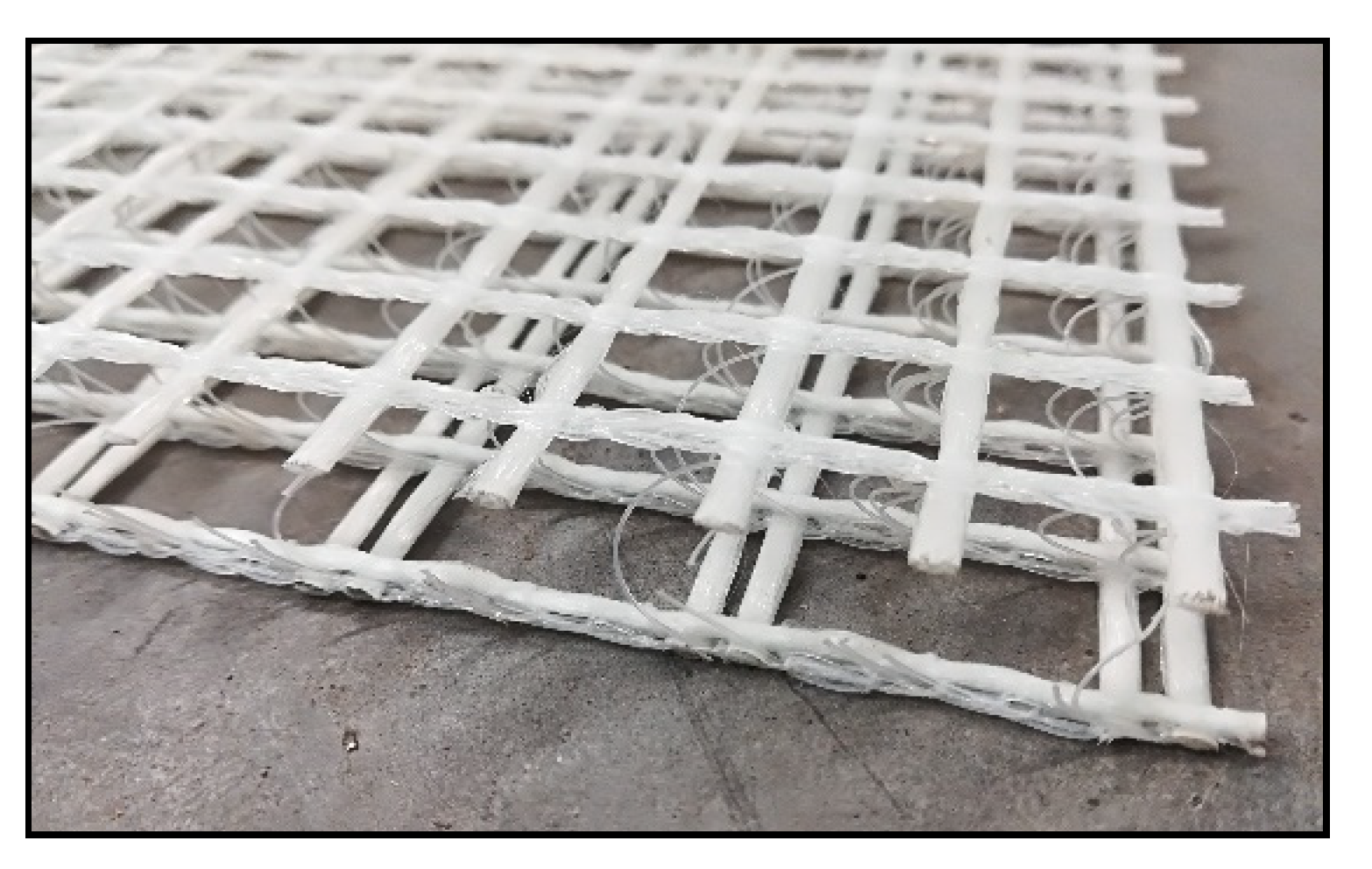
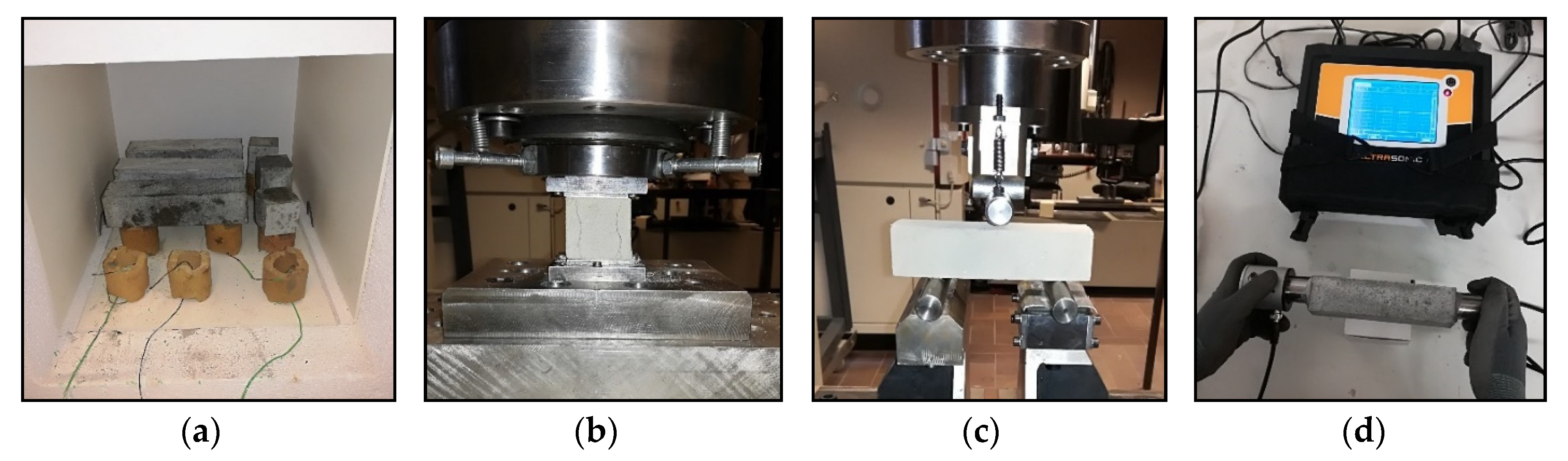
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
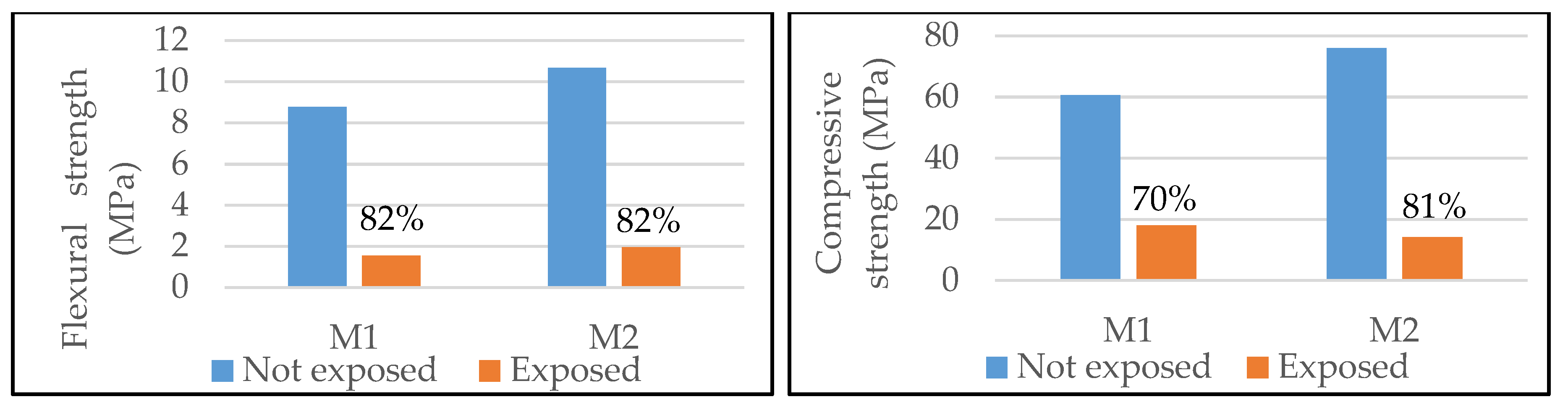
3.1. High Temperature Effect on Mortars
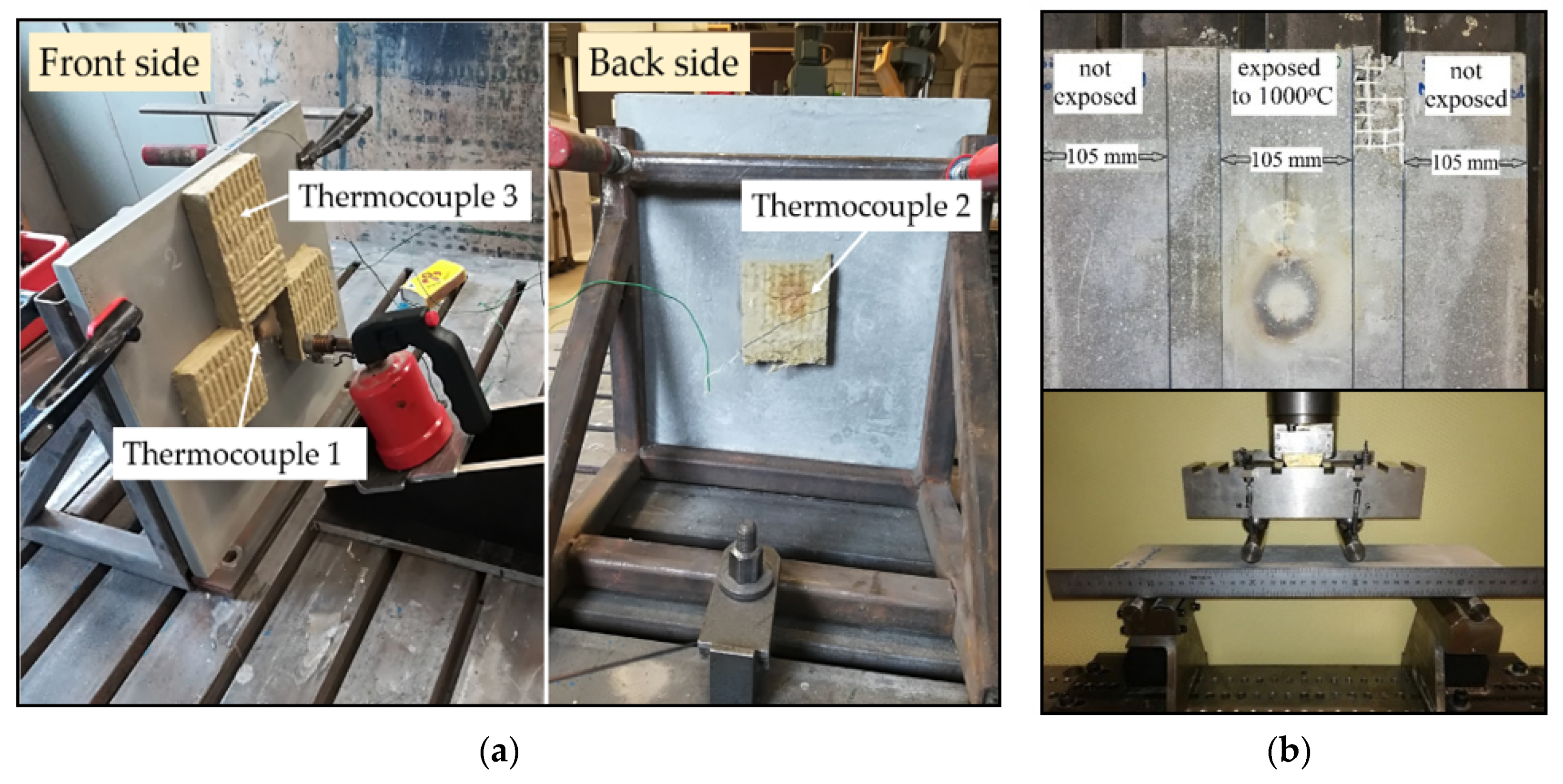
