Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease with an estimation of 10 million people living with the disease and it is increasing in prevalence every year. Familial cases of PD are source of valuable information to determine genetical risk factors yet sporadic cases can emerge from distinct mechanisms so, identifying common pathways of familial and sporadic cases of PD may provide worthwhile insights to determine underlying mechanisms through the progression. LRRK2 mutations are the most common indicators of both sporadic and familial cases of PD and α-synuclein aggregation is one of the hallmarks of both cases of PD as well as in other synucleinopathies. As in the case of most neurological diseases, human studies addressing the molecular basis of pathology are generally restricted to post-mortem materials. For this reason, cell culture systems and animal models are widely used. There are two main approaches for modelling PD: genetically constructed PD models and neuroxin-based models. In this study, we aim to construct and compare both approaches by overexpressing wild-type (WT) and A53T mutant α-synuclein and treating cells with well-known neurotoxin 6-hydroxidopamine (6-OHDA) using dopaminergic human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line. Our findings suggest that WT or A53T α-synuclein overexpression by itself is not sufficient to cause significant toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells in the presented time scale. As expected, 6-OHDA treatment caused toxicity with an IC50 value of ~100 µM. In addition, 6-OHDA treatment causes 3- and 2.5-fold increase in SNCA and LRRK2 expression respectively.
1. Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor symptoms and loss of dopaminergic cells in midbrain, particularly in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc). The PD etiology is not completely understood yet, but studies showed varied mutations in SNCA, PINK1, DJ-1 and LRRK2 genes in the familial cases of PD [1]. In case of SNCA, in addition to well-known point mutations (A30P, A53T, E46K), multiplications of SNCA locus is also sufficient to give rise to PD pathology [2]. To model PD, besides overexpressing wild type or mutant forms of α-synuclein, some neurotoxins are used to reproduce PD pathology. Rotenone, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) and 6-hydroxidopamine (6-OHDA) are the most used toxins to model PD [3].
In this study, we aim to utilize two different approaches for modelling PD using dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells: overexpression of wild-type (WT) and A53T mutant forms of α-synuclein and 6-OHDA induced PD. Transient overexpression of both WT and A53T forms of α-synuclein didn’t cause significant toxicity among SH-SY5Y cells and didn’t alter the endogenous α-synuclein expression. On the other hand, treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with 6-OHDA resulted with decreased cell viability with 3- and 2.5-fold increase in SNCA and LRRK2 expression respectively. 6-OHDA toxicity is mainly associated to oxidative stress in response to production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and triggering mitochondrial dysfunction. Besides these pathological processes, alterations in mRNA levels of disease associated genes in response to environmental risk factors like neurotoxins may also play an important role in sporadic cases of PD.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Transient Transfection
SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells (ATCC, CRL-2266) were maintained in high glucose DMEM (Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA) supplied with 10% FBS (Gibco) and 1% Penicilin/Streptomycin (Gibco). Cells were seeded at a density of 50.000 cell/cm2 on 6-well plates 24 h before transfection and transfected with aSyn-WT-EGFP or aSyn-A53T-EGFP plasmids which were gifts from David Rubinsztein (Addgene #40822, #40823) using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer instructions.
2.2. XTT Assay
Transfected or untransfected cells were trypsinized at 48 h of transfection and seeded at a density of 30.000 cell/well in 96-well plates before the day of 6-OHDA administration. Different concentrations of 6-OHDA were added each well in serum reduced (1%) medium. After 24 h incubation, XTT reagent (Intron Biotechnology, Burlington, MA, USA) was added to each well and absorbances were measured with a spectrophotometer after 3 h with a wavelength of 450 nm and 660 nm as reference channel. Cell viabilities were calculated as a percentage of nontreated cells in each separate experiment.
2.3. qPCR
The RNA was extracted from non-treated and 50 μM 6-OHDA treated SH-SY5Y cells and reverse transcribed with iScript cDNA Synthesis kit (Biorad, Hercules, CA, USA). qPCR was performed on a StepOnePlus System (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) with Sso Advanced Universal SYBR Green Supermix (Biorad) on 10 ng reverse transcribed RNA with the primer pairs of DJ-1, PINK1, SNCA and LRRK2. The relative expression of each transcript was calculated via normalizing to the expression of the house keeping genes GAPDH and ACTNB. The fold change of the transcript levels was calculated relative to control group.
2.4. Western Blotting
At 48 h of transfection, cells were lysed in RIPA buffer including protease inhibitor cocktail. Protein concentrations were determined using BCA assay, 30 µg of protein were loaded at each well of SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to PVDF membranes. PVDF membranes were blocked with 5% non-fat dried milk in 1× TBS-T for 1 h and incubated overnight with mouse anti α-synuclein (Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX, USA) and mouse anti β-actin (Santa Cruz) diluted 1:1000 in blocking solution. Primary antibodies were washed with TBS-T and incubated with goat anti-mouse HRP conjugated secondary antibody (Santa Cruz, sc-2005) at 1:3000 dilution in blocking solution. After washing secondary antibodies with TBS-T, HRP substrate was added and membranes were imaged with ChemiDoc imaging system (Biorad) and protein levels were quantified using ImageJ software.
3. Results
Overexpression of aSyn-WT-EGFP or aSyn-A53T-EGFP didn’t alter endogenous expression of α-synuclein in SH-SY5Y cells (Figure 1A,B).
