Optimal Robot Path Selection Using Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchical Process †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Brief Explanation of AHP
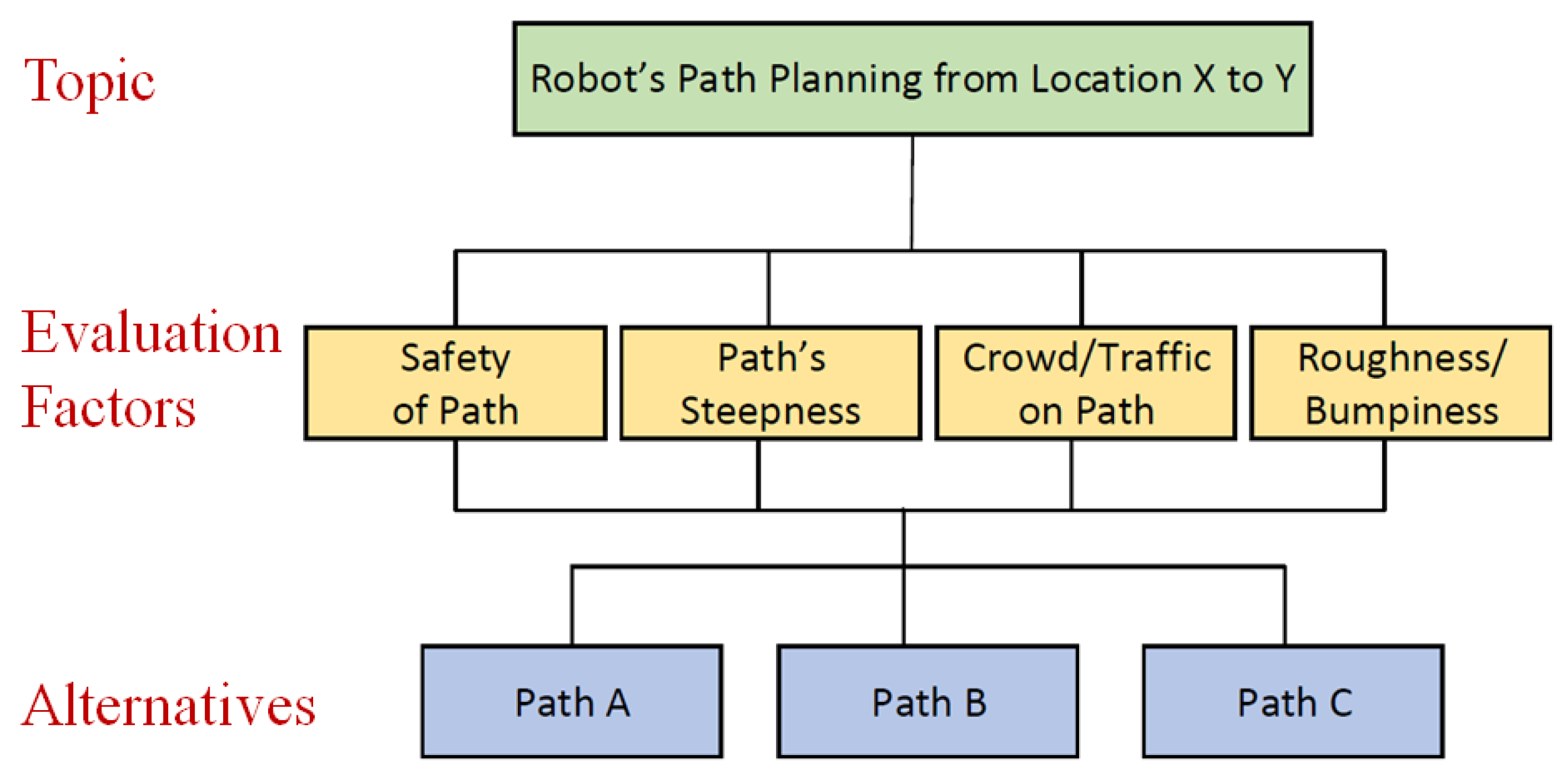
3. Use Case: Applying AHP for Path Planning
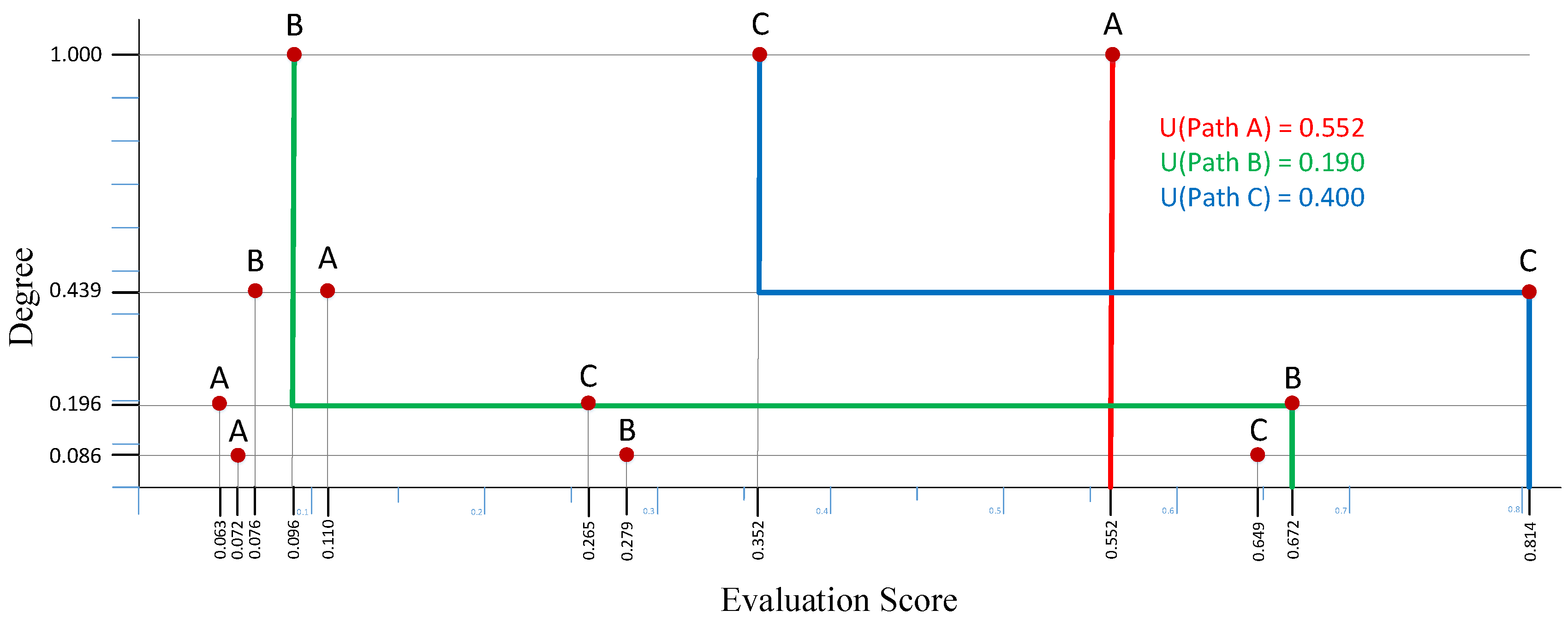
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ravankar, A.; Ravankar, A.A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Emaru, T. SHP: Smooth Hypocycloidal Paths with Collision-Free and Decoupled Multi-Robot Path Planning. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 13, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravankar, A.; Ravankar, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Emaru, T. Intelligent Robot Guidance in Fixed External Camera Network for Navigation in Crowded and Narrow Passages. Proceedings 2016, 1, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravankar, A.; Ravankar, A.A.; Hoshino, Y.; Emaru, T.; Kobayashi, Y. On a Hopping-points SVD and Hough Transform Based Line Detection Algorithm for Robot Localization and Mapping. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Langari, R. Analytical Hierarchy Process and Brain Limbic System combined strategy for mobile robot navigation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Montreal, QC, Canada, 6–9 July 2010; pp. 967–972. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.C.; Yu, S.R. Analytic hierarchy process and Zhou-Yi tagging method for knowledge map navigation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE 17Th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, Xiamen, China, 29–31 October 2010; pp. 1652–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka, A.; Labib, A. Review of the main developments in the analytic hierarchy process. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 14336–14345. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, S.S.; Shrabonti, G. Ranking by AHP: A rough approach. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Information Fusion, Annapolis, MD, USA, 8–11 July 2002; IEEE Cat.No.02EX5997. Volume 1, pp. 