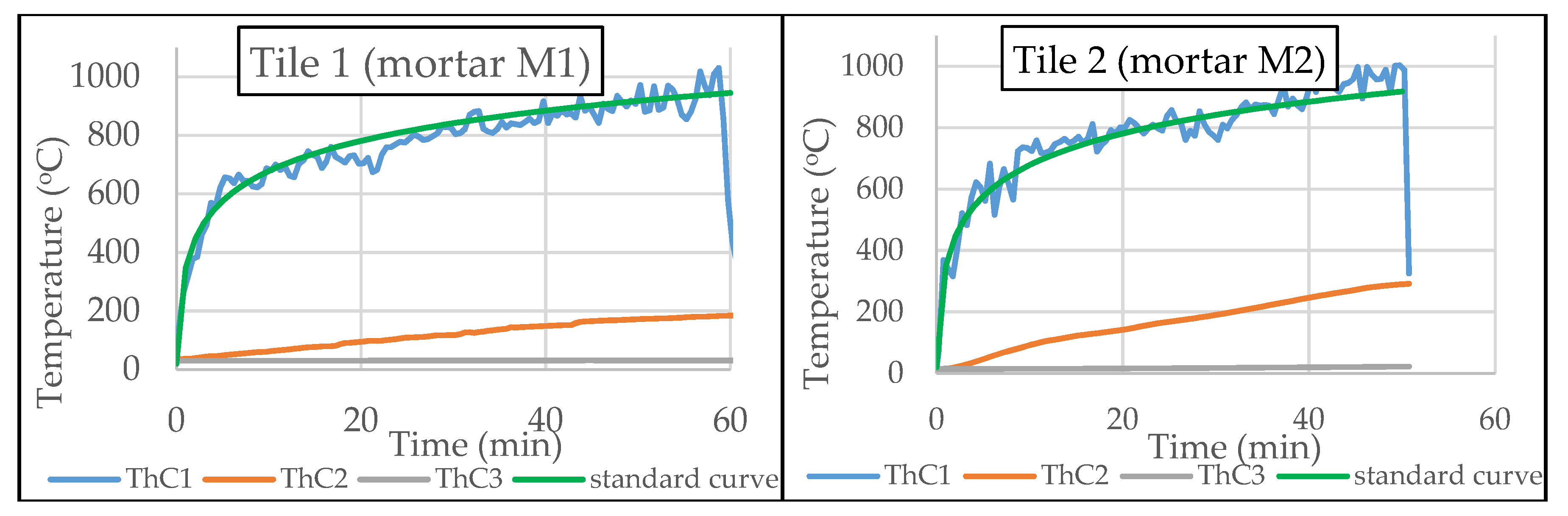
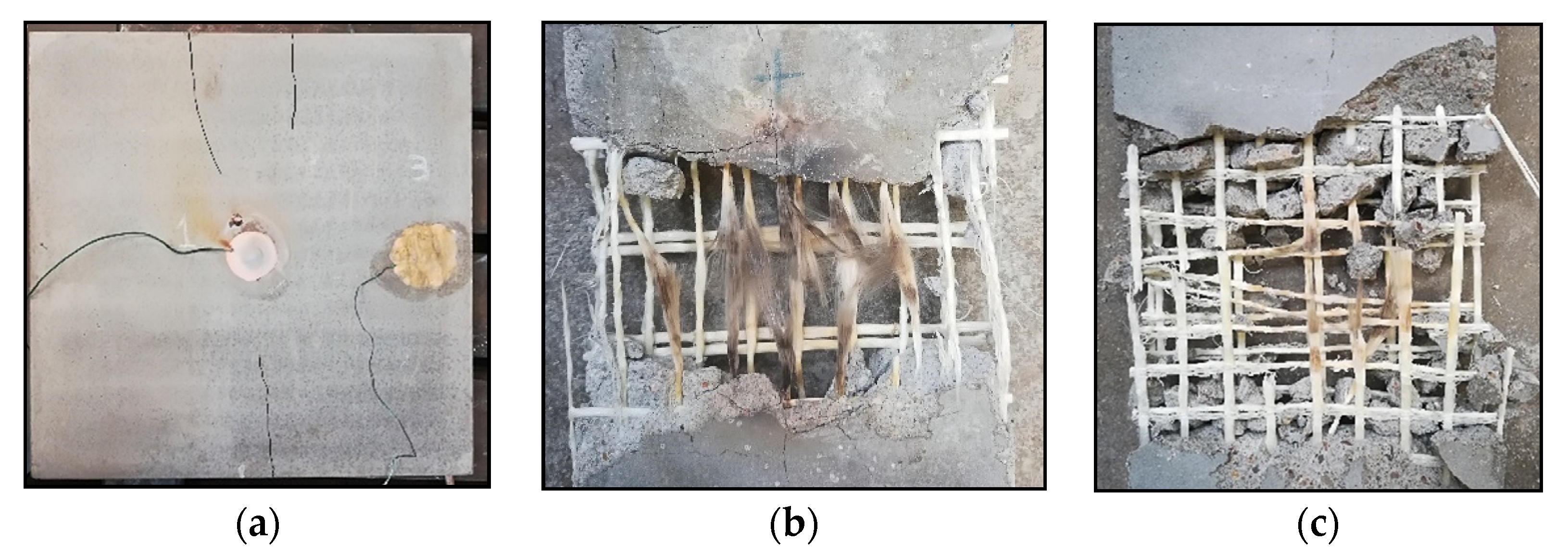
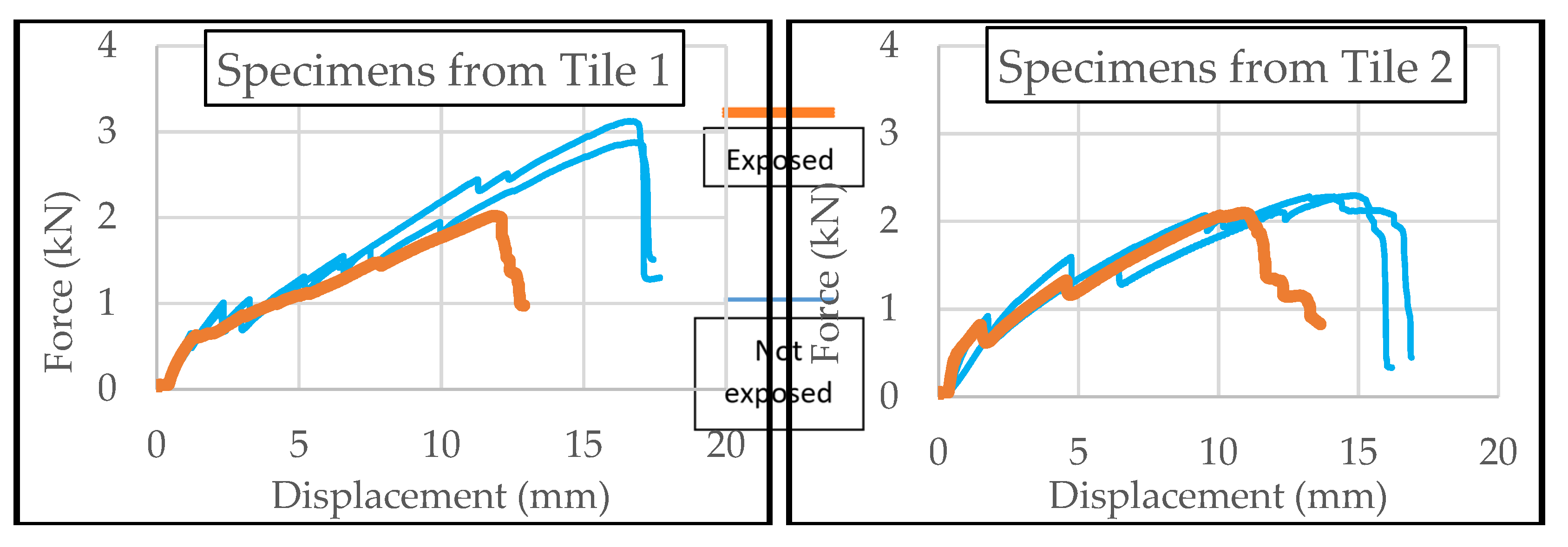
3.2. Fire Testing Effect on TRC
4. Conclusions—Future Work
- Extremely costly equipment is not always necessary to perform fire tests, but, at least for preliminary tests, interesting and useful results can be obtained with simple set-ups like the ones presented hereby, as long as an adequate number of specimens are tested.
- Fine grained mortars, as the ones described here, have a thermal conductivity that may provide a drop in temperature equal to 600–750 °C, in a member of only 22 mm thick.
- Mechanical performance of TRC specimens, before and after being subjected to fire-loading (with simple and more complicated set-ups). Parameters such as the cover thickness, the type of fibers, the time/temperature of exposure to fire, the moisture content of the specimens and the coating of the fibers should also be taken into consideration.