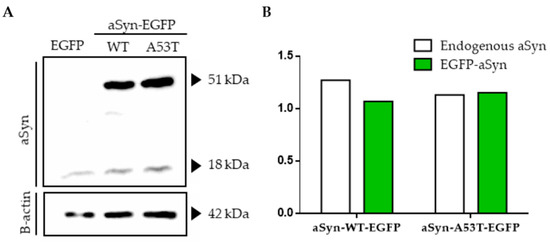
Figure 1.
Overexpression of WT and A53T α-synuclein in SH-SY5Y cells. (A) Western blot images showing both endogenous (18 kDa) and EGFP tagged α-synuclein (51 kDa) levels in transiently transfected cells with pEGFP, aSyn-WT-EGFP and aSyn-A53T-EGFP separately. (B) Quantification of α-synuclein protein levels in transfected cells relative to β-actin.
Also, aggregation of α-synuclein to toxic oligomers didn’t observed using fluorescence microscope (data not shown) or in western blots in the given period of time (Figure 1A). SH-SY5Y cells were treated with increasing concentrations of 6-OHDA. Cell viability was diminished to 10% when 250 µM 6-OHDA was applied in serum reduced medium (Figure 2a,b).
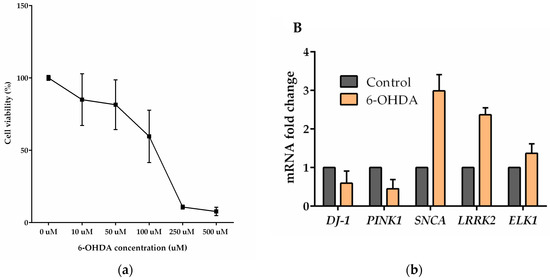
Figure 2.
6-OHDA treatment of SH-SY5Y cells. (a) Dose dependent toxicity of 6-OHDA treatment on SH-SY5Y cells measured by XTT assay. Cell viabilities were calculated relative to control group. (b) The expression levels of PD-related transcripts and ELK1 with 6-OHDA treatment in SH-5YSY cell line measured by qPCR assay. The fold change of the expressions was relative to the non-treated (control) group. The error bars represent standard errors of the mean (SEM).
SH-5YSY cells were treated with 50 μM 6-OHDA in serum reduced medium for 24 h and this treatment increased SNCA, LRRK2 and ELK1 transcript levels by 3-, 2.5- and 1.5-fold change respectively while PINK1 transcript levels were decreased by 0.5-fold change.
4. Discussion
Overexpression of WT and A53T α-synuclein didn’t increased toxicity significantly in SH-SY5Y cells. As it’s known that α-synuclein caused toxicity is related to its aggregation and PD is a slow progressing disease, 96 h time scale may not be sufficient to observe toxic outcomes and longer time scales must be investigated to determine α-synuclein dependent toxicity. Also, as [4] suggested, WT or A53T aSyn overexpression may not be sufficient to cause toxicity by its own but increases ROS production and extracellular administration of dopamine is needed to observe toxicity. On the other hand, 6-OHDA treatment of SH-SY5Y cells caused toxicity in a dose dependent manner as expected. In addition, we investigated if 6-OHDA treatment has altered familial PD-related gene expression levels. We found that 6-OHDA treatment of dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells caused 3-fold increase in SNCA expression which is consistent with a previous research that shows 5′-UTR of SNCA is upregulated in response to cellular stress factors like MPP+, FeSO4 and 6-OHDA and increases α-synuclein expression in HEK-293T cells [5]. DJ-1 is known to play a role as an oxidative stress sensor, upregulates at first hours of oxidative stimuli and activates Elk1, an ETS domain containing transcription factor as a neuroprotection response [6]. To determine if Elk-1 overexpression is neuroprotective, we have cotransfected WT or A53T overexpressing cells with Elk1 and found that Elk1 expression together A53T mutant decreased cell viability (data not shown). Elk1 and α-synuclein can form a complex as [7] indicated and this interaction might have a role in decreased cell viability. On the contrary, Elk-1 was found to be neuroprotective against cobalt chloride induced apoptosis and MPP model of PD as we have previously shown [8] while its effects on α-synuclein related toxicity remains to be understood.
References
- Klein, C.; Westenberger, A. Genetics of Parkinson’s Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a008888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, A.B.; Farrer, M.; Johnson, J.; Singleton, A.; Hague, S.; Kachergus, J.; Hulihan, M.; Peuralinna, T.; Dutra, A.; Nussbaum, R.; et al. alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 2003, 302, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bové, J.; Prou, D.; Perier, C.; Przedborski, S. Toxin-induced models of Parkinson’s disease. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junn, E.; Mouradian, M.M. Human alpha-synuclein over-expression increases intracellular reactive oxygen species levels and susceptibility to dopamine. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 320, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouraki, P.; Doxakis, E. Constitutive translation of human alpha-synuclein is mediated by the 5′-untranslated region. Open Biol. 2016, 6, 160022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.E.; Mouradian, M.M. Cytoprotective mechanisms of DJ-1 against oxidative stress through modulating ERK1/2 and ASK1 signal transduction. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, A.; Miura, S.; Kanazawa, I.; Sawada, M.; Nukina, N. α-Synuclein forms a complex with transcription factor Elk-1. J. Neurochem. 2001, 77, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, O.; Aysit, N.; Onder, Z.; Turkel, N.; Ozturk, G.; Sharrocks, A.D.; Kurnaz, I.A. ETS-domain Transcription Factor Elk-1 Mediates Neuronal Survival: SMN as A Potential Target. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).