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, W. Integrated analytic hierarchy process and its applications—A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 186, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia. Analytic Hierarchy Process. 2017. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Analytic_hierarchy_process (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Ravankar, A.A.; Hoshino, Y.; Ravankar, A.; Jixin, L.; Emaru, T.; Kobayashi, Y. Algorithms and a Framework for Indoor Robot Mapping in a Noisy Environment using Clustering in Spatial and Hough Domains. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2015, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravankar, A.; Ravankar, A.A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Jixin, L.; Emaru, T.; Hoshino, Y. An intelligent docking station manager for multiple mobile service robots. In Proceedings of the 2015 15th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Busan, Korea, 13–16 October 2015; pp. 72–78. [Google Scholar]


| Degree of Importance | Score |
|---|---|
| Same Importance | 1 |
| Little More Important | 3 |
| Very Important | 5 |
| Extremely Important | 7 |
| Absolutely Important | 9 |
| Safety | Steepness | Crowd | Bumpiness | Geometric Mean | Normalized Weight | Accountable Degree | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Safety | 1 | 9 | 3 | 5 | 3.408 | 0.581 | 1.000 |
| Steepness | 1/9 | 1 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 0.293 | 0.050 | 0.086 |
| Crowd | 1/3 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 1.495 | 0.255 | 0.436 |
| Bumpiness | 1/5 | 3 | 1/3 | 1 | 0.668 | 0.114 | 0.196 |
| Path A | Path B | Path C | Geometric Mean | Normalized Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Path A | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2.080 | 0.552 |
| Path B | 1/3 | 1 | 1/7 | 0.362 | 0.096 |
| Path C | 1/3 | 7 | 1 | 1.326 | 0.352 |
