Recent Design Optimization Methods for Energy-Efficient Electric Motors and Derived Requirements for a New Improved Method—Part 2 †
Abstract
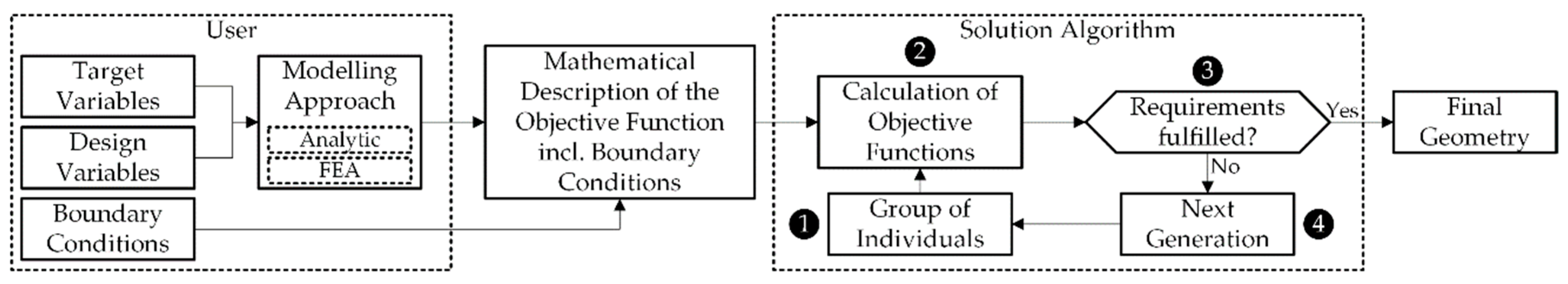
:1. Introduction
2. Models and Recent Design Optimization Methods
2.1. Deterministic Methods with Physical Models
2.2. Deterministic Methods with Surrogate Models
2.3. Stochastic Methods with Physical Models
2.4. Stochastic Methods with Surrogate Models
3. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bastos, J.P.; Sadowski, N. Electromagnetic Modeling by Finite Element Methods, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Bauer, P. Improved Analytical Model of a Permanent-Magnet Brushless DC Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 2299–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedot, L.; Friedrich, G.; Biedinger, J.-M.; Macret, P. Integrated Starter Generator: The Need for an Optimal Design and Control Approach. Application to a Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2007, 43, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.C.M.; Bernard, R.; Bigot, P.; Dubas, F.; Chamagne, D.; Espanet, C. Optimal design of a PMSM using concentrated winding for application urban hybrid vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Lille, France, 1–3 September 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msaddek, H.; Mansouri, A.; Brisset, S.; Trabelsi, H. Design and optimization of PMSM with outer rotor for electric vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 12th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD15), Mahdia, Tunisia, 16–19 March 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.H.; Anderson-Cook, C.; Montgomery, D.C. Response Surface Methodology. Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Buhmann, M.D. Radial Basis Functions. Theory and Implementations, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Low, T.-S.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z. Structural robust design for torque optimization of BLDC spindle motor using response surface methodology. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 2814–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochet, P.; Gillon, F. Screening and response surface method applied to the numerical optimization of electromagnetic devices. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2000, 36, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.K.; Low, T.S.; Liu, Z.J.; Chen, S.X. Robust design for torque optimization using response surface methodology. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2002, 38, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassimere, B.N.; Sudhoff, S.D. Population-Based Design of Surface-Mounted Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 2009, 24, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, L.; D’Andrea, M. High speed surface PM synchronous machine for wobble laser welding. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Coeur d’Alene, ID, USA, 10–13 May 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wu, Z.; Qian, H.; Sun, Z. Robust design for the 9-slot 8-pole surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor by analytical method-based multi-objectives particle swarm optimisation. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2016, 10, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinghua, L. Response surface methodology based design optimisation of interior permanent magnet synchronous motors for wide-speed operation. In Proceedings of the Second IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives, Edinburgh, UK, 31 March–2 April 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, L.; Jabbar, M.A.; Qinghua, L. Design optimization of permanent magnet motors using response surface methodology and genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 3928–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, F.; Hahn, I. Kriging-Assisted Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization of permanent magnet synchronous machine for hybrid and electric cars. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Chicago, IL, USA, 12–15 May 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmelcher, J.; Büning, M.K.; Kreisköther, K.; Gerling, D.; Kampker, A. Recent Design Optimization Methods for Energy-Efficient Electric Motors and Derived Requirements for a New Improved Method—Part 2. Proceedings 2018, 2, 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2221401
Schmelcher J, Büning MK, Kreisköther K, Gerling D, Kampker A. Recent Design Optimization Methods for Energy-Efficient Electric Motors and Derived Requirements for a New Improved Method—Part 2. Proceedings. 2018; 2(22):1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2221401
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmelcher, Johannes, Max Kleine Büning, Kai Kreisköther, Dieter Gerling, and Achim Kampker. 2018. "Recent Design Optimization Methods for Energy-Efficient Electric Motors and Derived Requirements for a New Improved Method—Part 2" Proceedings 2, no. 22: 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2221401
APA StyleSchmelcher, J., Büning, M. K., Kreisköther, K., Gerling, D., & Kampker, A. (2018). Recent Design Optimization Methods for Energy-Efficient Electric Motors and Derived Requirements for a New Improved Method—Part 2. Proceedings, 2(22), 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2221401