- Calibration of curves that correlate the Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity measured on fine grained mortars commonly used for TRC elements, with the compressive and flexural strength of the mortars.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Ehlig, D.; Hothan, S. Reinforced Concrete Slabs Strengthened with Textile Reinforced Concrete Subjected to Fire. In Proceedings of the 2nd International RILEM Workshop on Concrete Spalling Due to Fire Exposure, Delft, The Netherlands, 5–7 October 2011; pp. 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Maroudas, S.R.; Papanicolaou, C.G. Effect of High Temperatures on the TRM-to-Masonry Bond. Key Eng. Mater. 2017, 747, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.D.A.; Butler, M.; Hempel, S.; Filho, R.D.T.; Mechtcherine, V. Effects of elevated temperatures on the interface properties of carbon textile-reinforced concrete. Cem. and Conc. Compos. 2014, 48, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1363-1:1999; Fire Resistance Tests. General Requirements. BSI: UK, Brussels, 1999.
- Rambo, D.A.; de Andrade Silva, F.; Toledo Filho, R.D.; Ukrainczyk, N.; Koenders, E. Tensile strength of a calcium-aluminate cementitious composite reinforced with basalt textile in a high-temperature environment. Cem. Conc. Compos. 2016, 70, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trtnik, G.; Kavcic, F.; Turk, G. Prediction of concrete strength using ultrasonic pulse velocity and artificial neural networks. Ultrasonics 2009, 46, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
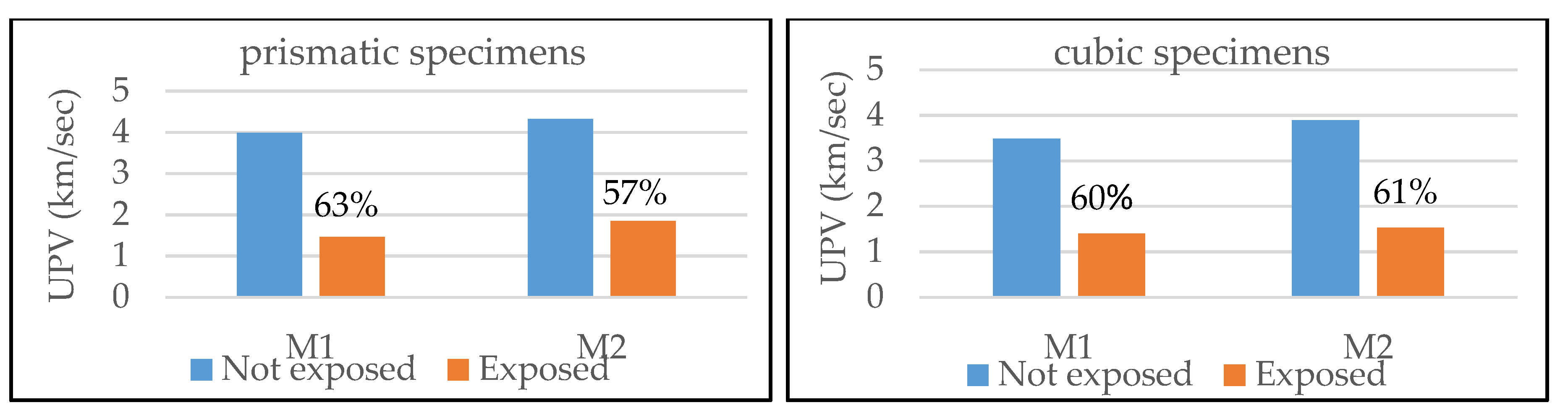
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kapsalis, P.; Tysmans, T.; Verbruggen, S.; Triantafillou, T. Preliminary High-Temperature Tests of Textile Reinforced Concrete (TRC). Proceedings 2018, 2, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ICEM18-05416
Kapsalis P, Tysmans T, Verbruggen S, Triantafillou T. Preliminary High-Temperature Tests of Textile Reinforced Concrete (TRC). Proceedings. 2018; 2(8):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ICEM18-05416
Chicago/Turabian StyleKapsalis, Panagiotis, Tine Tysmans, Svetlana Verbruggen, and Thanasis Triantafillou. 2018. "Preliminary High-Temperature Tests of Textile Reinforced Concrete (TRC)" Proceedings 2, no. 8: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ICEM18-05416
APA StyleKapsalis, P., Tysmans, T., Verbruggen, S., & Triantafillou, T. (2018). Preliminary High-Temperature Tests of Textile Reinforced Concrete (TRC). Proceedings, 2(8), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ICEM18-05416