| Path A | Path B | Path C | Geometric Mean | Normalized Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Path A | 1 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 0.306 | 0.072 |
| Path B | 5 | 1 | 1/3 | 1.186 | 0.279 |
| Path C | 7 | 3 | 1 | 2.759 | 0.649 |
| Path A | Path B | Path C | Geometric Mean | Normalized Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Path A | 1 | 5 | 1/3 | 0.405 | 0.110 |
| Path B | 1/5 | 1 | 1/9 | 0.281 | 0.076 |
| Path C | 3 | 9 | 1 | 3.000 | 0.814 |
| Path A | Path B | Path C | Geometric Mean | Normalized Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Path A | 1 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 0.281 | 0.063 |
| Path B | 9 | 1 | 3 | 3.000 | 0.672 |
| Path C | 5 | 1/3 | 1 | 1.186 | 0.265 |
| Safety | Steepness | Crowded | Bumpiness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Path A | 0.552 | 0.072 | 0.110 | 0.063 |
| Path B | 0.096 | 0.279 | 0.076 | 0.672 |
| Path C | 0.352 | 0.649 | 0.814 | 0.265 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ravankar, A.; Ravankar, A.A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Emaru, T. Optimal Robot Path Selection Using Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchical Process. Proceedings 2018, 2, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-4-04905
Ravankar A, Ravankar AA, Kobayashi Y, Emaru T. Optimal Robot Path Selection Using Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchical Process. Proceedings. 2018; 2(3):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-4-04905
Chicago/Turabian StyleRavankar, Abhijeet, Ankit A. Ravankar, Yukinori Kobayashi, and Takanori Emaru. 2018. "Optimal Robot Path Selection Using Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchical Process" Proceedings 2, no. 3: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-4-04905
APA StyleRavankar, A., Ravankar, A. A., Kobayashi, Y., & Emaru, T. (2018). Optimal Robot Path Selection Using Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchical Process. Proceedings, 2(3), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-4-04905





