Identification of the FGFR3G380R Mutant As a Likely Cause of Psychomotor Delay in an Achondroplastic Child: A Combined Clinical Exome Sequencing and Biomolecular Modeling Approach †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Exome Sequencing
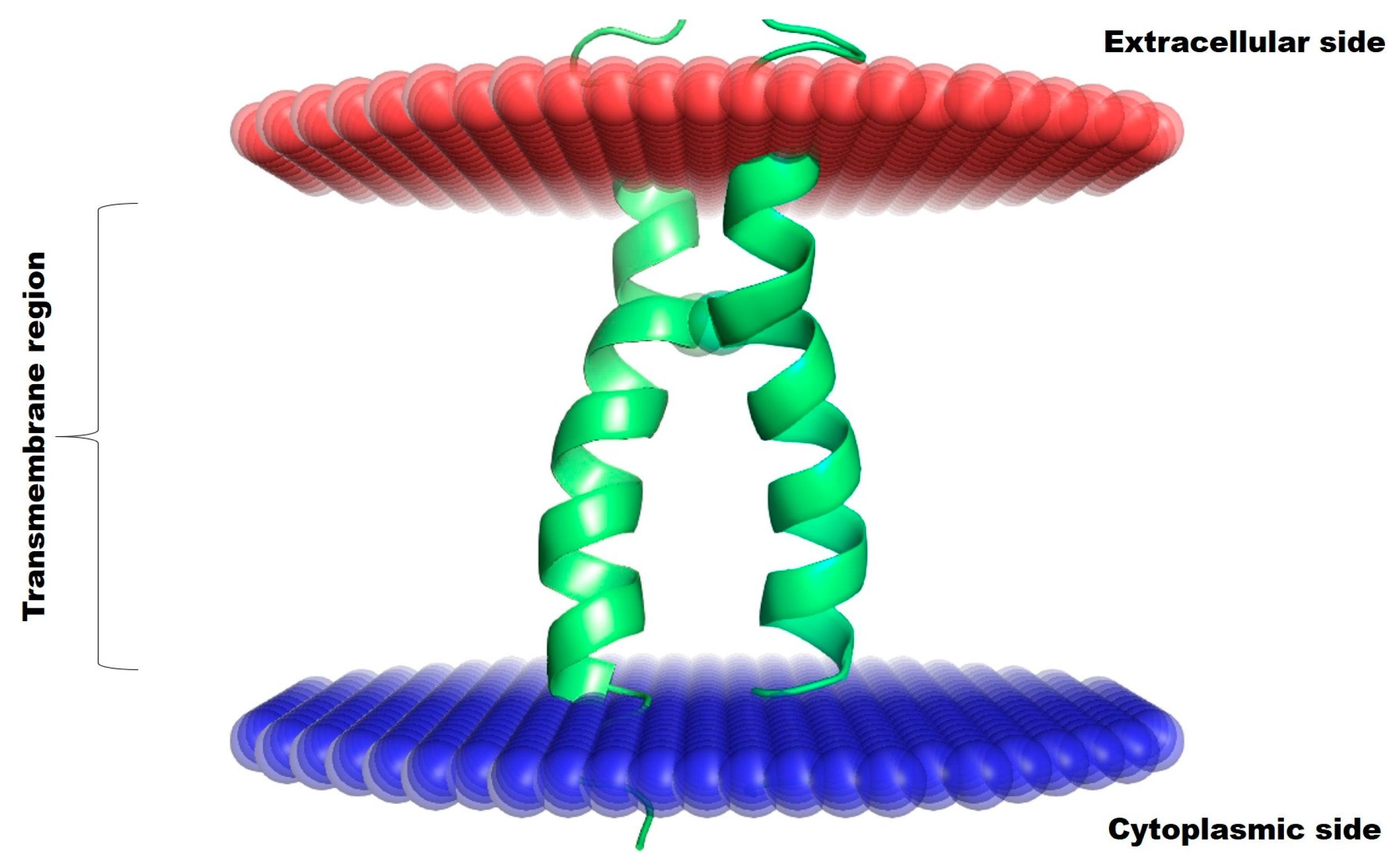
2.2. Biomolecular Modeling
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ornitz, D.M.; Legeai-Mallet, L. Achondroplasia: development, pathogenesis, and therapy. Dev. Dyn. 2017, 246, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, N.; Jin, M.; Chen, L. Role of FGF/FGFR signaling in skeletal development and homeostasis: learning from mouse models. Bone Res. 2014, 2, 14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, M.K.; Donoghue, D.J. Constitutive activation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 by the transmembrane domain point mutation found in achondroplasia. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomize, M.A.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Joo, H.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. OPM database and PPM web server: resources for positioning of proteins in membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D370–D376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Simonetti, F.L.; Goncearenco, A.; Panchenko, A.R. MutaBind estimates and interprets the effects of sequence variants on protein‒protein interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W494–W501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tina, K.G.; Bhadra, R.; Srinivasan, N. PIC: Protein Interactions Calculator. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W473–W476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, P.B.; Golovin, A. Cation‒π interactions in protein‒protein interfaces. Proteins 2005, 59, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teralı, K.; Gülsün Temel, Ş.; Eren, E. Identification of the FGFR3G380R Mutant As a Likely Cause of Psychomotor Delay in an Achondroplastic Child: A Combined Clinical Exome Sequencing and Biomolecular Modeling Approach. Proceedings 2018, 2, 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251551
Teralı K, Gülsün Temel Ş, Eren E. Identification of the FGFR3G380R Mutant As a Likely Cause of Psychomotor Delay in an Achondroplastic Child: A Combined Clinical Exome Sequencing and Biomolecular Modeling Approach. Proceedings. 2018; 2(25):1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251551
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeralı, Kerem, Şehime Gülsün Temel, and Erdal Eren. 2018. "Identification of the FGFR3G380R Mutant As a Likely Cause of Psychomotor Delay in an Achondroplastic Child: A Combined Clinical Exome Sequencing and Biomolecular Modeling Approach" Proceedings 2, no. 25: 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251551
APA StyleTeralı, K., Gülsün Temel, Ş., & Eren, E. (2018). Identification of the FGFR3G380R Mutant As a Likely Cause of Psychomotor Delay in an Achondroplastic Child: A Combined Clinical Exome Sequencing and Biomolecular Modeling Approach. Proceedings, 2(25), 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251551





